Parasitology Week 6
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
in the clinical laboratory, parasite usually refers to _____ organisms
eukaryotic
eukaryotic organisms that are common clinical laboratory parasites
protozoa: one celled organism
helminths: worm like animals
morbidity
rate of disease in a population
where are parasitic disease less prevalent?
developed countries with good sanitation
where are parasitic disease more common?
tropics and subtropics
why are parasites less common in industrialized countries?
sanitation and good hygiene practices
temperate climate that don’t let dormant stages of parasites survive
less suitable vectors, less intermediate and reservoir hosts
why have parasitic infections increased worldwide?
jet travel
wars
refugees
mosquitoes resistant to pesticides
drug resistance
increased immunocompromised patients
a successful parasite…
obtains part or all its nourishment from host
derives all the benefit of the association with host
ectoparasite
lives outside the host’s body
endoparasite
lives inside the hosts’s body
facultative parasite
can live with and without the host
obligate parasite
cannot survive without the host
incidental parasite
can live in a host that is not ordinarily used
pathogenic parasite
causes harm to the host
definitive host
host in which the parasite reaches sexual maturity and undergoes reproduction
intermediate host
host in which some development of the parasite occurs but does not reach sexual maturity
accidental host
host in which the parasite can live, but is not required for its life cycle
reservoir
host in which a parasite survives mostly without causing disease
vector
carries parasite that can multiply within their body and be delivered to new hosts, usually by biting
what can be mistaken for a parasite?
pseudoparasites or artifacts
spurious parasite
does not infect humans and can pass through intestinal tract without causing infection
what type of sample contains large amounts of debris that appear as artifacts and pseudoparasites?
fecal material
white blood cells as pseudoparasites
can be confused with amoebas
human cells have a higher nuclear material to cytoplasm ratio
types of artifacts/pseudoparasites
yeast
plant cells and root hairs
oil droplets
pollen grains
diatoms
vegetable and muscle fibers
charcot-leyden crystals
charcot-leyden crystals
formed from the degradation of eosinophils
associated with inflammation
three types of helminths (general categories)
nematodes
cestodes
trematodes
round worms
nematodes
tape worms
cestodes
flukes
trematodes
nematodes shape, sexes, head end, alimentary canal, and body cavity
elongated cylindrical, unsegmented
separate
no suckers, no hooks, well developed buccal cavity
present, complete anus
present
cestodes shape, sexes, head end, alimentary canal, and body cavity
tape-like, segmented
not separate
suckers often with hooks
absent
absent
trematodes shape, sexes, head end, alimentary canal, and body cavity
leaf-like, unsegmented
not separate, except Schisto
suckers, no hooks
incomplete, no anus
absent
species of intestinal nematodes
Enterobius vermicularis
Trichuris trichiura
Ascaris lumbricoides
Strongyloides stercoralis
Necator americanus
Ancylostoma duodenale
Ancylostoma braziliense
another name for Enterobius vermicularis
pinworm
disease caused by Enterobius vermicularis
enterobiasis
most common intestinal helminthic infection in the US
enterobiasis
where does enterobiasis commonly occur geographically?
temperate climates
only known host of Enterobius vermicularis
humans
people most commonly isolated with enterobiasis
preschool children and in crowded places
diagnostic stage of Enterobius vermicularis
eggs on the perianal folds
infective stage of Enterobius vermicularis
embryonated eggs ingested by humans
how long does it take Enterobius vermicularis larvae inside the eggs to mature to infective stage?
4 to 6 hours
where do Enterobius vermicularis hatch into larvae?
small intestine
where do adult Enterobius vermicularis occupy?
lumen of cecum (colon)
where and when do female Enterobius vermicularis lay eggs?
crawling on the skin of the perianal area at night
how else can enterobiasis be contracted other than hands scratching the anus?
contaminated surfaces with pinworm eggs like carpets and bedding
general life cycle of Enterobius vermicularis
eggs laid on perianal folds
embryonated eggs ingested by humans
eggs hatch in small intestine
adults establish in colon
females migrate to anus to lay eggs
common symptoms of enterobiasis
usually asymptomatic
perianal pruritus
vulvo vaginits
pelvic or peritoneal granulomas
less common symptoms of enterobiasis
anorexia
irritability
abdominal pain
lab diagnosis for enterobiasis
microscopic ID of eggs
adult worms found in perianal area during anorectal or vaginal examinations
microscopic identification and testing method of Enterobius vermicularis eggs
scotch test/cellulose tape slide test
done in morning before defecation
anal swabs
enterobiasis is not diagnosed by microscopic examination of _______
fecal matter
Enterobius vermicularis egg morphology
colorless and smooth
thick shell flattened on one side
elongate-oval
can contain fully developed larvae
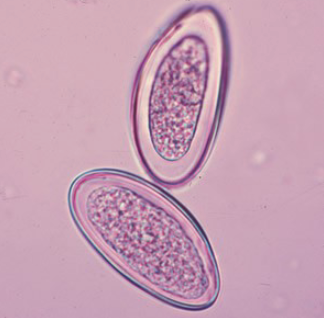
what species produces this egg?
Enterobius vermicularis
another name for Trichuris trichiura
whipworm
infection caused by Trichuris trichiura
trichuriasis
route of trichuriasis
fecal-oral route, no intermediate host
where do Trichuris trichiura ova mature?
external environment
where is trichuriasis mostly seen geographically?
tropical climates and areas with poor sanitation, sometimes southern US
diagnostic stage of Trichuris trichiura
unembryonated eggs passed in feces
infective stage of Trichuris trichiura
embryonated eggs that are ingested
when do Trichuris trichiura eggs become infective after deposited in soil via feces?
