Lab Midterm Practicum
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What 2 Factors Determine the Actual FiO2 Delivered to the Patient?
Flow
Patient’s Minute Ventilation
What 2 Devices are the Best for COPD Patients?
Nasal Cannula (2 LPM)
Venturi Mask (28%)
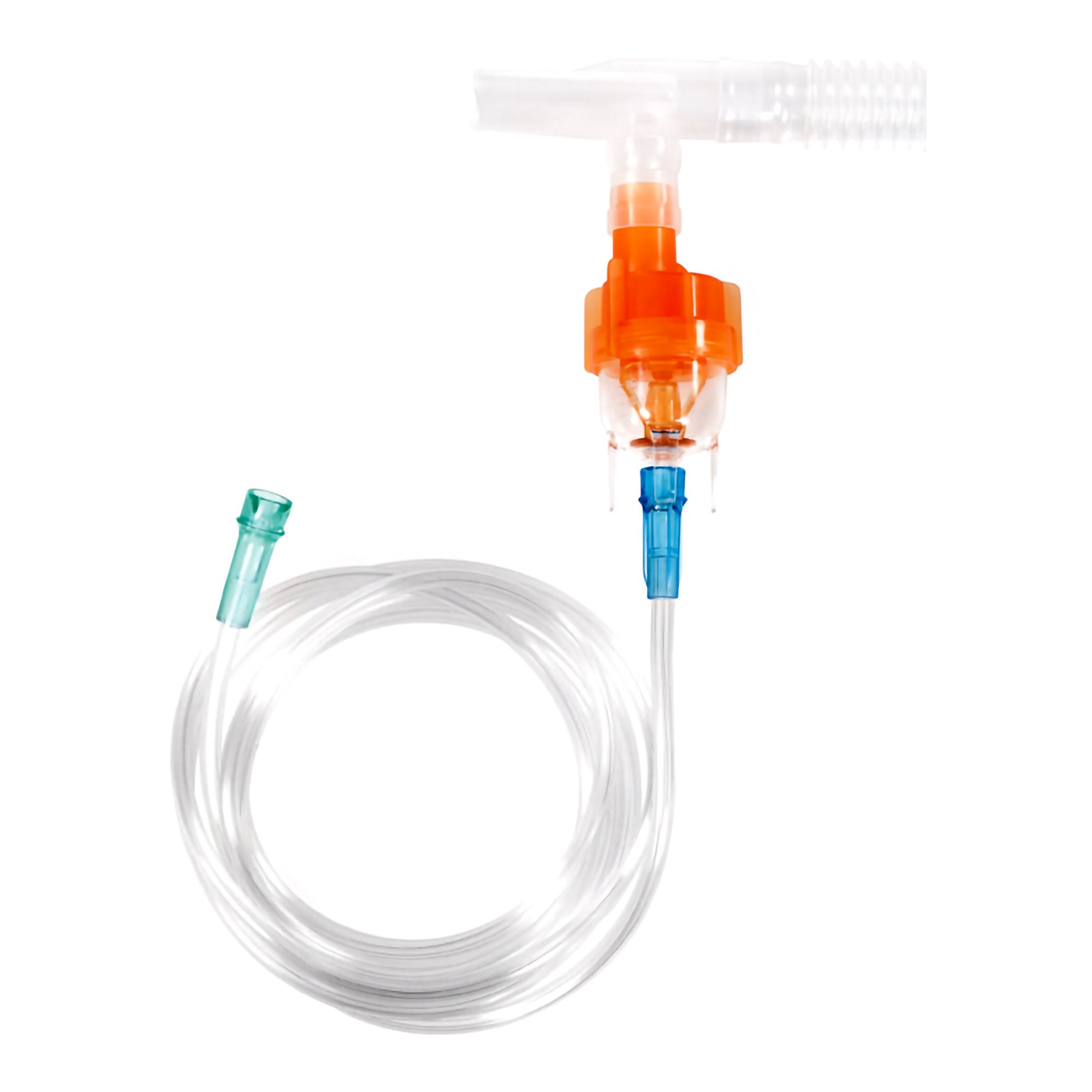
Misty Neb
Breath Enhanced
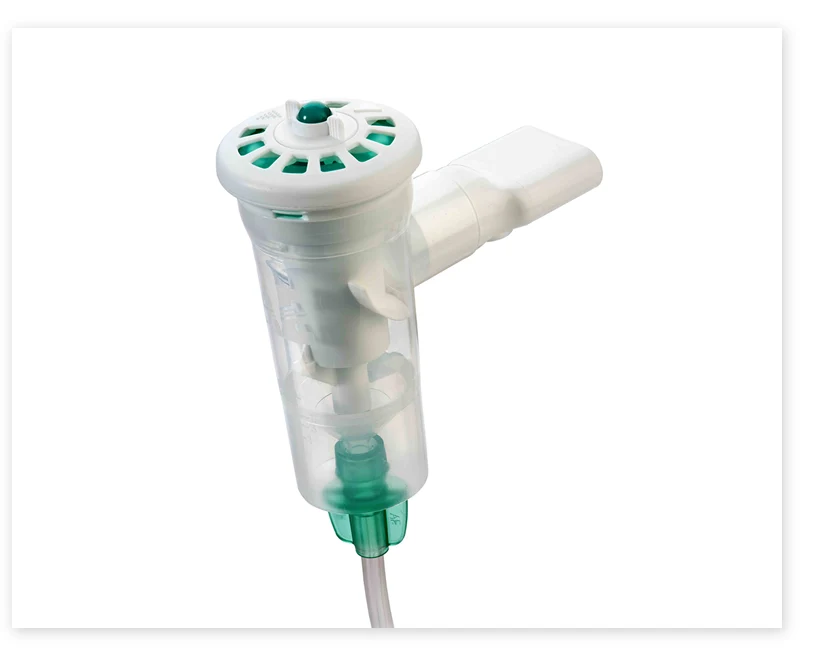
Aero-Eclipse "‘Mushroom Cap’
Breath Actuated
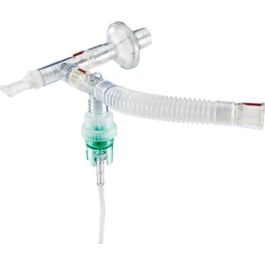
IsoNeb or Respirgard II
Continuous Flow and Filtered Neb
Used for Pentamidine
Pentamidine
Used for the Treatment of Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonia
Must Pretreat Patient with a Bronchodilator Before Treatment
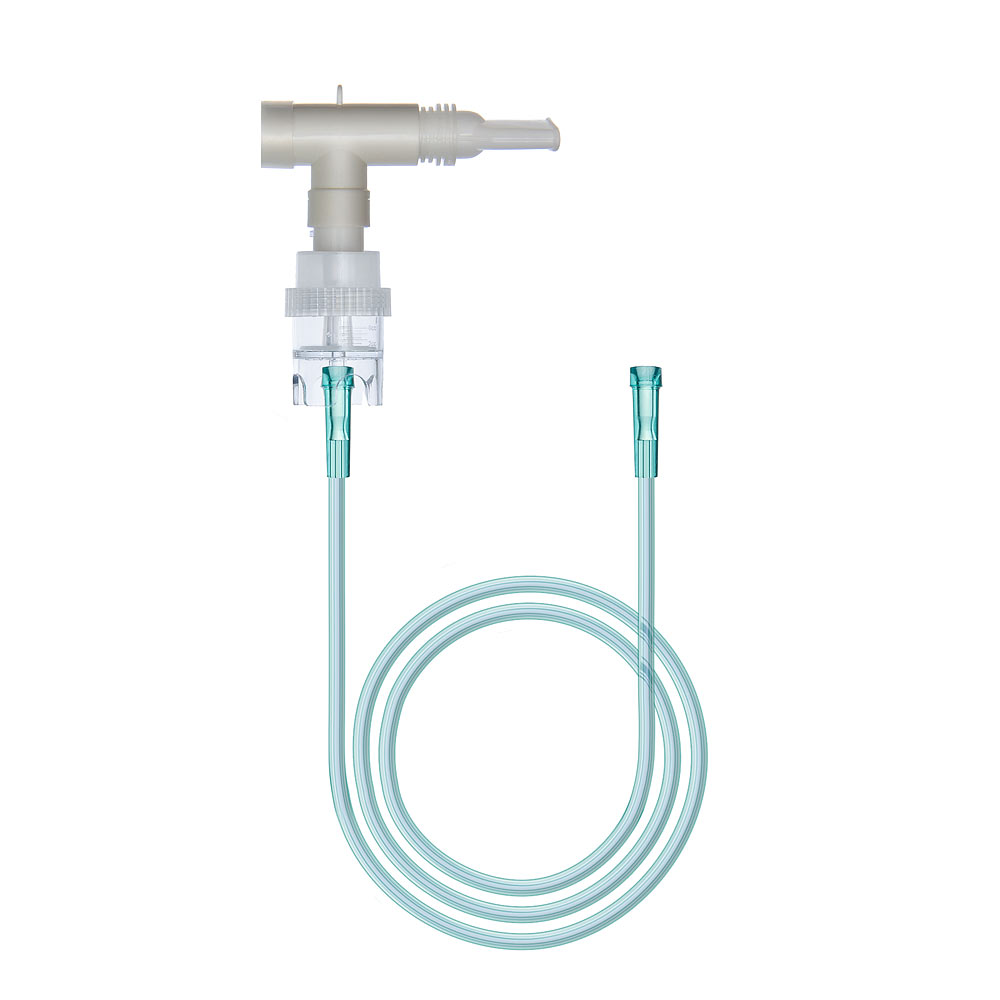
Standard Acorn Neb
Continuous/Jet Neb

Pari Nebulizer
Breath Enhanced
Used for Tobi and Dornase Alfa
Brovana
Generic: Arformoterol
LABA
Dosage: 15 mcg/2 mL
Frequency: BID
Used for Asthma and COPD
Racemic Epinephrine
Alpha-1 Adrenergic
Dosage: 11.25 mg
Frequency: Every 3-4 Hours
Used for Stridor/Croup
DuoNeb
Generic: Ipratropium and Albuterol
SAMA and SABA
Frequency: QID
Dosage: 0.5mg/3mg
