4.1.1. Economics methodology
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the similarities between natural and social science?
both study hypothesis
Both use empirical data
Both use measured data
What are the differences between natural and social sciences?
SS is subject to personal prejudice, whereas NS is based on facts
economists can’t conduct controlled laboratory experiments where only one variable is changed at a time.
How do economists get around the problem of the existence of multiple variables in an economy?
economists use the assumption known as ceteris paribus, which is Latin for ‘all other things remaining equal’.
What is the definition of a positive statement?
objective statements that can be tested by referring to the available evidence.
Statements are impartial/unbiased
Important because they can be tested to see whether or not economic ideas are correct
What is the definition of a normative statement?
subjective statements which contain a value judgement — they’re opinions.
important because value judgements influence decision-making and government policy,
What is the definition for an economic agent?
any organisation/individual that impacts the economy by their actions
There are 4 different types
Households
Businesses
Government
Central banks
What is the purpose of economic activity?
The production of goods and services to satisfy needs and wants
What are the key economic decisions?
what to produce
How to produce
Who is to benefit from the goods and services produced
What are free market economists?
-where firms decided what goods and services to produce with limited intervention from the government
What is the definition of a want?
those things that are desired but not essential to survive
What is the definition of a need?
Those things required that are essential to maintain survival
What is the basic economic problem?
How can the available scarce resources be used to satisfy people’s infinite needs and wants as effectively as possible?
The scarce resources (inputs) used to make the things people want and need (outputs) can be divided into four factors of production.
What are they?
land
Labour
Capital
Enterprise
Expand on labour:
includes all the workforce in an economy
Value of a worker= human capital
Reward = wages
Expand on land:
all natural resources that come from the earth that are used in the production of goods and services
E.G oil,crops, air, fish
Reward= rent
Expand on Capital:
man made aids that are used in the production process
E.g machinery, tools, factories and offices
Bring a stream of income in the future
Reward= interest
Expand on Enterprise:
an individual/s that take the factors and organises them into order to ridicule products that will be profitable
Take risks to create wealth and employment in the economy
Reward = profit
What is the fundamental economic problem?
scarcity = it means there are limited resources
however in the economy there are unlimited wants
Choices have to be made about how the scarce resources are allocated between different uses
What does opportunity cost mean?
Give an example
benefit lost of choosing the next best alternative
20 instant coffees vs 1 £3 Starbucks coffee
What does production possibilities mean?
maximum output an economy can achieve when all its resources are fully/efficiently employed
different combinations of output for two products e.g. good 𝑥 and good 𝑦 given the resources available
What can a PPF illustrate?
the features of the fundamental economic problem
Resource allocation
An opportunity cost
Trade offs
What are the key points of a PPF/C?
as the output of good (x) increases the good (y) decreases and vice versa
Illustrates problem of choosing scarce resources to when producing goods and services
Opportunity cost in deciding what combinations of good (x) and (y) to produce
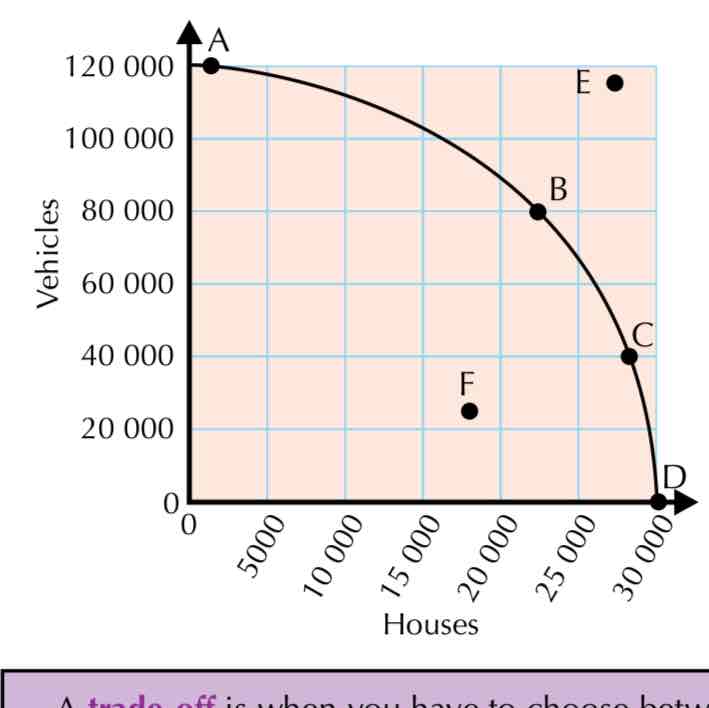
What does this PPF show?
