Epithelial Transport of Glucose in Biosci107
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Epithelial tissue
Cells arranged in continuous sheets, single or multiple layers.
Basement membrane
Layer cells sit on, separating from underlying tissues.
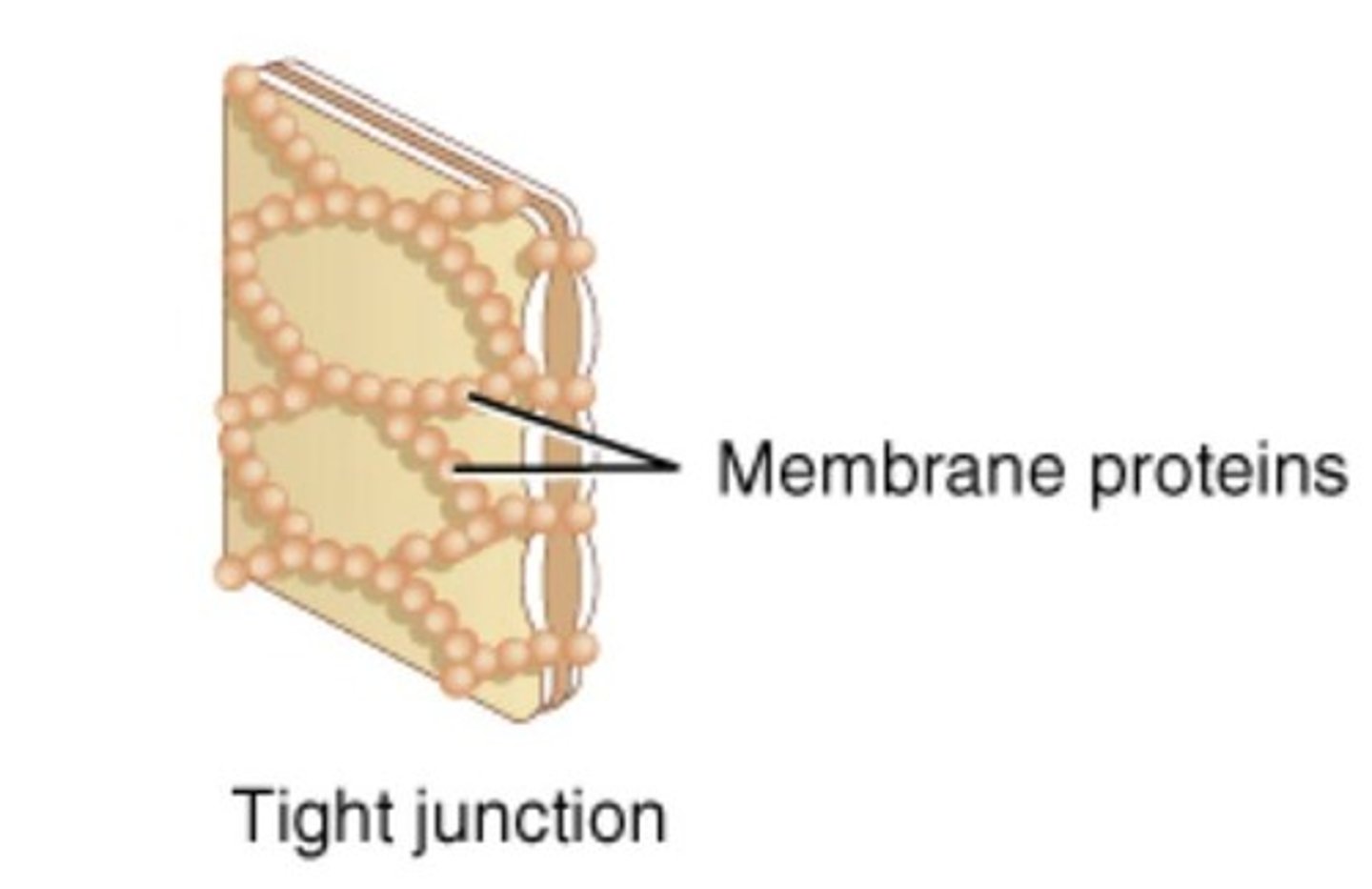
Tight junctions
Structures that restrict movement between epithelial cells.
