sports psychology - attitudes, motivation, goal setting, social facilitation, group dynamics, attributions, confidence, leadership, stress
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
* ‘the direction and intensity of ones efforts’ sage
1. may have a more significant impact
2. may improve confidence
3. badges and stickers may help children start a sport
1. may be more valuable as taking part for their own benefit ie. satisfaction
2. may be more long term motivation
3. more self sufficient as don’t need anyone else to notice
1. fun and enjoyment may disappear as intrinsic may not maintain motivation
2. cognitive learner may find it difficult to keep participating
1. may not be as valuable
2. may not be long term motivation
3. if the extrinsic rewards are removed motivation may decline ie. achieved all swim badges
4. may be demotivating if you don’t reach the level for the reward
1. role models
2. social
3. SMART goals
4. positive reinforcement
5. fun
6. skill and fitness development
1. forming (model of group development)
* little agreement on aims
* roles are unclear
2. storming (model of group development)
* clearer focus and stronger sense of purpose
* power struggles form
* members jostle for position
3. norming (model of group development)
* roles are clearer
* decisions are better made through agreement
* less important decisions are delegated
* stronger sense of commitment
* general respect for leader
4. performing (model of group development)
* focus on achieving goals
* team members are trusted
* team make decisions
* inability to work together
* inadequate leadership
* ringleman effect
* lack of confidence
* lack of identifiable roles for the team
* injury, illness, fatigue
* environmental stressors
* individual efforts not recognised
what are attributions
the perceived causes of a particular outcome or the reasons given.
what does Weiner identify as the 2 main variables that affect attributions
locus of causality (internal/external)
stability (stable/unstable)
Weiner Attribution Theory
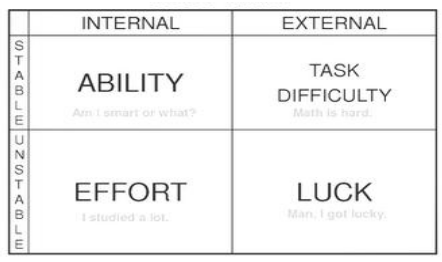
what is the 3rd dimension of Weiner’s Attribution Theory
whether the attributions are under the control of the performer or the others
what is the impact of attributing failure to external causes
sustains confidence
reassures success is possible in the future
maintains motivation
BUT can result in avoiding areas that need improvement
what is the impact of attributing success to internal causes
elevates confidence and pride
endorses expectation of achievement
used to reinforce success
BUT can cause inflated perceptions of competency
what is the impact of attributions depending on the performer (high achiever)
demonstrates approach behaviour, attribute success to internal factors and failure to external factors
what is the impact of attributions depending on the performer (low achiever)
demonstrates avoidance behaviour, attributes success to external factors and failure to internal factors, repeated failure therefore results in learned helplessness
what is learned helplessness
the belief that failure is inevitable and the individual has no control over the factors that cause failure
what is mastery orientation
individual is motivated by becoming an expert in skill development to optimise performance
what is attribution retraining
refers to the changing of someone’s belief for success or failure
what is self serving bias
sports performers who lose tend to attribute failure to external causes and successes to internal causes
what is self confidence
the belief of certainty individuals possess about their ability to be successful in sport
what is self esteem
the feeling of self-worth that determines how valuable and competent we feel
impact of high sports confidence
more likely to achieve peak flow and be successful, show approach
impact of low sports confidence
underachievement, avoidance behaviour, disruptive behaviour hindering others
what is veeley’s model of sports confidence
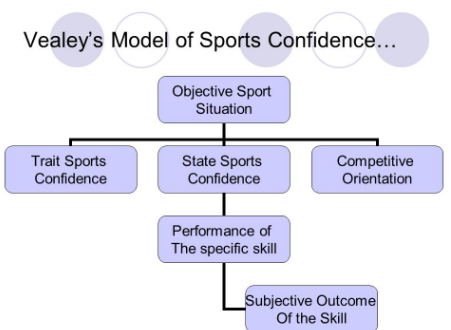
what is trait sports confidence
the stable and innate level of self-belief in sport, existing level of confidence
what is competitive orientation
the level of competitiveness that the performer may have
what is a state sports confidence
the confidence that you have in a specific situation or environment and is changeable
what is behavioural response
high state confidence performance is confident, positive
low state confidence performance is likely to be tentative, weak or indecisive
what is a subjective outcome
after the performance, the performer will either be satisfied or disappointed with how the performance went and is based o how the performer judges the outcome
what is self efficacy
the self-confidence we feel in specific situations
Bandura’s Model of Self Efficacy
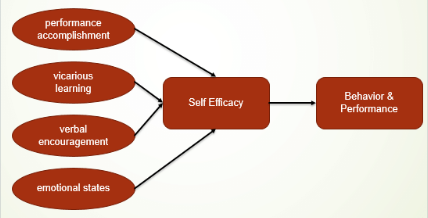
what factors affect self efficacy
performance accomplishments, vicarious experiences, verbal persuasion, emotional arousal
what is performance accomplishments (self efficacy)
a reminder of previous successes in the related skill or situation
what is vicarious experiences (self efficacy)
watching others perform the skill in question
what is verbal persuasion
convincing the athlete of their ability to perform the skill
what is emotional arousal
the evaluation the performer makes of a physiological state
how can self-efficacy be improved
encouraged attribution of any previous failure or learned helplessness to controllable/internal factors/unstable factors, give encouragement, give anxiety management strategies, give early success
what does effective leadership involve
good communication skills
high motivation
enthusiasm
clear goal
empathy
what are prescribed leaders
selected from outside the group or externally appointed,
what are advantages of prescribed leaders
more objective, more authority or power
what are disadvantages of prescribed leaders
may not be accepted by the group, may not be aware of the team culture
what are emergent leaders
the leader already belongs to the group, selection through voting by group or readily assumed due their skill level