Chapter 10 Microeconomics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
When P > MC in a monopolistically competitive market, that industry will most likely produce than would be found in a perfectly competitive industry.
a lower quantity of a good and charge a higher price
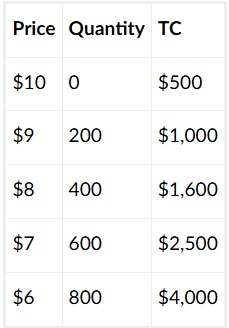
What quantity should they produce to maximize their profits?
600 units
The perceived demand for a monopolistic competitor
takes competitors into account.
The desire of businesses to _, so that they can raise the prices that they charge and earn higher profits, has been well-understood by economists for a long time.
avoid competing with each other
The demand curve as perceived by a perfectly competitive firm is _.
flat
Through the process of exit, monopolistically competitive firms remaining in the market
are no longer earning losses.
A _ refers to a group of firms colluding with one another to produce at the monopoly output and sell at the monopoly price.
cartel
Which of the following represents a difference in the process by which a monopolistic competitor and a monopolist make their respective decisions about quantity and price?
a monopolist need not fear entry and the monopolist's perceived demand curve is market demand
In a monopolistically competitive market, the rule for maximizing profit is to set MR = MC, which means
price is higher than marginal revenue.
The first step to be undertaken by a profit-maximizing monopolistic competitor wanting to decide what price to charge is to
select the profit maximizing quantity to produce
If the firm is producing at a quantity of output where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, then,
the firm should keep expanding production.
In the framework of monopolistic competition, advertising works because it causes
a steeper perceived demand curve. And. perceived demand curve to shift to the right.
How can parties who find themselves in a prisoner's dilemma situation avoid the undesired outcome and cooperate with each other?
find effective ways to penalize firms who do not cooperate
Monopolistic competitors in the food industry will often include a recyclable symbol on packaging used for their product as a means to
differentiate their product.
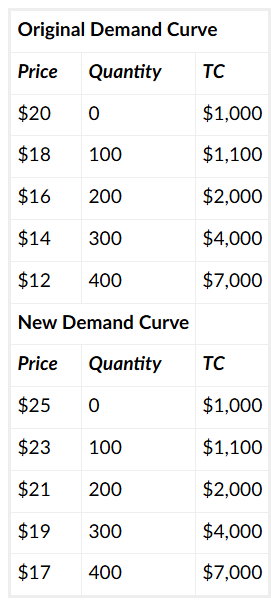
Joe owns a restaurant. Many of the restaurants that he competes with recently closed, shifting his perceived demand curve. The following 2 tables show his old and new perceived demand curves. Assume that Joe can only choose from the quantities of output given in the table. By how much does the price that he charges change after the restaurants leave the market?
increase by 5
In the highly competitive setting in which oligopoly firms operate, which of the following are considered to be typical temptations each may face?
to cooperate to generate and then divide up monopoly-like profits. And. to cooperate to mutually decide what price to charge. And. to cooperate to make decisions about what quantity to produce. And. to cooperate to act as a single monopoly
When exit occurs in a monopolistically competitive industry the
perceived demand and marginal revenue curves will shift to the right.
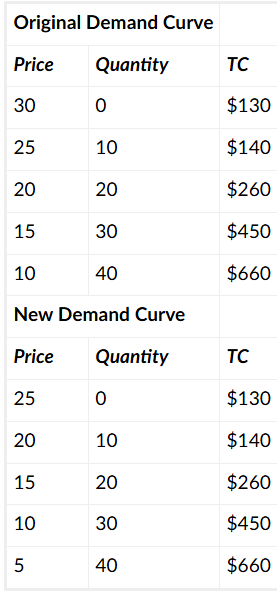
Mary competes in a monopolistically competitive market. Suddenly, 5 new firms enter the market, causing her perceived demand curve to shift. The following tables show her original and new demand curves and her cost information. Assume that Mary can only choose from the quantities of output given in the table. By how much will the quantity that she produces change after the new firms enter the market?
decrease by 10
The typical slope of the demand curve as perceived by a monopolistic competitor will
reflect that firm's ability to raise its price without losing all of its customers.
In the competitive market for figure skate blades, manufacturers offer an array of products that are
distinctly different in a particular way.
