Edema - this ones really long :/ (that's what she said)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
50-60%, 2/3, 1/3, 80, 20, veins
Lotta numbers:
The body is _____% water
what fraction of that water is intracellular?
What fraction is extracellular?
What percent of extracellular is in the interstitium?
What percent is in plasma?
The majority of blood in circulation is located in the _______
sympathetic innervation, local intrinsic stimuli
arterial lumen diameter is controlled by _________________ and ____________________
Starling equation: net filtration = K[(Pcap-Pint)-o(πcap-πint)]
Water distribution between plasma and interstitium determined by what?
K, P, O, π, cap, int,
symbol for capillary endothelial permiability constant
symbol for hydrostatic pressure
reflection coefficient symbol
symbol for colloid osmotic pressure
symbol for capillaries
symbol for interstitium
retention
normal conditions favor fluid [release/retention]
hydrostatic pressure
pressure exerted by fluid in a confined space
Pcap
_____: Pressure of the blood against the vessel wall
Pint
_____: Determined by the interstitial fluid volume and the compliance of the tissue interstitium
colloid osmotic pressure
form of osmotic pressure exerted by proteins
oncotic pressure
whats another name for colloid oncotic pressure
push fluid out
Hydrostatic pressure tends to [push fluid out of/pull fluid into] vessels
higher on arteriole, lower on venous
Is hydrostatic pressure higher on the arteriole or venous side in the capillaries?
relatively constant
Is hydrostatic pressure higher on the arteriole or venous side in the interstitium?
relatively constant
Is colloid osmotic pressure higher on the arteriole or venous side in the capillaries?
relatively constant
Is colloid osmotic pressure higher on the arteriole or venous side in the interstitium?
pulls fluid in
Osmotic pressure [pushes fluid out of/pulls fluid into] vessels
ALBUMIN, and other plasma proteins
What is responsible for the majority of colloid osmotic pressure?
sodium and chloride
what substance also contributes to colloid osmotic pressure, but less than albumin (and other proteins) because it is freely movable over membranes
"ugh, why can't you just put all the info here" - f*ck off man there's 69 slides in this ppt.
Read over slide 9 for more pressure timeline stuff in the vessels...
lymphatic vessels
fluid that is pushed out of arteries/veins but is not returned to venules enters what instead?
hypervolemia
___________________: movement of additional water into the interstitium and ultimately into the cell → cell swelling
hypovolemia
_____________: movement of water into plasma → cell shrinkage and decreased interstitial volume
edema
issues with the distribution between Intravascular and Interstitial compartments is most commonly manifested as ________________
edema
____________: The pathological accumulation of fluid in interstitial spaces or body cavities
Hydrostatic pressure, Colloidal osmotic pressure, Vascular integrity, Cell membrane integrity
important contributing factors to edema (4)
Clear to slightly yellow watery fluid that thickens and expands affected interstitium
what does edema look like morphologically (sorry)
maybe, either, nope
Do swollen organs or tissues ooze fluid?
Are they firm or are they gelatinous?
Is there notable pain/redness/heat?
hydrothorax
____________: fluid in the thoracic cavity
hydropericardium
____________: fluid in the pericardial sac
ascites
___________: edema/fluid in the abdominal cavity
pulmonary edema
_______________: fluid/edema in the alveolar lumens
submandibular edema/bottle jaw
What?
