Motivation Unit
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is Motivation?
A need or desire that energizes and directs behavior toward a goal.
What is an Instinct?
A complex, inherited, behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species.
Williams James listed 37 instincts.
Instincts both label and explain behaviors.
What are Drives?
Aroused tension states created by imbalances.
Prompts an organism to restore the balance, typically reducing the drive.
Part of drive-reduction theory.
What is the Drive-Reduction Theory?
The idea that a physiological need creates a state of tension (a drive) that motivates an organism to satisfy the need.
Eating and drinking are examples of drive-reducing behaviors.
Step before achieving homeostasis.
What is Arousal?
Levels of alertness and responsiveness.
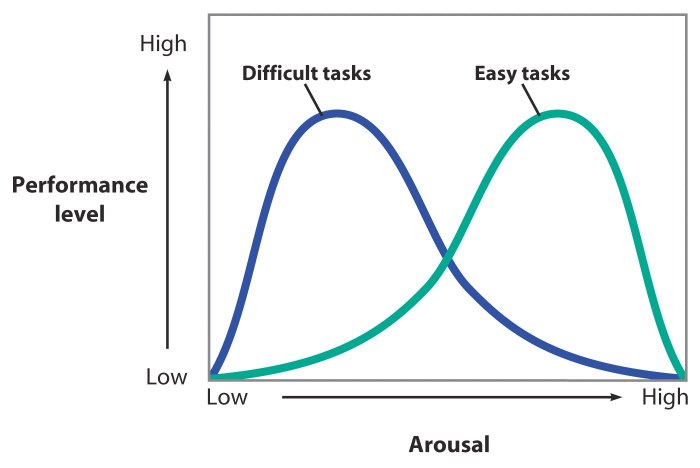
What is the Yerkes-Dodson Law?
The theory that a degree of psychological arousal helps performance, but only up to a point.
Optimum level of arousal depends on the difficulty of task.
Each person has an optimum level of stimulation they like to maintain.
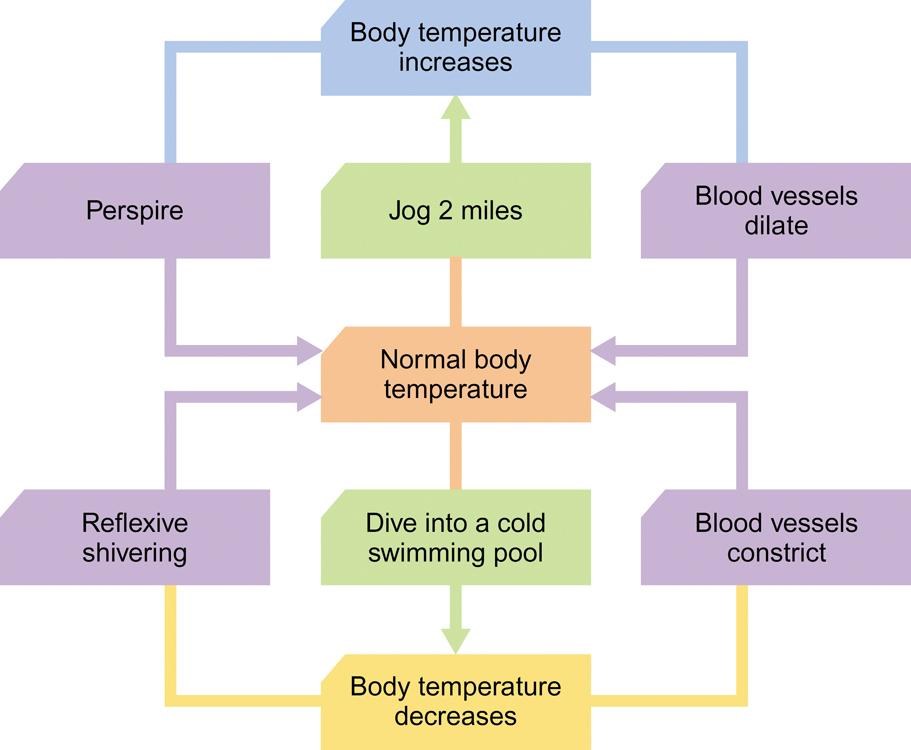
What is homeostasis?
The body’s tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state.
The regulation of any aspect of body chemistry.
Any change in levels, up or down, results in being motivated to bring the level back to normal.
What is Extrinsic Motivation?
A desire to perform a behavior because of promised rewards or threats of punishment.
What is Intrinsic Motivation?
A desire to perform a behavior for its own sake and to be effective.
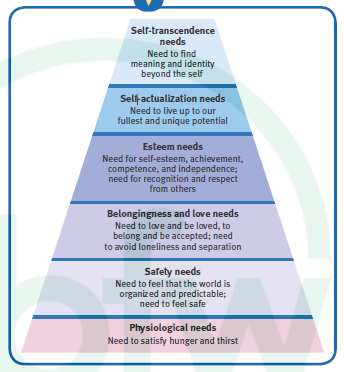
Who was Abraham Maslow?
Humanistic psychologist who proposed the Hierarchy of Needs, with self-transcendence as the ultimate psychological need.
What is the Hierarchy of Needs?
Maslow states that you must reach the needs at the bottom, in order to achieve the needs at the top. But this is not always necessarily true.
What is Achievement Motivation?
A desire for significant accomplishment; and or the mastery of people, things, or ideas.
High Standard
What is Glucose?
Form of sugar which circulates through the body.
Hunger happens when glucose levels drop.
What is Insulin?
Hormone which allows the body to use glucose for energy or fat production.
As insulin levels increase, glucose levels decrease.
What is Leptin?
Protein produced by bloated fat cells.
Sends a message to stop eating.
What is Orexin?
Hunger-triggering hormone produced by the hypothalamus.
As glucose levels drop, orexin levels increase, and a person feels hungry.
What is the Hypothalamus?
Regulates appetite and monitors leptin levels.
What is a Set Point?
The point at which an individual’s “weight thermostat” is supposedly set; when the body falls below this weight, hunger increases, and a lowered metabolic rate may act to restore the lost weight.
What is the Basal Metabolic Rate?
The body’s resting rate at which we burn calories for energy.
What are External Incentives?
Include the sight, sound, and smell of food.
Cultural Influences
Culture influences the food we like and dislike.
Cultural views on body image and beauty vary dramatically in different times and places.
What is Anorexia Nervosa?
An eating disorder in which normal-weight people (usually in adolescent females) have a distorted self-perception of being “fat,” put themselves on self-starvation regimens, and become dangerously underweight (15 percent or more below normal).
What is Bulimia Nervosa?
An eating disorder characterized by episodes of overeating - usually of high-calorie foods - followed by committing, use of laxatives, fasting, or excessive exercise.
Do identical twins share the same increased risk for eating disorders?
Yes, yes they do. Due to the fact that their eating disorders genetically linked.