IB Biology - Topic 6.2 + D.4: Cardiovascular System
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
draw and label a heart diagram
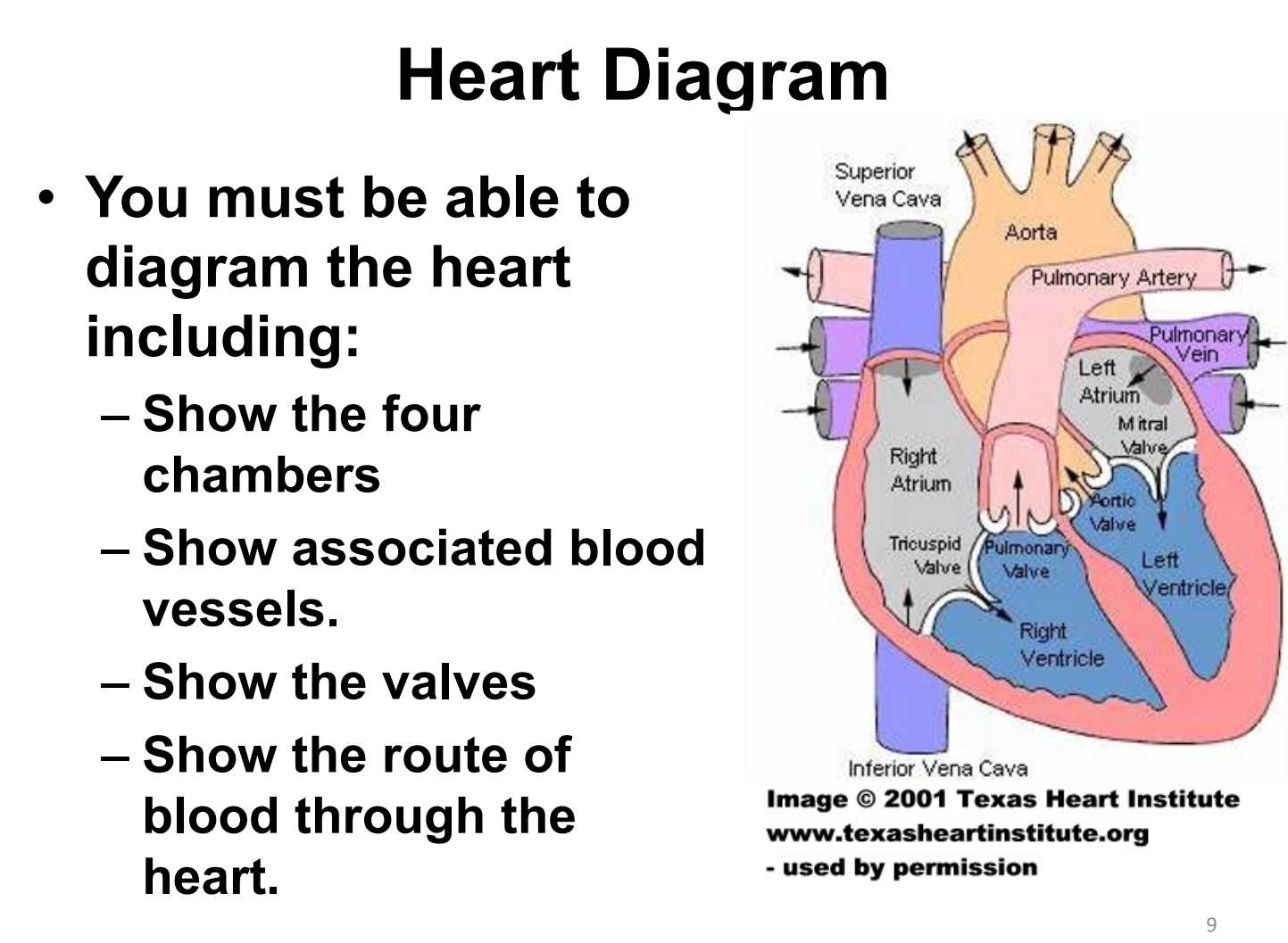
list and describe the role of the three parts that make up the cardiovascular system
the heart: pump blood by creating a pressure gradient
blood vessels: carry blood to and from the heart to other tissues
blood: medium in which the transport of materials such as nutrients is carried
list what the cardiovascular system transports
oxygen
nutrients
antibodies
hormones
heat
carbon dioxide
urea
list and describe the components of blood
plasma: dissolves or carries other components of blood
erythrocytes (red blood cells): transport oxygen in the hemoglobin
leucocytes (white blood cells):
phagocytes: eat up pathogens + dead cells
lymphocytes (b-cells, t-cells): for immune response
platelets: clotting of blood following damage to cells or erethrocytes
outline the basic flow of blood
deoxygenated blood enters the atria via the veins
atrial contraction pushes blood into the ventricles
ventricular contraction pushes blood out of the heart into the arteries to the lungs (pulmonary) OR body (systemic)
explain the features of the heart that keep blood flow constant
atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral) prevent backflow
semilunar valves (pulmonary and aortic) prevent backflow
pressure gradient (higher pressure in the ventricles) pushes blood under pressure into the arteries
stroke volume
amount of blood pumped in a single contraction
cardiac output
volume of blood pumped into the systemic circulation per minute; depends on both heart rate and stroke volume
outline the path of deoxygenated blood
deoxygenated blood flows to the heart via the veins leading to the vena cava
deoxygenated blood enters the heart in the right atrium
