Muscle Tissue: Types, Structure, and Function 2/2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
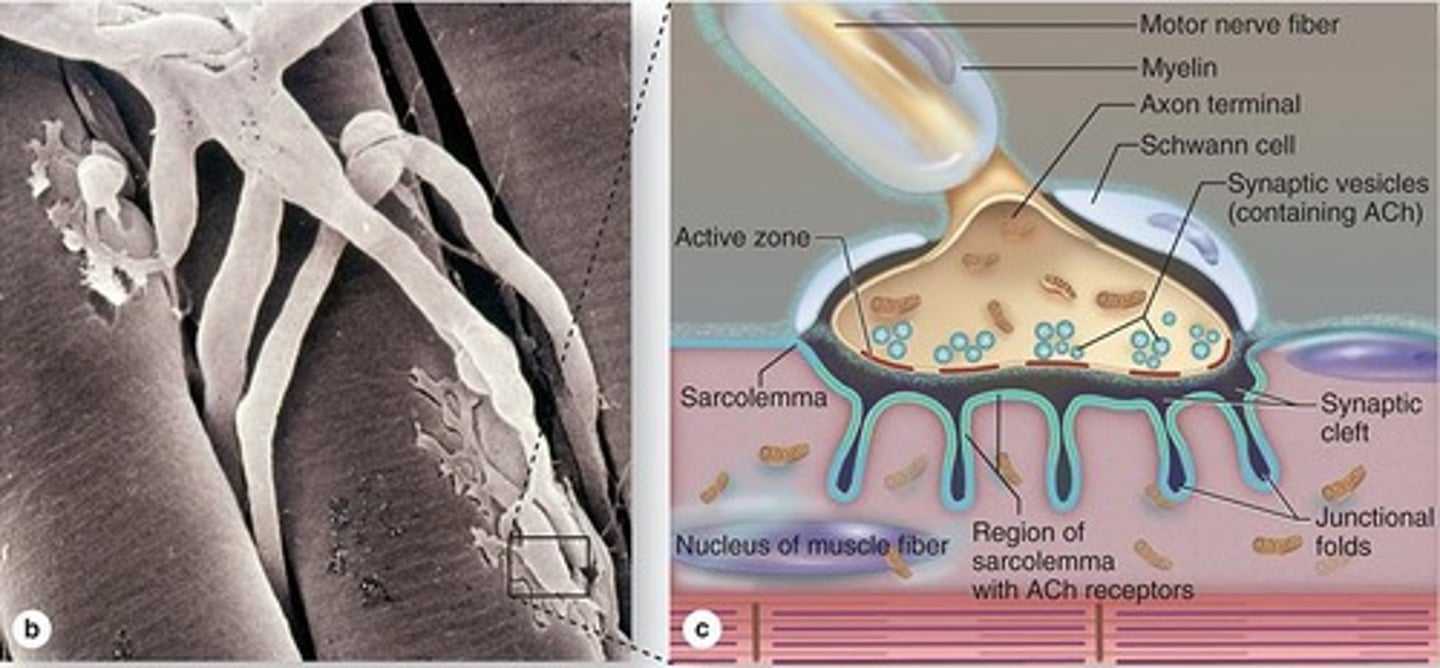
Terminal fibers pass through the endomysium and synapse with muscle fibers (MEP)
Nerves branch out in the perimysium, and their terminal fibers go where?
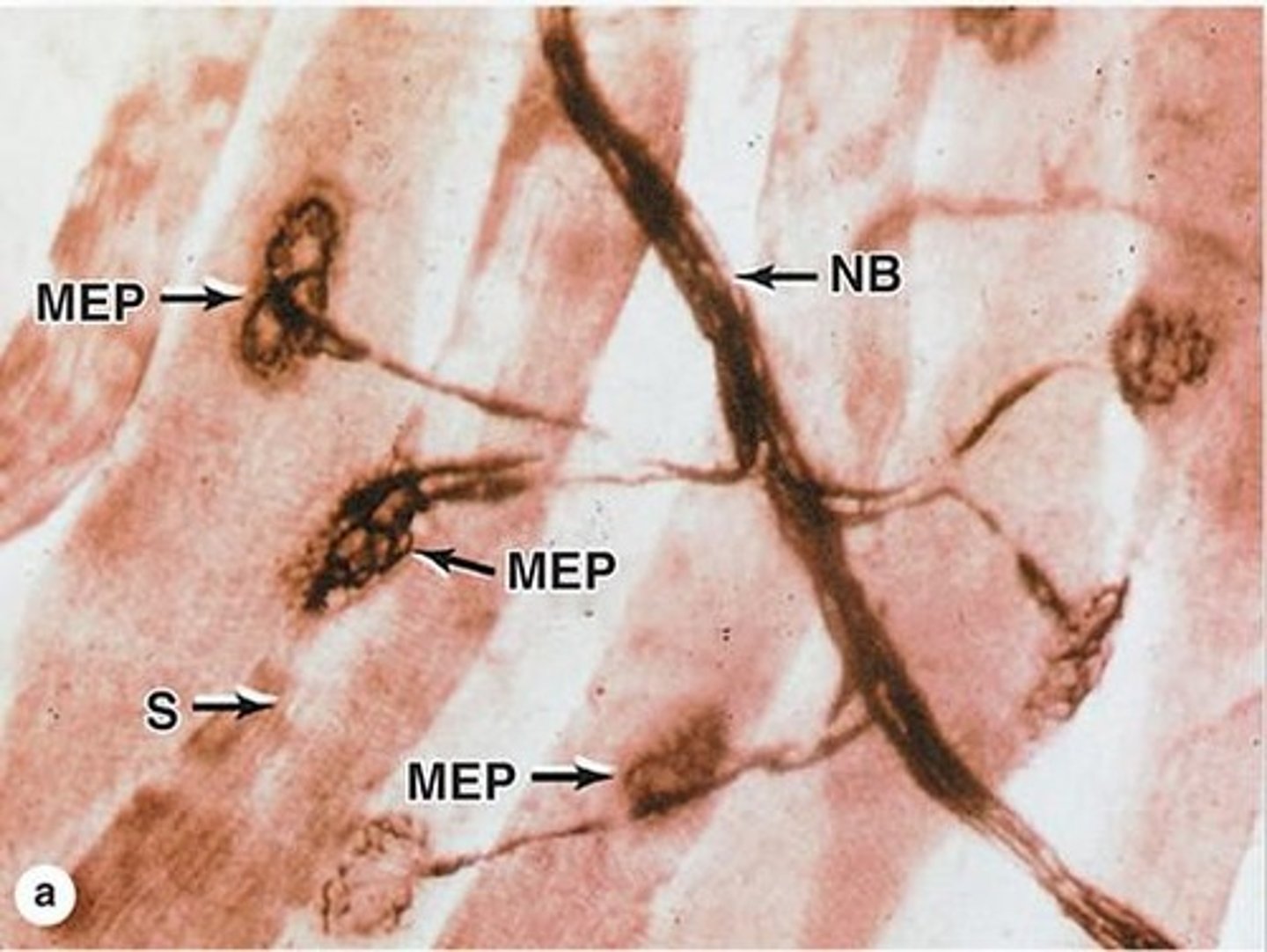
the axon has branches that reach every muscle fiber (covered by Schawnn cells)
How does one motor neuron innervate several muscle fibers?
