6 - Brainstem
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what are the contents of the brainstem?
midbrain, pons, medulla
what does the brainstem connect?
cerebrum superiorly, cerebellum posteriorly, and spinal cord inferiorly
where does pyramidal decussation occur?
right below medulla before becoming spinal cord
brainstem functions
communication between cerebrum, cerebellum and spinal cord
contains cardiovascular, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers
contains passageway for different neural pathways
home to many cranial nerve nuclei
what is another name for the midbrain?
mesencephalon
what is the functional significance of the midbrain?
coordinated eye movements
pupillary light reflex
consciousness and arousal
what are the structures in the midbrain
tectum (roof)
- quadrigeminal plate - superior and inferior colliculi
- cerebral aqueduct - periaqueductal gray
tegmentum
- red nucleus
- reticular formation
- substantia nigra
cerebral peduncles (crus cerebri)
the tectum is ____ to the cerebral aqueduct
dorsal
the quadrigeminal plate has ___ swellings on the ____ part of the midbrain. it contains the ______ and ______.
4, dorsal, superior, inferior
what are the functions of the superior and inferior colliculi?
superior: visual processing (gaze)
inferior: auditory processing
what surrounds the cerebral aqueduct? what does it do?
the periaqueductal gray
is the control center for descending pain modulation
what does the cerebral aqueduct contain? what does it connect? what direction does it go?
CSF
3rd and 4th ventricles
goes vertically
what is the tegmentum? what are its structures?
it is the region between the cerebral peduncles and cerebral aqueduct
contains the red nucleus and reticular formation
what does the red nucleus do? where is it found?
motor coordination in the extra pyramidal system (basal nuclei modulates rather than corticospinal tract)
only present at the same level as superior colliculi, not present at level of inferior colliculi
what is the reticular formation in tegmentum? what does it do?
