Small Animal Nursing I Lab 8 - Electrocardiography (ECG)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
The force of electricity that moves blood through the heart
What makes the heart contract?
• Arrhythmia
• History of syncope or episodic weakness
• Cardiac chamber enlargement
• Pericardial effusion
• Monitoring drug therapy
• Monitoring during anesthesia
List indications for electrocardiography
• Detects, magnifies, and records the electrical forces generated by the heart
• Heart rate
• Rhythm/arrhythmias
• Hypoxia/electrolyte disturbances
• Gross chamber enlargements
List the functions of an ECG
• Mechanical function of the heart
• Anatomic pathology of valves, arteries, endocardium, or pericardium
What can an ECG not identify?
• Measures electrical activity of the heart using positive and negative electrodes on the skin
• Lead tracings (waves)
List the principles of the ECG
Bipolar leads
ECG leads I, II, and III are known as
Augmented leads
ECG leads aVR, aVL, and aVF are known as
aVR, aVL, and aVF
List the augmented ECG leads
White on the right forelimb
Black on the left forelimb
Green on the right hindlimb
Red on the left hindlimb
"White" goes on the "right"
"Smoke" (black) over "fire" (red)
When doing an ECG , where do you place the white, black, red, and green electrodes on the patient?
Right lateral recumbency
In what position should a patient be placed for an ECG?
Use alcohol to minimize electrical ("60 cycle") artifacts
What solution must you apply to the interface of the ECG clips, and what is its purpose?
• Use alcohol to wet the clips on the limb leads
• Unplug electrical appliances on the same outlet as the ECG machine
• Avoid use of wristwatches
• Have patient lie on a towel or mat when using a metal table
List methods of minimizing electrical artifacts
Atrial depolarization (contraction) to form the P wave as it travels through the atria
What is the sinoatrial node (SA) responsible for during cardiac conduction?
Atrial contraction
What does the P wave represent?
Completes atrial contraction and slows down cardiac conduction to allow the ventricle to fill
What is the atrioventricular node (AV) responsible for during cardiac conduction?
Delay between atrial and ventricular contraction
What does a P-R interval represent?
Conducts electricity to the ventricular apex
What is the function of Bundle of His during cardiac conduction?
Coordinate contraction of the ventricles that form the QRS wave to cause ventricular contraction to delivery blood to the body and lungs
What are the L and R bundle branches and Purkinje fibers responsible for during cardiac conduction?
Ventricular repolarization (relaxation)
What does the T wave represent?
Noninvasive equipment attached to a patient to analyze cardiac rhythms over 24 hours
What is a holter monitor used for?
• Heart rate
• Heart rhythm
• Wave forms P-QRS-T complexes and intervals
• Mean electrical axis (average of electrical travel)
What information is provided by an ECG?
Height of the wave measured in millivolts (mV)
What does the vertical measurement in the ECG represent?
1 mV = 1 cm
What is the standard sensitivity that most dog and cat ECGs run at?
1 mV = 0.5 cm (1/2 sensitivity)
What setting will permit visualization of larger waveforms by reducing the size of the wave?
1 mV = 2 cm (Double or 2x sensitivity)
*This setting also increases movement artifacts
What setting will permit visualization of smaller waveforms by doubling the size of the image?
Width of the wave measured in mm/sec
What does the horizontal measurement in the ECG represent?
• 50 mm/sec for dogs and cats
• 100 mm/sec for small animals (high HR)
• 25 mm/sec in large animals (low HR)
List the standard paper speed settings in mm/sec
0.02 seconds
• Each box is worth 0.01 secs at 100 mm/sec
• Each box us worth 0.04 secs at 25 mm/sec
At a standard speed of 50 mm/sec, the width of each tiny box on the ECG is worth how many seconds?
20 method and 3000 method
Name the two methods of ECG calculation of heart rate that can be used with a tracing speed of 50 mm/sec
Count the # of ECG complexes that occur in 3 seconds (or under three black marks) and multiply by 20
How do you estimate heart rate using the 20 method (50 mm/sec) on ECG?
Calipers
Multiply # of complexes by 2 and then multiply 20 to get the heart rate
What instrument can use to cover the distance between the three dots (equals 3 seconds) at the top margin of ECG paper?
How do you get a heart rate if you only see 2 dots at the top margin?
3000 divided by the # of tiny boxes (equal to 0.06 secs) counted between two R waves
How do you estimate heart rate using the 3000 method (50 mm/sec) on ECG?