atrial contraction pushes the deoxygenated blood into the right ventricle, past the atrioventricular valve (tricuspid valve)
ventricular contraction pushes the deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary arteries, past the semilunar valve (pulmonary valve)
pulmonary arteries lead to the lung for gas exchange to occur
*pulmonary arteries are the only arteries in the body that carry deoxygenated blood
outline the circulation of oxygenated blood
oxygenated blood returns to the heart in the left atrium via the pulmonary veins
atrial contraction pushes the oxygenated blood into the left ventricle, past the atrioventricular valve (mitral valve)
ventricular contraction pushes the oxygenated blood into the aorta, past the semilunar valve (aortic valve)
the aorta brings oxygenated blood to the rest of the body
*pulmonary veins are the only veins in the body that carry oxygenated blood
describe the structure and function of the arteries
carry oxygenated blood away from the heart at high pressure to body tissues
contain thick walls to withstand high pressure
have muscle cells and elastic fibers that assist in maintaining blood pressure and its movement
describe the structure and function of the capillaries
permeable walls for rapid exchange of gases, nutrients, waste, and diffusion of phagocytes
narrow so it can penetrate all parts of the tissue
large total surface area
describe the structure and function of the veins
collect blood at low pressure from body tissues and return it to the heart
thinner walls than arteries because they face lower pressure, allows them to be squeezed by muscles
fewer muscles + elastic fibers than arteries because they face lower pressure
valves are present to prevent backflow or pooling of blood
cardiomyogenic muscle contraction