central core of brainstem where intermingling of axons occurs
mediates level of consciousness
where is the substantia nigra? what is its main pathway? what does it do?
consistent landmark throughout the midbrain (in tegmentum)
dopaminergic pathways
responsible for reward (addiction), learning (cognition), and movement (extra-pyramidal system - basal nuclei)
where are the cerebral peduncles (crus cerebri) located? what does it do?
lateral, under diencephalon, lateral to mammillary bodies
fiber bundle that connects cerebral cortex with spinal cord, pons, and brainstem
what are the tracts in the midbrain?
corticospinal tract, spinothalamic tract, dorsal column - medial lemniscus tract
where are the tracts in the midbrain located?
green - corticospinal
red - spinothalamic
blue - dorsal column - medial lemniscus
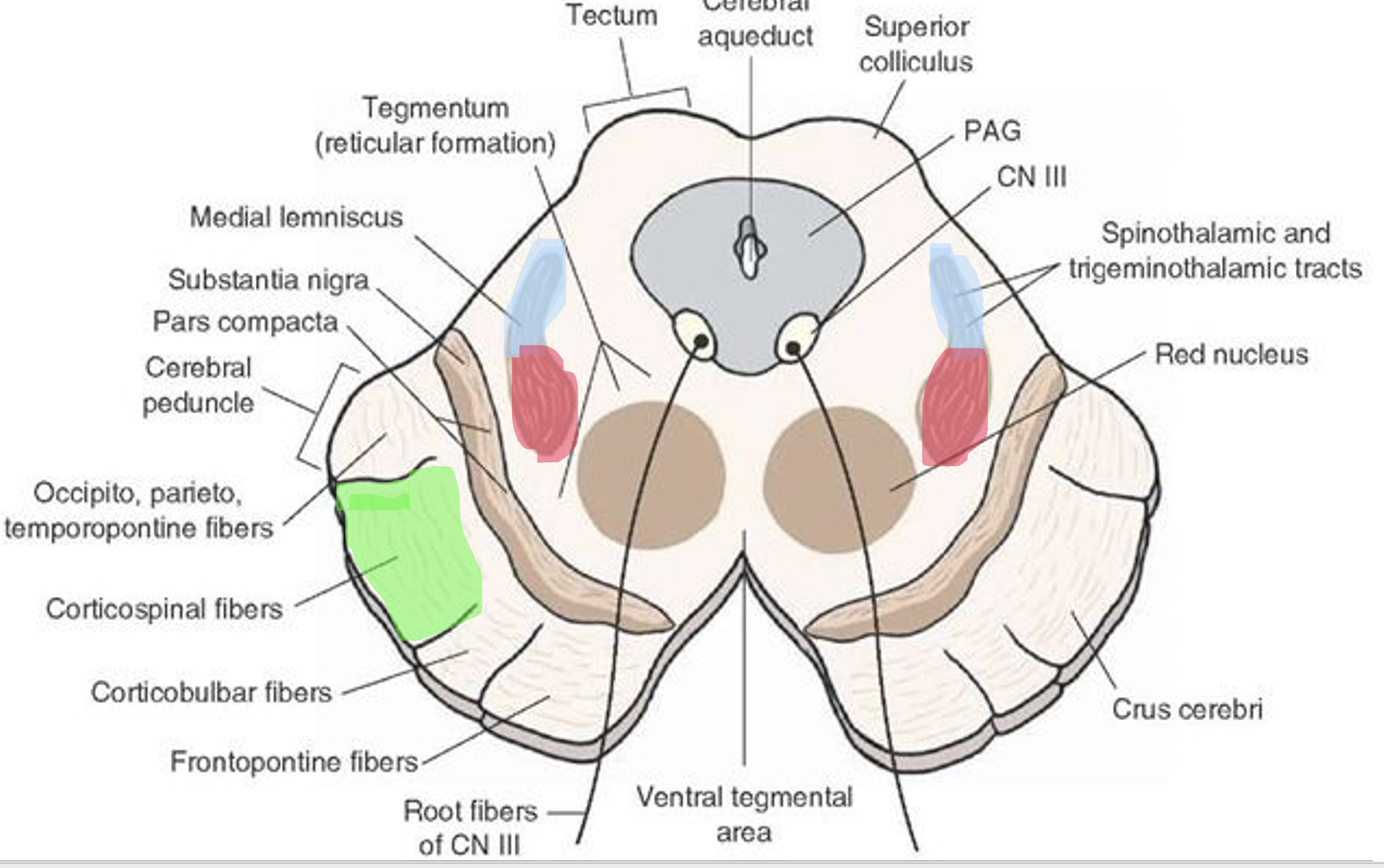
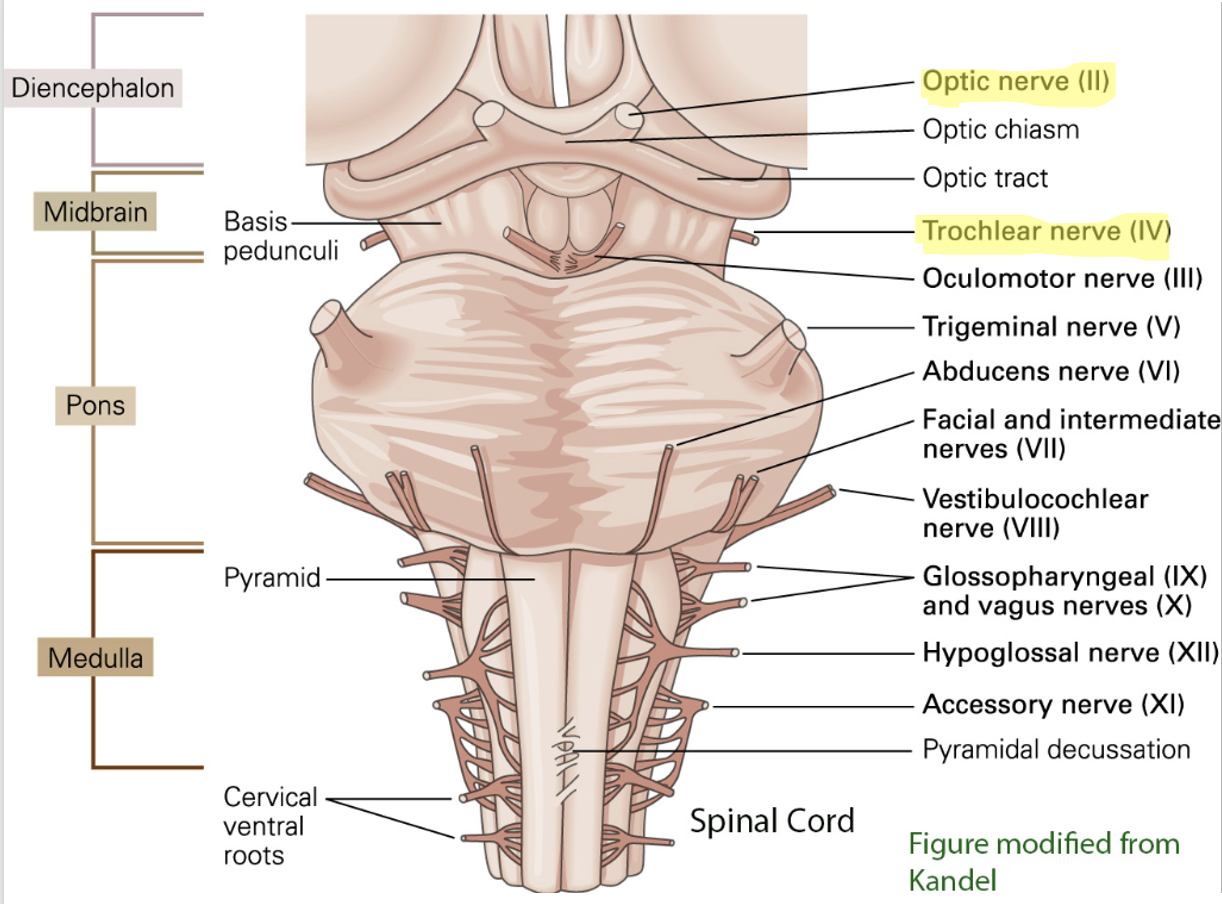
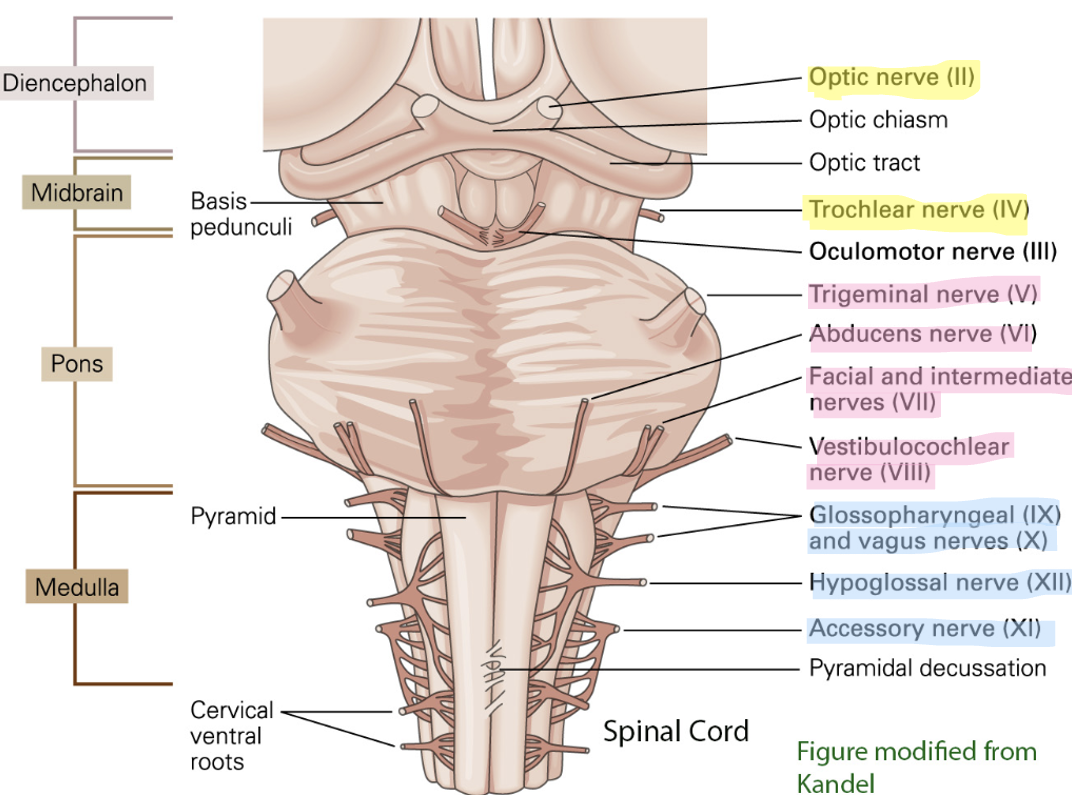
what are the cranial nerves in the midbrain?