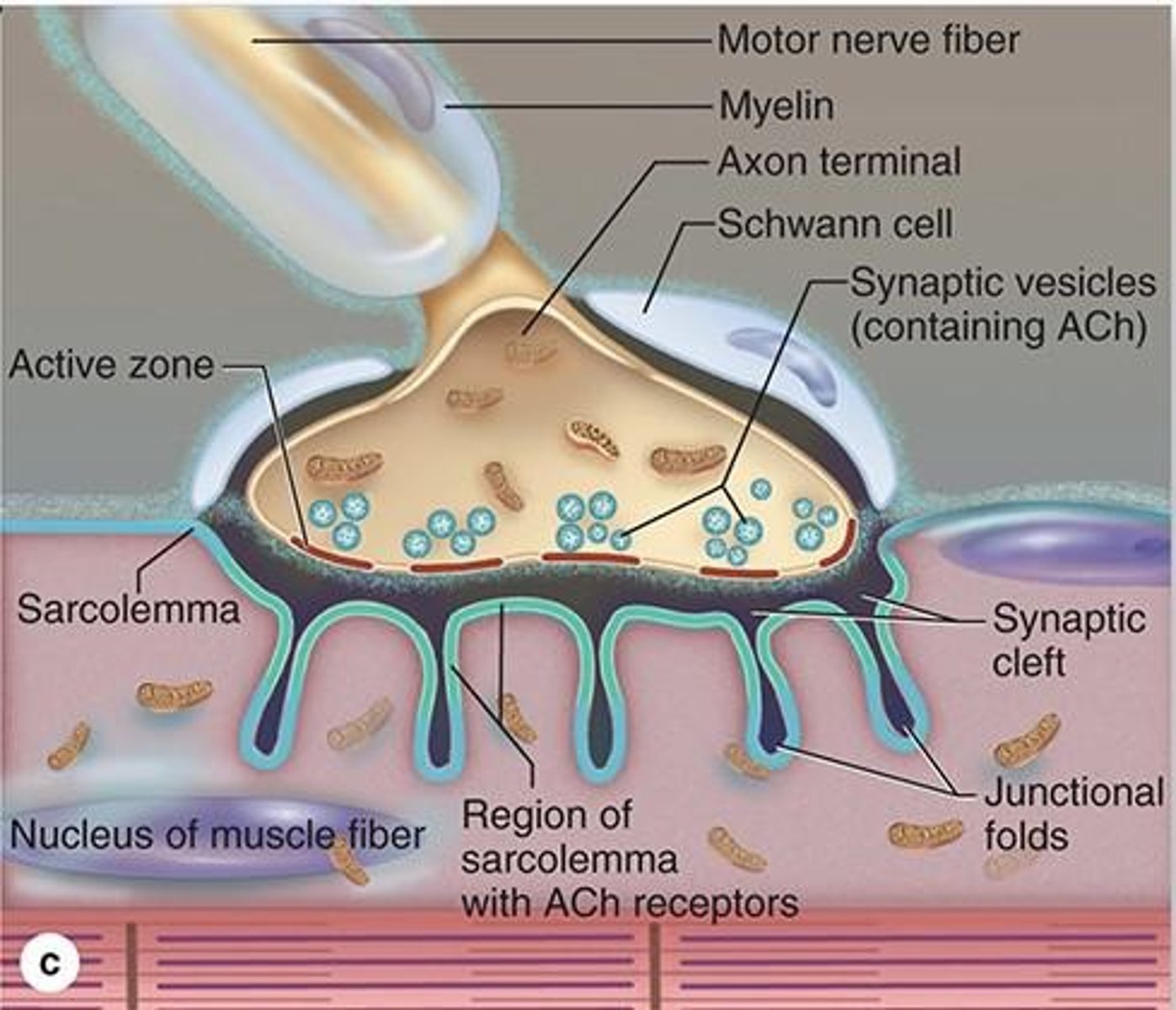
form dilations located within trough of the muscle cell
The end of axonal branches form what?
Mitochondria and synaptic vesicles (stores Ach)
The axon terminal contains what key structures?
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane of muscle fibers.
between axon and sarcolemma
What is the synaptic cleft?
Motor unit
One motor neuron and all its innervated muscle fibers is called a?
Junctional folds
Folds in sarcolemma with Ach receptors.
Proprioceptors
Sensory receptors providing body position awareness.
Muscle spindle
Stretch receptor within skeletal muscle.