Transcellular transport
Transport through epithelial cells, involving membranes.
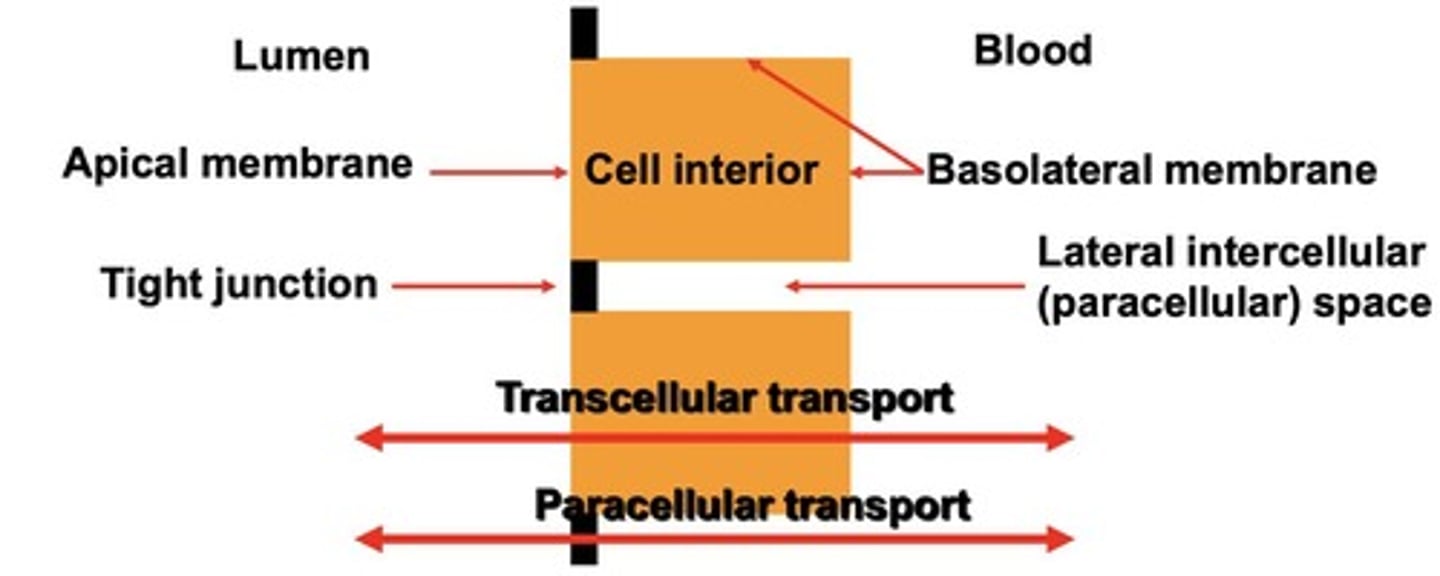
Paracellular transport
Transport between epithelial cells, governed by diffusion.
Apical membrane
Membrane facing the lumen of an organ.
Basolateral membrane
Membrane facing the blood and basement membrane.
Glucose absorption
Process of glucose moving from lumen to blood.
Glucosuria
Presence of glucose in urine, often due to diabetes.
Sodium-glucose symporter (SGLT)
Transporter using Na+ gradient to absorb glucose.