CN III - oculomotor
CN IV - trochlear
where are the pons located?
anterior to cerebellum and IV ventricle
inferior to midbrain
superior to medulla
what is the functional significance of pons?
reflex control, respiratory system
eye movements and coordinated movements in eye and head
corneal reflex
what are structures in the pons?
middle cerebellar peduncle, 4th ventricle, reticular formation
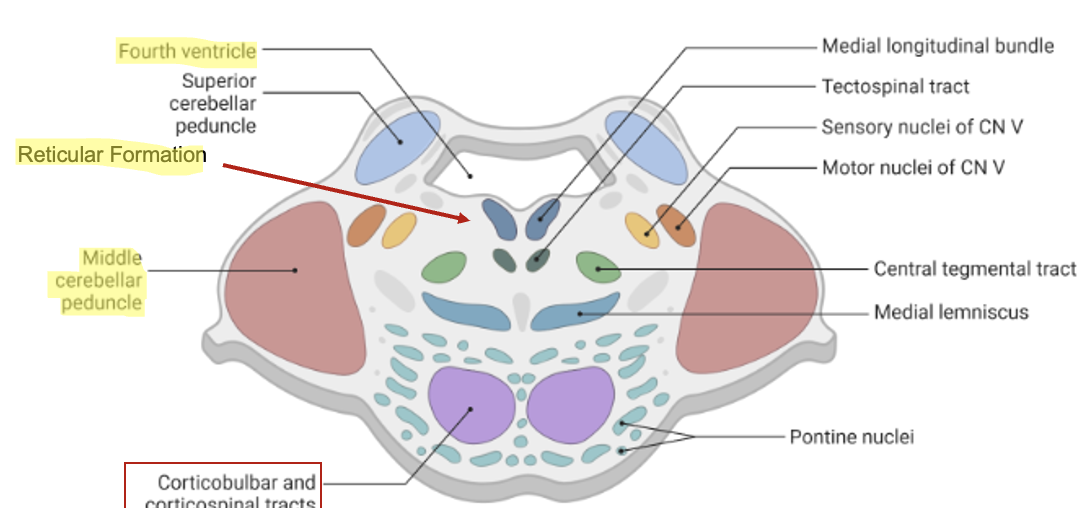
where is the reticular formation located?
between pons proper (bulge) and 4th ventricle
what are the neural pathways in the pons?