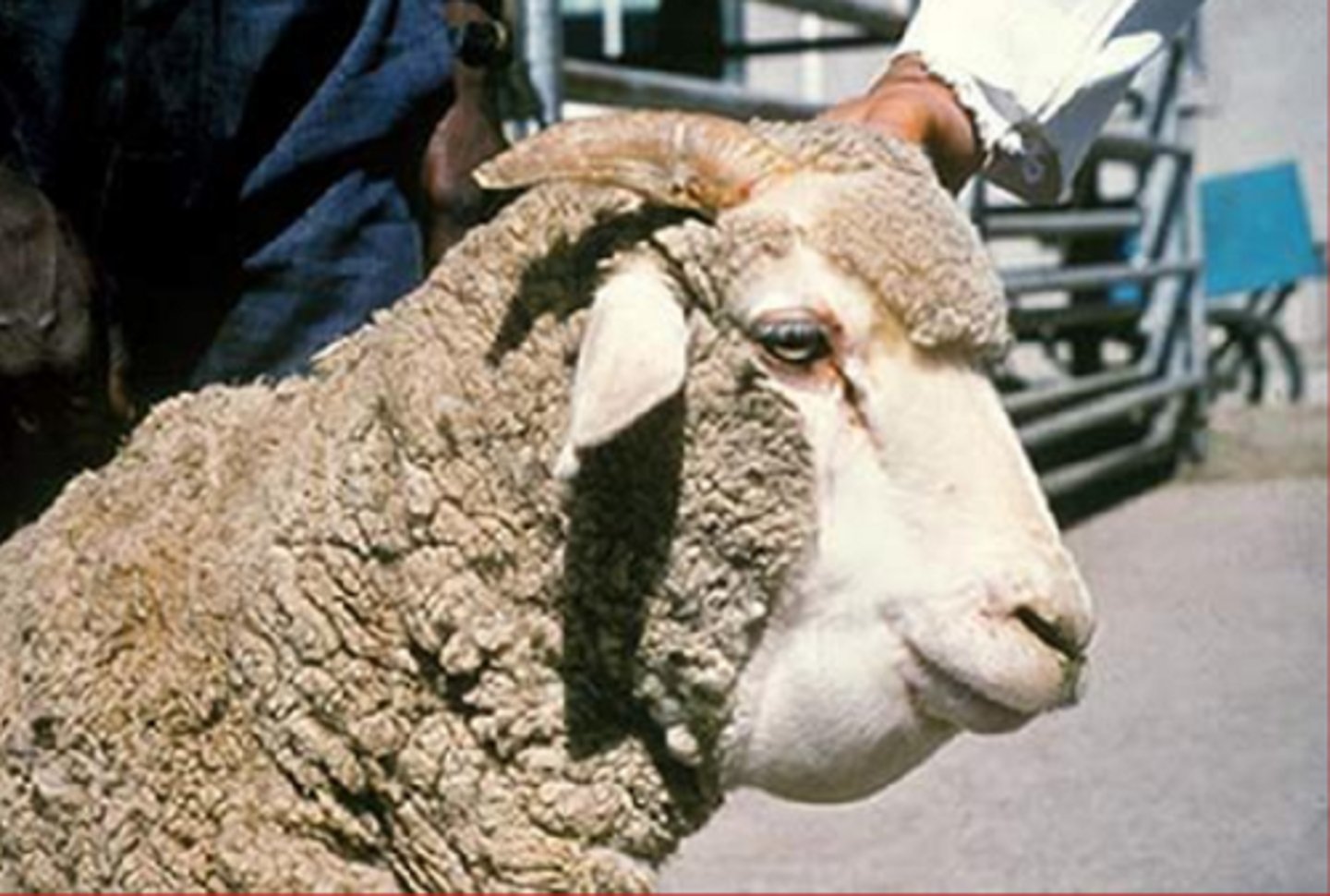

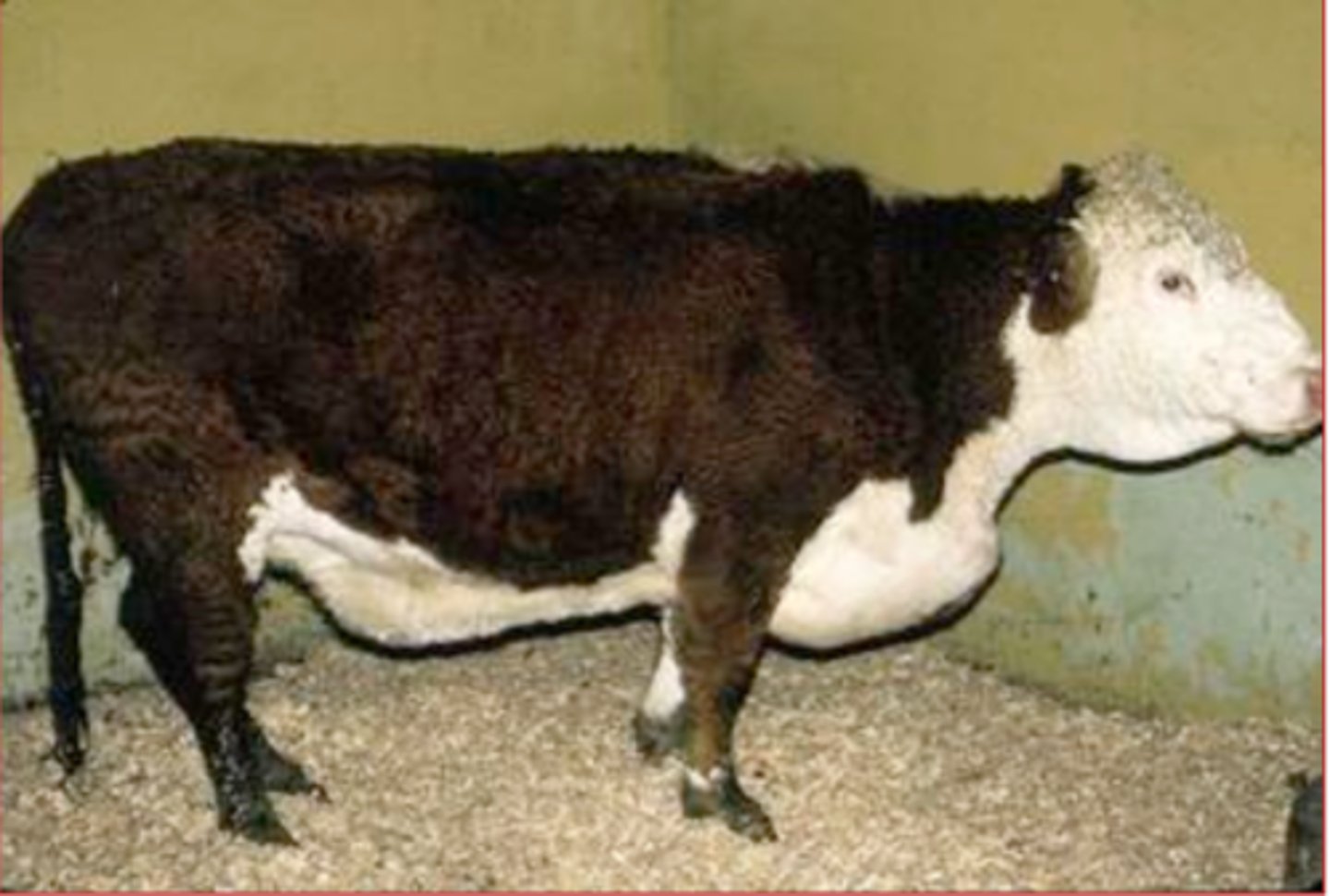
