Year 10 Psychology Exam
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Human Brain, Born or Made, Eye Witness Testimony, Culture, Neuroplasticity, Sigmund Freud, The Social Dilemma, Sports Psychology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
VIPCARDD
voluntary participation, informed consent, protection from harm, confidentiality, anonymity, right to withdraw, deception, debriefing
Nature
Genetics (provides the characteristics)
Nurture
Environment (influences existing characteristics)
Socialisation
the process in which people learn behaviours, attitudes, customs and beliefs. It occurs throughout our whole lives, with the biggest impacts occurring during childhood
Agents of Socialisation
the things (people, groups, etc.) that can influence socialisation
Primary Socialisation
when we are young children living only in the family home
Secondary Socialisation
occurs after primary socialisation, independent from immediate family
Localisation of Function
the theory that specific areas of the brain have particular functions; each area is in charge of different mental processes and behaviours
Forebrain
one of the largest parts of the brain, it includes the cerebrum (all four lobes) and limbic system
Midbrain
consists of the uppermost part of the brainstem, acting as a relay station for information surrounding sensory and motor functions
Hindbrain
lower rear section of the brain in charge of involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, balance and coordination of movement
Cerebral cortex
outermost layer of the forebrain in charge of higher cognitive functions
Corpus callosum
nerve fibers connecting the left and right hemispheres
Brain Stem
connected to the spinal cord
Pons
unconscious processing such as breathing, sleep cycles, and information to do with senses in the head and face
Medulla
involved in the coordination of nerve signals, taking charge of processes such as heart beat, blood pressure and breathing
Cerebrum
largest part of the brain divided into two hemispheres
Frontal Lobe
in charge of self-regulation and awareness
Broca's
crucial in terms of speech production including tasks surrounding grammar, articulation, and transformation of thoughts to spoken language (left frontal lobe)
Motor Cortex
dictates movements across muscle groups in order to enact tasks with purpose and fluidity
Somatosensory Cortex
receives and processes senses such as pain, touch, and temperature
Parietal Lobe
sensory regulation, attention span, and spatial regulation
Occipital Lobe
processes visual imagery
Temporal Lobe
manages emotions, processes information from various senses, stores and recalls memories, and is involved in interpreting language
Wernicke's Area
responsible for comprehending written and spoken language (left temporal lobe)
Cerebellum
regulates muscle movements and coordination of muscle groups whilst also having a degree of involvement in emotions
Limbic system
core survival functions
Thalamus
relays information for senses except smell throughout the brain. It is involved in sleep, memory, learning, and consciousness
Hypothalamus
connects to the nervous and endocrine systems, keeping the body in homeostasis. Aid in regulation of blood pressure, body temperature, mood, hunger, and thirst
Hippocampus
learning, awareness, long- and short-term memory
Amygdala
major role in processing emotions and linking them to other areas of the brain, particularly associating emotions with memories
Pituitary Gland
releases hormones and is connected to the functions of other glands relating the the endocrine system. It helps with tasks surrounding metabolism, stress responses, and growth
Epigenetics
Environment and other factors influence how genes are expressed
Personality
What differentiates people: varied ways of thinking, feeling and behaviour. The activation of temperament through ones environment.
Personality disorder
Long term patterns of behaviour and experiences that differ significantly from the norm
Personality disorders impact a minimum of two
Way of thinking about oneself and others, way of responding emotionally, way of relating to others, way of controlling ones behaviour
Antisocial Personality Disorder (APD)
People who repeatedly disregard or violate the rights of others
APD diagnosis must have
Minimum 3 of ACCRRID
ACCRRID
Aggressiveness, Conform (failure to), Consistent irresponsibility, Reckless disregard for safety, Remorse (lack of), Impulsivity, Deceitfulness
Neuroimaging techniques
PET scan, MRI, FMRI, EEG
PET scan
Positron Emission Tomography: produces a functional and structural view of the brain through the injection of a radioactive tracer
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: produces structural imaging and can identify tumors
FMRI
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: produces functional imaging
EEG
Electroencephalogram: cap of electrodes detecting electrical activity of neurons firing
Leading Questions
Questions that lead a person to think and respond in a specific manner, altering memory
Ronald Cotton
Previous offender falsely incarcerated when a victim wrongly chose him out of two lineups. This altered her recollection of the event to the point where she could not remember the actual offender, Bobby Poole.