10-14 days
where do Trichuris trichiura eggs hatch into larvae?
small intestine
where do adult Trichuris trichiura mature and occupy?
cecum (colon)
general life cycle of Trichuris trichiura
undeveloped eggs in feces
eggs embryonate in soil by 1 month
ingested eggs hatch in small intestine
larvae mature into adults in colon
how do Trichuris trichiura live in the intestines?
they bury their threadlike anterior half into the intestinal mucosa to feed on tissue secretions
symptoms of heavy infections with Trichuris trichiura
abdominal pain
nocturnal loose stools
dysentery
rectal prolapse
stunted growth
who is more at risk for severe cases of trichuriasis?
children
endoscopy and microscopy lab diagnoses of trichuriasis
endoscopy: showing adult whipworms attached to bowel mucosa
microscopy: ova and parasites in stool samples
formalin ethyl acetate sedimentation FAS technique
recommended for light infections of trichuriasis
Trichuris trichiura egg morphology
football shaped
bipolar colorless plugs
thick shell
unembyronated in feces
yellow or brown shell
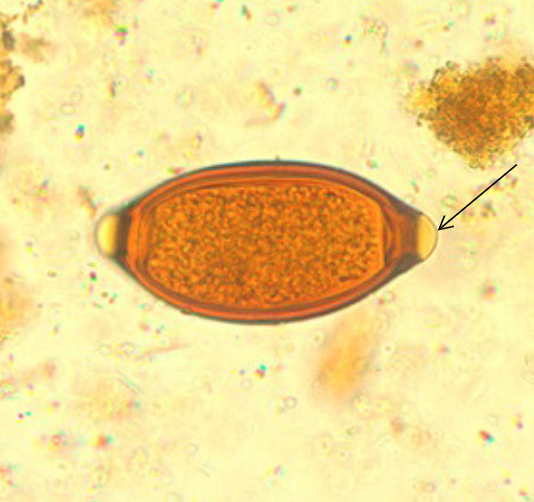
what species produces this egg?
Trichuris trichiura
distinctive morphology of female whipworms
long pointed tail
distinctive morphology of male whipworms
blunted posterior ends
what is the largest intestinal nematode parasite to humans?
Ascaris lumbricoides
disease caused by Ascaris lumbricoides
ascariasis
source of transmission for ascariasis
contaminated soil and vegetation
where is ascariasis most common geographically?
tropics and subtropics, rural areas of southeastern US
diagnostic stages of Ascaris lumbricoides
fertilized and unfertilized eggs
adult worm
infective stage of Ascaris lumbricoides
fertilized eggs that are ingested
how long does the whole life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides take?
2-3 months
where do Ascaris lumbricoides eggs hatch into larvae?
small intestine
where do Ascaris lumbricoides larvae mature into adults?
small intestine
where do adult Ascaris lumbricoides occupy?
lumen of small intestine
general life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides
fertilized eggs are ingested
eggs hatch in small intestine
larvae invade gut into blood vessels
liver
lung capillaries
alveoli
bronchioles
coughed up to pharynx
swallowed back down to small intestine
mature to adults in small intestine
symptoms of ascariasis
diarrhea, vomiting, fever
stunted growth
abdominal pain and intestinal obstruction
symptoms of migrating Ascaris lumbricoides
migrating adult worms cause occlusion of biliary tract or oral expulsion
migrating larvae in lung cause cough, dyspnea, hemoptysis, eosinophilic pneumonitis (Loeffler’s syndrome)
samples taken for ascariasis diagnosis
stool
sputum
gastric aspirate
laboratory diagnosis of ascariasis
microscopic identification of eggs
presence of larvae
presence of adult worms
direct wet mounts with heavy infections
morphology of unfertilized Ascaris lumbricoides eggs
elongated
larger than fertile eggs
thinner shell
with or without mammillated layer
refractile granules
morphology of fertilized Ascaris lumbricoides eggs
round and thick shell
mammillated layer
decorticated eggs lack outer layer
fully developed larva in developed eggs
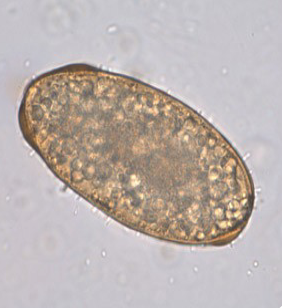
what species produces this egg, and is it fertilized or unfertilized?
Ascaris lumbricoides, unfertilized
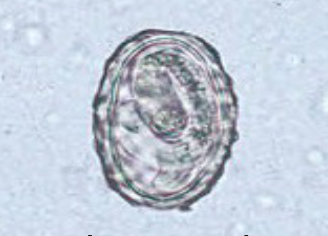
what species produces this egg, and is it fertilized or unfertilized?
Ascaris lumbricoides, fertilized

what is shown here?
Ascaris lumbricoides has three lips with teeth to help attach to intestinal wall
what is Strongyloides stercoralis also called?
threadworm
what disease does Strongyloides stercoralis cause?
strongyloidiasis
where is strongyloidiasis most common geographically?
tropics and subtropics
which intestinal nematode species alternates between free-living and parasitic cycles?
Strongyloides stercoralis
where does reproduction occur with Strongyloides stercoralis?
natural environment and host
diagnostic stage of Strongyloides stercoralis
rhabditiform larvae