SSS Week 5
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Nail Clubbing clinical features + treatment
usual small diamond window cannot be seen when the index fingers are brought together with the distal phalanges placed adjacent to each other
soft nail beds
increased nail convexity
thickening of the finger
Treatment: treat underlying disease
Causes of nail clubbing
Resp
interstitial lung disease
lung cancer
tb
sarcoidosis
abscess, emphysema
CF
Cardio
congenital heart disease
subcute bacterial endocarditis
AA
Endocrine
hyperthyroidism
thyroid cancer
secondary parathyroidism
GIT
IBD - crohns and UC
hepatocellular carcinoma
achalasia
celiac disease
liver cirrhosis
other
hodgkin lymphoma
asbestos
Koilonychia
spoon-shaped fingernails
concavitiy in fingernail itself, resulting in a depression in the nail
associated with iron deficiency, sometimes be seen in normal infants, but disappears as child ages
Alopecia Areata description (clinical features, stages, aetiology)
autoimmune
non-scarring alopecia
subtypes: totalis and universalis
clinical features
discrete annular areas of hair loss anywhere on body
more likely on scalp, eyebrows and beard
aetiology
inflammation of anagen hair bulb causing hair growth to halt and catagen to be induced
onset or reoccurrence triggered by stress, trauma, infection, and hormonal changes
STAGES
sudden onset of hair loss
increasing areas of hair loss which have a smooth surface, with scattered exclamation mark hairs
Trichotillomania
compulsive pulling out of hair
can signify stress-relieving habit , or depression, and impulse control
there is normal hair growth in balding areas
DDx
alopecia areata and tinea capitis
Scarring vs non-scarring alopecia
Scarring refers to irreversible destruction and replacement of hair follicles with scar tissue, which leads to permanent hair loss eg. can occur in SLE/lupus
Non-scarring refers to temporary hair loss where hair follicles remain intact and can regrow
Telogen effluvium (acute vs chronic) and how to confirm
premature shift into telogen phase from anagen in response to shock to the system. which results in shedding prematurely (in exogen)
Acute vs chronic telogen effluvium
Acute - may follow childbirth or stopping pill, any acute illness, major surgery or severe dieting
Chronic - less common, it may be primary and idiopathic or
secondary to
hypothyroidism
hyperthyroidism
malnutrition
cancer
TB
iron deficiency anemia
drug side effect
Anagen effluvium
direct injury to anagen hair growth by drugs (chemo), toxins or inflammation
inflammation - alopecia areata a cause
Hirsutism vs Hypertrichosis
hirsutism
increased hair growth in women, male pattern of hair in the moustache and beard areas or occurring more thickly than usual on the limbs … usually genetic
ANDROGEN DEPENDENT
lower face and midline of trunk that are preferentially affected by androgens
hypertrichosis
widespread overgrowth of NON-ANDROGEN-DEPENDENT hair, seen with drugs like cyclosporin and phenytoin
areas like FOREHEAD and FOREARMS have increased hair growth (rather than lower face and midline of trunk that are preferentially affected by androgens)
DDx for non-scarring alopecia
alopecia areata
androgenetic alopecia
traction alopecia
trichotillomania
Androgenetic alopecia (clinical features and aetiology)
occurs with advancing age
progressive miniaturisation of pigment scalp hair to fine hypopigmented hair
(thick terminal hair to thin vellus hair)
genetic predisposition
DIC pathogenesis, clin features, aetiology
arises as a complication of different serious and life-threatening diseases
caused by uncontrolled activation of coagulation cascade
depletes platelets and clotting factors
increased haemorrhage into urine, stool and skin
acute clin features
bruises
mucous membrane involvement
internal haemorrhage
malaise and high fever purpuric rash affecting extremities
petechiae and purpura
chronic clin features
thromboembolism
DVT
acute
infection
septicemia (sepsis)
tissue injury eg. burns
chronic
cancer
tb infection
CKD
PE
8 signs of liver cirrhosis
pruritis —> cholestasis? hard to treat
bruising (inability of liver to produce clotting factors)
palmar and facial erythema
jaundice
spider naevi
feminisation (impaired metabolism of oestrogen)
photosensitivity, skin erosions and mucosal changes eg. pellagra
leukonychia or half and half nails
Bacterial endocarditis (+ risk factors, + cutaneous signs)
infection of endocardium - usually strep viridians or staph aureus
Risk factors
rheumatic heart disease
iv drug abuse
previous cardiac surgery
congenital heart disease
Cutaneous signs
splinter haemorrhages
osler’s nodes - tender red papule on pads of fingers and toes
janeway lesions - macular erythema of palms
septic emboli - pustular and purpuric lesions of lower legs and toes
roth’s spots - haemorrhages of conjunctiva
General signs of cardiac disease
peripheral and central cyanosis
erythema due to compensatory polycythaemia
finger clubbing
flushing of nail bed in time with aortic incompetence
diagonal ear lobe crease in coronary artery disease
peripheral oedema
elevated JVP
SKIN SIGNS of sarcoidosis
Lupus pernio - asymptomatic violaceous or erythematous (red, purple) indurated plaques or papules or nodules, distributed on nose, cheeks, chin and ears
erythematous nodosum - a type of panniculitis, painful nodules most common on anterior surface of lower extremities (like shins)
ALSO seen in TB, IBD and strep infection
DIABETES PRESENTATIONS
necrobiosis lipoidica
early plaques are violaceous (of a violet colour) but atrophy and become brown-red or slightly yellow, blood vessels are visible under the skin
mostly appearing on shins
refractory to treatment (resistant?)