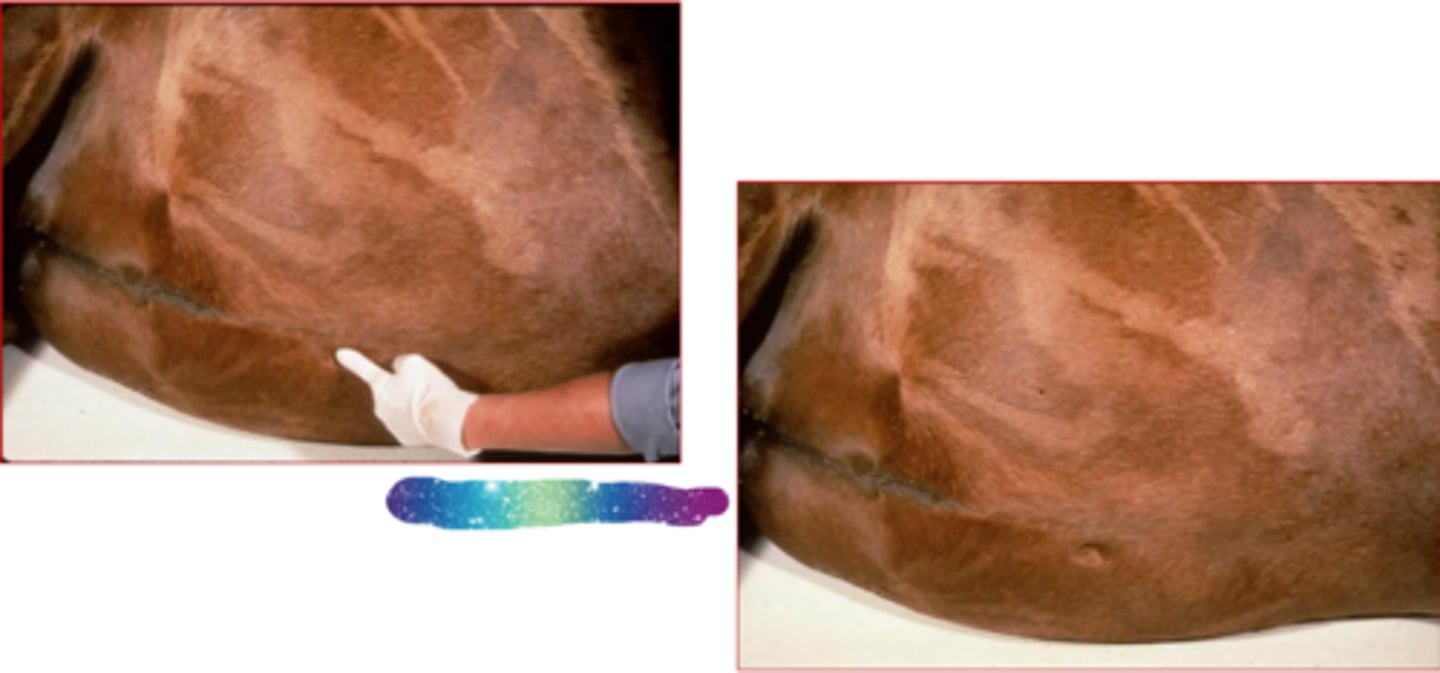
ventral edema/brisket edema
What?