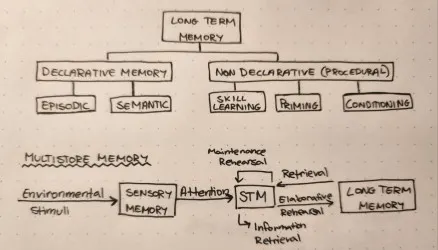
Memory
The process of encoding, storing and retrieving information
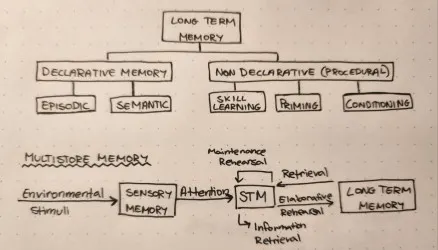
Long Term Memory
The proccess of encoding, storing and retrieving information
Short Term Memory
Temporary information holding area, it can store 7±2
Multistore Model of Memory
Long term memory structure
Loftus and Palmer aim
To deduce whether leading questions play a role in altering or impacting memory in any manner
Loftus and Palmer method 1
5 groups each with 9 participants
Loftus and Palmer results 1
Smashed - 41mph; collided - 39mph; bumped - 38mph; hit - 34; contacted - 32
Loftus and Palmer method 2
A week after, they were asked if they had seen glass. 3 groups of 50. 1/3 asked hit, 1/3 asked smashed, 1/3 control
Loftus and Palmer results 2
A larger number of those who were asked smashed answered yes than those asked hit or those in the control
Loftus and Palmer conclusion
Questioning techniques can distort memory; our recollection of events is incredibly malleable and unreliable
Declarative memory
A part of long term memory to do with facts
Episodic memory
Part of declarative memory to do with experiences in ones life
Semantic memory
Part of declarative memory to do with facts and general knowledge
Procedural memory
A part of long term memory to do with muscle memory
Priming
Part of procedural memory; a set of things leading a person to think in a certain way
Skill learning
Part of procedural memory; muscle memory
Conditioning
Part of procedural memory; similar to Pavlov’s dogs
Culture
The values, beliefs, attitudes, language, customs and other behiviours that are passed down from one generation to another
Surface Culture
The visible and tangible aspects of a culture such as art, cuisine, behaviours and language
Deep Culture
The unconscious, deeply embedded values, beliefs and assumptions of a culture
Low/pop culture
Cultural behaviours and ideas that are popular in society
High culture
Cultural patterns that distinguish a society’s elite
Sub-culture
What sets apart a segment of society’s population
Counterculture
Way of life/set of attitudes opposing or varying from the prevailing social norm
Stereotypes
Assumptions/generalisations made about groups of people
Enculturation
The gradual aqcuisition of the characteristics and norms of a culture by a person or other culture
Multiculturalism
The presence of several distinct cultural groups within a society
Individualist culture
A culture in which the freedom of the individual is favoured over collective needs or state control
Aspects of an individualist culture
Feminist care ethics and egoism prevail as the ethical theories. People learn to think in terms of I and me. Social goal is to achieve self-actualisation
Collectivist culture
A culture where the principal of prioritising the needs of the group over the individuals in it is the prevailing idea
Aspects of a collectivist culture
Utilitarianism approach where people learn to think in terms of we and us. The societal goal is to achieve harmony and consensus
Assumption of Bandura’s social learning theory
Assumes that people gain knowledge through observational learn in which they watch models and imitate their behaviour
Factors of Bandura’s social learning theory
Attention, retention, motor reproduction, motivational response
Attention Process
Where one develops the cognitive processes to pay attention to the model. The more developed the process, the better the attention. It must be accurate enough observation to allow for imitation
Retention Proces
Remembering aspects of the behaviours modelled is done through imaginal internal representations and verbal systems
Motor reproduction
Turning imaginal and verbal representations to overt behaviour through rehearsal
Incentive and motivation
Incentive turns observation into action, it is influenced by anticipation reinforcements whether they be positive, negative or none
Influencing factors of learning
Identification with the model, characteristics of the observer, vicarious reinforcement, consistency and attraction
Bobo doll experiment aim
Can aggressive behaviour in children be learned through observation?
Bobo doll experiment participants
72 children (1/2 boys, ½ girls) and 2 adult models (1 man, 1 woman)
Bobo doll experiment variables
Aggression and the sex of the model
Bobo doll experiment conditions
Non aggressive, aggressive, and control (6 girls, 6 boys to each model)
Bobo doll experiment results
The children imitate the behaviour of the models. Those exposed to aggression showed more non-imitative aggression. Furthermore, the boys were seen to be more physically aggressive than verbal.
Bobo doll experiment conclusion
Learning can and does occur through model observation
Genie Wiley aim
Investigate her acquisition of language after total isolation
Genie Wiley method
Scientists raised her and studied how she learned through interactions
Genie Wiley results
She had a significantly reduced brain size. Due to this, despite her learning many words, she struggled with sentences. She showed developments but then deteriorated because her Broca’s and other areas were so reduced with lack of use
Genie Wiley conclusion
With lack of use, areas of the brain can worsen to the point where certain things cannot be learned
Neuroplasticity
The ability to learn new things due to the malleable nature of the mind
Nerual pruning
As we age, we undergo this process where certain connections are elimnated whilst others are allowed to strengthen