How Did Earth and Its Biosphere Originate? (PART I); Microscopy exercise (Onion root tip slide)
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 6: Monday, September 29th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
the _______, proposed by Georges Lemaitre in 1931, describes how the uniiverse expanded from high density and temperature compressed matter about 14 billion years ago
big bang theory
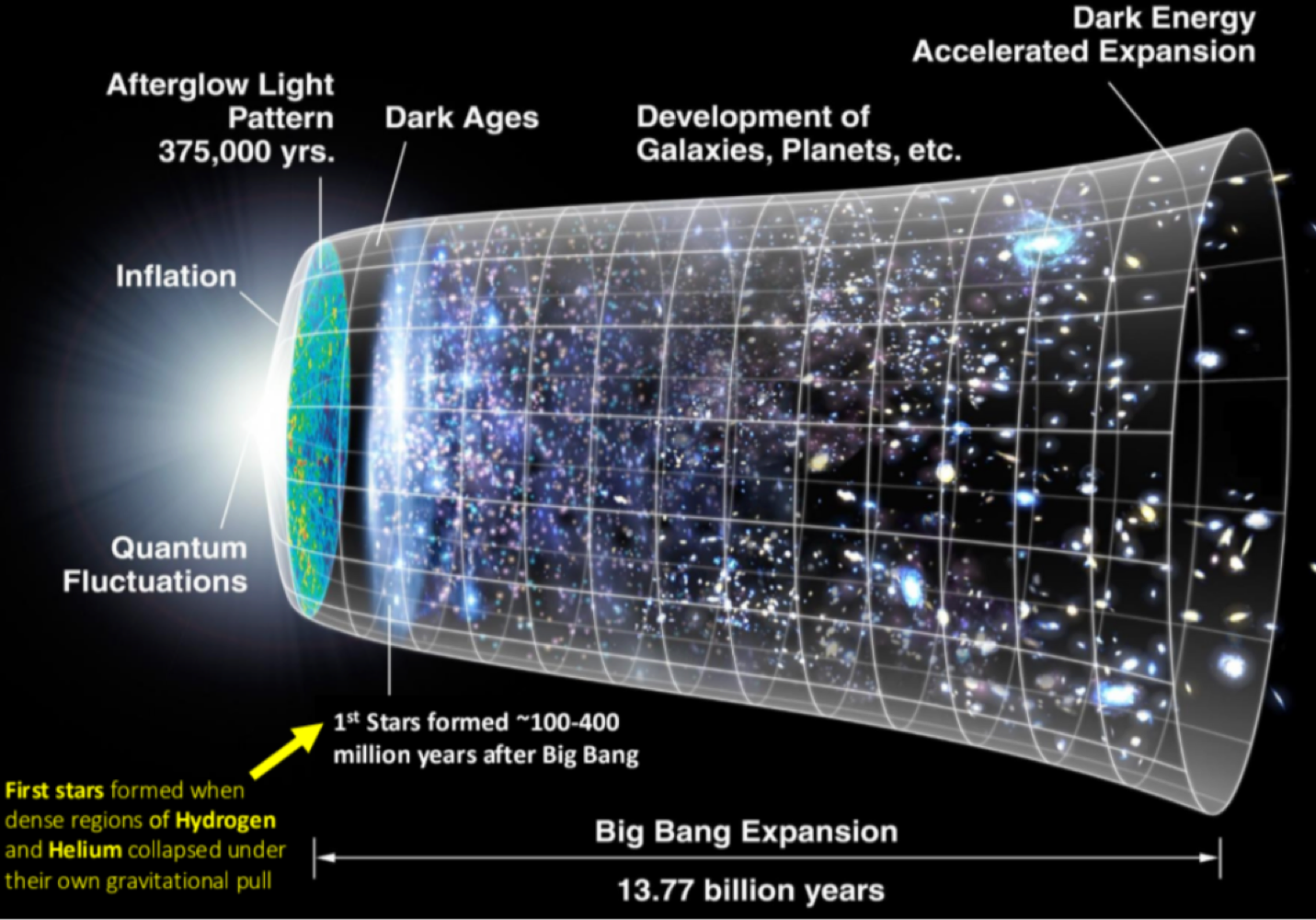
_______ is compused of the sum of all matter and energy, superclusters, voids, and everything within it
the universe
planets are within a _______, which is the sun an dits orbiting objects (planets, their moons, smalle robjects [asteroids, comets])
solar system
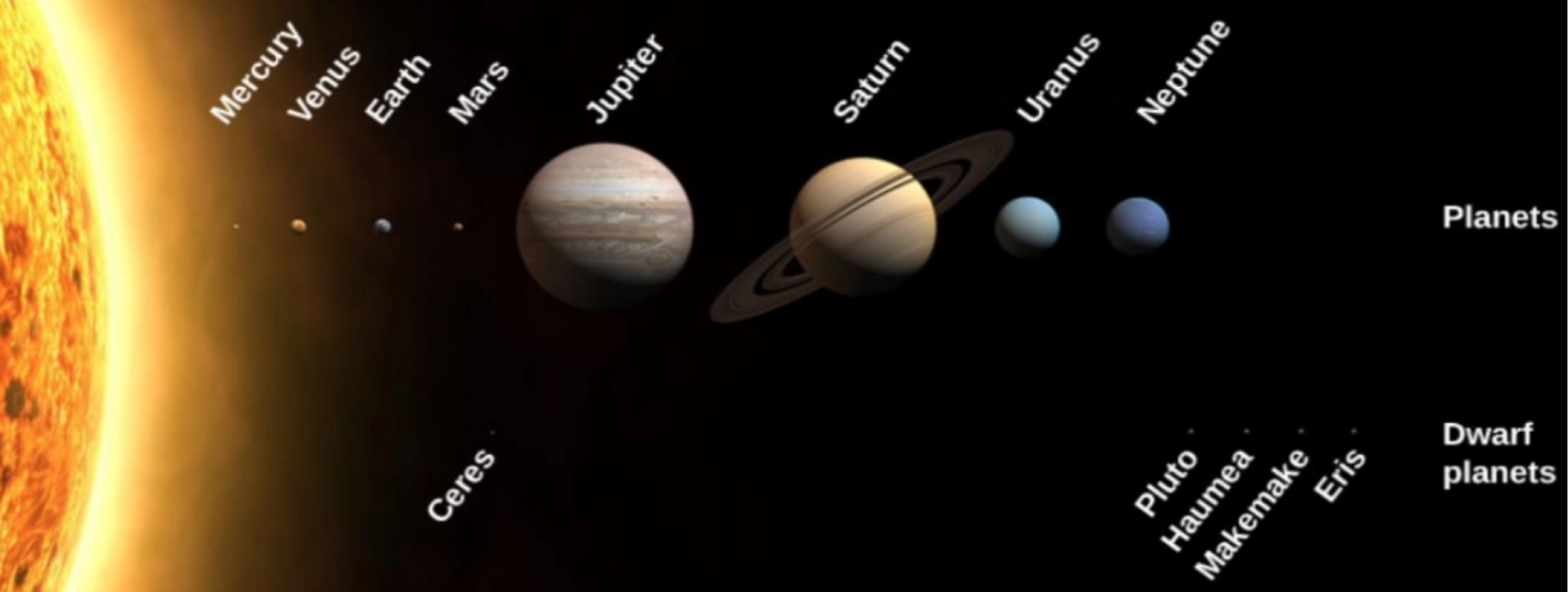