diabetic dermopathy
brownish scars on skin, mostly on shins
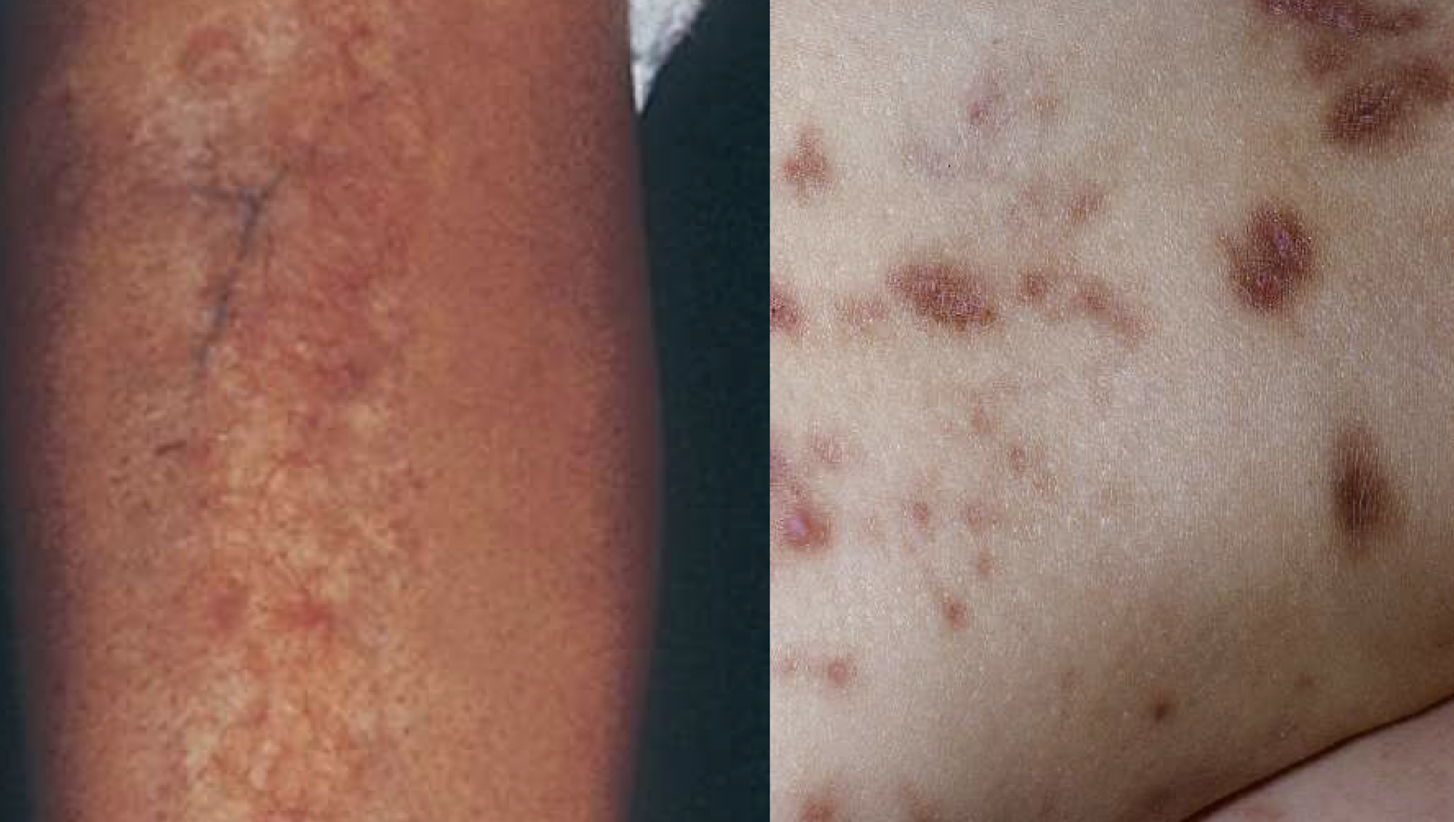
granuloma annulare
skin coloured or light pink annular lesions over knuckles
composed of dermal nodules fused into a rough circle
candida infections
staph infections
eruptive xanthomas - crops of yellow papules with erythematous base
neuropathic foot ulcers
skin tags
acanthosis nigricans - hyperpigmented velvety thickening of skin folds
Xanthelasma - investigations and treatment
xanthelasna palpebrarum a common example used this week
what investigations - lipids, U&E, liver, glucose, TFT
treatment is lipid lowering medication & surgery
Specific manifestations of graves disease (hyperthyroidism) + other classic signs
pretibial myxoedema - either diffuse or nodular swelling of shins
ophthalmopathy
acropachy - triad is: digital clubbing, soft-tissue swelling of hands and feet, periosteal reaction in long bones.
