Sex Differences Across Animals
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Describe the gynandromorphic bird example.
Half of the rooster/zebra finch has testes and the other half has ovaries; leads to asymmetrical coloring and features
in zebra finch song nuclei developed on the male side
Chromosomes take priority in gene expression in chickens, cell by cell basis of expressing phenotype; can’t happen in mammals, each cell is guided by gonadal hormones
Birds - morphology is sex-determined; “balkanization” : states separated, don’t pay attention to nearby cells
Mammals - morphology guided mostly by hormones traveling through bloodstream, with some chromosomal influences (i.e. four core genotypes)
What are the modes of sex determination across vertebrates?
Genetic sex determination (GSD)
XX-XY (mammals, some reptiles)
WZ-ZZ (birds)
Environmental sex determination (ESD)
temperature
Social context
Describe the different types of chromosomes.
Autosomes: all chromosomes, except sex chromosomes
parts of chromosomes can cross-over and recombine during meiosis in a process called recombination, adds to genetic diversity
Sex chromosomes: one set of chromosomes that determine the sex of the organism
many more non-homologous regions, very little recombination (don’t exchange same level of DNA like autosomes do)
Some traits are more adaptive for one sex over the other
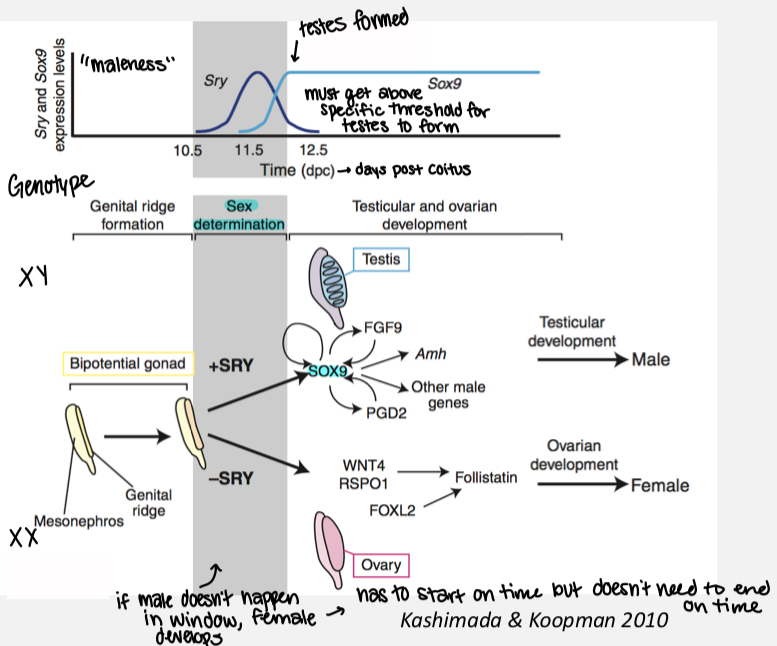
Describe the XX-XY mode of genetic sex determination.
Mammalian pattern (and some reptiles like snakes) - XX/XY
males are the heterogametic sex (XY) → high dosage of SRY
Females are the homogametic sex (XX) → no dosage of SRY
Depends on timing of SRY, threshold of SRY, and threshold of XY cells (>35% for testes i.e. Y chromosome needs to be present in at least 35% of somatic cells to form testes even if there’s a Y chromosome)
* Chimera: lab constructed half and half animal
What are the exceptions of XX/XY determination in mammals?
Spiny rat and mole vole have lost their Y chromosome - both sexes are XO
other genes have taken over in activating SOX9 pathway in males
Some grass mice females can be either XX or XY*
African pygmy mouse males can be either X*X or XY
* designates an unknown change in the chromosome, that functionally results in sex-reversal
Describe the WZ-ZZ mode of genetic sex determination.
Bird pattern - ZW/ZZ
males are the homogametic sex (ZZ) → high dosage of DMRT1
Females are the heterogametic sex (ZW) → low dosage of DMRT1
Eggs highly sensitive to estrogens → feminizes body and brain in birds
DMRT1 is SRY equivalent but it’s on the more common chromosome
Estrogen in birds feminizes (opposite to rodents)
ZZ can be sex reversed to female if estrogen is added during critical period of gonad formation
How is the song system organized in zebra finches?
It is not hormonally organized
Male zebra finches sing courtship songs, females do not
Brain regions controlling song in male brains are 5-6 times larger than in female brains
Organizational estradiol does not demasculinize (males still develop the song system)
Sex differentiation of the song system in the zebra finch follows genetic sex not gonadal sex
although some estradiol exposure will reduce the ability of typical song pattern in most songbirds where males sing - even when taught by tutor
How do activational hormones work in birds?