merry, venus, earth, and mars are _______ planets, whereas jupiter, uranus, and neptule are _______ planets
terrestrial/rocky, jovian/gas
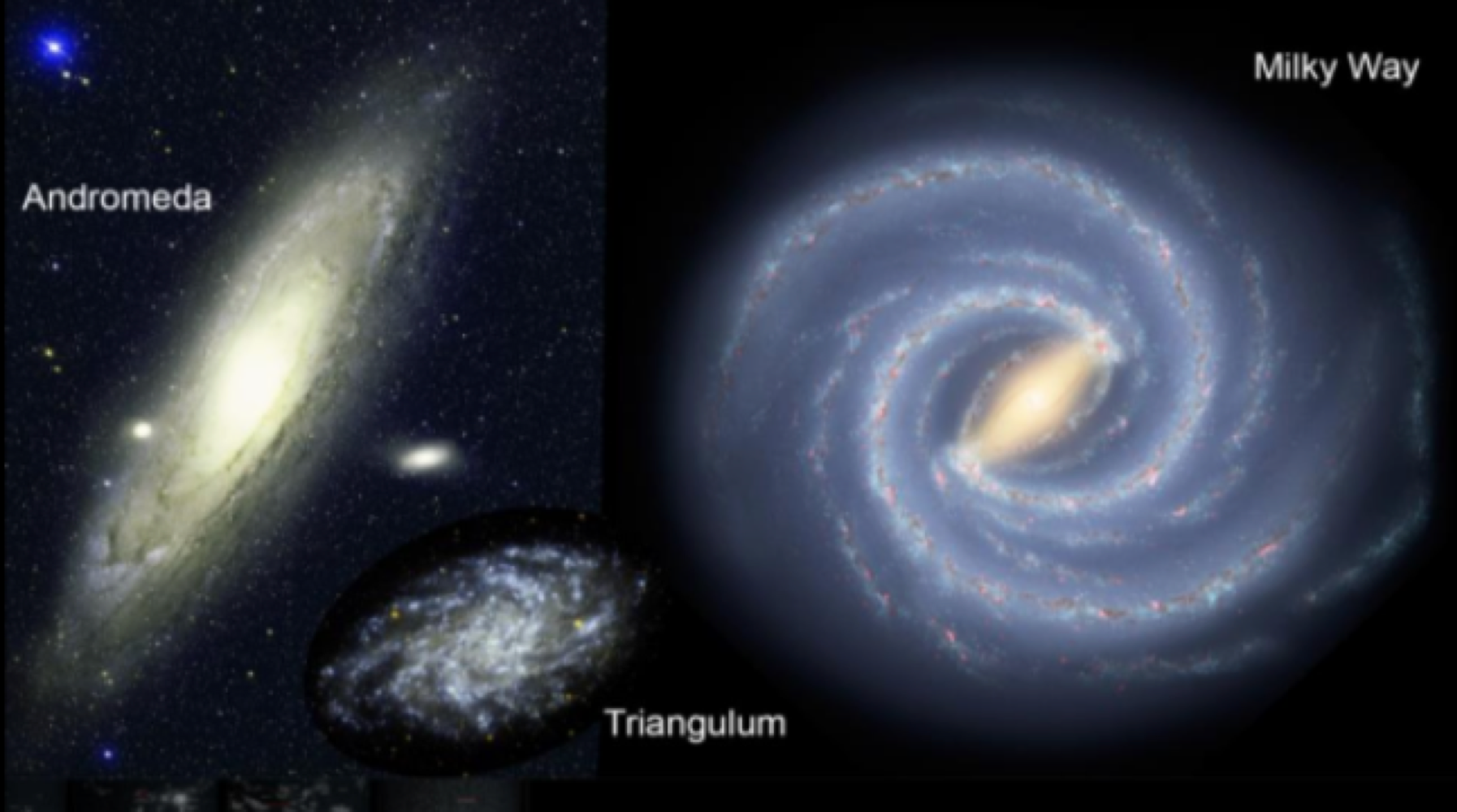
_______ contain solar systems, gas, dust, and billions of stars, which are located in the local galactic group
galaxies

_______ are large groups of galaxies bound together by gravity
local superclusters
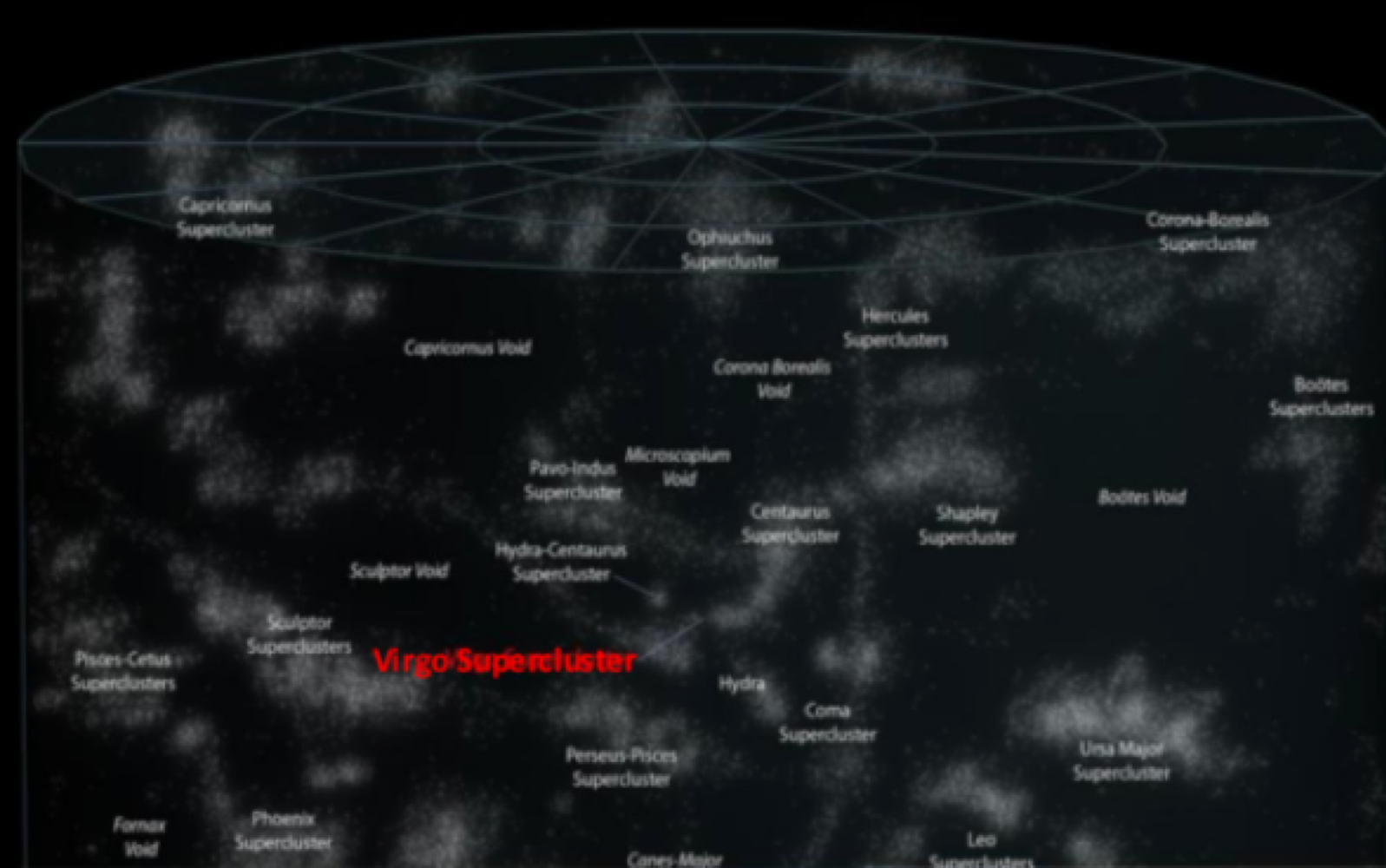
the _______ is the shpherical region of the universe (all mater) visible from earth
observable universe

