Biology Final
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
What are the most 4 common elements in living things?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
Ionic Bonds
weak bond formed by transfer of electrons between atoms but they do not make a molecule, only stick them together
Hydrogen Bonds
polar water molecules create weak molecular attractions to each other
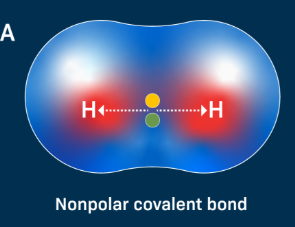
Polar Covalent Bonds
strong bonds formed when atoms share electrons equally, resulting in the formation of molecules
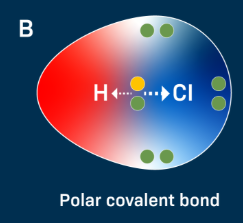
Non-Polar Covalent Bonds
strong bonds formed when atoms physically share electrons unequally, resulting in the formation of molecules
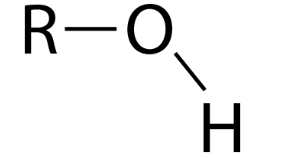
What functional group is this?
Hydroxyl
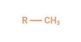
What functional group is this?
Methyl
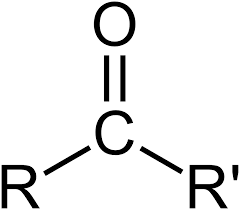
What functional group is this?
Carbonyl
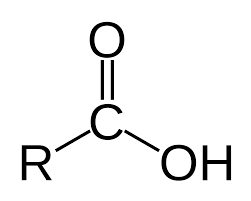
What functional group is this?
Carboxyl
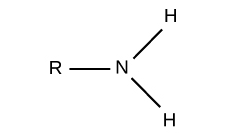
What functional group is this?
Amino
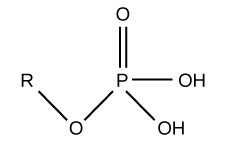
What functional group is this?
Phosphate
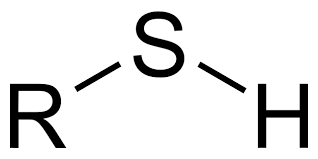
What functional group is this?
Sulfhydryl
Why is carbon so good for life?
can form 4 covalent bonds with other elements, is the ultimate lego building block and can create multiple different compounds
What pH value(s) correlate with acidity?
1-6
What pH value(s) correlate with neutral?
7
What pH value(s) correlate with basic?
8-14
What are the properties of water?
polar, unique structure, and high specific heat capacity
Explain Polar property of water
have positive charge on one side (H) and negative charge on the other side (O2), leading to its ability to form hydrogen bonds.
Explain Unique Structure property of water
covalent bonds that hold O2 to H within molecule so Oxygen and Hydrogen electrons are shared
Explain High Specific Heat property of water
can absorb large amounts of heat without significantly changing temperature, which helps regulate temperature in environments.
How does water dissolve in ions like NaCl?
molecules surround and interact with the Na+ and Cl- ions due to its polar nature, allowing it to pull the ions apart and dissolve them in solution.
Carbohydrate Elements
C, H, O
Carbohydrate Monomer
monosaccharide
Carbohydrate Examples
cellulose, sucrose, and glucose
Carbohydrate Roles
quick energy, storage, building material, used in cellular respiration
Lipid Elements
C,H,O,P
Lipid Monomer
glycerol and fatty acids
Lipid Examples
Steroids (cortisol), phospholipids, and waxes
Lipid Roles
fats (insulation), store energy, chemical messenger (steroids), protection (waxes), components of cell membrane
Protein Elements
C,H,O,N,S
Protein Monomer
amino acids
Protein Examples
enzymes and antibodies
Protein Roles
messenger, structural, transport, storage
Nucleic Acid Elements
C, H,O,N,P
Nucleic Acid Monomer
nucleotides
Nucleic Acid Examples
DNA and RNA
Nucleic Acid Roles
store, transmit, and express genetic information
What are the functional groups inside of the base amino acid?
Carboxyl, Amino, and R-side chain
Which biomolecule can have mutations?
nucleic acid
What kind of bond is formed between amino acids to build proteins?
polypeptide bonds
Hydrolysis
using water to break bonds
Dehydration Synthesis
remove water to form bonds
What is an independent variable?
factor that is manipulated in an experiment to determine its effect on a dependent variable
What is an dependent variable?
factor that is measured in an experiment to assess the impact of the independent variable
What is an enzyme?
a protein that acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions
What does it mean when an enzyme/protein denatures?
a change in shape that prevents it from functioning properly.
What causes enzymes/proteins to denature?
