Biology Chapter 14: Coordination and response
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What travels along the neurones
Electrical impulses
Describe the mammalian nervous system
Central Nervous System ( CNS) -Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) -nerves outside brain and spinal cord
What is the role of nervous system ?
Coordination and regulation of body functions
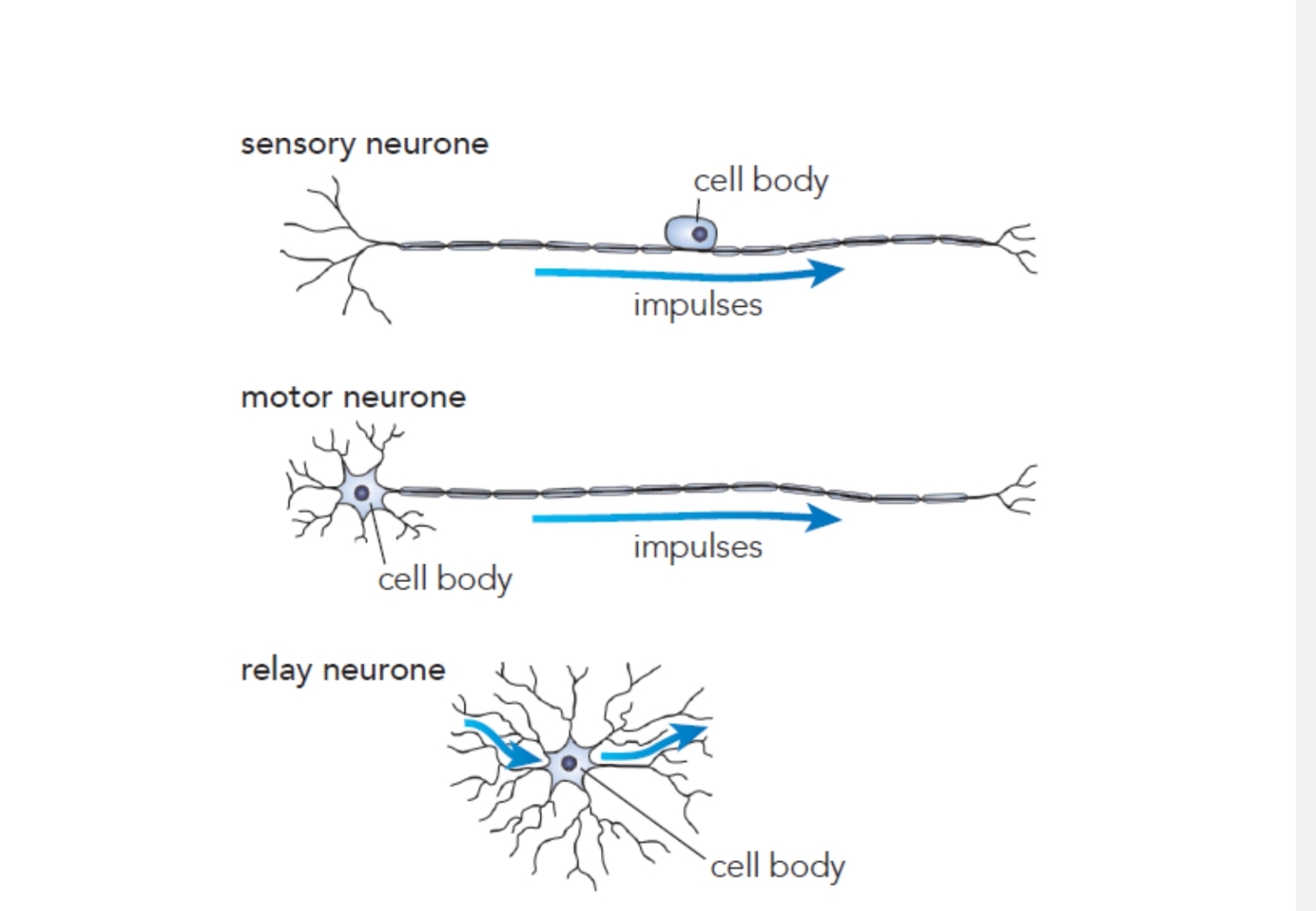
Describe the 3 neurones
Sensory ( from sense organs ( or receptors ) to CNS )
Relay ( from sensory neurones CNS to Motor neurones CNS)
Motor ( from CNS to effectors)
Describe a simple reflex arc
Receptors dectect stimulus and generate impulse
It travels to sensory neurone, then relay neurone , then to motor neurone then to the effector
What is a reflex action
Automatically and rapidly integrating and coordinating stimulus with the responses of effectors ( muscles and glands)
What is a synapse ?
