DEVPSY COMPRE REVIEW
1/326
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
327 Terms
Developmental Psychology
continuities and changes that individuals display overtime
Normative Development
characterising all members of a species
Ideographic Development
describe those that vary across individuals
Human Development
changes individuals and their relationships go through as they continue to grow
Holistic Perspective
social, emotional, physical, mental, and intellectual growth
Plasticity
the potential to be shaped by experience
Reliability
produces consistent, replicable results
Validity
accurately measures what it is intended to measure
Correlational Design
examine relationships without intervention
design for detecting relationships
Experimental Design
identifies cause and effect relationships
design for detecting relationships
Cross-sectional Design
compares age groups at a single point in time
design for studying development
Longitudinal Design
repeatedly examining the same participants as they grow older
design for studying development
Sequential Design
combination of cross-sectional and longitudinal designs
design for studying development
Microgenetic Design
studies children when developmental changes normally occur
design for studying development
Research Ethics
standards of conduct to protect participants from harm
Rights of Participants
Protection from harm
Confidentiality
Explanation for any deception
Informed consent
Nature vs Nurture
Are biological dispositions or environmental influences the most influential?
Continuity vs Discontinuity
Are developmental changes quantitative and continuous (gradual) or qualitative and discontinuous (stage-like)?
Active vs Passive
Are children active contributors to their own development or passive recipients of their environment?
Universality vs Context Specific
Are developmental changes common to everyone or vary by individual, culture, or subculture?
Sigmund Freud
Psychosexual Theory
Psychosexual Theory
people are driven by sexual and aggressive instincts that must be controlled
people's behavior was said to reflect unconscious motives that people repress
Oral Stage
Fixation: Smoking, overeating, nail-biting
Oral Stage
Erogenous Zone: Mouth
Oral Stage
Major Development: Coming off breastfeeding
Oral Stage
Age: 0-1 yrs (Psychosexual Stage)
Anal Stage
Age: 1-3 Years (Psychosexual Stage)
Anal Stage
Erogenous Zone: Anus
Anal Stage
Major Development: Toilet Training
Anal Stage
Fixation: Orderliness, Messiness
Phallic Stage
Age: 3-6 yrs (Psychosexual Stage)
Phallic Stage
Age: 3-6 yrs (Psychosexual Stage)
Phallic Stage
Major Development: Oedipus/Electra Complex
Phallic Stage
Fixation: Sexual Dysfunction
Latency Stage
Age: 6-12 yrs (Psychosexual Stage)
Latency Stage
Major Development: Defense Mechanism
Genital Stage
Age: 12+ yrs (Psychosexual Stage)
Genital Stage
Erogenous Zone: Potential Sexual Partners; Genitals
Genital Stage
Major Development: Full Sexual Maturity
Genital Stage
Fixation: Mental Health
Id
Pleasure Principle
Ego
Reality Principle
Superego
Morality Principle
Erik Erikson
Theory of Psychosocial Development
Theory of Psychosocial Development
people advance through the stages of development based on how they adjust to social crises throughout their lives
Infancy Stage
Age: 0-1 yrs (Psychosocial Development)
Infancy Stage
Basic Conflict: Trust vs Mistrust
Infancy Stage
Virtue: Hope
Early Childhood
Age: 1-3 yrs (Psychosocial Development)
Early Childhood
Basic Conflict: Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt
Early Childhood
Virtue: Will
Play Age
Age: 3-6 yrs (Psychosocial Development)
Play Age
Basic Conflict: Initiative vs Guilt
Play Age
Virtue: Purpose
School Age
Age: 7-11 yrs (Psychosocial Development)
School Age
Basic Conflict: Industry vs Inferiority
School Age
Virtue: Competence
Adolescence
Age: 12-18 yrs (Psychosocial Development)
Adolescence
Basic Conflict: Identity vs Role Confusion
Adolescence
Basic Virtue: Fidelity
Early Adulthood
Age: 19-29 yrs (Psychosocial Development)
Early Adulthood
Basic Conflict: Intimacy vs Isolation
Early Adulthood
Virtue: Love
Middle Age
Age: 30-64 yrs (Psychosocial Development)
Middle Age
Basic Conflict: Generativity vs Stagnation
Middle Age
Virtue: Care
Old Age (Late Adulthood)
Age: 65+ yrs (Psychosocial Development)
Old Age (Late Adulthood)
Basic Conflict: Integrity vs Despair
Old Age (Late Adulthood)
Virtue: Wisdom
BF Skinner
Operant Learning Theory
Operant Learning Theory
when a stimulus (antecedent) leads to a behavior, which then leads to a consequence
Reinforcement
increase of desirable behavior
Positive Reinforcement
adding a stimulus to strengthen behavior
Negative Reinforcement
removing a stimulus to strengthen a behavior
Punishment
decrease undesirable behavior
Positive Punishment
adding of stimulus to weaken behavior
Negative Punishment
removing of stimulus to strengthen behavior
Albert Bandura
Social Learning Theory
Social Learning Theory
viewed observational learning as the source of children's learning
Jean Piaget
Cognitive Development Theory
Cognitive Development Theory
views children as active explorers who construct cognitive schemes
Sensorimotor Stage
0-2 yrs
understand the world through senses and actions
Preoperational Stage
2-7 yrs
understand the world through language and images
Concrete Operational Stage
7-12 yrs
understand the world through logical thinking and categories
Formal Operational
12 yrs onwards
understand the world through hypothetical thinking and scientific reasoning
Lev Vygotsky
Sociocultural Theory
Sociocultural Theory
views cognitive growth as a socially mediated activity
Information-Processing Theory
information flows into the system, is operated on, and is converted to output
George Miller
Information-Processing Theory
Konrad Lorenz
Ethological Theory
Ethological Theory
views humans as born with adaptive attributes that have evolved through natural selection
Urie Bronfenbrenner
Ecological Systems Theory
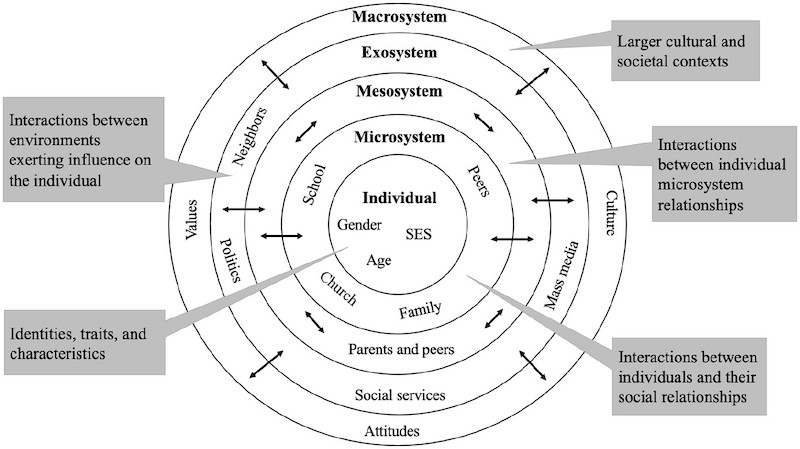
Ecological Systems Theory
most accepted explanations on the influence of social environments on human development
Person/Individual
where identities, traits, and characteristics are found
Microsystem
family, school, peers, religious affiliation, workplace
Mesosystem
family, school, peers, religious affiliation, workplace PLUS neighborhood
Exosystem
economic, political, educational, governmental, and religious systems
Macrosystem
overarching values and beliefs
Chronosystem
time
Lawrence Kohlberg
Moral Development Theory