diffuse hair loss
heat intolerance and sweatiness
facial flushing
palmar erythema
itch
acropachy (what is it a manifestation of)
triad is: digital clubbing, soft-tissue swelling of hands and feet, periosteal reaction in long bones.
and is a manifestation of hyperthyroidism
Classical signs of hypothyroidism
dry yellowish skin
diffuse hair loss
loss of outer third of eyebrows
loss of body ahir
puffiness of eyelids, hands and face
itch
absence of sweating
bruising and purpura
brittle nails
cold sensitivity
Skin signs of Cushing’s syndrome
facial roundness (moon face) and plethora (redness)
buffalo hump
central adipositiy
striae
fragile skin
telangiectasia
bruising
acne
excess facial and body hair
Signs and symptoms of addisons disease
fatigue
weakness
weight loss
nausea
abdo pain
diarrhoea
vomiting
mood disturbances
3 cutaneous signs of GIT disease
dermatitis herpetiformis
pruritis vesicles, papules and bullae on elbows, knees and lumbosacral areas, needs to biopsy to confirm
erythema nodosum
pyoderma gangrenosum (also a internal malignant sign)
begins as a papule and breaks down to form rapidly enlarging ulcer, raised purple undermined edges , needs biopsy to differentiate infective vs malignant cause
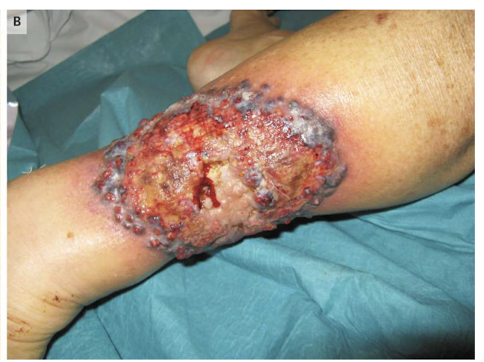
chronic cutaneous (discoid) LE
well defined red scaly plaques
occurs on sun exposed areas
secondary changes of hyper or hypopigmentation and atrophic scarring → scarring can cause alopecia
treatment
sun protection
topical corticsteroids
systemic agents eg. hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate
SLE
butterfly rash
severe photosensitivity
mucosal erosions and ulcer
Scleroderma
connective tissue disorder characterised by symmetrical hardening of skin which can be local or systemic
progression
initial oedema → eventual contractures and atrophy with ulceration of fingers and toes
Localised or limited
type of limited systemic scleroderma: CREST syndrome which is characterised by
Skin involvement: mainly hands, face, forearms.
Internal organ involvement: usually milder, often lungs (pulmonary hypertension) or GI tract.
Hallmark features: Calcinosis, Raynaud, Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasia (CREST).
Extensive/diffuse
scleroderma which involves skin of distal limbs and face as well as arms, legs and trunk
this one is associated with severe systemic disease particularly affecting the kidney, GIT and lugns
other clinical signs present in extensive/diffuse scleroderma include
Thickened, indurate white plaques occurring anywhere on the skin surface.
They may have an erythematous or purple peripheral rim.