Factors such as high temperatures, extreme pH levels, or certain chemicals
A cell with 40% solute is put in a solution of 90% water, is it hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic?
hypotonic
A cell with 40% solute is put in a solution of 90% water, does it shrink, swell or stay the same?
swells
Eukaryotes
Organisms with complex cells containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Prokaryotes
Single-celled organisms without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
Viruses
Small infectious agents that replicate only inside the living cells of an organism
What traits do eukaryotes, prokaryotes and viruses all have in common?
all evolve and have DNA
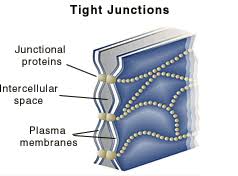
Tight Junction
impermeable, and fuses cells (ex. stomach lining)
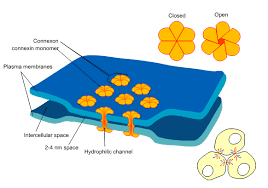
Gap Junction
permeable, proteins channels that connect cells, and allows for easy exchange
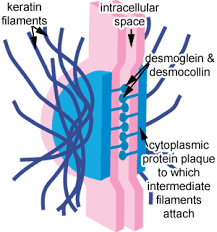
Anchoring Junction
semipermeable, connect at single point, and link using cytoskeleton
What is the pathway for making a protein?
transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, followed by translation of mRNA to an amino acid chain at the rough ER, then folding and post-translational modifications in the Golgi apparatus, and finally the export of the protein from the cell membrane
What are the two main structures found on cell membranes used for cell signaling and recognition?
membrane proteins and glycolipids
What is the role of glucose in living organisms?
simple sugar that is a main source of energy for cells
What process is glucose a reactant for?
Cellular Respiration
What kind of surface area to volume ratio is ideal for cells? Why?
high ratio because it facilitates efficient transport of materials in and out of the cell, supporting better metabolic functioning.
Diffusion
the passive movement of molecules from high to low concentration
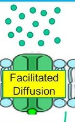
Facilitated Diffusion
how molecules pass through the cell membrane via specific transport proteins, allowing substances that can't directly go thru bilayer to cross in/out of cell
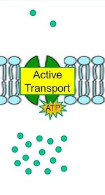
Active Transport
moving molecules across cell membrane against concentration gradient using energy, typically in the form of ATP.
Nucleus
control center, protects DNA, and site of ribosomal assembly
Nucleolus
site of ribosomal assembly
Rough ER
studded with ribosomes, has tubular cisternae, and produces proteins for export
Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes, has tubular cisternae, produces lipids, and detoxes poisons
Golgi Apparatus
fat sacs, received vesicle from ER, and modified packages/sorts substances
Lysosome
contains enzymes, digests foods, breaks down worn out organelles, eats invaders, and made at golgi
Centriole/Centrosome
made of microtubules and organizes them (directs mitosis/meiosis)
Mitochondria
site of cellular respiration, all eukaryotes have them, and inner membrane is called cristae
Chloroplast
site of photosynthesis, originated from cyanobacteria, and produces glucose (not ATP)
Vacuole
stores water/waste/sugars, and is central/large in plants
Ribosome (not an organelle)
made of RNA/proteins, synthesizes proteins, found in rough ER/cytoplasm and both Eukaryotic and prokaryotic have them
What is the equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
light + 6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6 O2
How do cellular respiration and photosynthesis relate to each other?
They are complementary processes and both involve the flow of energy
Aerobic
uses oxygen
Anaerobic
does not use oxygen
NADH and FADH2
electron carriers that transfer energy during cellular respiration
Glucose in Cellular Respiration
a simple sugar that is a primary energy source for cells during cellular respiration
Oxygen in Cellular Respiration
molecule used as the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration, enabling ATP production
CO2 in Cellular Respiration
product of cellular respiration during the Krebs cycle.
H2O in Photosynthesis
breaks down into O2 and H+ which releases electrons to start the light dependent reactions
CO2 in Photosynthesis
product utilized during the Calvin cycle to synthesize glucose
NADPH and ATP in Photosynthesis
energy carriers produced in the light-dependent reactions that provide energy for the Calvin cycle
Light in Photosynthesis
necessary for the light-dependent reactions to occur, as it drives the conversion of water into oxygen and energizes electrons.
What are the mains steps in aerobic respiration?
Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, ETC, and ATP Synthase (oxidative phosphorylation)
Which step is in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
glycolysis
Why/how is glycolysis found in all living things?
it is the 1st step of any kind of ATP generation, whether there’s oxygen or not
Where does light dependent reactions occur?
inside thylakoid membrane
Where does Calvin cycle occur in photosynthesis?
inside stroma
What are the products of photosynthesis?
oxygen and glucose
What are the inputs of photosynthesis?
water, CO2, and light
What “batteries” go into Calvin Cycle from Light Reactions?
ATP and NADPH
What “batteries” go out if Calvin Cycle and into Light Reactions?
NADP+ and ADP
Oxidized
loss of electrons
Reduced
gain of electrons
How much ATP is made from glycolysis?
4 (net 2)