Slower speed for animals with lower heart rates
What does the use of a 25 mm/sec paper speed indicate?
10 method and 1500 method
Name the two methods of ECG calculation of heart rate that can be used with a tracing speed of 25 mm/sec
When R-R intervals are NOT regular
When is using the 10 method of HR calculation useful?
Multiply # of complexes found under 3 marks (which equals 6 seconds) and multiply by 10
How do you estimate heart rate using the 10 method (25 mm/sec) on ECG?
1500 divided by # of tiny boxes between the R wave of two successive ECG waves
How do you estimate heart rate using the 1500 method (25 mm/sec) on ECG?
Patient has a fast or slow heart rate especially if mentation is abnormal
When should a doctor be alerted about a patient's heart rate?
1) General rhythm evaluation - regular or irregular?
2) Identification of P waves - atrial contraction or systole
3) Identification of QRS complexes - ventricular contraction or systole
4) Interpretation of relationship between P waves and QRS complexes
5) Determine if all P waves look alike and QRS waves look alike
List the five rules of cardiac rhythm
P wave
For every QRS complex, there should be a _____ and vice versa
The same electric current that travels in the atria is traveling through the ventricles (P wave is related to QRS)
How do you interpret the relationship between P waves and QRS complexes?
• A pulse should follow every beat
• HR is auscultated and counted
• Pulse is palpated at the same time
How do you know if a heartbeat is regular?
• SA and AV nodes
• Bundle of His (R and L bundle branches)
• Purkinje fibers
List the components of the heart's conduction system
SA node
Where does conduction of the heart begin?
• Sinus bradycardia
• Sinus tachycardia
• Sinus arrhythmia
List common rhythms associated with the SA node
Electricity traveling through the heart (R to L and base to apex)
What creates an ECG wave?
Electrical travel in the frontal plane
What does a basic 6-lead ECG detect?
Electrical travel to the positive pole of lead II
Each ECG lead has a negative and positive pole. Where is electrical travel most commonly observed?
Wave formation
_____ is based on the travel of electricity through the heart
Mean electrical axis (MEA)
What is the average travel of electrical impulses referred to as on Bailey's six-axis reference system?
40-110 degrees
What is the normal mean electrical axis (MEA) is the canine?
0-155 degrees
What is the normal mean electrical axis (MEA) is the feline?
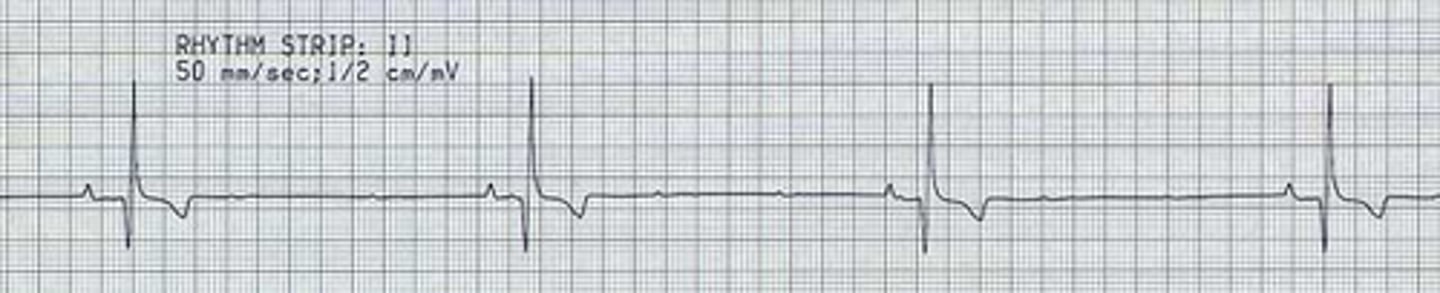
Sinus bradycardia
Slower than normal rhythm that originates from the SA node
• High vagal tone (acetylcholine)
• Systemic disease such as hypothermia or hypothyroidism
• Drugs such as beta blockers and anesthetics
What is sinus bradycardia associated with?
Artopine
What can be used to increase heart rate or vagal origin?
