Thermal physics
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
A small block of ice is placed on a large aluminium block which has been sitting for time in a laboratory.
Estimate the initial temperatures of the Aluminium block and ice.
What will the final temperature of the ice be?
Describe what happens to the ice over time. State the direction and type of the flow of thermal energy
Describe the motion and spacing of the water molecules before and at the end. Relate this to temperature, kinetic, potential and internal energy.
Describe and explain the temperature change while the ice is changing phase.
Innitial temperature: Ice -18 °C, Aluminium 20 °C
0 °C
The temperature of the ice will increase towards 0 °C as thermal energy flows from the aluminium (higher temperature) to the ice (lower temperature) due to conduction.
Start: molecules vibrate about a fixed point, molecules are closely packed. End: molecules are closely packed but now free to move past each other. Internal energy increases due to heating of ice (more KE) and melting (more PE)
When the water changes from solid ice to liquid water, this is a phase change at constant temperature. There is an increase of potential energy during this change no change in KE
A student investigates Brownian motion by observing through a microscope smoke particles suspended in air.
Describe the behaviour of the smoke particles as observed by the student. In your answer, you should use appropriate technical terms spelled correctly.
State how the observations lead to conclusions about the nature and properties of the molecules of a gas.
The smoke particles move in random / haphazard / zig-zag / jiggling / jerky manner (random / haphazard / zig-zag / jiggling / jerky must be spelled correctly)
Link observations to an appropriate conclusion:
The movement of smoke particles caused by (being hit by) randomly moving air molecules
The smoke particles are continuously moving because the air molecules are continuously moving
The smoke particles are visible but air molecules are not hence air molecules must be (very) small.
The small movement of smoke particles is due to the large numbers of air molecules hitting from all sides
Discuss and note on a mini whiteboard how the crowd surfing analogy is similar and different to Brownian motion observed for pollen grains in water.
Similar:
Many people are pushing on the crowd surfer and the resultant force determines the direction of motion.
They are unlikely to travel in a straight path.
Different:
The size of the people surfing and holding them up is the same. The water molecules have a much smaller volume and mass.
The pollen grains are pushed in random directions at random speeds. The resultant path is therefore random.
In an electric shower water flows through a pipe and is heated by an electric heater coil surrounding the pipe. The water flows through the heating section at a flow rate of 0.0001 m3s-1.
The electric heater has a voltage of 230V across it and a current of 60A running through it and 85% of the energy it produces ends up at internal energy in the water.
What is the temperature rise of the water?
Specific Heat Capacity of Water = 4200 J kg-1 K-1
Density of water = 1 g cm-3



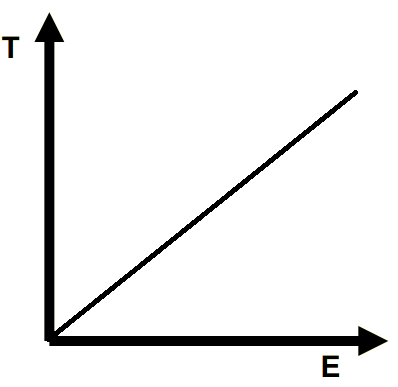
Draw the line of a Temp (T)-heat (E) graph of a solid substance with heat being added to it.
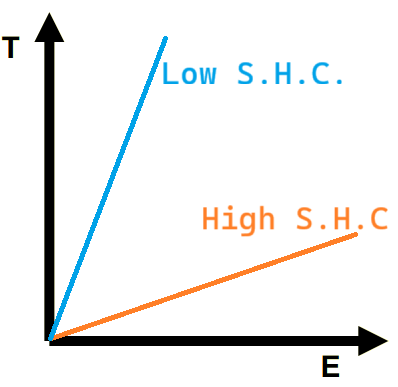
Draw the line on a Temp (T)-Heat (E) graph of a solid with high specific heat capacity (H) and another with low specific heat capacity (L) with the same mass
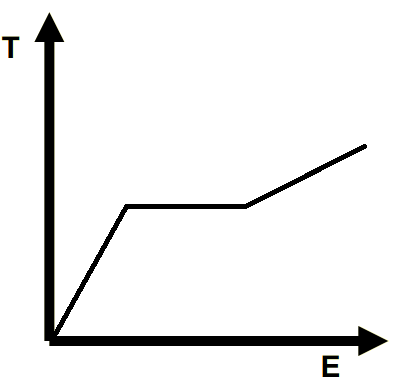
Draw the heating line of a solid heating up, then melting into a liquid with a higher specific heat capacity, then the liquid heating up.
What is internal energy?
Internal energy is the sum of the randomly distributed kinetic and potential energies of atoms or molecules in substance
What happens to internal energy, kinetic and potential energy when:
the temperature increases
there is a change of state.
As temperature rises: the KE increases but not the PE.
As state changes: no change in KE, potential energy changes as spacing of atoms/molecules changes
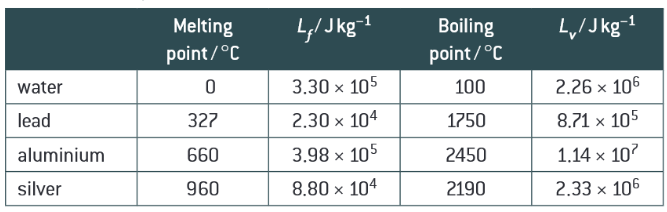
Compare Lf and Lv for the same substance. Explain this.
Larger difference between the internal energy of the gas and the liquid than between the liquid and the solid. Interatomic/molecular spacing change greater for liquid to gas than solid to liquid
A coffee machine in a café passes steam at 100 °C through 0.18 kg of cold coffee to warm it. If the initial temperature of the coffee is 14 °C and 21 g of steam passes through it, what will the final temperature of the coffee be?
cw = specific heat capacity of water/coffee = 4200 Jkg-1K-1
Lw = specific latent heat of vaporisation of water = 2.26 x 106 Jkg-1
Latent heat lost by steam condensing at 100 ℃ + Energy lost by condensed steam cooling from 100 C to = energy gained by coffee heating from 14 °C to θ
msLv + msCw(100-θ) = mc Cw (θ -14)
(0.021x2.26x106) + (0.021x4200(100-θ)) = 0.18 x 4200(θ - 14)
θ = 79 °C
A block of paraffin wax is melting at a constant temperature of 52 °C. Use the behaviour of paraffin molecules to describe and explain the changes to the internal energy of the molecules of the paraffin wax as it melts.
There is no change in KE because temperature is constant during melting
PE of the molecules increases during melting
Internal energy = KE + PE, so the internal energy increase