Perfect competition displays because the social benefits of additional production, as measured by the price that people are willing to pay, are in balance with the ___ to society of that production.
allocative efficiency; marginal costs
Oligopoly firms acting individually may seek to gain profits _.
by expanding levels of output and cutting prices
Why are the underlying economic meanings of the perceived demand curves for a monopolist and monopolistic competitor different?
a monopolist faces the market demand curve and a monopolist competitor does not
As the name monopolistic competition implies, a firm's decisions in this setting will in certain ways resemble and in other ways resemble __.
monopoly; perfect competition
The shape of the perceived demand curve for a perfectly competitive firm reflects that firm's ability to
sell any quantity it wishes at the prevailing market price.
In monopolistic competition, the end result of entry and exit is that firms end up with a price that lies
on the downward-sloping portion of the average cost curve.
A monopolistically competitive industry does not display _ in either the short-run, when firms are making , nor in the long-run, when firms are earning
productive and allocative efficiency; profits and losses; zero profits
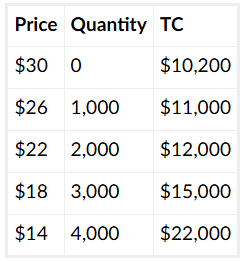
If they maximize their profits, what will their revenue equal?
$54,000
Product differentiation may occur in because __ created strong preferences for certain brands.
the minds of buyers; past habits and advertising
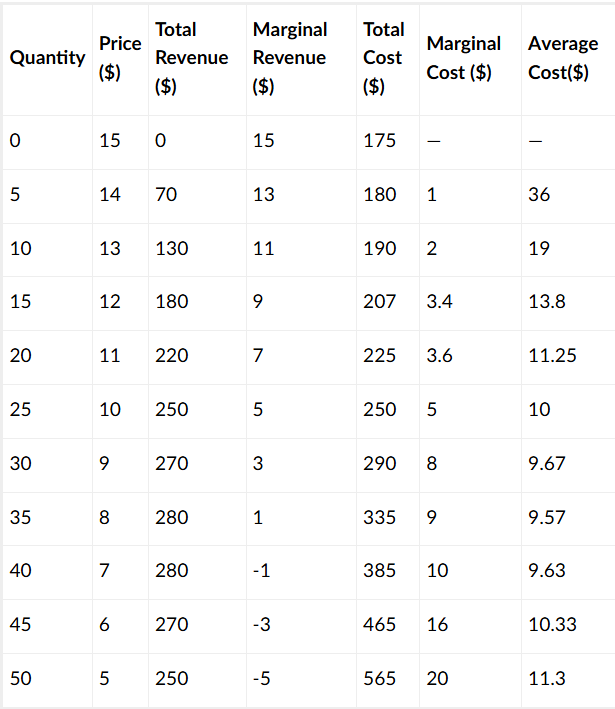
What will this firm's profits equal in the long run?
$0
The perceived demand curve for a group of competing oligopoly firms will appear kinked as a result of their commitment to
match price cuts, but not price increases.
When entry occurs in a monopolistically competitive industry,
a smaller quantity will be demanded at any given price.
The long-term result of entry and exit in a perfectly competitive market is that all firms end up selling at the price level determined by the lowest point on the
average cost curve.
Would raising the price for a product create a larger decline in quantity demanded for a monopolistic competitor than it would for a monopoly?
yes; consumers will buy from competitors offering lower priced substitutes
The demand curve as perceived by a monopolistic competitor is .
downward-sloping
arises when firms act together to reduce output and keep prices high.
A cartel
___ occurs when circumstances have allowed several large firms to have all or most of the sales in an industry.
An oligopoly
The branch of mathematics that analyzes situations in which players must make decisions and then receive payoffs most often used by economists is
game theory.
If a monopoly or a monopolistic competitor raises their prices, then
decline in quantity demanded will be larger for the monopolistic competitor.
Which of the following best identifies what the concept of differentiated products is closely related to?
the degree of product variety that is available.
If monopolistic competitors must expect a process of entry and exit like perfectly competitive firms,
they will be unable to earn higher-than-normal profits in the long run.
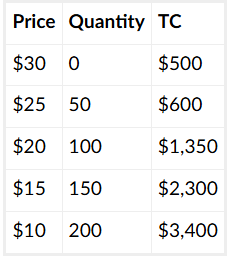
If they maximize their profits, what will their profits equal?
$650
If a perfectly competitive market involves many firms selling identical products, then, in the face of such competition,
each of these firms must act as a price-taker.