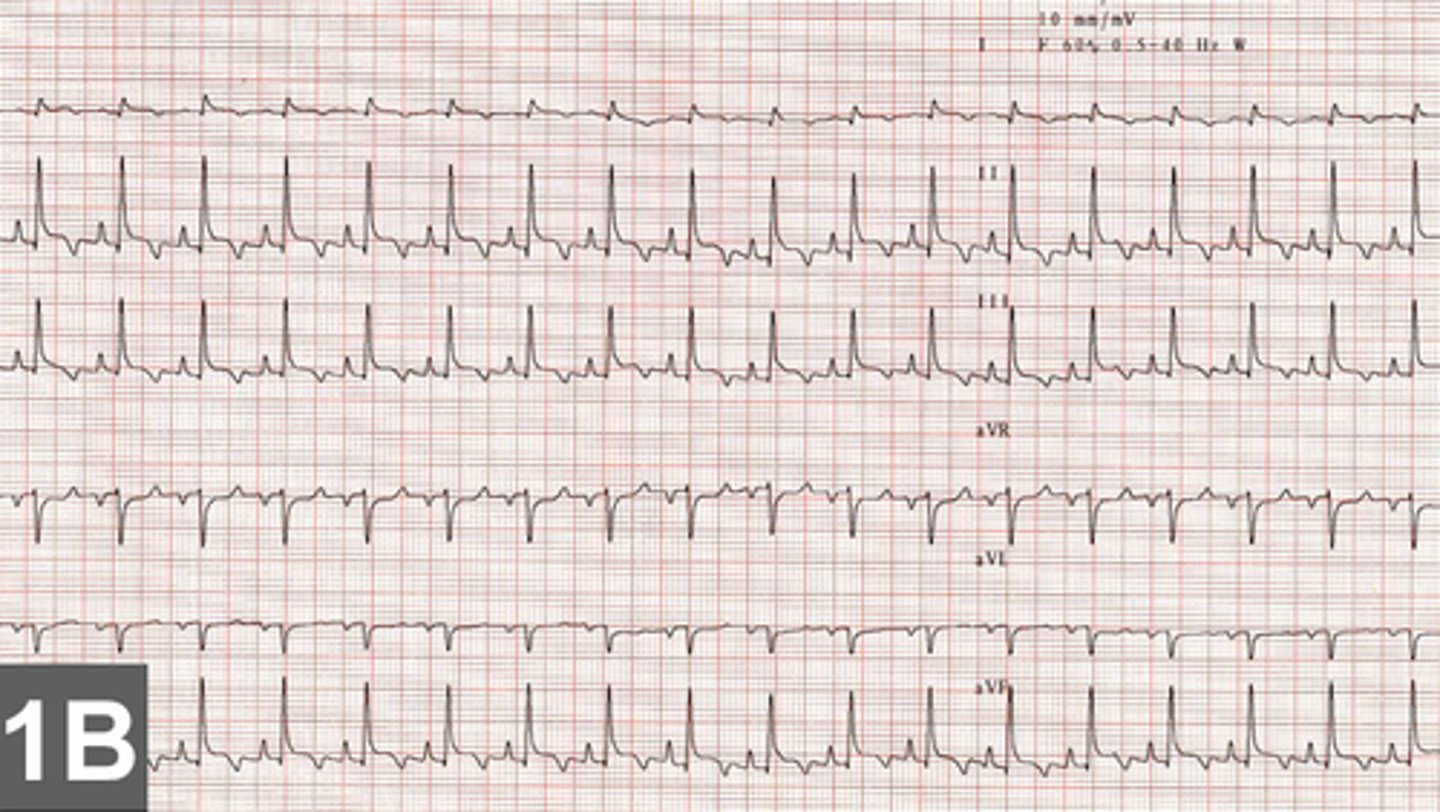
Sinus tachycardia
Faster than normal rhythm that originates from the SA node
• High sympathetic tone caused by pain, stress, excitement
• High sympathetic tone caused by drugs (atropine, catecholamines)
• A response to fever, shock, or hemorrhage
What is sinus tachycardia associated with?
Sinus arrhythmia (pulse deficits NOT present)
A "regularly irregular" rhythm that varies with inspiration and is not usually harmful
• Increases with inhalation (P wave height increases)
• Decreases with exhalation (P wave height decreases)
During a sinus arrhythmia, heart rate _____ with inhalation, and _____ with exhalation
P pulmonale
Right atrial enlargement that causes a tall P wave
P mitrale
Left atrial enlargement that causes a wide P wave
First heart sound produces a "lub"
What is S1 and what sound does it make?
Closure of AV valves (mitral and tricuspid)
What does the first heart sound (S1) represent?
Second heart sound produces a "dub"
What is S2 and what sound does it make?
Closure of semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonic)
What does the second heart sound (S2) represent?