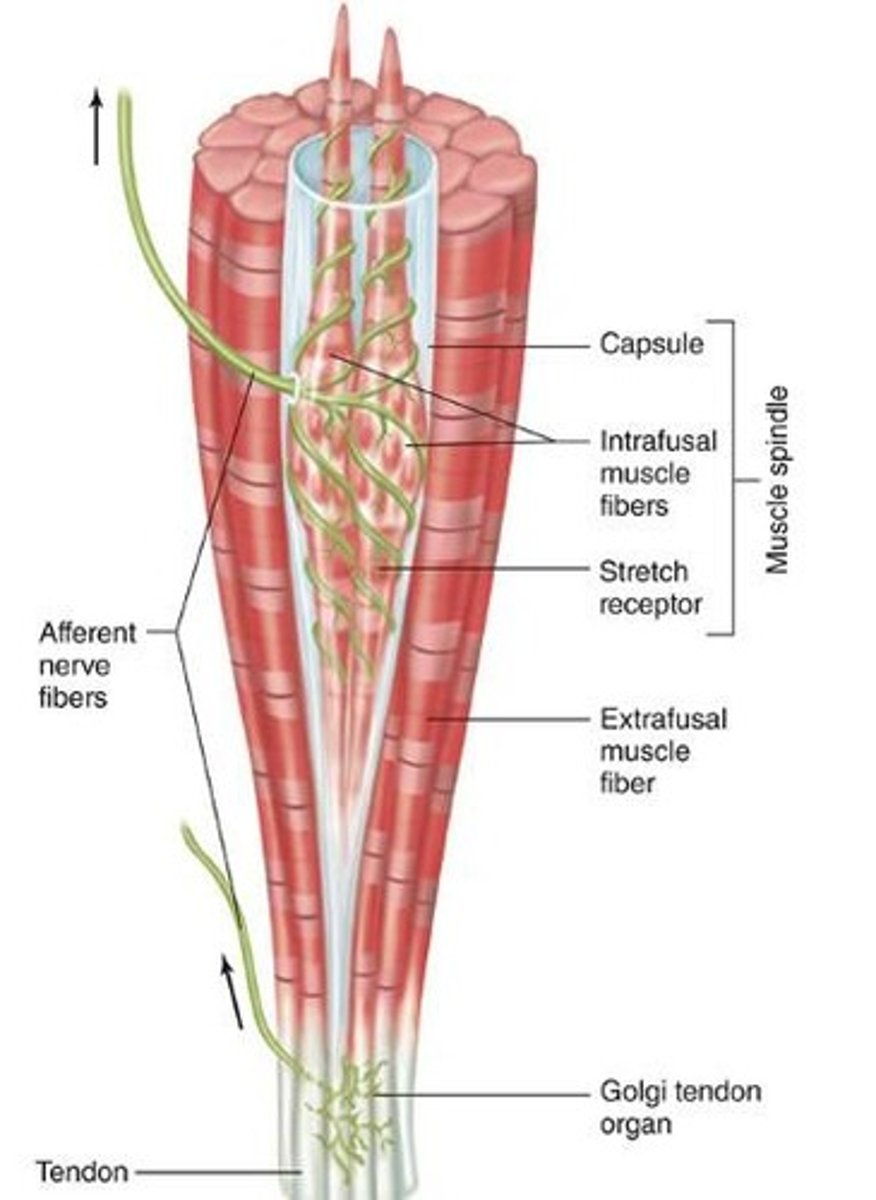
Proprioceptor
Muscle spindle is a type of?
Modified perimysium (DCT)
What encapsulates a muscle spindle?
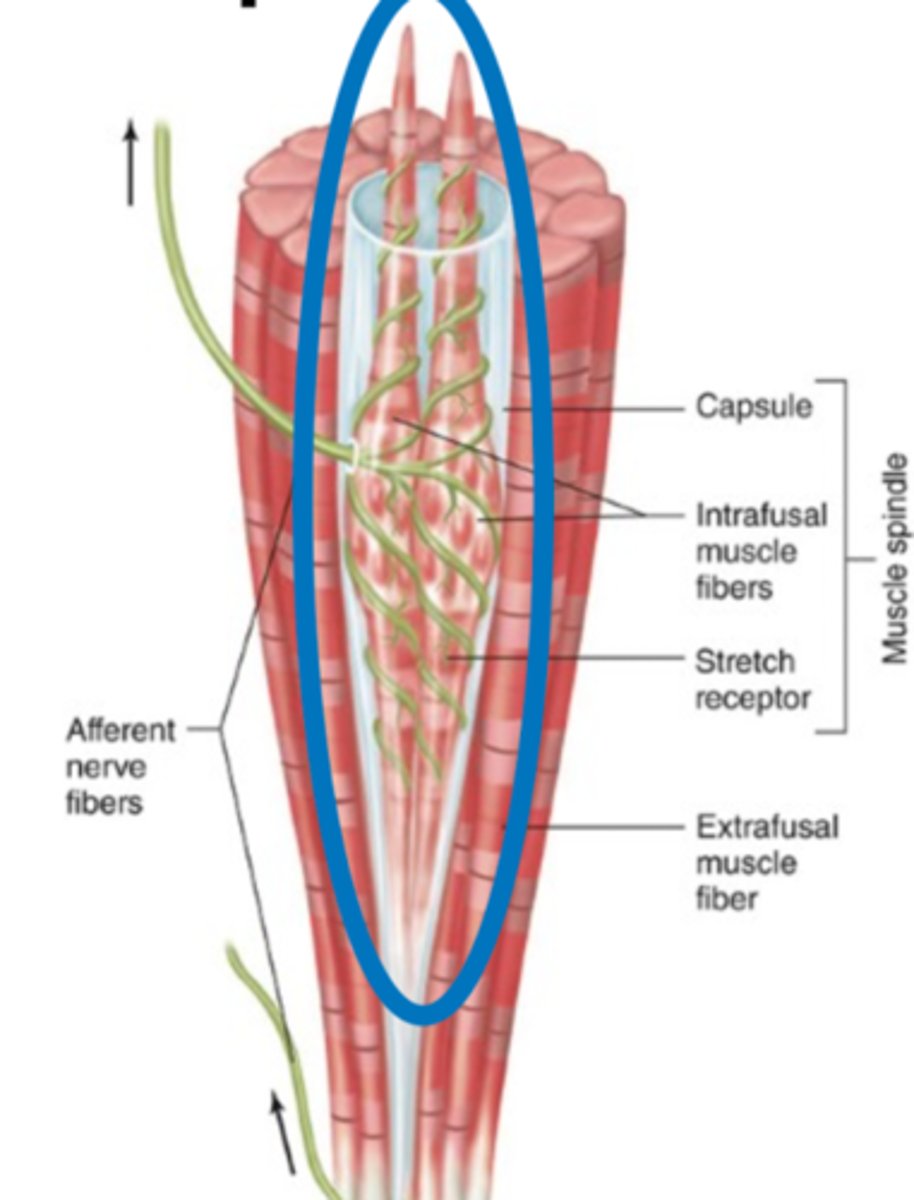
Intrafusal fibers (thin muscle cells)
What is found on the INSIDE of the muscle spindle?
Sensory axons
What surrounds the intrafusal fibers?