interstellar distances are measured in light years; 1 light year = the distance that light can travel in 1 year, which is _______
10 trillion km
_______ is the closest star system to our planet, and is 4.4 light years away
Alpha Centauri
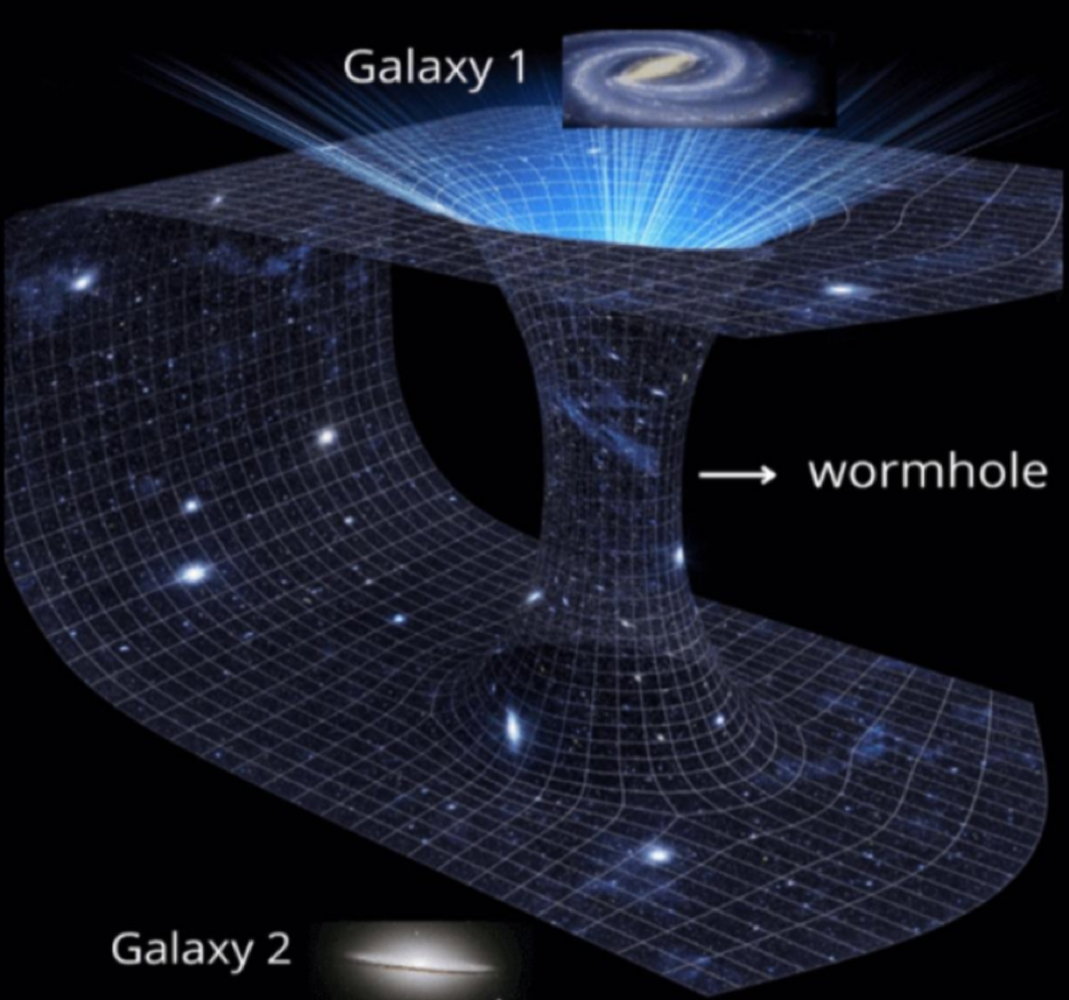
a _______ is a shortcut to travel the interstellar space
wormhole
_______ are leftover icy bodies that releasese gases as it orbits the sun
comets