Indication: Asthma and COPD
What Must a Patient be Instructed to Do After Any Treatments?
Cough
What Technique Must be Used to Deliver a Neb treatment to an Infant?
Blow Buy
What Tests are Run to Confirm a Pneumonia Diagnosis?
Sputum Culture
CBC w/ Differential
Culture and Sensitivity
What are the Side Effects of Albuterol?
Tachycardia
Tremors
What is a Side Effect of Ipratropium?
Dried Out Secretions
Formula to Calculate Oxygen Content (CaO2)
(1.34 x Hb x SaO2) + (PaO2 × 0.003)
Polycythemia
High Hb Levels
Normal Range of Hemoglobin
12 - 16 mEq/L
What Conditions Can Cause Polycythemia?
Chronic Hypoxemia
Severe Emphysema or Bronchitis
Bronchiectasis
CF
Congenital Heart Defect
Atrovent
Generic: Ipratropium
Dose: 0.5 mg/vial
SAMA or Anticholinergic
Frequency: QID
Indication: Asthma and COPD
Nebulizer with Misty Neb
Estimated Inspiratory Flow
3 x VE
Formula for Total Flow
(Sum of Ratio) x Flow
Use “Magic Box”
N-Acetylcysteine
Brand: Mucomyst
Class: Mucolytic
Dose: 20% - 3-5 mL
Frequency: TID or QID
Indication: Thick Secretions
Must Pretreat w/ Bronchodilator
What is the Target I:E (Inspiratory-to-Expiratory) Ratio for Most PEP Devices