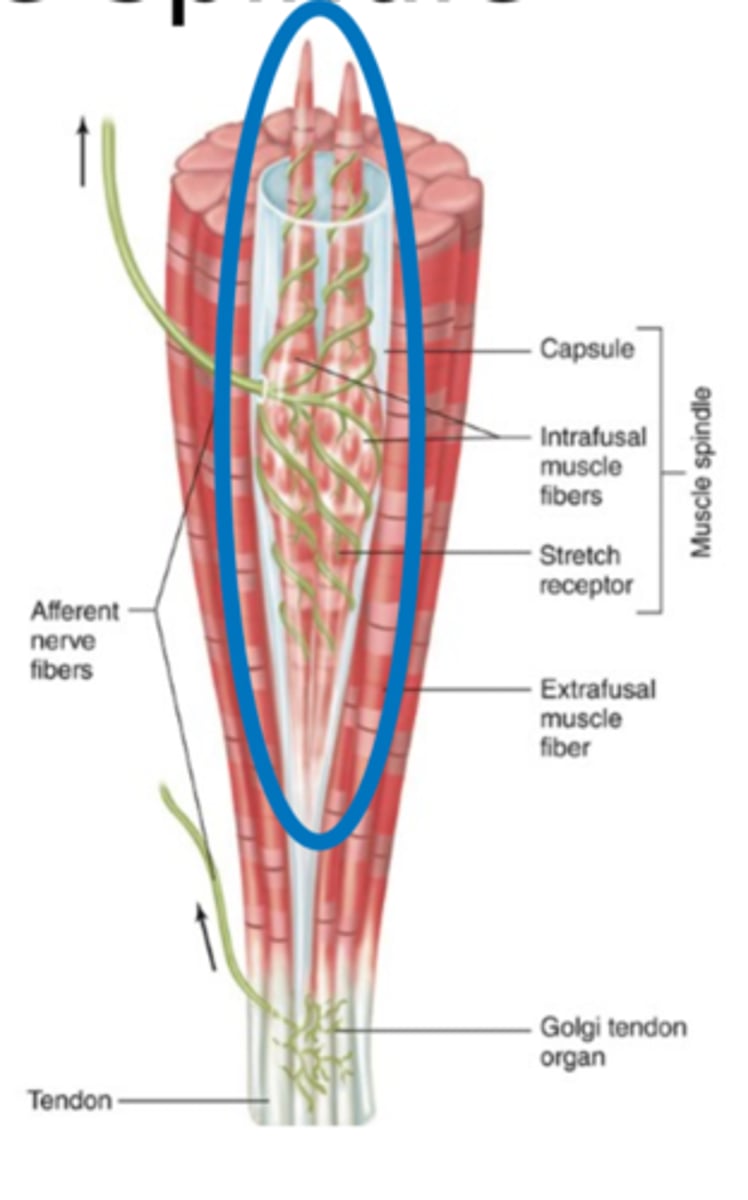
Found among collagen fibers of myotendinous junction.
Golgi tendon organ is a type of stretch receptor that is found where?
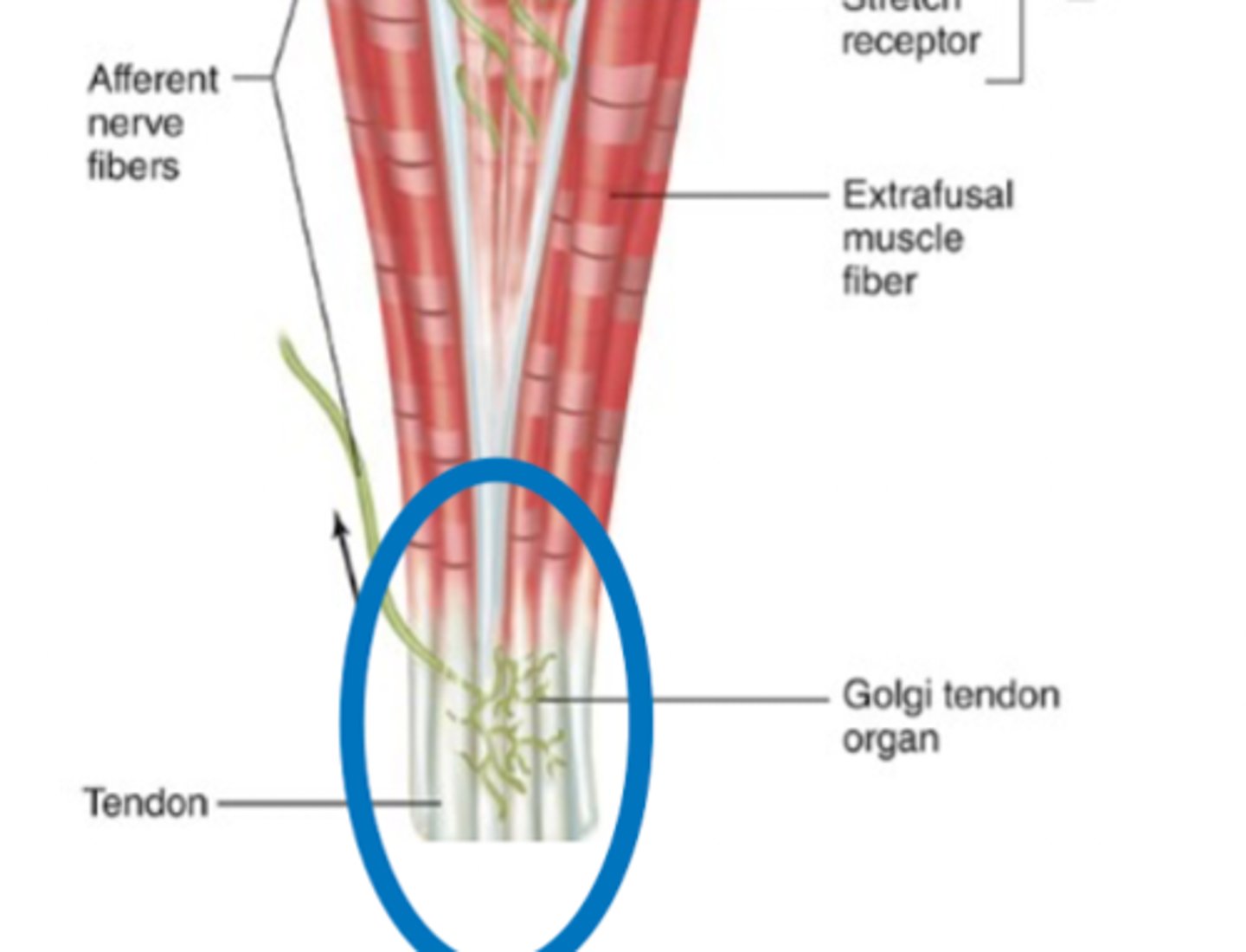
It is smaller than the muscle spindle
Compare the size of a golgi tendon organ to the muscle spindle