Points A, B, C and D (and every other point on the PPF) are all achievable without using any extra resources. However, they are only achievable when all the available resources are used as efficiently as is actually possible.
• Notice how, as you move along the curve from A to B, you’re building more houses (about 22 500 instead of 1000) but fewer vehicles (80 000 instead of 120 000).
• Moving along the curve from A to B like this corresponds to allocating more resources to the production of houses, and fewer resources to the production of vehicles.
• In other words, there’s a trade-off between ‘building more houses’ and ‘making more vehicles’
— to do more of one, you have to do less of the other.
E = unobtainable as there aren’t enough resources to produce this level of output
F= inefficient as not all resources are being used , under use of resources
What is a trade off on the PPF?
Movement along the PPF away from one product to another
What are investment goods?
Goods that produce a stream of income in the future (capital goods)
What are consumption goods?
Those that produce an immediate benefit to the consumer
Car for personal life
We know that if the total amount of resources changes, there is only movement along the PPF
What happens if the amount of resources increases?
the PPF itself moves (either inwards or outwards)
an outward shift of the PPF shows economic growth
An inward shift shows negative economic growth
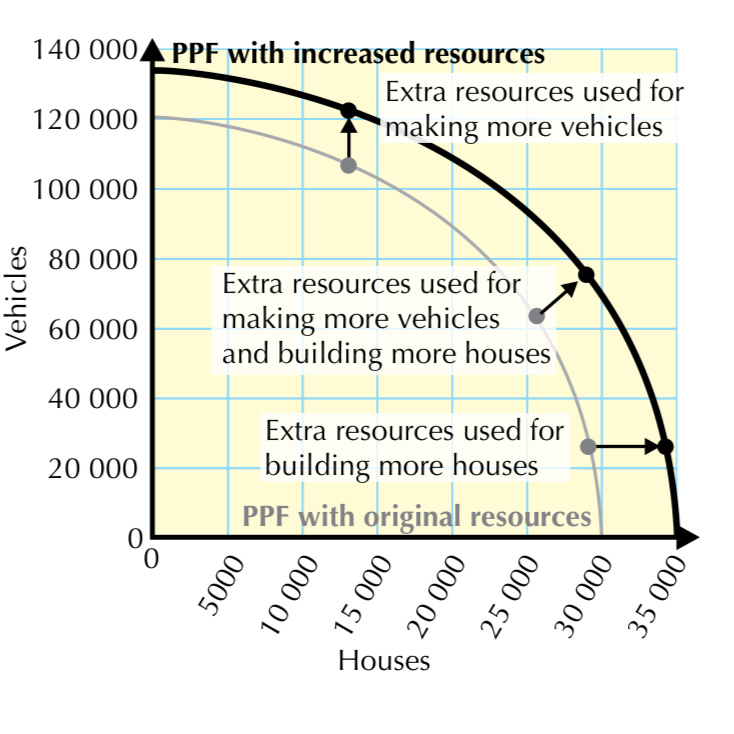
What can cause the PPF to shift outwards?
increased resources
Increased workers
Any increase in the FOP
Improved technology
Improvements to labour
This is due to more output being produced using the same resources