_______ are leftover rocky bodies smaller thana planet that orbits the sun
asteroid

_______ are leftover rocky/metallic fragments of an asteroid,c omet, or planet
meteoroid

_______ are streaks of light seen when a meteoroid hets up in the atmosphere
meteor

_______ are leftover meteor fragments that reaches the ground
meteorite

_______ is between Mars and Jupiter, and contains most of the ateroids in our solar system
asteroid belt
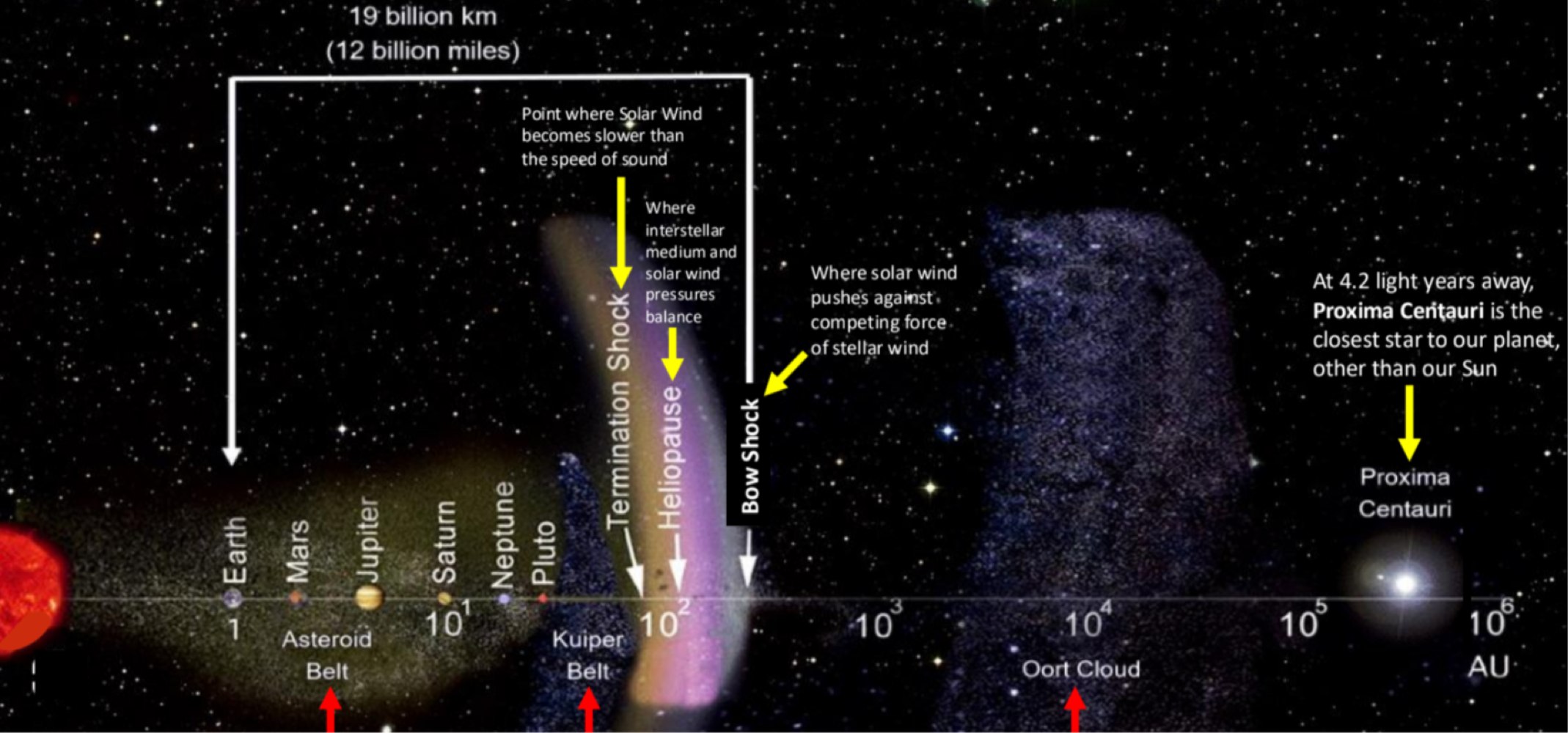
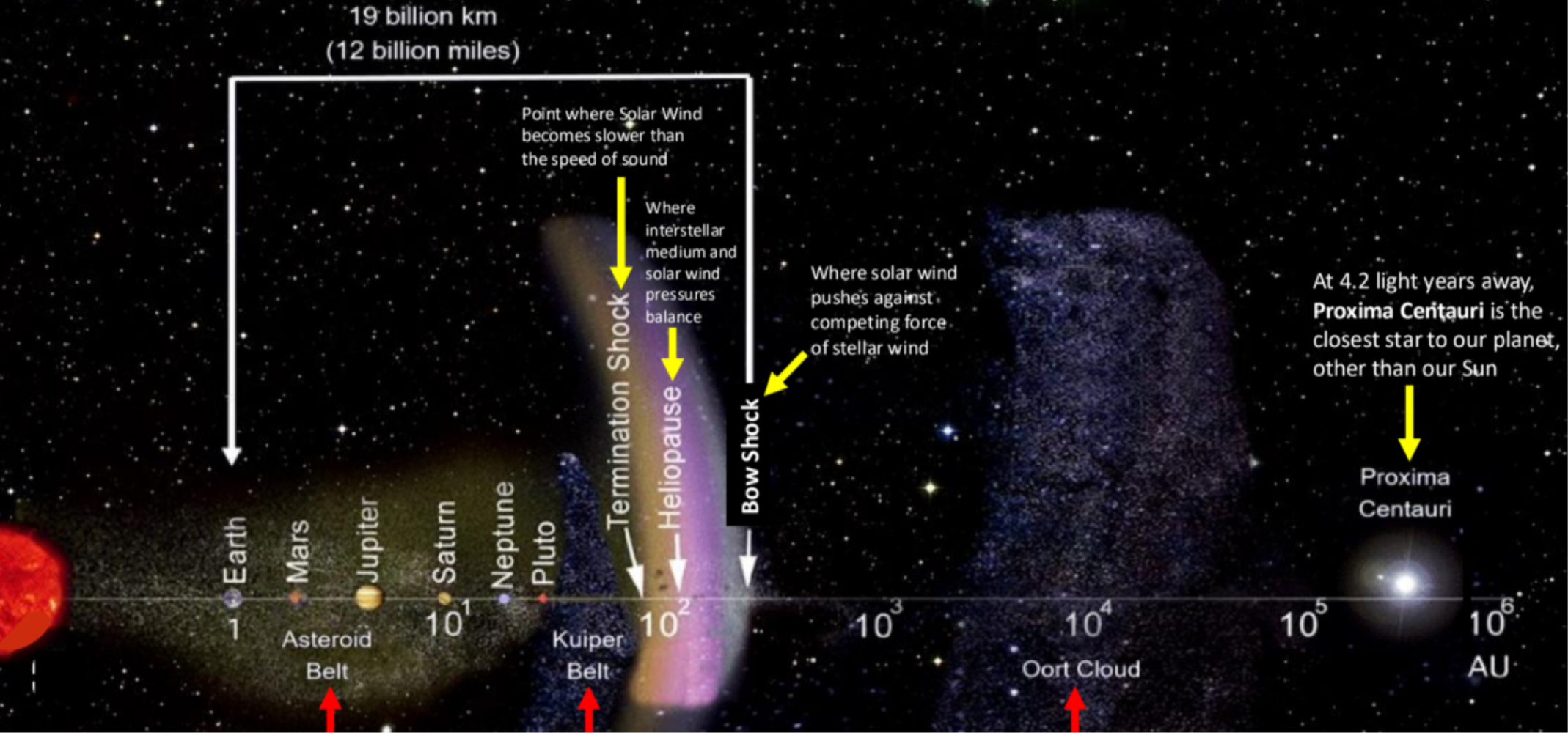
_______ is between pluto and the termination shock (where solar winds are slower than the speed of sound)
Kulper Belt
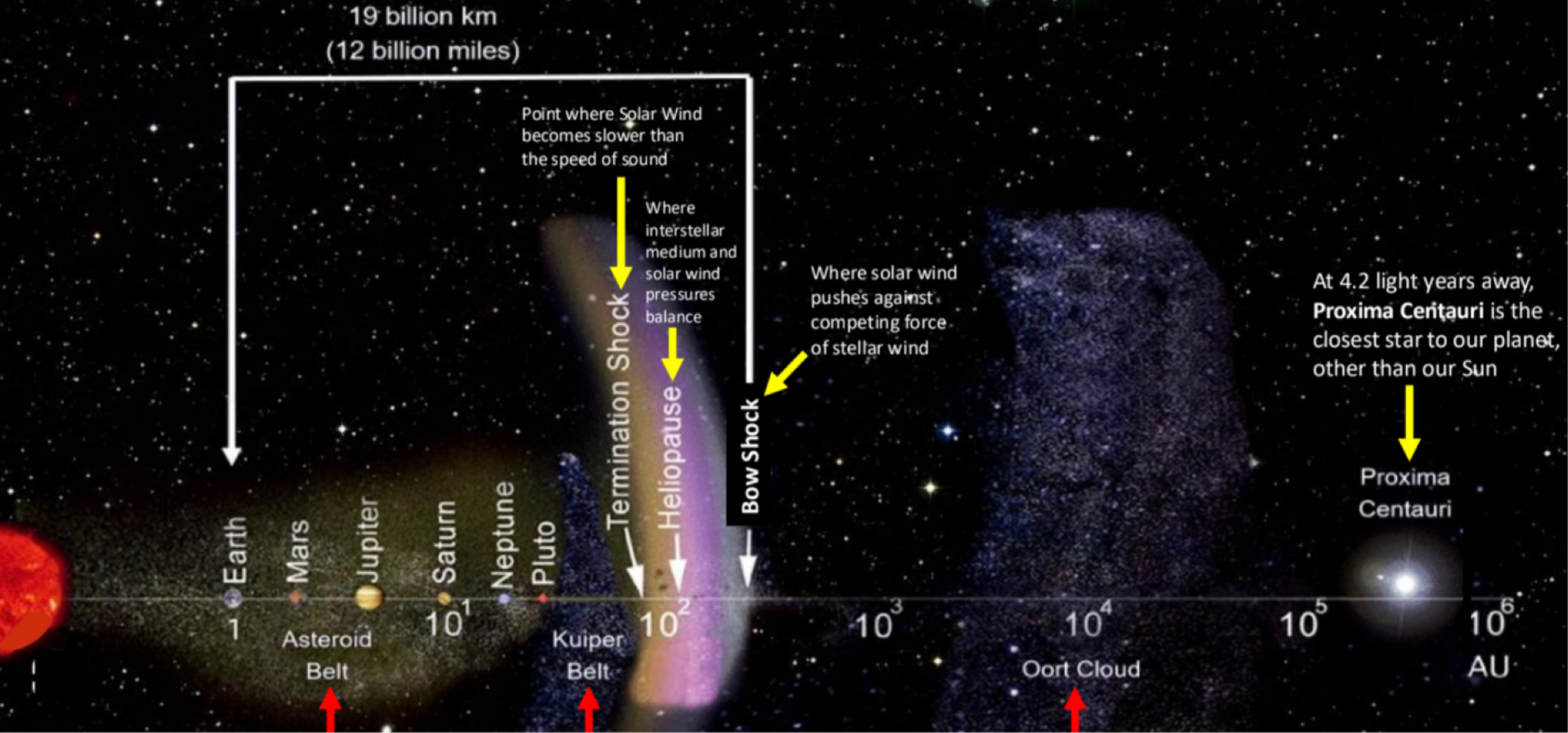
_______ is beyond Pluto’s orbit where comets come from
Oort Cloud
all chemical elements ae formed in _______, the addition/removal of nucleons (protons/neutrons)
nucleosynthetic processes
earliest element synthesis occurred during the _______, which produced most of the universe’s hydrogen and helium
Big Bang nucleosynthesis
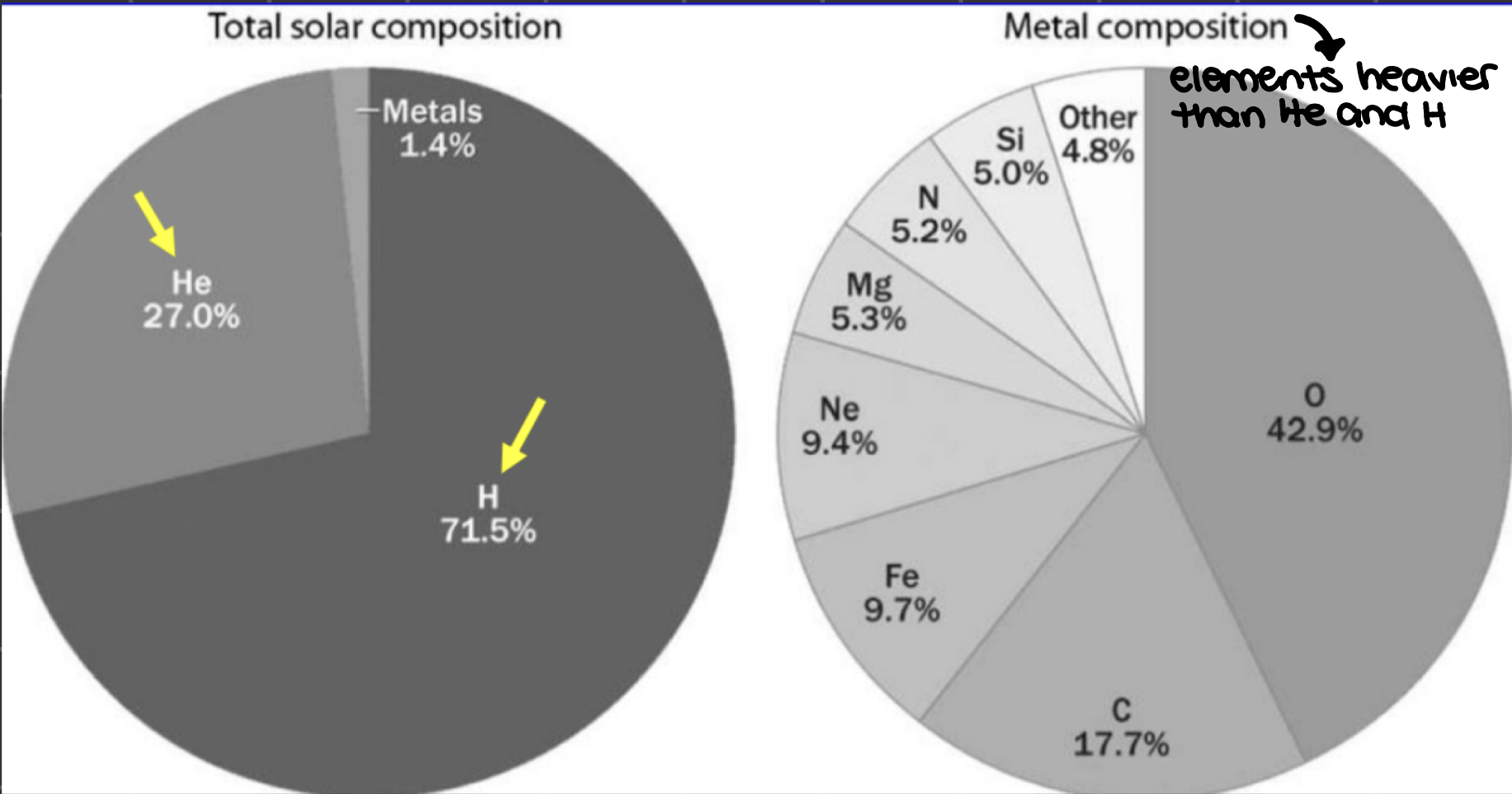
_______ in stars produced the majority of other nautrally occurring elements
stellar nucleosynthesis
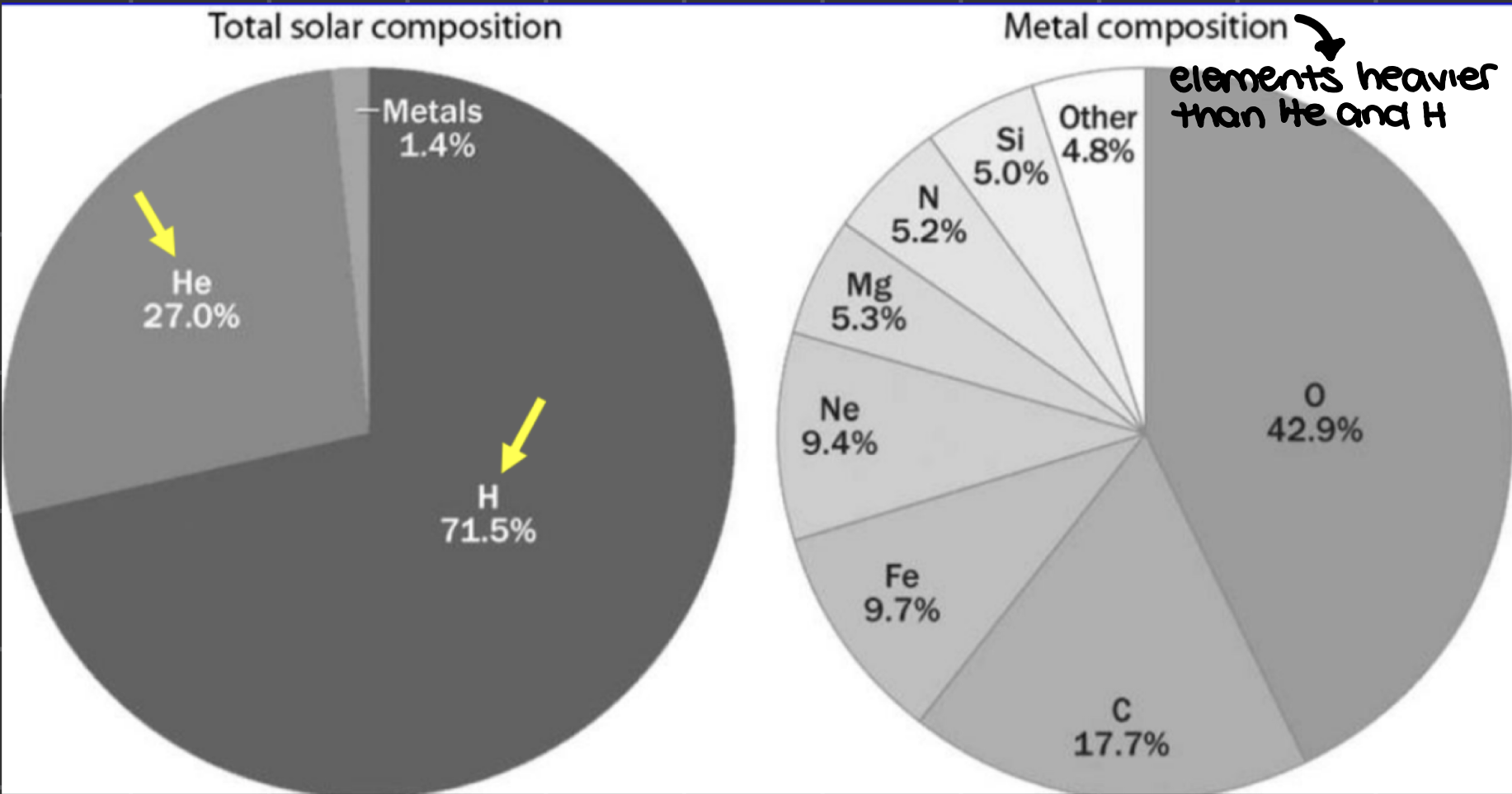
stars are formed by _______, gravitational collapse of giant dust and gas clouds made of hydrogen and helium
nebulae