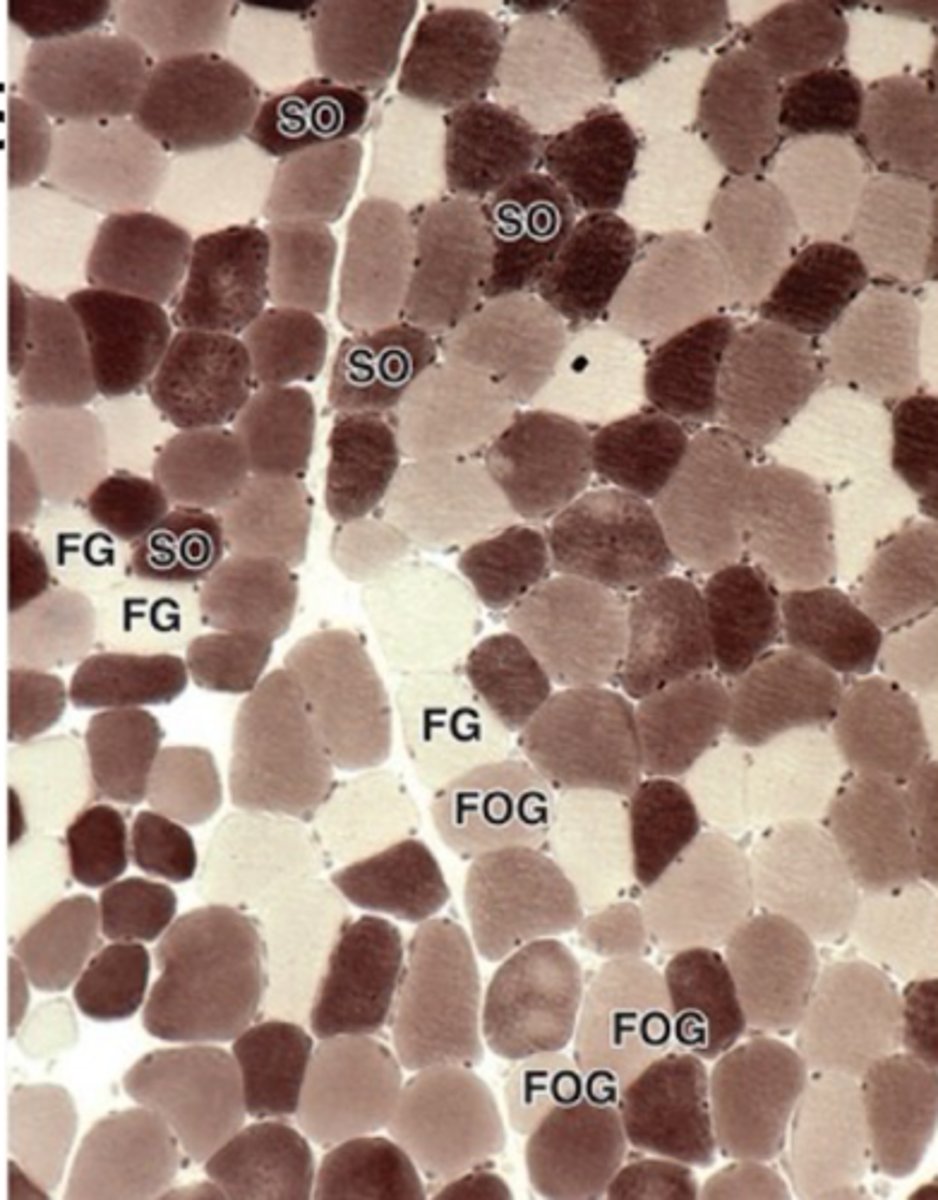
Slow oxidative fibers
Fatigue-resistant fibers with high mitochondria content.
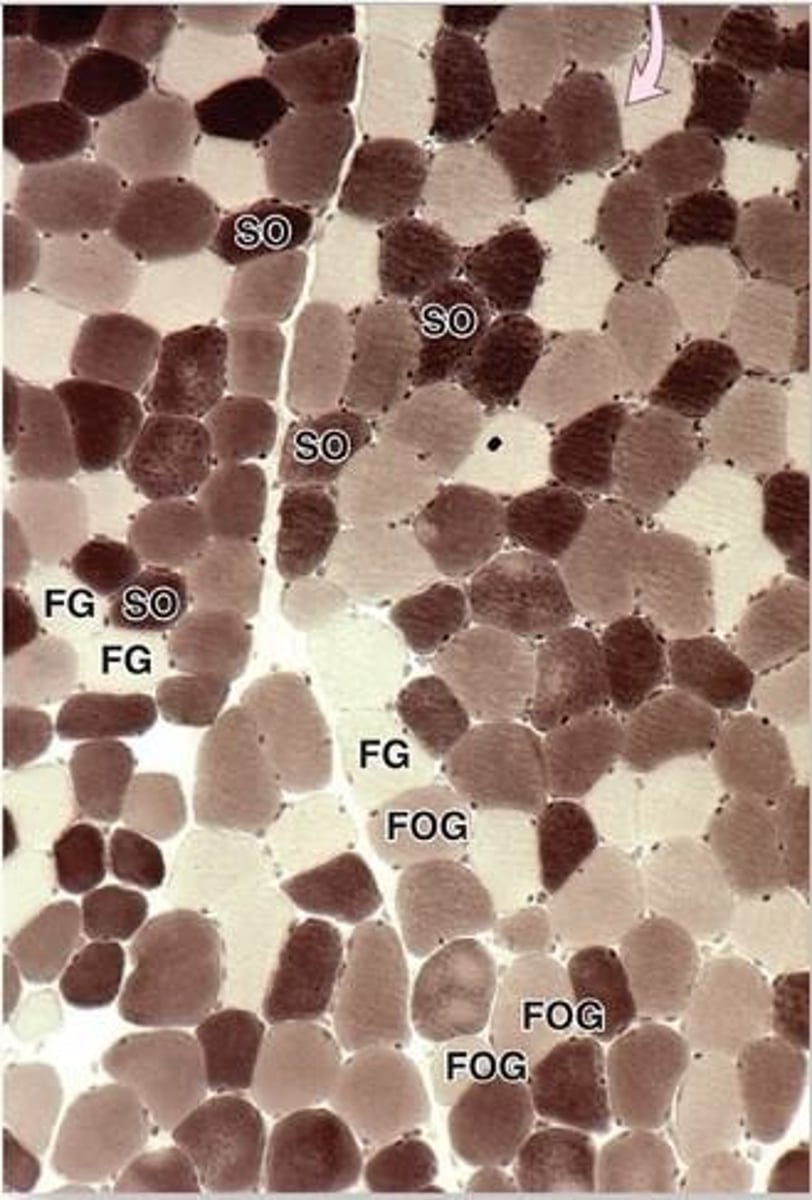
Myoglobin and many surrounding capillaries
Aside from high mitochondria, slow oxidative fibers also contain an abundance of ?