Linear lesions which may extend the length of an arm or leg sometimes causing contractures
Hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation
Investigations for bullous pemphigoid, treatment
investigations
skin autoantibodies
skin biopsy and direct immunofluorescence
treatment
potent topical steroids or oral steroids
long term alternatives include doxycycline, or nicotinamide (steroid sparing agents)
Vitiligo classical presentation
Milky white patches of skin
Disfiguring condition where colour is lost from the skin. It is usually patchy but in rare cases can be widespread.
Pigment loss in vitiligo is complete, so the skin is white and sunburns easily. The edge of the lesion in vitiligo is always sharp and well defined.
Aetiology of pruritis and tests
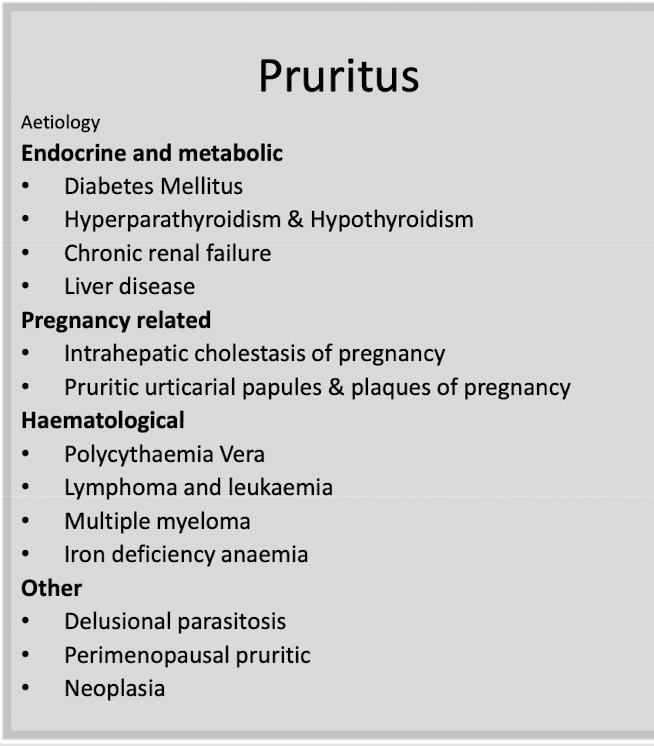
FBC - infection, WBC, eosinophil count
U&E - if suspect renal failure
LFT - liver failure
CRP, ESR - inflammatory markers
Ferritin
TSH
could also be due to malignancy
3 cutaneous signs of internal malignancy (+skin signs for no.3)
acanthosis nigricans - gastric adenocarcinomas, with other adenocarcinomas
pyoderma gangrenosum - the purple raised edge, starts as papule or pustule that breaks down into a rapidly enlarging ulcer
dermatomyositis
periorbital macular violaceous erhythema (heliotrope rash)
scaly, reddish papules on dorsum of interphalangeal joints (gottron’s papules)
violaceous rash involving sun exposed sites
rugged cuticles and nail fold telangiectasia
poikiloderma (skin atrophy, telangiectasia, pigmentation)
photosensitivity
generallised pruritis
superficial thrombophlebitis
erythroderma
sweets syndrome
Sudden onset of painful oedematous, erythematous to blue plaques
on face, neck and limbs.
Plaques may be vesicular or pustular
Often a fever and neutrophil leucocytosis
associated with haematological malignancy, some solid neoplastic tumours and… strep throat infection
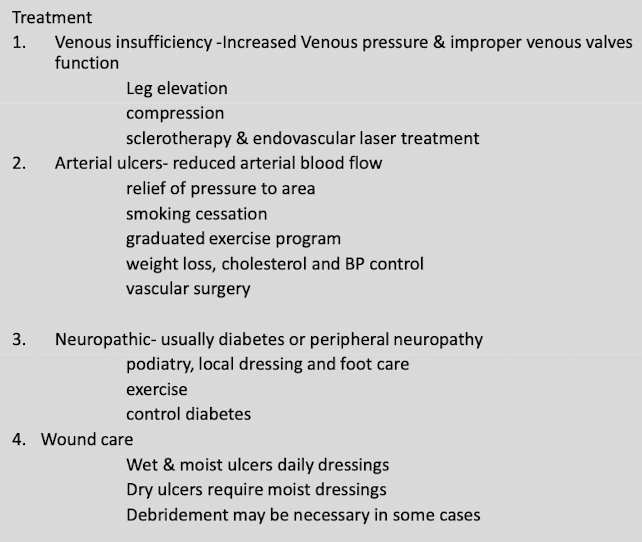
Chronic leg ulcers aetiology + treatment
chronic so full thickness skin defect >4 weeks