myogenic contraction is contraction initiated by the cell itself rather than a nervous stimulus; heart beat doesn’t rely on impulses from the brain to keep contracting
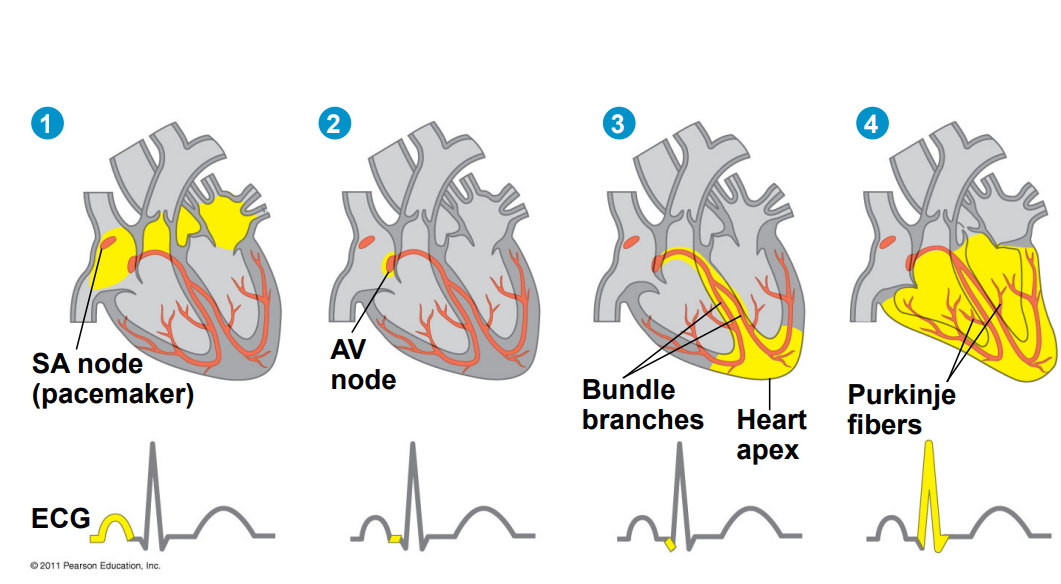
sinoatrial node
sets the pace and initiates the heartbeat by sending the first signal and causes the atria to contract; it can be independent or moderated by the autonomic nervous system
atrioventricular node
triggered by the signal of the SA node, carries out signal for ventricular contraction; between the SA node and VA node there is a delay that allows the switch from diastole to systole
outline the steps of the spread of the electrical signal
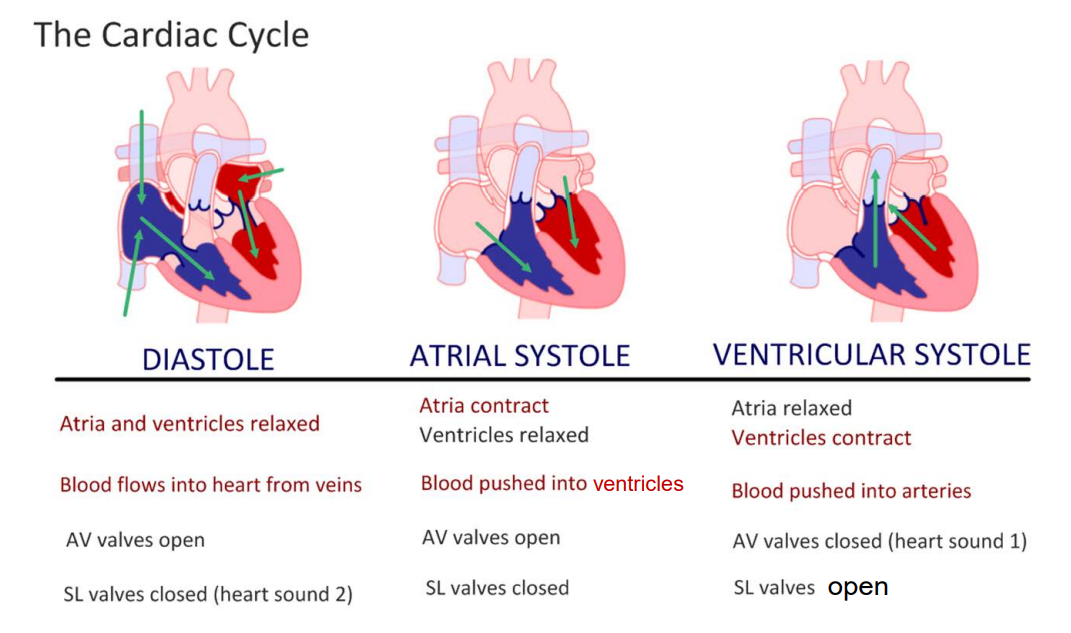
outline the events of the cardiac cycle
SA node receives signal to fire when the ventricles are 70% full (during late ventricular diastole)
AV valves (mitral + tricuspid) open and ventricles are filled to the max (atrial systole)
pressure increase in the ventricles closes the AV valves (ventricular systole)
AV nodes fire
Purkinje fibers carry impulse to all areas of ventricles for simultaneous fire
pressure increase causes semilunar valves (pulmonary + aortic) to open
blood is pumped from ventricles to pulmonary arteries/aorta (systole sound) (ventricular systole)
pressure decrease in the ventricles closes the SA valves (diastole sound)
pressure in the ventricle is lower than in the atria so the AV valves open
blood volume increases in ventricle (70%)
both atria + ventricles are relaxed (diastole)
atria receives blood from veins
cycle repeats
cardiac cycle summed up
describe and explain the adaptations to carry electrical signal
branched cells with intercalated discs that prevents separation under strain of pumping blood and signal can be passed quickly
large interconnected network is created allowing easier propagation