1:3 or 1:4 cmH20
What Do you Do if the Patient is Breathing Above the 1:4 Ratio with a PEP Device?
Increase the Resistance
What Do you Do if the Patient is Breathing Below the 1:3 Ratio with a PEP Device?
Decrease the Resistance
What is the Target Expiratory Pressure During Most PEP Therapy?
10 to 20 cmH2O
What Interfaces can be Used with PEP Therapy?
Ambu Mask
Mouthpieces
Trach Interfaces
Which 2 PEP Device Cannot be Used In-Line with Nebulizers?
AerbiKa
Incentive Spirometry
What is the Normal Set Up for a Nebulizer?
Place on Room air (FiO2 = 21%)
Flow set to 6-8 LPM
Do Pediatric Patients Need a ‘Bubbler’/Humification When Receiving O2 via Nasal Cannula?
Yes
When Do Adult Patient Require a ‘Bubbler’ with a Nasal Cannula?
When the Flow is at or Above 4 LPM
FiO2 Range for Nasal Cannula
24 - 44%
Adult Flow Range for Nasal Cannula?
1 - 6 LPM
Infant Flow Range for Nasal Cannula
0.25 - 2 LPM
Children’s Flow Range for Nasal Cannula
up to 3 LPM
FiO2 Range for Simple Mask
35 - 50%
Flow Range for Simple Mask
5 - 10 LPM
Does a PRBM Mask have Any Valves?
No
What is the Minimum Flow Required for a PRBM to Prevent Rebreathing?