dorsal column - medial lemniscus tract
corticospinal tract
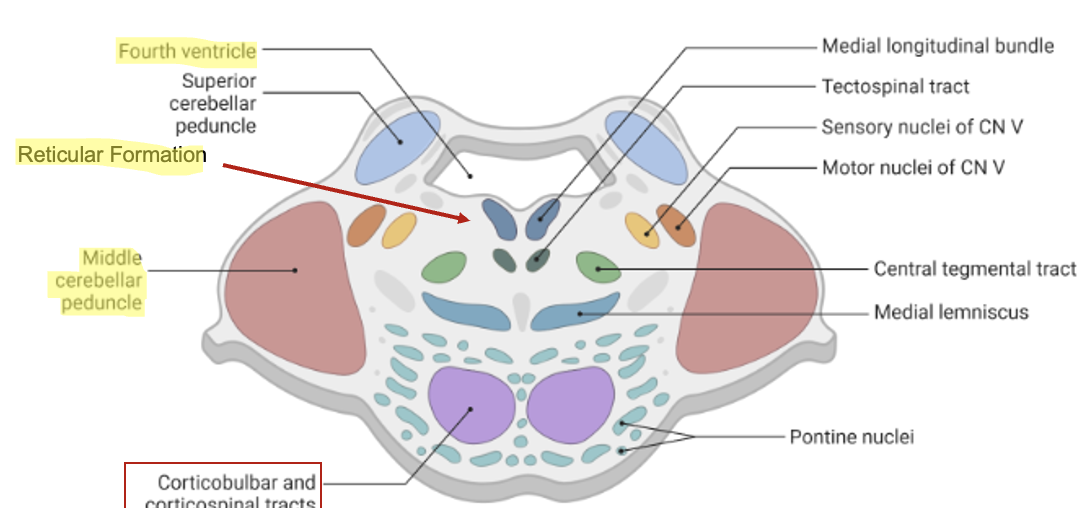
spinothalamic tract
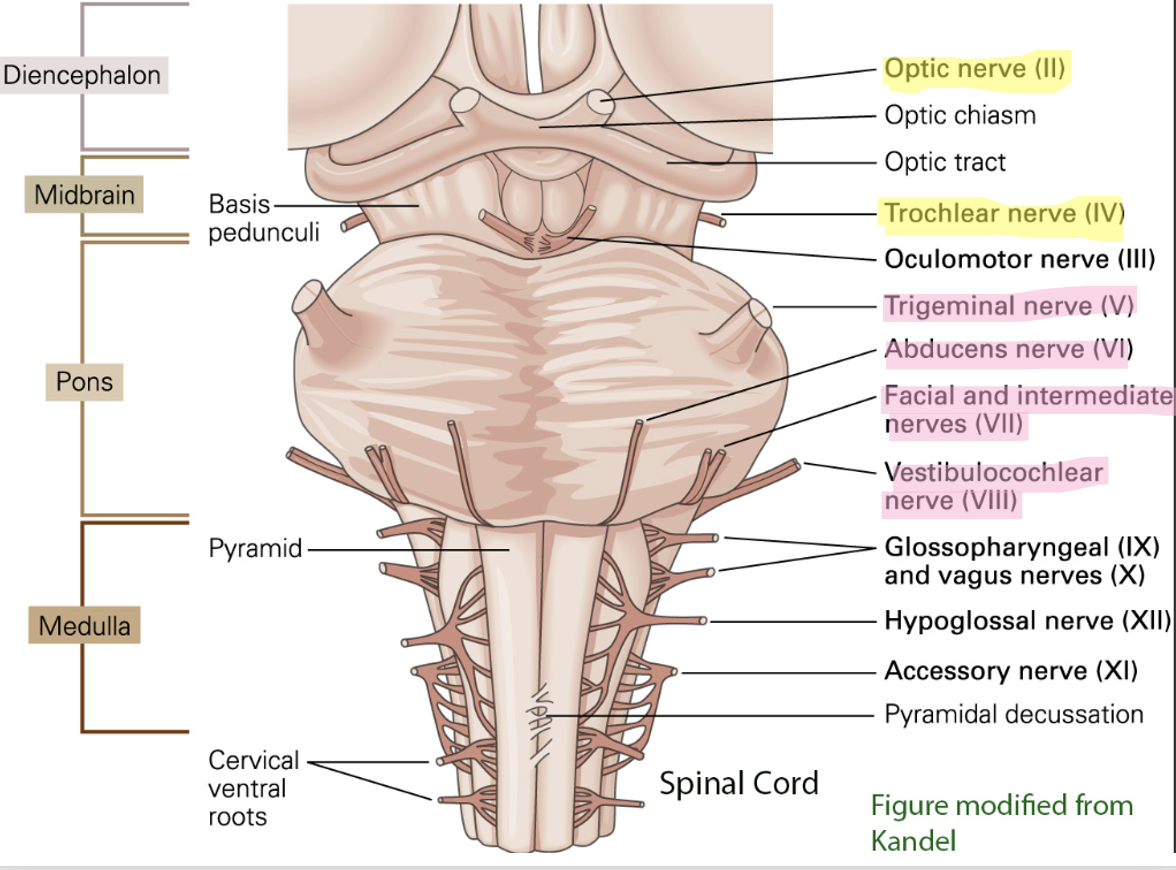
what are the cranial nerves in the pons?