Dark or red when fresh
Slow oxidative (slow contracting) muscle fibers stain what color?
Fast glycolytic fibers
Fatigable fibers relying on anaerobic glycolysis.
few mitochondria
few surrounding capillaries
Fast glycolytic muscle fibers contain few ________ and ________.
Rapid, short-term contractions and accumalates lactic acid
Describe the contractions of fast glycolytic fibers
White when fresh
What color do fast glycolytic muscle fibers stain?
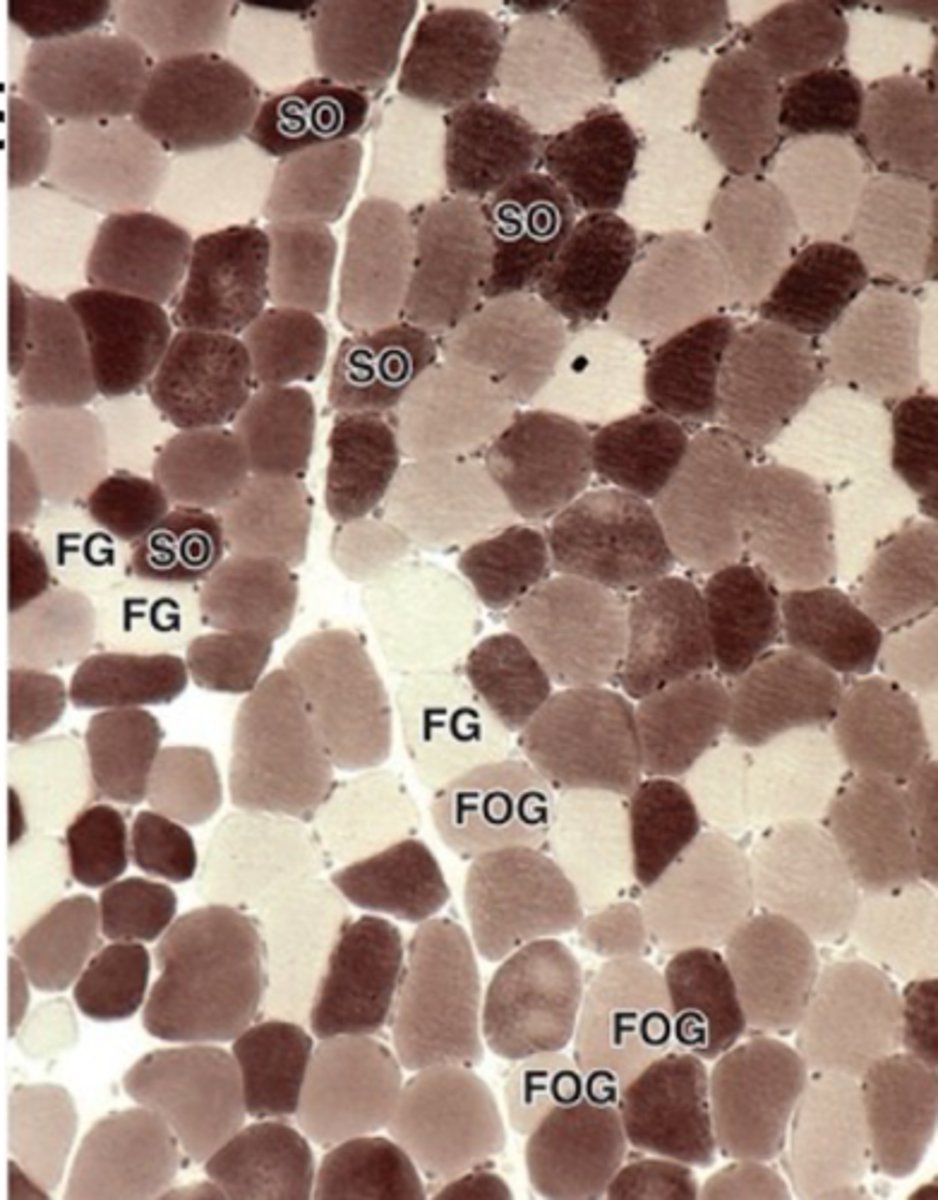
Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers
Intermediate fibers with mixed characteristics.
Cardiocytes or myocytes
Cardiac muscle cells with striated appearance and a single nucleus.