gravity will pull hydrogen into a nebula, then it starts to spin and heat up, eventually forming a _______, the result of a nebulae
protostar
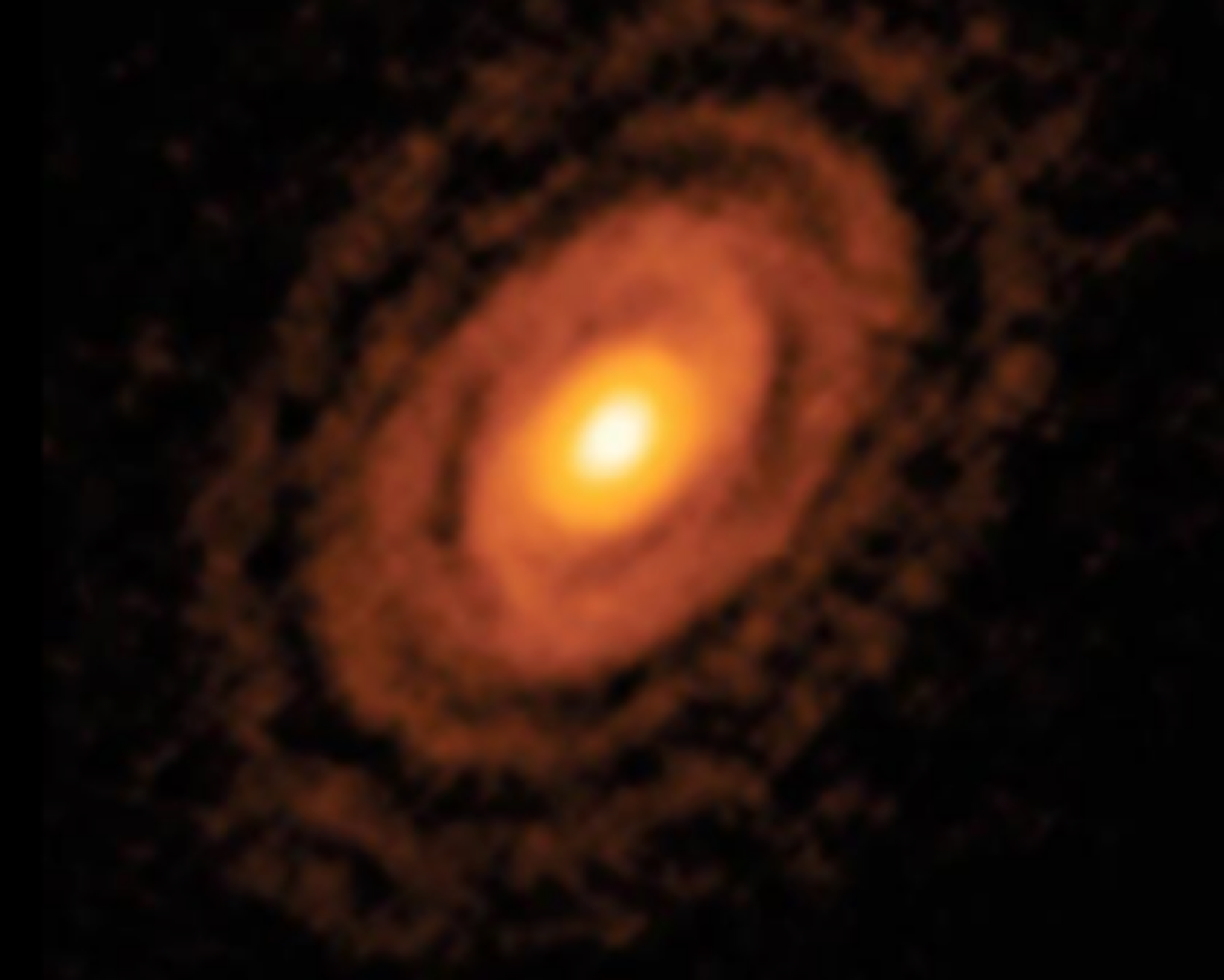