CN V: trigeminal
CN VI: abducens
CN VII: facial
CN VIII: vestibulocochlear
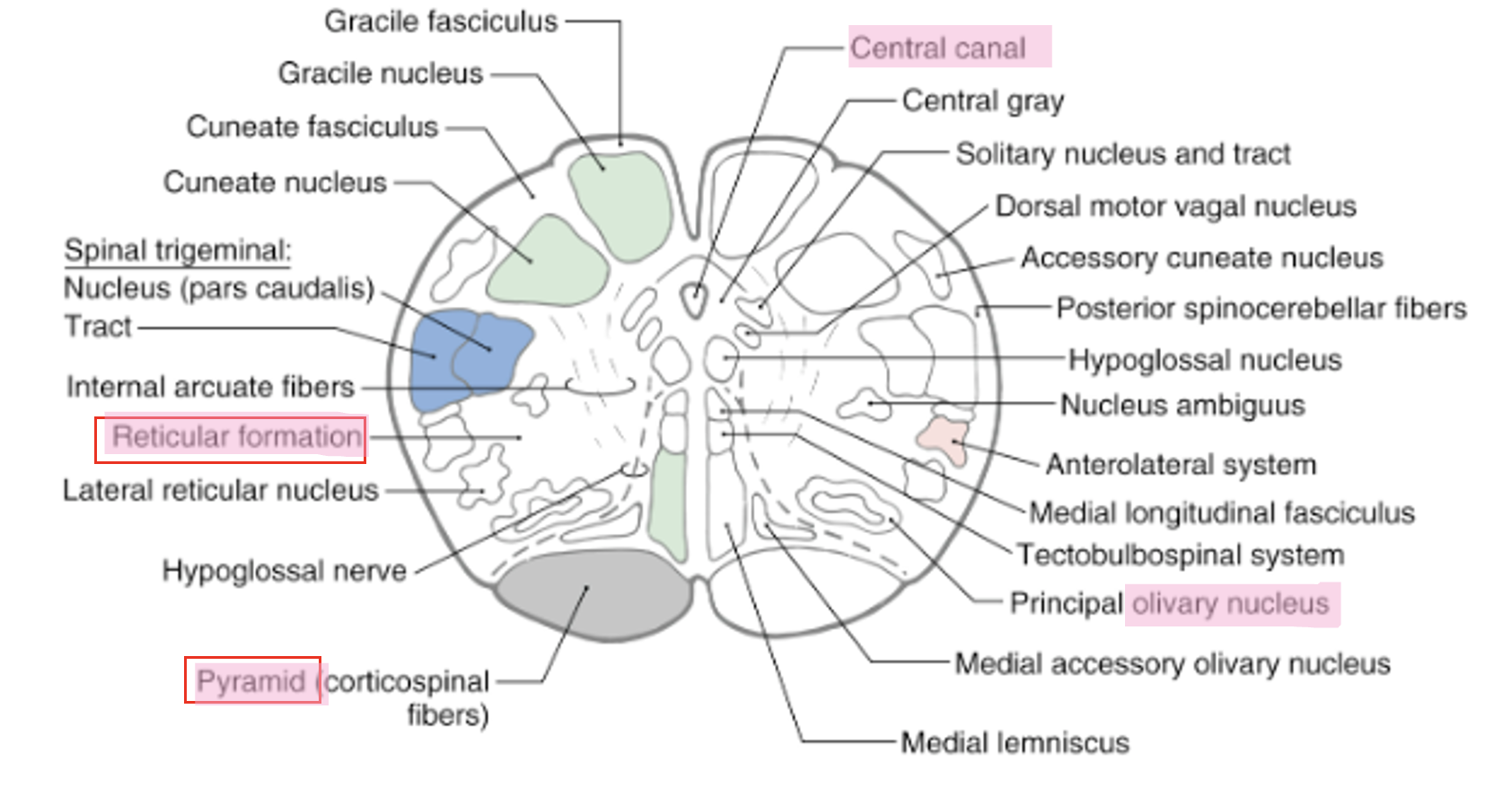
where is the medulla located?
