major patterns of evolution Evolution test 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
2 reasons why phenotypes are similar in different species:
homology and Homoplasy
Homology
phenotypes are similar because they are inherited from a common ancestor
Homoplasy
phenotypes are similar but are independently evolved
vestigial structure
a reduced, non-functional, or significantly less-functional body part or feature of an organism that is a leftover from its ancestors.
what are vestigial structures strong evidence for?
descent from a common ancestor
ex of homology
limb bones in all modern tetrapods
Evolution acts on
available variation
Ancestral traits can be modified…., which makes them ….
different functions
homologous- they are evolved and share genetic and developmental origin
convergence
A type of homoplasy.
Independent evolution of similar traits because of common selection pressure
Bones in mammal legs and mammal flippers
• Shape of mammal limbs and insect limbs
are homologous (shared with common mammal ancestor)
convergent (not shared with common ancestor)
parallel evolution
– Homoplasy that results from similar (parallel) origins
– Not the same as convergence, or homology
– The same change happens independently, by the same process, in different organisms
Selection acts on
available variation
Can evolution of totally new features happen? What is more common?
yes, but it is rare
it is more common that existing features are modified for new purposes
Different characters evolve at same/different rates?
different
when do characters evolve slowly?
Characters with strong functional relationships (many parts that have to be coordinated to function) evolve slowly
mosaic evolution
leads to?
characters often evolve independently of one another.
– This leads to species composed of some fast evolving characters and some slow-evolving characters
conserved evolution
ex?
slow evolution
frog body form
highly variable evolution
ex.
fast evolution
reproductive biology
slow, smooth transitions in traits happen when evolution is? Where can it be seen?
gradual
seen in fossil records
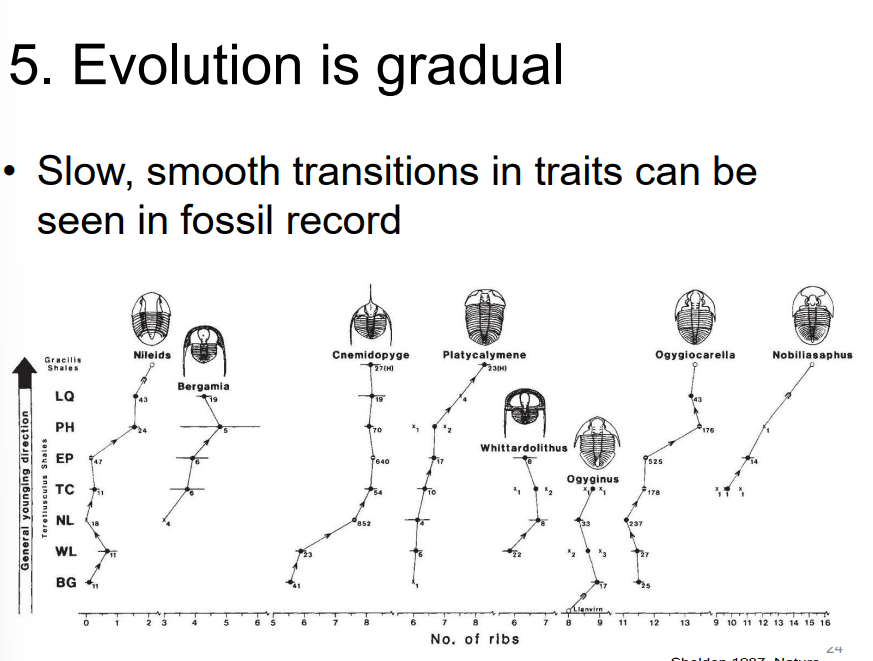
Gradualism
species continuously change (slowly) over their history
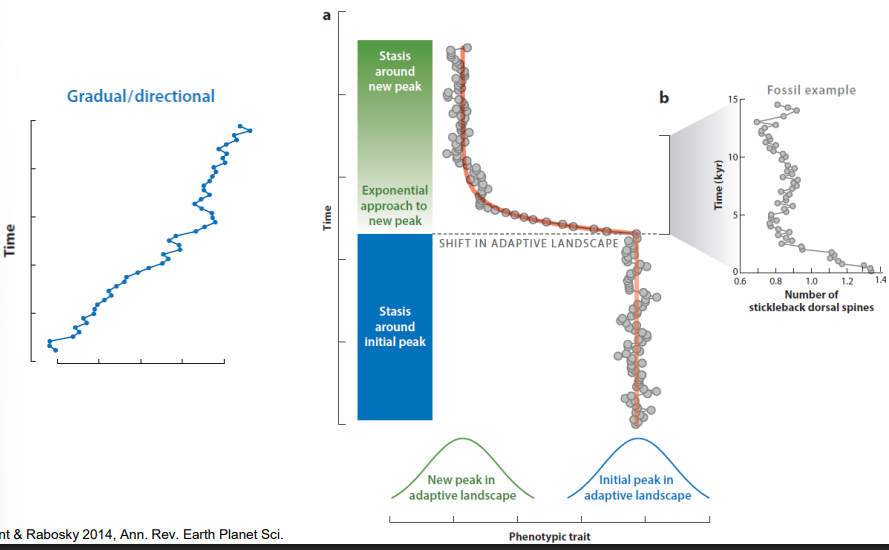
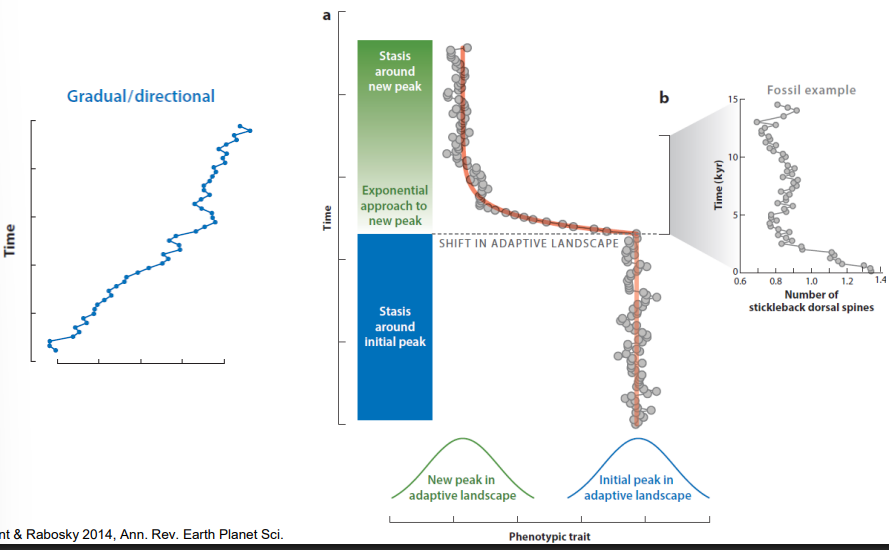
Punctuated Equilibrium
hypothesis: species are static for most of their history, then undergo rapid change during speciation
– There is still a debate over which is most important
stratigraphy
tells us the relative order of geological changes
Radiometric
dating tells us the absolute age of igneous rock layers
Different isotopes cover different time spans
C isotope covers
Rubidium:
14.5 life= 5730 yrs
87.5 life-48.8 billion
The geological time scale name based on
distinctive fossil taxa
The fossil record is highly incomplete. Why?
