Principles of Microeconomics: Market Structures, Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a market?
A group of buyers and sellers who exchange goods or services for payment.
What characterizes a competitive market?
Many buyers and sellers with negligible effect on price, where all goods are identical.
What is the Law of Demand?
As the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded increases, and vice versa.
What is a Demand Schedule?
A table showing the relationship between quantity demanded and the price of a good.
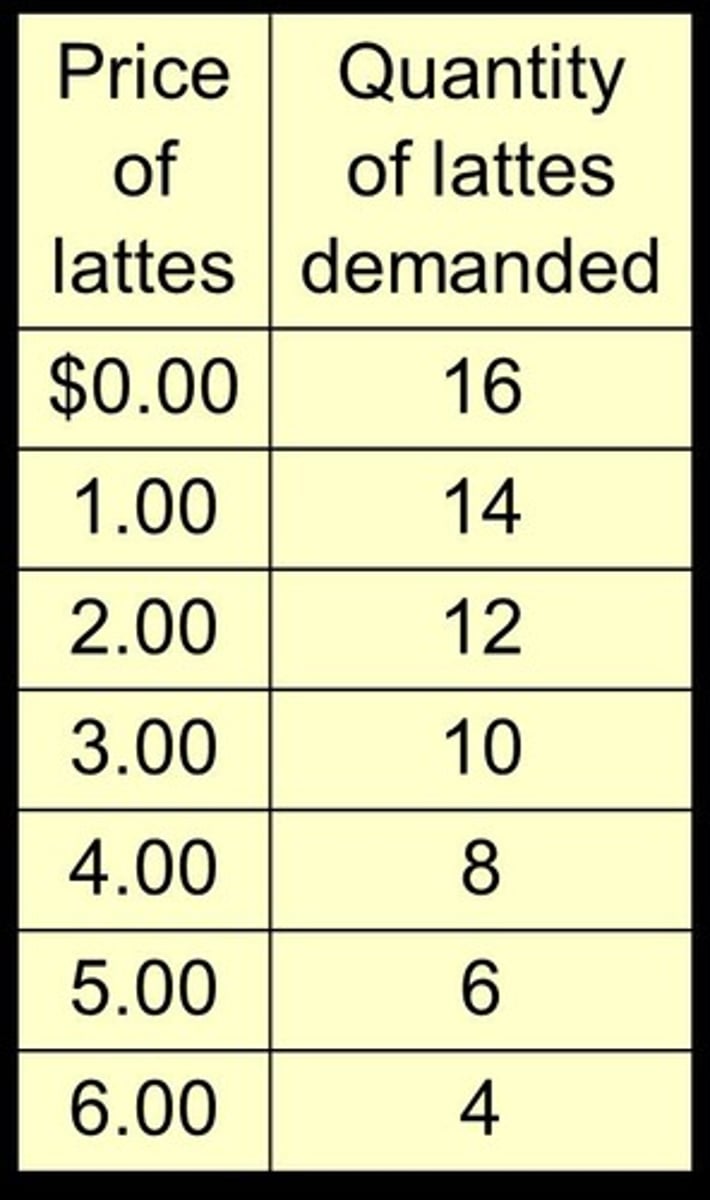
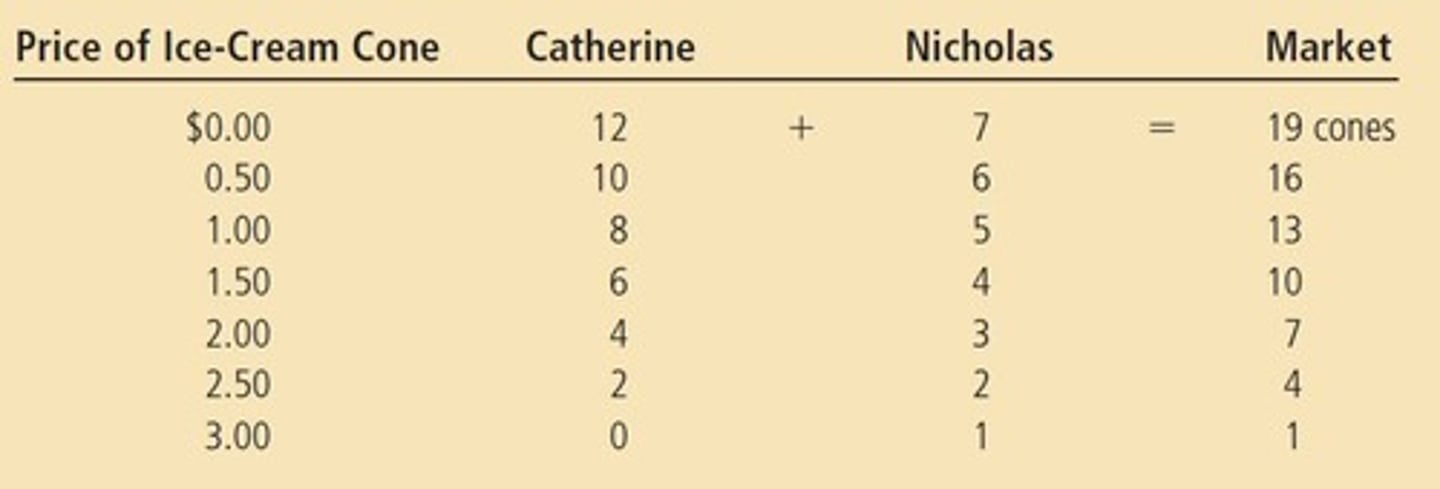
What is the difference between Individual Demand and Market Demand?
Individual Demand refers to the demand of a single consumer, while Market Demand is the sum of all individual demands in the market.
What are the determinants of demand?
Price of the good, income (normal and inferior goods), prices of related goods (substitutes and complements), taste/preferences, future expectations, and number of buyers.
What causes a shift in the demand curve?
Changes in non-price determinants of demand, such as income or preferences.
What is Quantity Demanded?
The amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase at a given price.
What is Quantity Supplied?
The amount that sellers are willing and able to sell at a given price.
What is the Law of Supply?
As the price of a good increases, the quantity supplied increases, and vice versa.
What is a Supply Schedule?
A table showing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied.
What are the determinants of supply?
Price of the commodity, input prices, prices of related goods, technology, expectations about future prices, and number of sellers.
What is the difference between Individual Supply and Market Supply?
Individual Supply refers to the supply from a single seller, while Market Supply is the sum of all individual supplies in the market.
What happens to the demand curve when demand increases?
The demand curve shifts to the right.
What happens to the supply curve when supply decreases?
The supply curve shifts to the left.
What is the equilibrium price?
The price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied.
What is the effect of a decrease in the price of a substitute good on the demand for a product?
It typically decreases the demand for the product.
What is a normal good?
A good for which demand increases as consumer income rises.
What is an inferior good?
A good for which demand decreases as consumer income rises.
What is the role of prices in a market economy?
Prices adjust to balance supply and demand, guiding economic decisions and allocating scarce resources.
What is the relationship between price and quantity demanded according to the law of demand?
There is a negative relationship; as price decreases, quantity demanded increases.
What happens to equilibrium price and quantity when demand increases?
Equilibrium price and quantity both increase.
What happens to equilibrium price and quantity when supply decreases?
Equilibrium price increases and quantity decreases.
What is the significance of the demand curve's downward slope?
It reflects the law of demand, indicating that lower prices lead to higher quantities demanded.