a protostar moves in to the _______ (pre-main sequence; still forming), the transform into a _______ (like ours) or a _______ (Sirius)
T-Tauri Phase, low/medium mass star, higher mass/massive star

low/medium mass stars fransform into _______ → _______ (can birth planets) → _______ → _______ (emits no heat or light)
red giants → planetary nebula → white dwarf → black dwarf

higher mass/massive stars transform into _______ → _______ (death of a large star) → _______ or _______
red super giants → supernova → neutron star or black hole
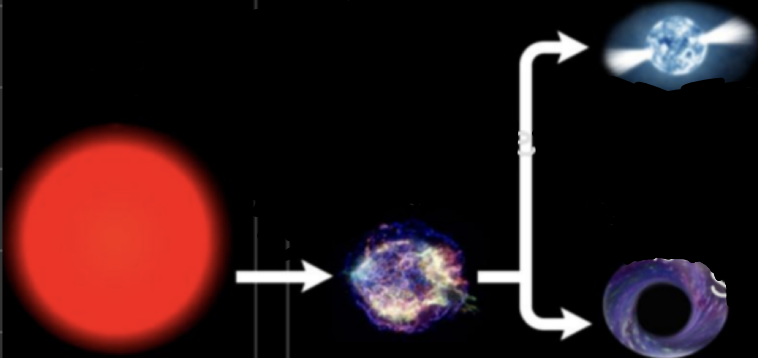
a _______ is a dense city-size ball of neutrons
neutron star
a _______ is an enourmous star that emits no light and has a strong gravity prevents the pastest particles in the universe from escaping
black hole
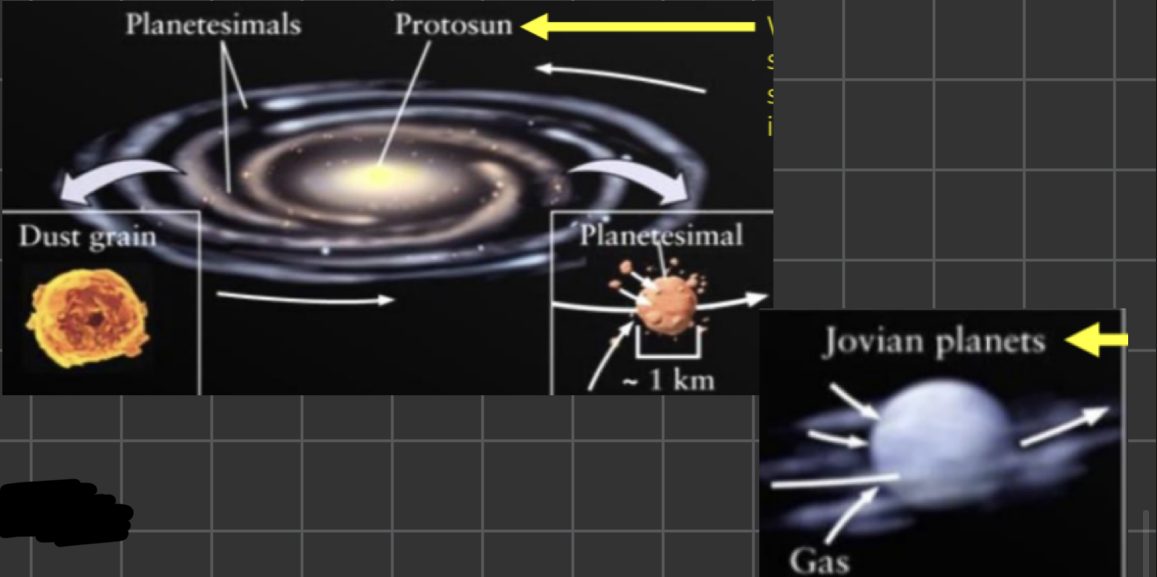
planets start of as dust grains and emerge from _______, giant donut-shaped disk of gas and dust that circles young stars
protosuns
terrestrial planets form from collisions and the accretion of _______ by gravitational attraction, whereas jovian planets are formed by _______
planetsimals, gas accretion
the last giant impact that formed earth was the _______, which threw rock, gas, and dust into space to form the moon
moon-forming impact
the _______ of the protosun is where metals and minerals condens einto planets
central region
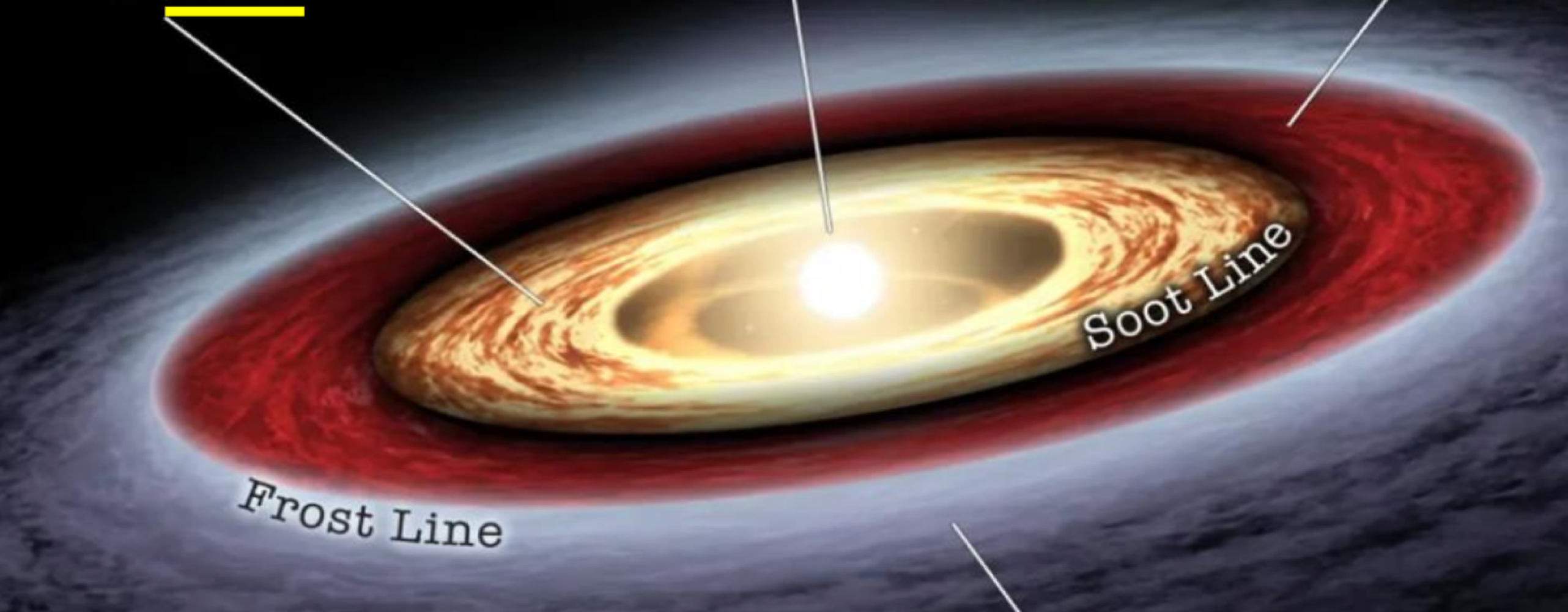