– Mostly hard parts fossilize (*Exceptions: amber fossils and imprints)
* – Only some environments will allow fossilization BEFORE decomposition
– Rock needs to persist over time (older fossils harder to find)
– Rock must be accessible for discoveries
bc of that major discoveries are still common
How can we predict where to find certain fossils?
its not random
. Rocks of the right age -Use phylogeny and common ancestry to guess (~375 mya in this case)
2. Rocks of the right type
-Sedimentary rocks preserve well; igneous & metamorphic don’t
Needs to be from right ancient environment (stream in this case)
3. Rocks exposed on the surface
Tiktaalik fossil?
a transitional fossil with traits from both fish and early land-dwelling tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates), providing crucial evidence for the evolutionary transition from aquatic to terrestrial life
key features like a neck, lungs, strong ribs for body support, and fins with bones like wrist and elbow, which foreshadowed the limbs and walking ability of land animals
what did the tikaalik do for paleontology
Confirmed predictions of paleontology
– Found at the right time (375 Myr)
– Found in the right ancestral environment (stream)
Showed key transition that only fossils can tell us
• The fact that we can predict where transitional fossils found is strong evidence for evolution
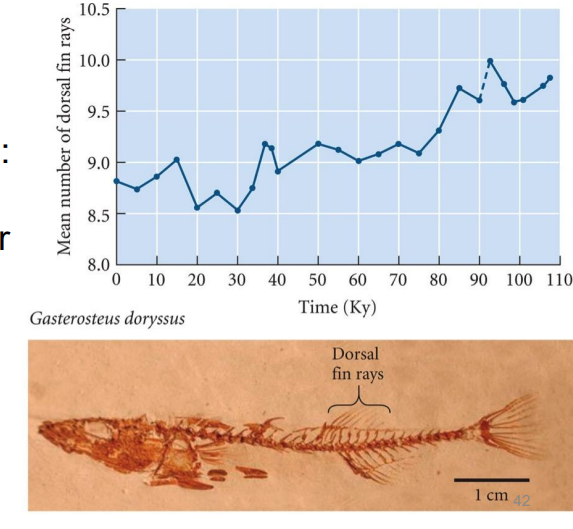
Phenotypic change in the fossil record which shows
Evidence for evolutionary change over time
can we see variation in rates of evolutionary change over time? of so, how
yes,
evolution rates high at short intervals
evolution rates low at long intervals
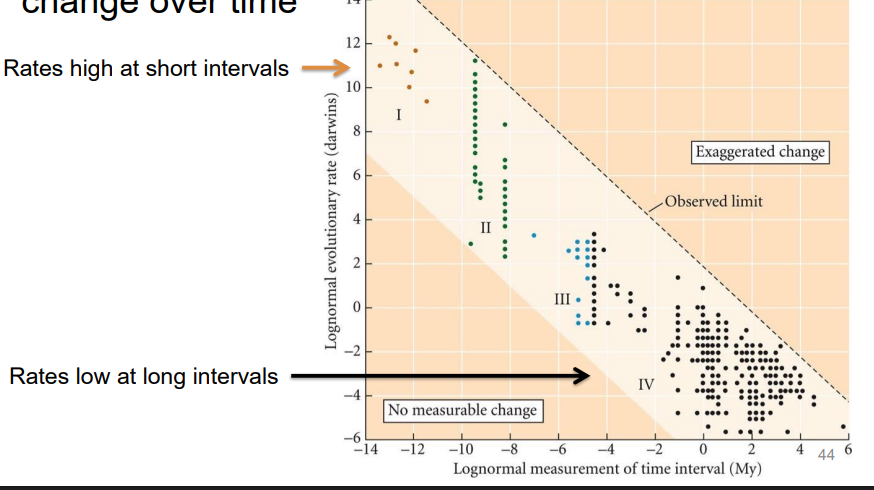
variation rates in evolutionary can
change over time
paradox of stasis
evolutionary change doesnt accumulate until
after 1 Myr
is evolution progressive by definition?
Evolution is not by definition progressive
there is not an innate
tendency for organisms to
evolve towards a goalThis misconception
persists, usually with the
idea that humans are the
goa
contingency vs predictability