Minimum Flow of 6 LPM
FiO2 Range for PRBM
40 - 70%
Flow Range for PRBM
8 - 15 LPM
For Both the PRBM and the NRBM, What Must the RT make Sure of Before Placing Mask on the Patient?
Make Sure Reservoir Bag is 2/3s Inflated
How Many One-Way Valves Does a NRBM Have?
2
How Does a One-Way Valve Work?
Only Allows Air to Flow in One Direction and Automatically Closes to Prevent Backflow
FiO2 Range for Open Oxygen Mask
24 - 90%
Flow Range for Open Oxygen Mask
1 - 15 LPM
What System Does a Open Oxygen Mask Use to Deliver Oxygen?
Pin and Diffuser System
Redistributes Flow of O2 and Creates a Mushroom Cloud of Concentrated O2
Why does an Open Oxygen Mask Have Large Openings?
To Allow for Flushing of CO2
Flow Range for Reservoir Nasal Cannula
1 - 12 LPM
What is Another Name for an Air-Entrainment Mask?
Venturi Mask
Types of High Flow Devices
Venturi Mask
Aerosol Face Mask
ATT or ATC
Aerosol Face Tent
What are the Advantages to Using a High Flow Device?
Can Deliver a Precise FiO2 at High Flow Rates
Is Able to Meet a Patient’s Inspiratory Flow Demand
Can be Used in Patients with a Highly Variable Respiratory Pattern
Characteristics of Low Flow Delivery Devices
Delivery Devices Include Reservoirs
Output Does Not Meet Patient’s Total Inspiratory Flow Demand
Cannot Guarantee a Precise FiO2
Types of Low Flow Delivery Devices
Nasal Cannula
Transtracheal catheter
Simple Mask
Partial Rebreathing Mask (PRBM)
Non-Rebreathing Mask (NRBM)
Open O2 Mask
FiO2 Range of Venturi Masks
24 - 50%
Flow Range of Venturi Mask
4 - 15 LPM
Based on Manufacturer Recommendation
FiO2 Range of Aerosol Face Mask
24 - 100%
Flow Range for Aerosol Face Mask
O2 Flow Setting Per Manufacturer Guideline
Used Large Volume Nebulizer

Large Volume Nebulizer
FiO2 Range for ATT/ATC
21 -100%
Use Air Flowmeter to Achieve 21%
FiO2 Range for Aerosol Face Tent
21 - 40%
Use Air Flowmeter to Achieve 21%
FiO2 Range for Aerosol T-Piece (ATP)
21 - 100%
Use Air Flowmeter to Achieve 21%
What Should Do Prior to Administering a New MDI?
Prime MDI
Shake and Spray 4 Times Before Use
Requirements of DPIs
Requires Patient Cooperation
Minimum Inspiratory Flow of > 40 - 60 LPM
Vacuum Pressure Required for Suction of Adult Patient
< 150 mmHg
Vacuum Pressure Required for Suction of Child Patient
< 120 mmHg
Vacuum Pressure Required for Suction of Infant Patient
-80 mmHg - (-100)
What Flow Should the Ambu Bag/ Resuscitation Bag be Set to Prior to Suctioning?
15 LPM
How to Calculate Catheter Size for Suctioning?
(Size of Trach on Box - 1) x 2
How Long Should You Preoxygenate a Patient Prior to Suctioning?
30 Seconds to 1 Minute
How Long Should Each Round of Suctioning Be?
No Longer than 15 Seconds
What Sats Should You Monitor When Suctioning to Monitor for Adverse Reactions?
VS
SpO2
ECG
Supplies Needed to Suction a Patient
Sterile Suction Catheter Kit
Resuscitation Bag
Luken’s Trap *If Sample is Needed
How Long Do You Need to Reoxygenate a Patient Inbetween Suctioning Rounds?
1 Minute
What Type of Trach Do You Need to Use For Use of a Speaking Valve?
Fenestrated
When Placing a Fenestrated Trach, What Test Should Be Performed to Check Placement or Obstruction?
