higher chemistry unit 2
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
alkanes
saturated hydrocarbons (C to C single bond)
alkenes
unsaturated hydrocarbons (C to C double bonds)
cycloalkanes
saturated hydrocarbons arranged in a ring structure. (c-c)
cycloalkanes
unsaturated hydrocarbons arranged in a ring structure. (C=C)
alkynes
unsaturated hydrocarbons ( C to C triple bonds)
carboxylic acids
contains a carboxyl group (-COOH)
alcohols
contains a hydroxyl groups (-OH)
methyl
CH3
ethyl
C2H5
meth-
1 carbon
eth-
2 carbons
prop-
3 carbons
but-
4 carbons
pent-
5 carbons
hex-
6 carbons
hept-
7 carbons
oct-
8 carbons
non-
9 carbons
isomers
compounds which have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas
isomer steps
shorten the carbon chain and add a branch
move functional group
alkenes are isomers of cycloalkanes
hydration equations
reactions of carboxylic acids
metal oxide+carboxylic acid→salt+water
metal hydroxide+carboxylic acid→salt+water
metal carbonate+carboxylic acid→salt+water+carbon dioxide
saturated
contains C-C bonds
unsaturated
contains C=C bonds
what can C=C take part in
addition reactions
test for unsaturation
rapidly decolourise bromine solution
primary alcohol
hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon attached to one carbon
secondary alcohol
hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon attached to 2 other carbon
tertiary alcohol
hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon attached to 3 other carbon
diol
alcohols containing 2 hydroxyl groups (OH)
triol
alcohols containing 3 hydroxyl groups (OH)
esters
molecule containing an ester link
ester link
O
I I
O - C
how are esters formed
by a condensation reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid
use of esters
commonly used as fragrances as many have a fruity pleasant smell
what is glycerol known as?
propan-1,2,3-triol
Explain fully why fats have higher melting points than oils.Explain fully why fats have higher melting points than oils.
Fats are more saturated
they can pack together more closely
Stronger LDF between the molecules
what are fats and oils?
a concentrated source of energy
they are essential for the transport and storage of fat-soluble vitamins in the body
fats
solid at room temperature (high mp/bp)
more saturated/ less unsaturated
fat molecules pack closely together
stronger LDFs which need to be overcome
oils
liquid at room temperature (low mp/bp)
less saturated/ more unsaturated
oils can’t pack closely together due to kinles in the chain
weaker LDFs which need to be overcome.
soaps
water-soluble ionic salts
soaps structure
ionic head, which dissolves in water and is hydrophillic so is water soluble
hydrophobic tail, which dissolves in non polar substances e.g. oil and is hydrophobic so is non water soluble
use of soap
hydrophobic tail dissolves in oil
hydrophilic head dissolves in water
agitation causes micelles to form which repel eachother and they are suspended in the water until it drains away.
soapless detegent
used in areas with hard water (high metal ion concentration)
prevents scum from forming
emulsions
contains small droplets of one liquid dispersed in another liquid. Eg. oil and water
emulsifiers
can be used to prevent non polar and polar liquids from separating into layers
emulsifiers for use of food can be made by?
reacting edible oils with glycerol.
what are proteins?
the major structural materials of animal tissue and are also involved in the matainance and regulation of life processes
what are enzymes?
a protein that acts as a biological catalyst
amino acids
building blocks that make up a protein molecule, which contain an amino group, —NH2, and a carboxyl group, —COOH.
proteins are made by?
many amino acid molecules linked together by condensation reactions. In these reactions, the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another amino acid join, with the elimination of water.
link between two amino acids
peptide link/ amide link
essential amino acids
the body cannot make these amino acids so they must be acquired from the diet
proteins which fulfill different roles in the body are formed by
linking together different sequences of amino acids
denaturing causes
low pH
high temperature
what happens when a protein denatures?
changes shape
intermolecular forces/hydrogen bonds break
During digestion, enzyme hydrolysis of protein produces
amino acids
For cabin compounds: oxidation and reduction
oxidation: an increase in the oxygen to hydrogen ratio
reduction: decrease in the oxygen to hydrogen ratio
oxidisation of primary alcohol
Hot copper(II) oxide or acidified dichromate(VI) solutions can be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes and then to carboxylic acids
hot copper (II) oxide: color change
black→brown
acidified dichromate: colour change
orange→green
oxidisation of secondary alcohol
Hot copper(II) oxide or acidified dichromate(VI) solutions can be used to oxidise
secondary alcohols to ketones
oxidisation of tertiary alcohols
no further oxidisation
fehlings: colour change
blue→brick red
tollens: colour change
colourless→silver mirror
what defines a aldehydes
a carbonyl group and a hydrogen directly attached
what defines a ketone
a carbonyl group
many flavor and aroma molecules are?
aldehydes
Oxygen from the air causes the ___ of food?
oxidisation
oxidisation of edible oils gives food a bad taste
a rancid flavor
antioxidants
are substances that prevent unwanted oxidation reactions occuring, helping to maintain flavor and freshness in food.
essential oils
are concentrated extracts from plants that capture their scent and flavor
what are the key parts of an essential oil
terpenes
what is a terpene
unsaturated compounds formed by joining isoprene units
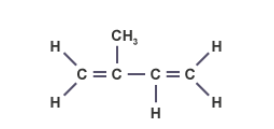
draw an isoprene
UV light causes
sun burn
aging skin
how are free radicals formed
when UV light breaks bonds
what are free radicals
atoms or molecules that are highly reactive due to the presence of unpaired electrons
what are free radical scavengers
molecules that react with free radicals to form stable molecules
3 steps of the free radical chain reactions
Initiation, propagation, termination.
Initiation, propagation, termination example
CH4+Br2→CH3+HBr
Br2→Br*+Br* initiation
CH4+Br*→HBr+CH3* propagation
Br*+Br*→Br2 termination