ecological succession
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
ecological succession
process of gradual and predictable changes in the composition and structure of an ecological community over time
pioneer species (definition)
first to colonize an area with no soil
primary succession (definition)
occurs and area where NO previous community or SOIL exists
primary succession (examples)
newly found volcanic islands, glacier retreats, bare rock surfaces
secondary succession (definition)
occurs in an area that HAS been previously inhabited by a community or had SOIL, but has experienced a disturbance.
secondary succession (examples)
fire, logging, natural disaster that clears existing vegetation
Gross Primary Production, GPP (definition)
the total energy fixed by a plant during photosynthesis
Gross Primary Production, GPP (equation)
= energy production per unit area / units of time
Net Primary Production, NPP (definition)
represents the amount of stored chemical energy that will be available to consumers in an ecosystem
Net Primary Production, NPP (equation)
= GPP - R x (loss of energy through respiration)
Biomass
the collective amount of this of a living matter in a given place or time.
High biomass equals
high NPP
Low biomass equals
low NPP
Ecosystem productivity
the rate of production of biomass for an ecosystem
Ecological efficiency
the amount of energy transfer between trophic levels to the next (10% rule)
Incomplete consumption (definition)
predators don’t consume the entire prey, which contain energy that is not transferred to the next level
Incomplete consumption (example)
not eating the bones or shell of an animal
Energy lost through excretion
animals dispose of waste materials
Indigestible matter (definition)
some parts of the organism are difficult to digest and provide little energy to the consumer
Indigestible matter (examples)
cellulose in plants or chitin in arthropods
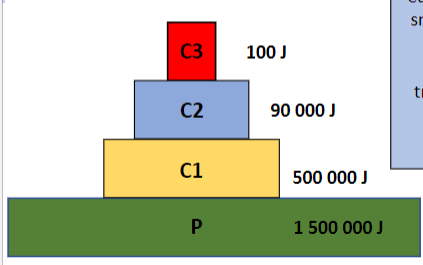
pyramid of energy (definition)
shows the amount of energy available at each trophic level and the decrease in energy as it moves up the food chain
pyramid of energy (photo)
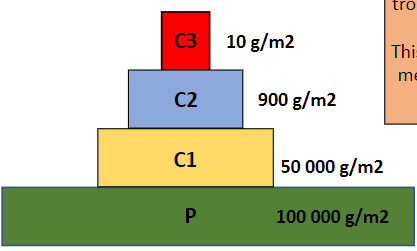
pyramid of biomass (definition)
shows the amount of biomass available at each trophic level and the decrease in biomass as it moves up the food chain
pyramid of biomass (photo)
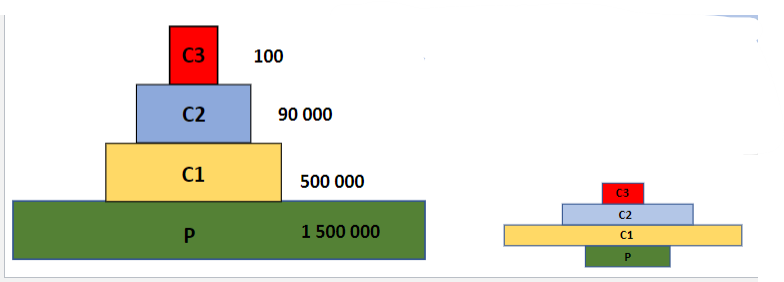
pyramid of numbers (definition)
represents the number of individual organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem
pyramid of numbers (photo)
how to make pyramid of energy
upright, with each successive trophic level representing a smaller amount of energy compared to the one below it
how to make pyramid of biomass
typically upright, with each higher trophic level having less biomass than the one below it
how to make pyramid of numbers
in some cases, this pyramid may be upright, with each higher trophic level having fewer individuals than the trophic level below it. In others, the pyramid can be inverted.
why are some pyramid of numbers inverted?
this can occur when there is a large number of small primary producers supporting a smaller number of larger consumers
primary succession process
pioneer species → more complex plants, soil forms → climax community, nutrient rich soil
primary succession pioneer species
lichens and mosses
primary succession complex plants
grass and shrubs
primary succession climax community
larger, diverse plants (trees)
which succession reaches climax community faster?
secondary succession
secondary succession process
soil still present, regeneration of species from seeds → early successional species, fast-growing and opportunistic species → climax community, nutrient rich soil