Place Finger on Trach Opening and Feel for Resistance
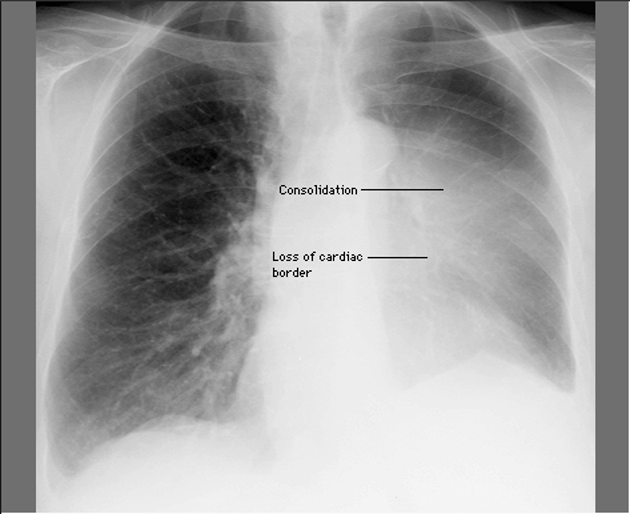
Atelectasis
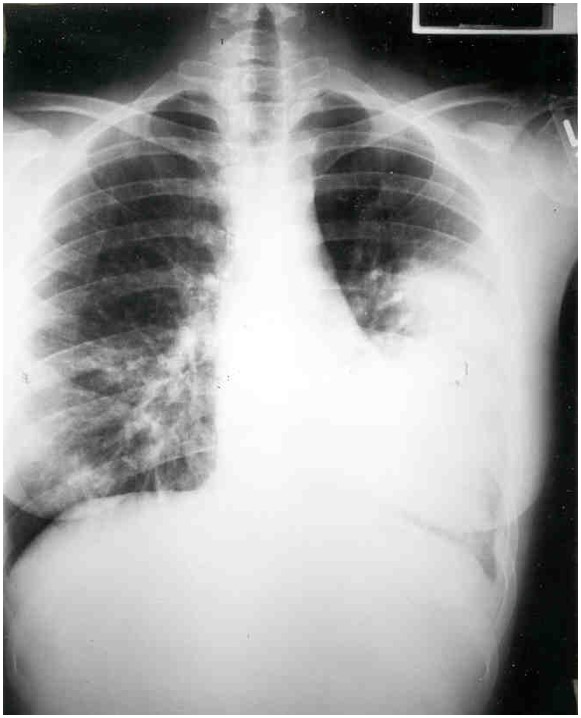
Pneumonia
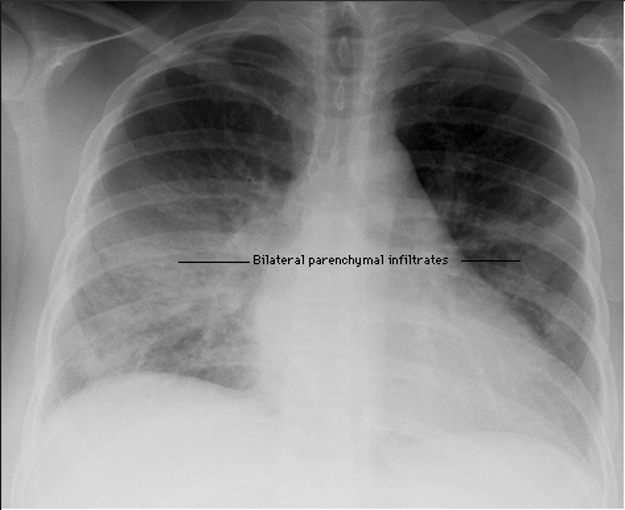
Bilateral Pneumonia
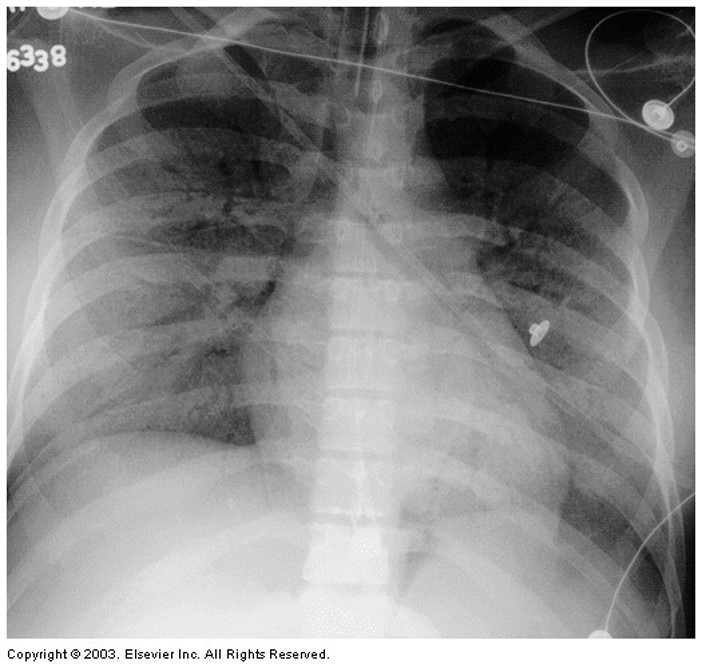
Air Bronchograms
Indicates:
Pneumonia