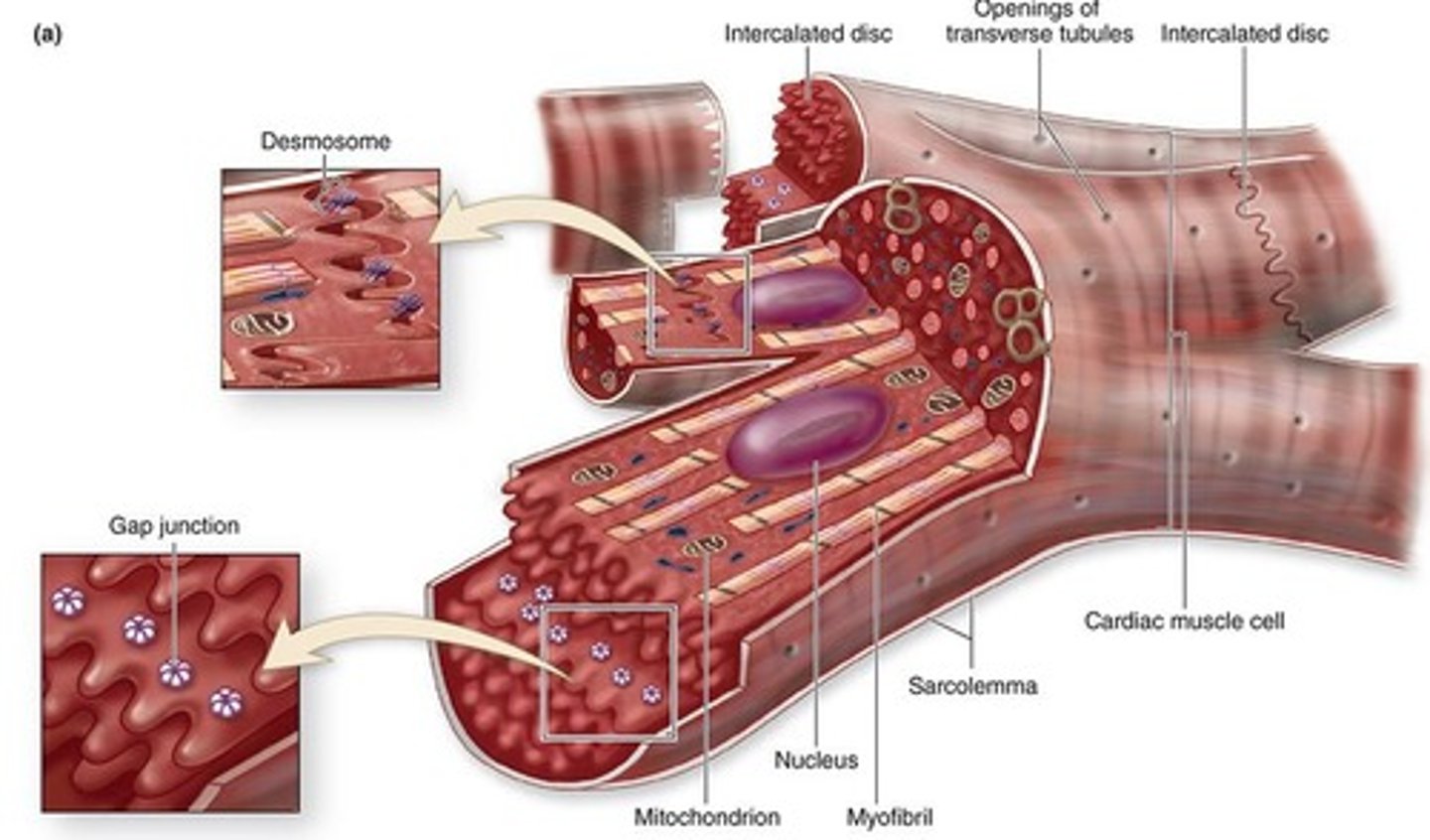
Intercalated discs
Connections between cardiocytes for synchronized contraction.
Thin endomysium
&
Thick perimysium
Subtypes of tissues in cardiac muscle
Surrounds myocytes
Thin endomysium surrounds what?
The thick perimysium that encloses the fasicles
What form the cardiac skeleton?
Desmosomes and adherens junctions
What is found in the transverse regions of intercalated discs?
Gap junctions (electrical synapses)
What is found in the longitudinal regions of intercalated discs? (parallel to myofibrils)
Long and abundant mitochondria
T-tubules longer in ventricles
Secretory granules
Organized sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ultrastructure of cardiocytes reveal what features?
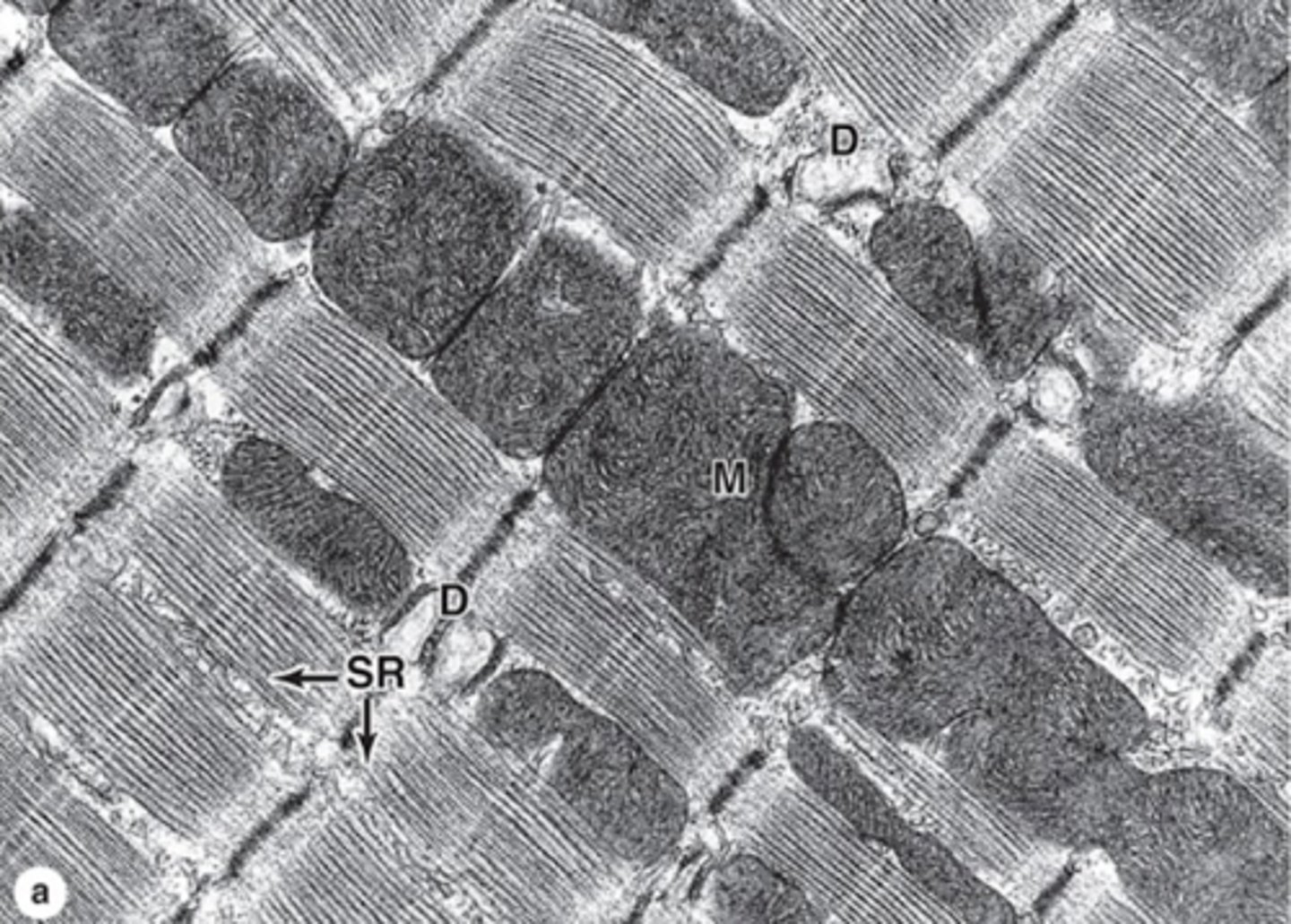

Dyads (found in cardiocytes)
T-tubule + one terminal cisterna forms a ?