In male birds, like rodents and primates, the activational hormone is primarily testosterone
However, unlike rodents and primates, there are a few behaviors in birds that require aromatized estradiol to bind to estrogen receptors for activation
proper song production and learning (in songbirds)
Territorial aggression in some species (in song sparrows)
Courtship displays (in Japanese quail)
Organizational E2 demasculinizes males, organizational androgens do nothing (as long as we prevent aromatization to E2)
Birds are mirror image of mammals
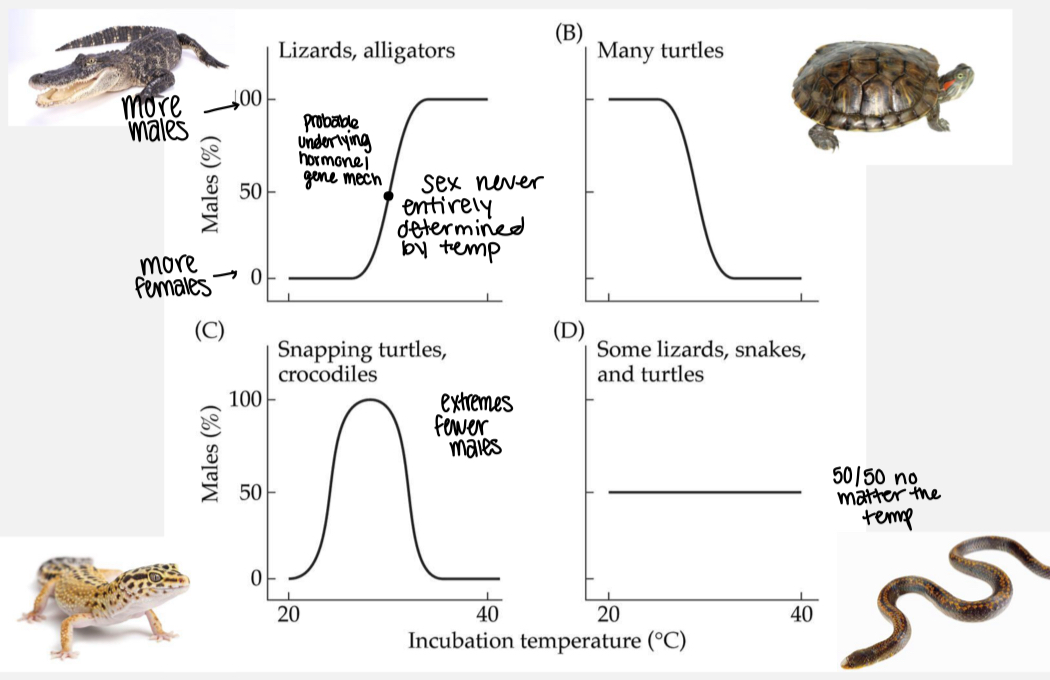
Describe the temperature mode of environmental sex determination.
TSD taxa and climate change caveat: short heatwaves during fluctuating incubation regimes produce females under temperature-dependent sex determination with implications for sex ratios in nature
What are the social context modes of environmental sex determination.
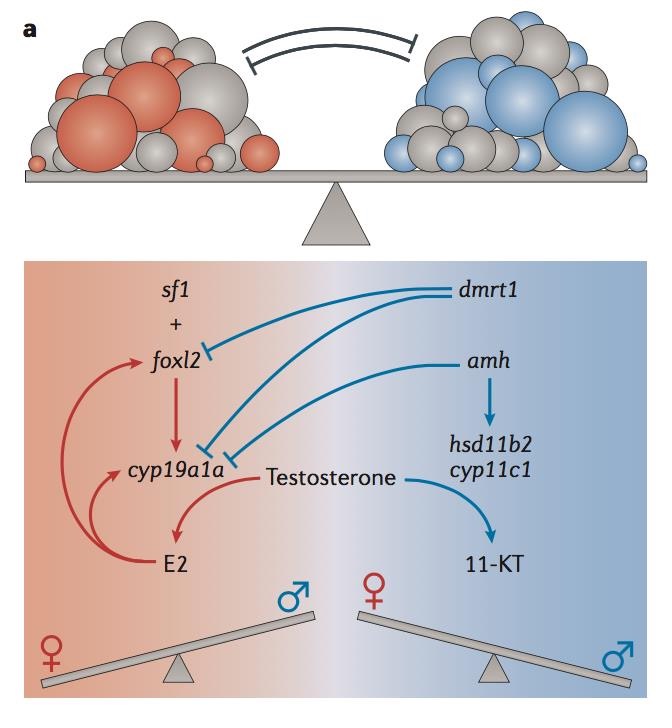
Gonochoristic fish
Sequential hermaphroditism
Simultaneous hermaphroditism
What is a gonochoristic fish?
Gonochoristic fish: an individual remains the same sex throughout their life
Often XX/XY
DMY is sex determining region on Y chromosome
E.g. Medaka fish
What are sequential hermaphrodites?
an individual is born one sex but changes to the other sex at some point during their life
sex change accompanied by complete changes in gonads and hormones
Protogyny: beginning as female, switching to male
Most common in fish
There are primary males and primary females
Primary females may turn into terminal males
E.g. parrotfish
Protoandry: beginning as male, switching to female
E.g. clownfish
What are simultaneous hermaphrodites?
the sex organ is partitioned into both male and female parts
Ovotestes produce both eggs and sperm
Still practice sexual reproduction (alternate roles)
E.g. black hamlet fish
What are some other environmental sex determiners besides temperature and social factors?
Multi-component, mutually antagonistic pathways: Social status, density, growth rate, pH, oxygen concentration, background color, temperature, sex chromosomes, dominant genes, germ cell numbers
Master regulator or a “parliamentary decision”
selection has retained antagonism between the male and female pathways across vertebrates
The specific genes/proteins/enzymes/metabolic pathways involved vary from system to system