_______ of the protosun is where polycyclic aromatic hydrogarcoms (PAHs) exisst, allowing forming planets to include condense carbon compounds
outside the soot line
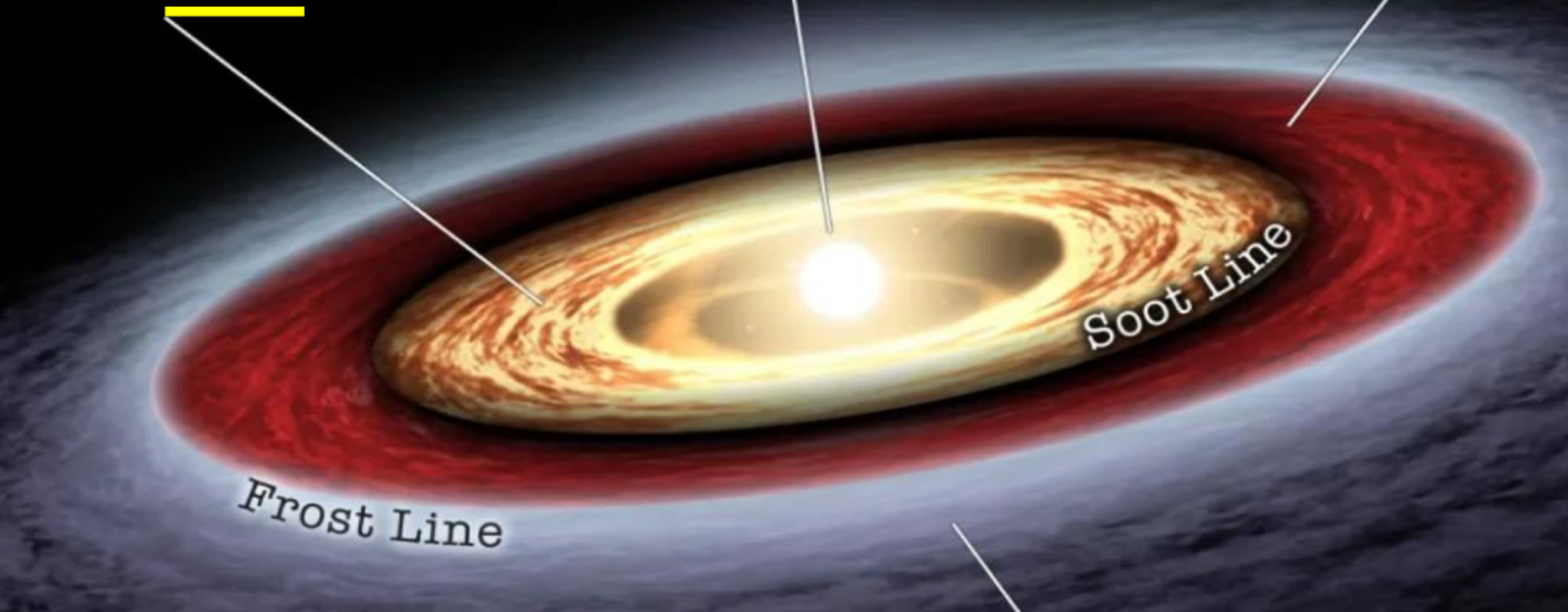