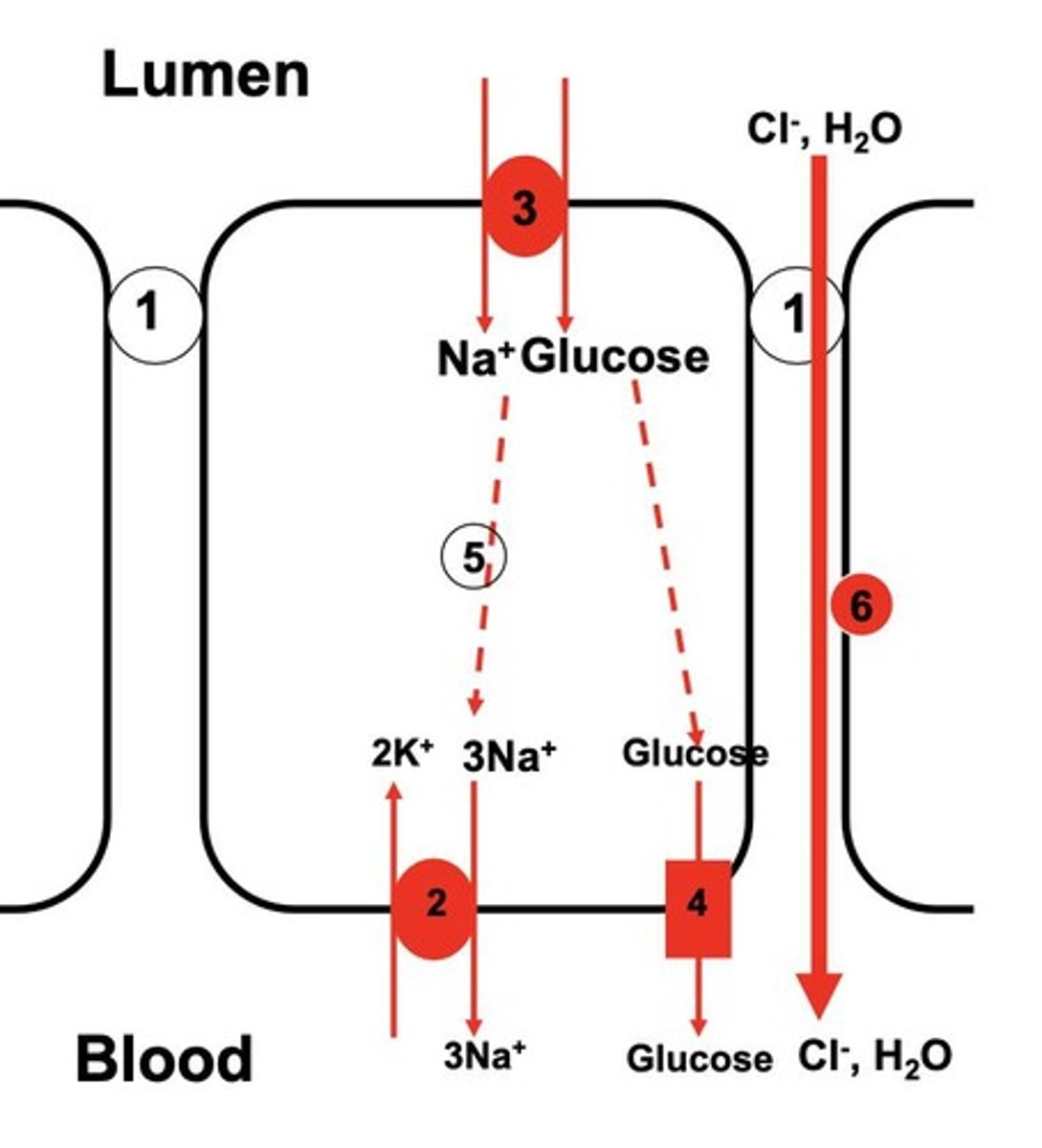
Facilitative glucose transporter (GLUT)
Mediates glucose exit via passive diffusion.
Oral rehydration therapy
Uses glucose to enhance Na+ and water absorption.
Glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome
Mutation in symporter causing sugar retention in intestine.
Renal threshold
Maximum glucose reabsorption capacity of kidney transporters.