Pulmonary Hemorrhage
Pulmonary Edema
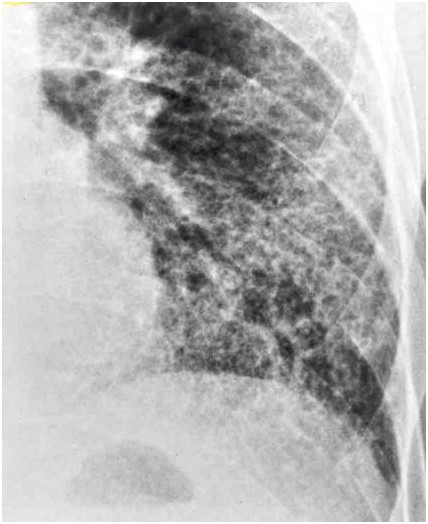
Honeycombing
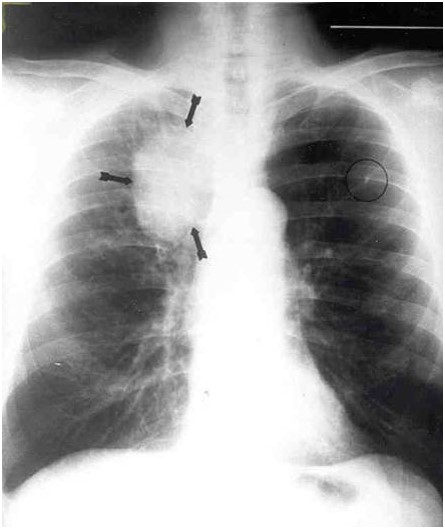
Pulmonary Mass
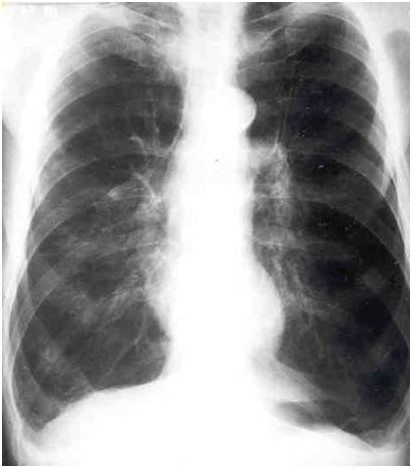
Emphysema
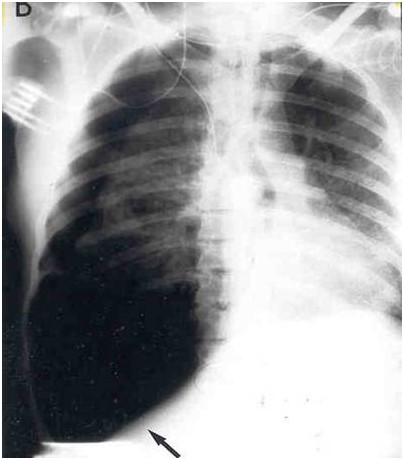
Pneumothorax
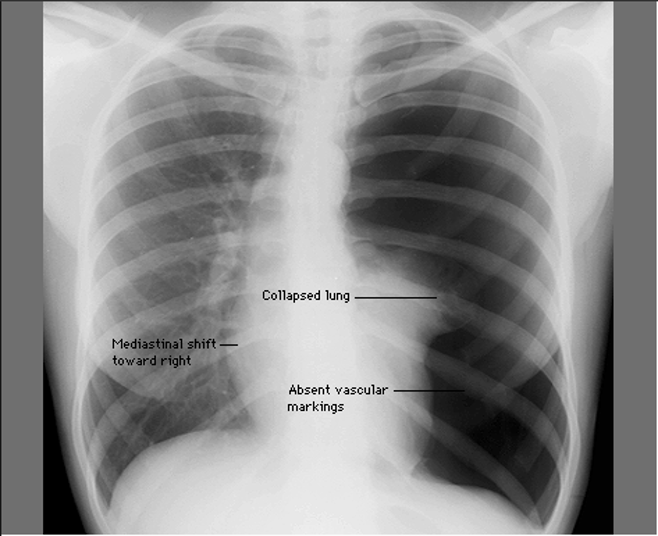
Pneumothorax