Perinuclear glycogen granules (appears clear)
The nucleus of a cardiocyte is surrounded by what?
Fatty acids as triglycerides
In cardiocytes, what is stored in their lipid droplets?
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Hormone that reduces blood pressure when the atrium stretches too much.
1. Slow, steady contraction
2. Synthesis of ECM components
Two functions of smooth muscle include?
Visceral muscle
Another name for smooth muscle?
Thick, branching perimysium
Endomysium composed of type I and type III collagen**
Describe the perimysium and enomysium of smooth muscle
Fusiform cells
Spindle-shaped smooth muscle cells with one elongated nucleus.
Closely packed, non striated, and linked by numerous gap junctions
Describe the organization of smooth muscle cells.
Caveolae
Smooth muscle cells lack T-tubules but instead contain what?
Plasmalemma invaginations that control Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Caveolae is an invagination of the ?
Bundles of thick and thin filaments crisscross the sarcoplasm obliquely. Mechanism similar to striated muscle (but fewer crossbridges)
How does smooth muscle contract?
Calmodulin and MCLK [myosin light chain kinase]
Calcium binds to troponin in skeletal muscle, but what binds Ca2+ in smooth muscle?
Dense bodies (similar to Z discs)
Anchors actin filaments in smooth muscle through the use of a-actin.
Transmitters of contractile force within and between cell
Dense bodies function as transmitters of ?
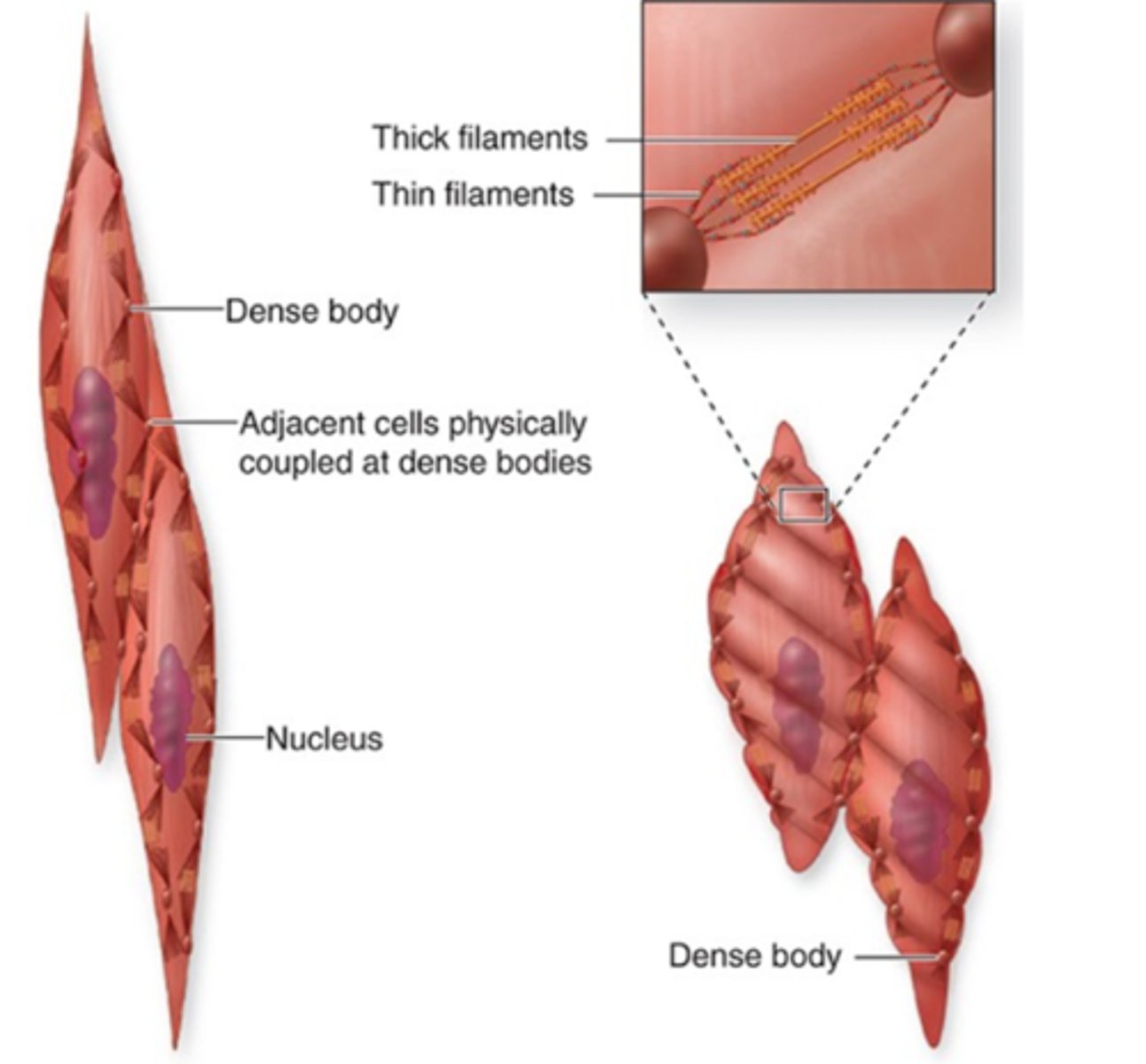
Distorts the cells and nucleus
Contractions does what to the cells and nuclei
1. ANS
2. Paracrine factors (GI)
3. Hormones (uterus)
4. No well-defined junctions
5. Swellings of ANS nerves
6. Synaptic vesicles (ACh)
7. Gap junction propagations
What are the regulators of contraction? (7 total)
Regeneration of skeletal muscle
Slow process using satellite cells for repair.
Regeneration of cardiac muscle
Very poor due to lack of satellite cells.
Regeneration of visceral muscle (smooth muscle)
Rapid due to undifferentiated cells allowing repair.