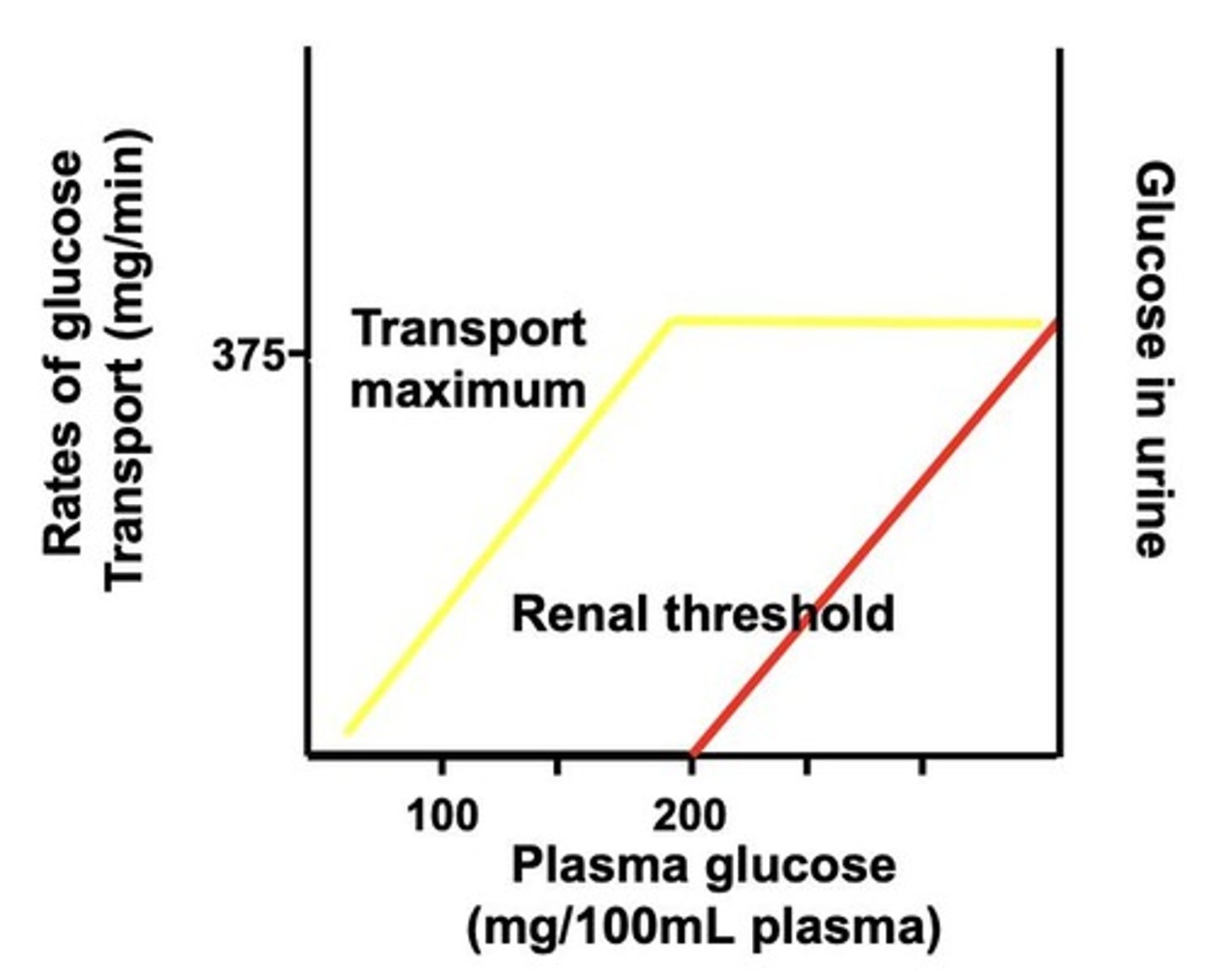
Transport maximum
Point where glucose reabsorption saturates in kidneys.
Leaky epithelium
Type where paracellular transport is predominant.
Tight epithelium
Type where transcellular transport is predominant.
Electrical resistance
Measured resistance to ion flow through tight junctions.
Osmolarity
Concentration of solutes in a solution affecting water flow.
Counter ion
Ion that accompanies another ion to maintain charge balance.
Diabetes mellitus
Condition causing high blood sugar and glucosuria.
Ion gradients
Differences in ion concentration across membranes.
Water efflux
Movement of water out of cells due to osmolarity.
Transporters and channels
Proteins mediating secretion or absorption in epithelial cells.