_______ of the protosun is where low temperatures allow condensing planets to include volatile molecules such as water, ammonia, and methane
outside the frost line
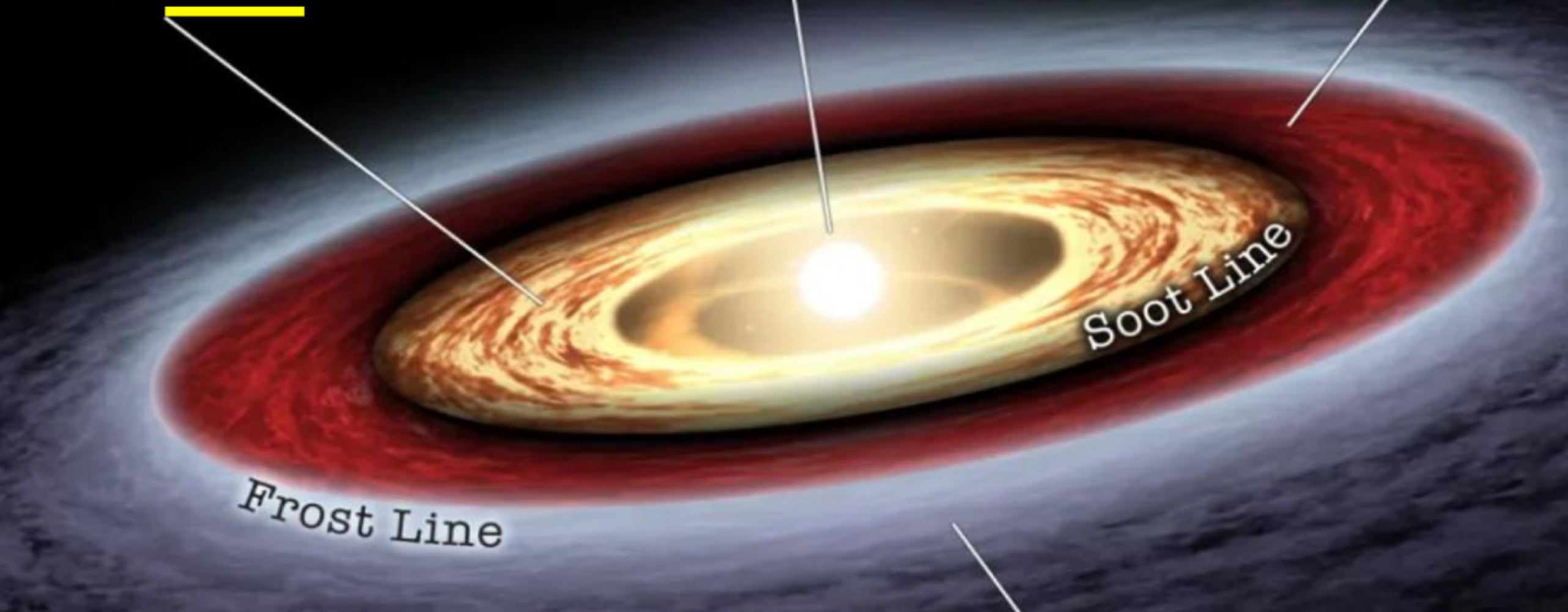

the biosphere formed from _______ and _______ (chondrites), both of which brought volatile elements (hydrogen and oxygen; mostly water), carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus (dissolved salts/gas)
comets, primitive meteorites (chondrites)
true or false: organic molecules (glycine( were found in comet dust
true
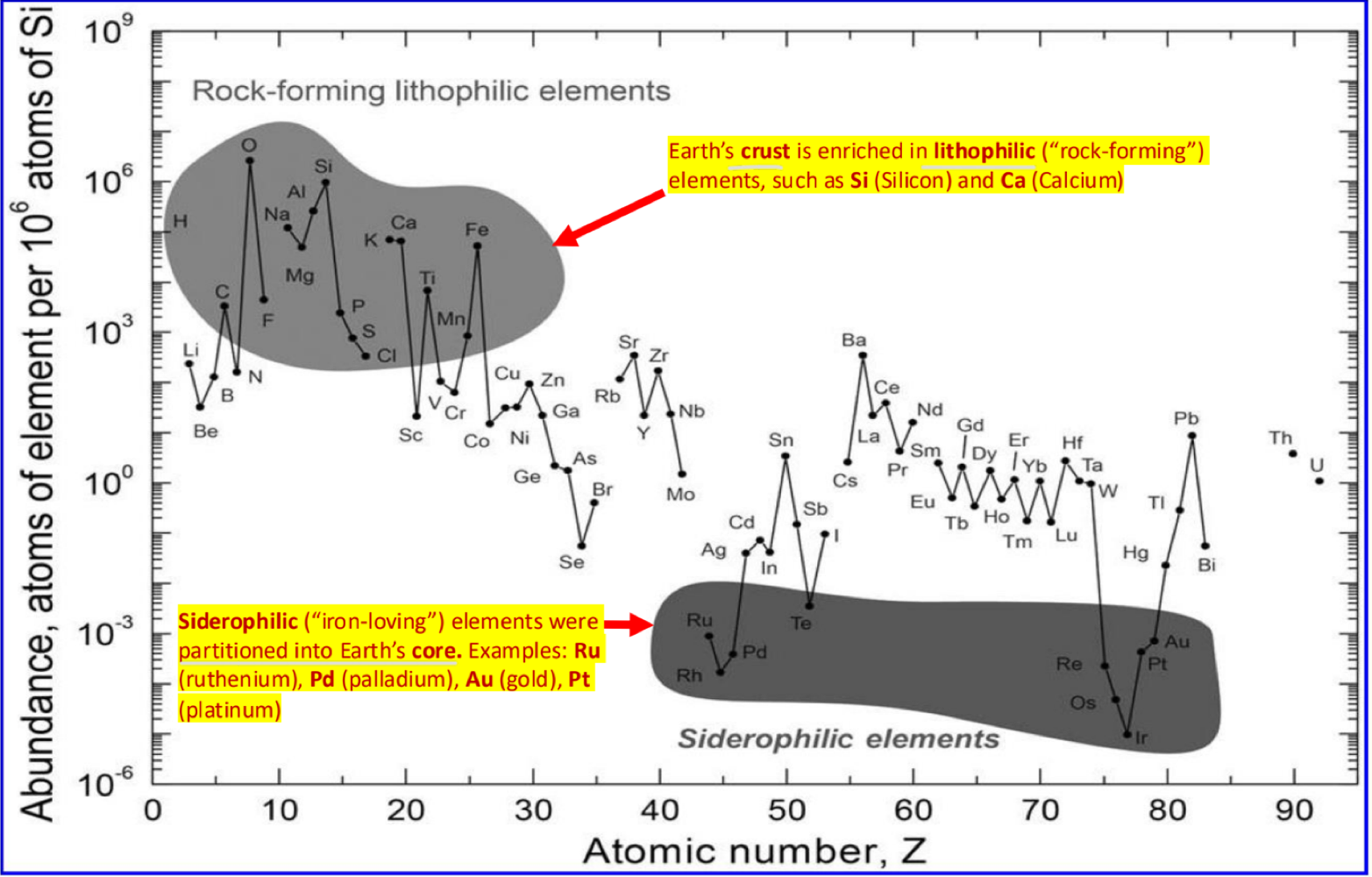
_______ elements compose the surface dn crust of earth, while _______ elements compose the core
lithophilic (rock-loving), siderophilic (iron-loving)
like other terrestrial planets, Earth went through 4 developmental stages, such as _______, partitioning in to different sections
differentiation
like other terrestrial planets, Earth went through 4 developmental stages, such as _______, impact from other objects (comets, asteroids)
catering
like other terrestrial planets, Earth went through 4 developmental stages, such as _______, low land areas filled with water and magna
flooding
like other terrestrial planets, Earth went through 4 developmental stages, such as _______, active geology, tectonic plates, mountain ranges, recyclation of minerals, weathering, erosion
slow surface evolution (habitability
_______ activates root growth, and the _______ (embryonic root) develops into root systems
seed germination, radicle
the _______ protects the growing root tip, and is constantly replaced when damanged from pushing through soil
root cap
the rootcap contains _______, gravity sensing cells (gravitropic)
statocytes
the _______ has actively dividing root meristem cells
zome of division
the _______ has new cell stretch, which lengthens the root
zone of elongation
the _______ has cells differentiate into specialzied types
zone of differentiation
statocytes contain _______, whch are amylplats filled with starch that settle at the bottom of cells due to gravity
statoliths
in roots, the central _______ cells of the root cap serve as pravity0sensing statocytes
columella
statolith movement triggers _______ release,which regulates platn growth
auxin (IAA)
_______ is when roots bend in response to gravity due to a regulated movement of auxin
polar auxin transport
_______ is when plants sense gravity adn guide their growth with respect to the gravity vector
gravitropism
_______ is when roots grow downward along gravity, while _______ is when h=shoots grow upward, against gravity
positive gravitropism, negative gravitropism
_______ is when experimentally changing plant or orientation to study gravity effects
gravistimulation