A junction between two neurones
Describe the structure of a synapse
The presence of vesicle containing nerotransmitter molecules
The synaptic gap
Receptor protein
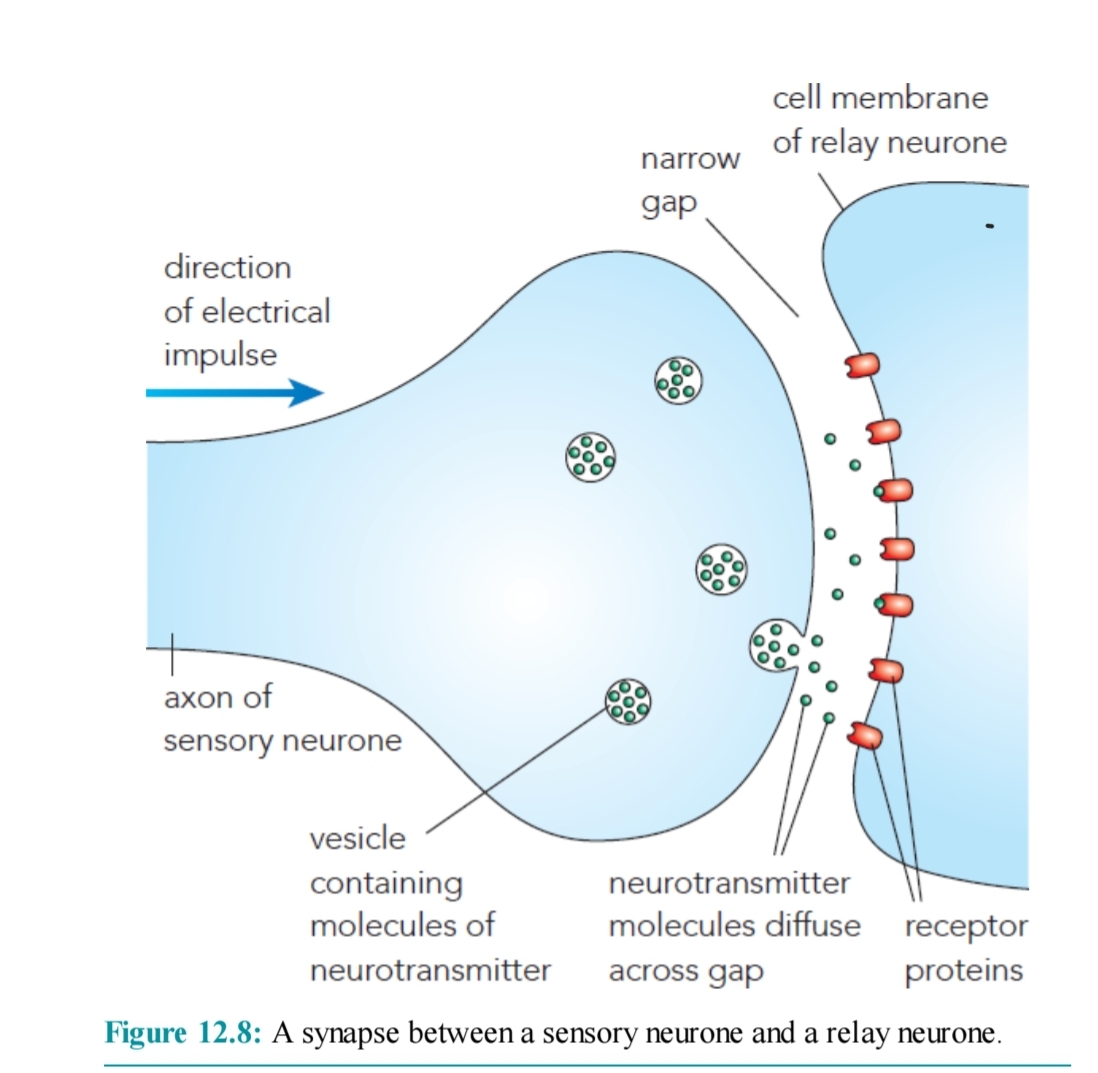
Describe the events at a synapse
An impulse stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecule from vesicles into the synaptic gap
The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the gap
The neurotransmitter molecules bind with receptor proteins on the next neurone ( complementary to each other)
An impulse is then stimulated in the next neurone
Statement about the function of synapse
Synapse ensures that impulses travel in one direction only
Because the vesicles containing the neurotransmitter are only present in the presynaptic neurone, while the receptors are only present in the presynaptic neurone
Impulse cannot go backwards