inferior to the pons and superior to the spinal cord
what is the functional significance of the medulla?
reflex control of CV and respiratory systems
reflex control of swallowing and vomiting
important in phonation (control of tongue, larynx, pharynx)

what are the structures in the medulla?
pyramid
olive
- inferior olivary nucleus
4th ventricle
reticular formation
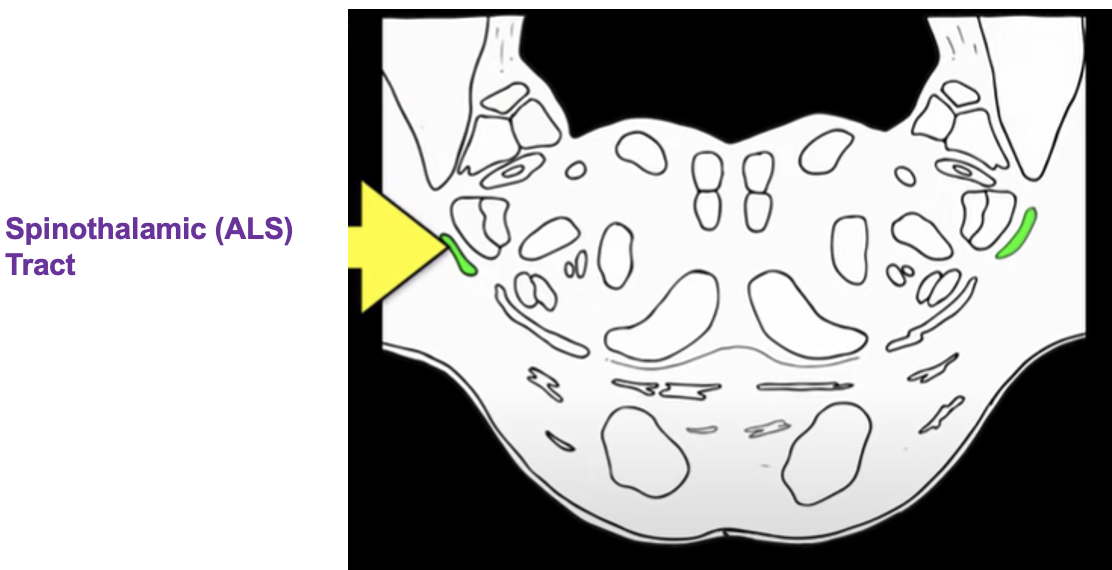
what tracts are in the medulla?
corticospinal tract
spinothalamic tract (ALS system)
dorsal column medial lemniscus
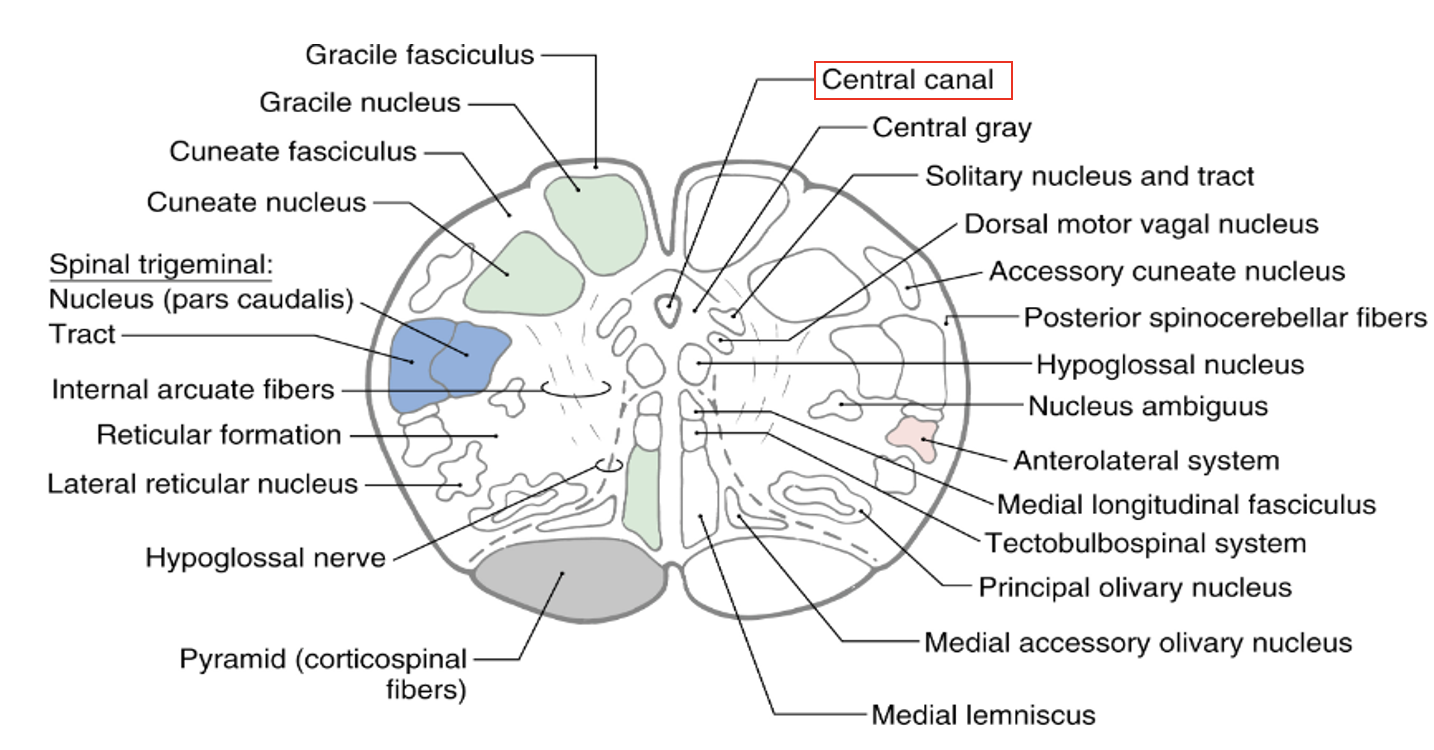
where does the dorsal column cross?
crosses at internal arcuate fibers, not at pyramid decussation or anterior white commissure
what does the pyramid of medulla contain? where does it travel?
contains corticospinal tract (majority of corticospinal fibers cross to form lateral corticospinal tract but some stay ipsilateral as anterior corticospinal tract)
courses inferiorly to the pyramidal decussation
where is the olive of medulla? what does it contain?
paired anterolateral bulges lateral to pyramids
contains olivary nucleus, neurons in the olive are related to the cerebellum that is constant getting proprioceptive and motor input. olivary fibers are one kind of input
what are the cranial nerves in the medulla?
CN IX: glossopharyngeal
CN X: vagus
CN XI: accessory
CN XII: hypoglossal
what is the central canal in the medulla?
continues in the spinal cord
continuation of 4th ventricle
is the red nucleus present at the level of the superior colliculus? inferior colliculus?
yes, no
4 structures in the midline that begin with “M”
motor pathway (corticospinal tract)
medial lemniscus (discriminative touch)
medial longitudinal fasciculus (occular reflexes)
motor nucleus and nerves
4 structures in the side that begin with “S”
spinocerebellar pathway (unconscious proprioceptive info)
spinothalamic pathway (pain/temperature)
sensory nucleus of CN V
sympathetic pathway
4 cranial nerves in each group
4 above the pons: 2 in cerebrum (I, II) and 2 in midbrain (III, IV)
4 in the pons: V, VI, VII, VIII
4 in the medulla: IX, X, XI, XII
what tract is a motor pathway from M1 to the opposite side of the body?
corticospinal tract
what tract carries pain and temperature information from other side of body to S1?
spinothalamic tract via anterolateral system
what tract contains vibration and proprioception from other side of body to S1?
dorsal column - medial lemniscus tract