Active Transport
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
active transport
requires energy to transport across cell membrane
involves moving molecules against a concentration gradient
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
a nucleotide
ATP conversion
converts to ADP and releases energy and an inorganic phosphate (Pi) molecule
the energy is available for cell processes e.g. muscle contraction
ADP
adenosine diphosphate
what does ATP release when converted?
energy
what is the energy released from ATP used for?
cell processes e.g. muscle contraction
sodium-potassium pump process
Na-K pump binds 3 sodium ions and a molecule of ATP
the splitting of ATP provides energy to change the shape of the channel. The Na+ are driven through the channel
Na+ are released on the outside of the membrane and the new shape of the channel allows 2 K+ to bind
Release of the phosphate allows the channel to revert to its original form, releasing the K+’s on the inside of the membrane
movement of substance in a Na-K pump
move from a lower to higher concentration
energy is gained through respiration in the form of ATP
types of active transport
endocytosis, exocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis
endocytosis
‘into the cell’
important because most molecules needed for cell to survive cannot normally pass through the plasma membrane
phagocytosis and pinocytosis are types of endocytosis
types of endocytosis
phagocytosis and pinocytosis
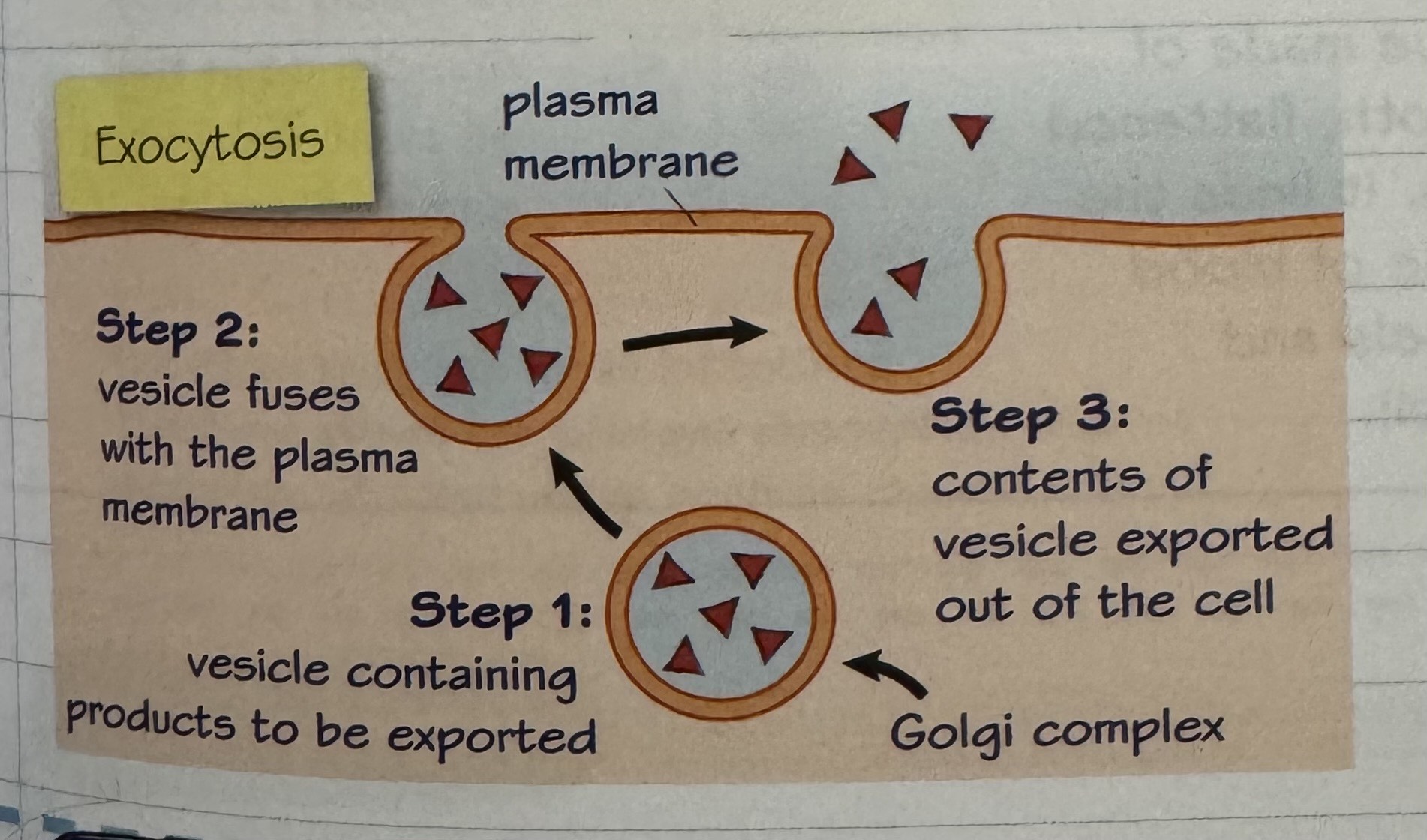
exocytosis
‘out of the cell’
material is exported out of the cell via secretory vesicles
important in removing waste materials from the cell and in secreting cellular products e.g. enzymes or hormones
exocytosis process diagram
phagocytosis
cell’s plasma membrane surrounds a molecule, e.g. a food particle, in the extracellular environment and buds off to form a vacuole that contains the molecule. The molecule is then digested by enzymes
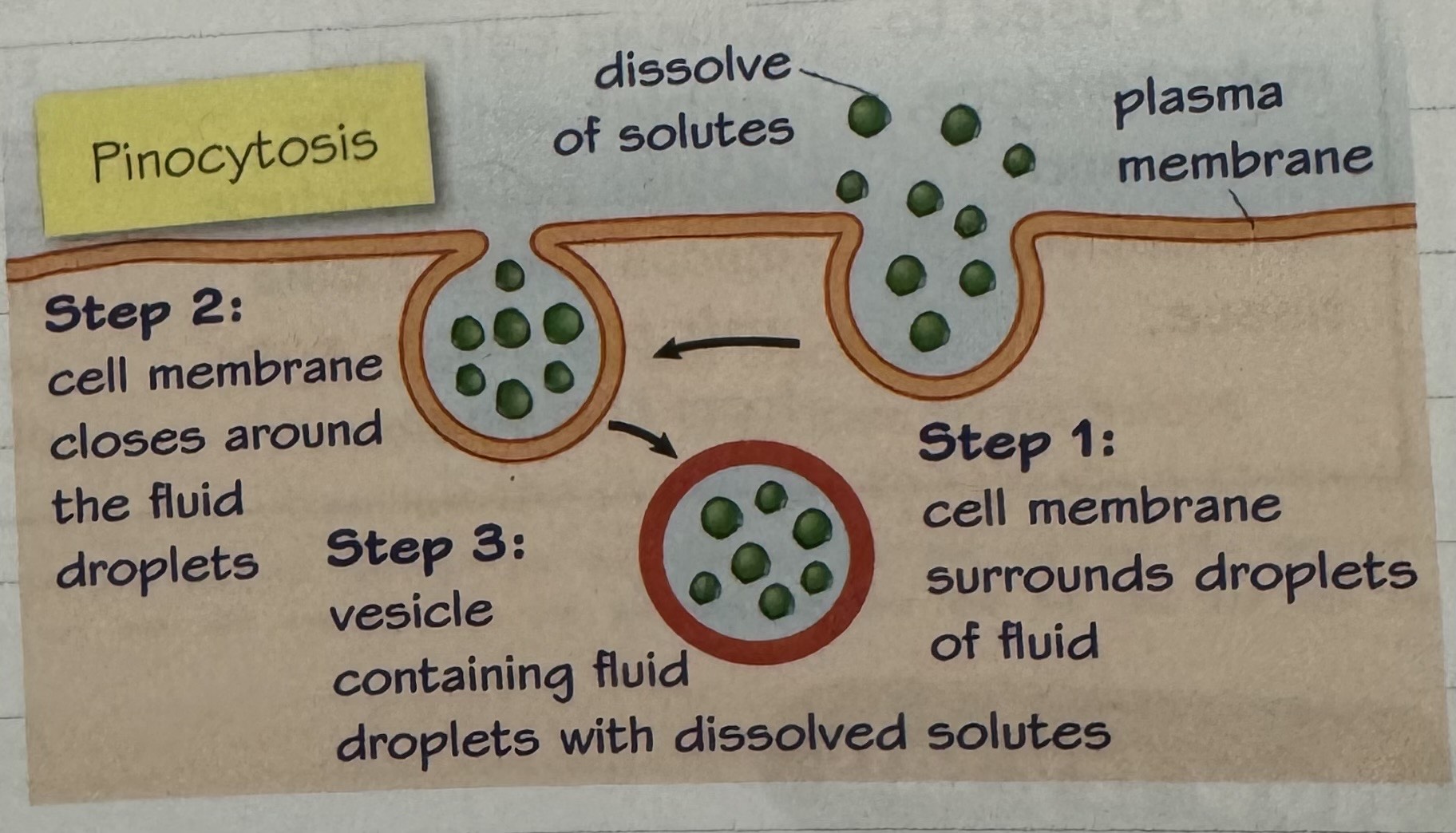
pinocytosis
cell’s plasma membrane surrounds droplets of fluid containing dissolved solutes, in the extracellular environment and buds off to form a vacuole that contains the molecule. The molecule is then digested by enzymes
pinocytosis process diagram