pitting edema
__________: when an indentation remains after the swollen skin is pressed
pitting edema
Whats going on here?
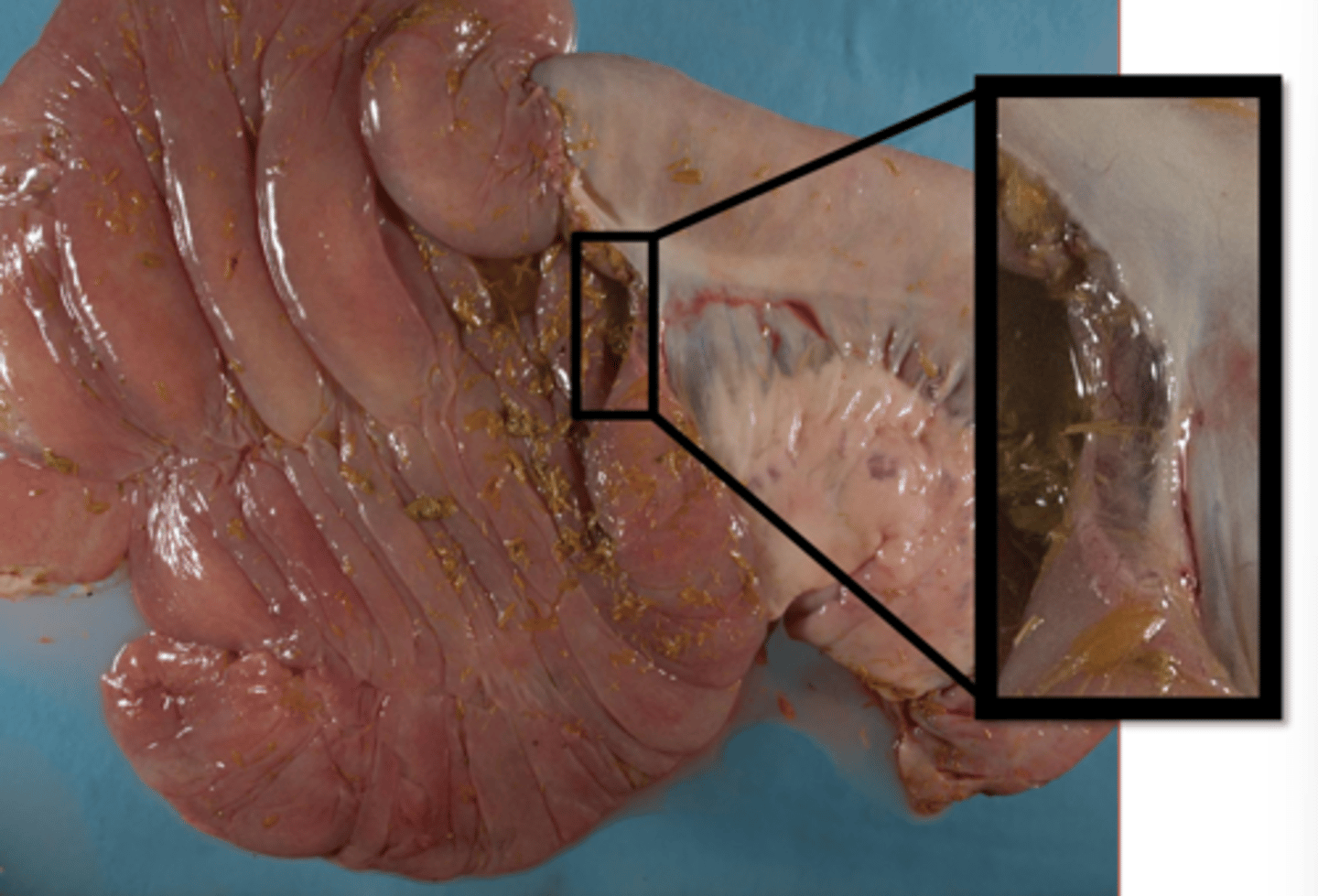
intestinal submucosal edema
What
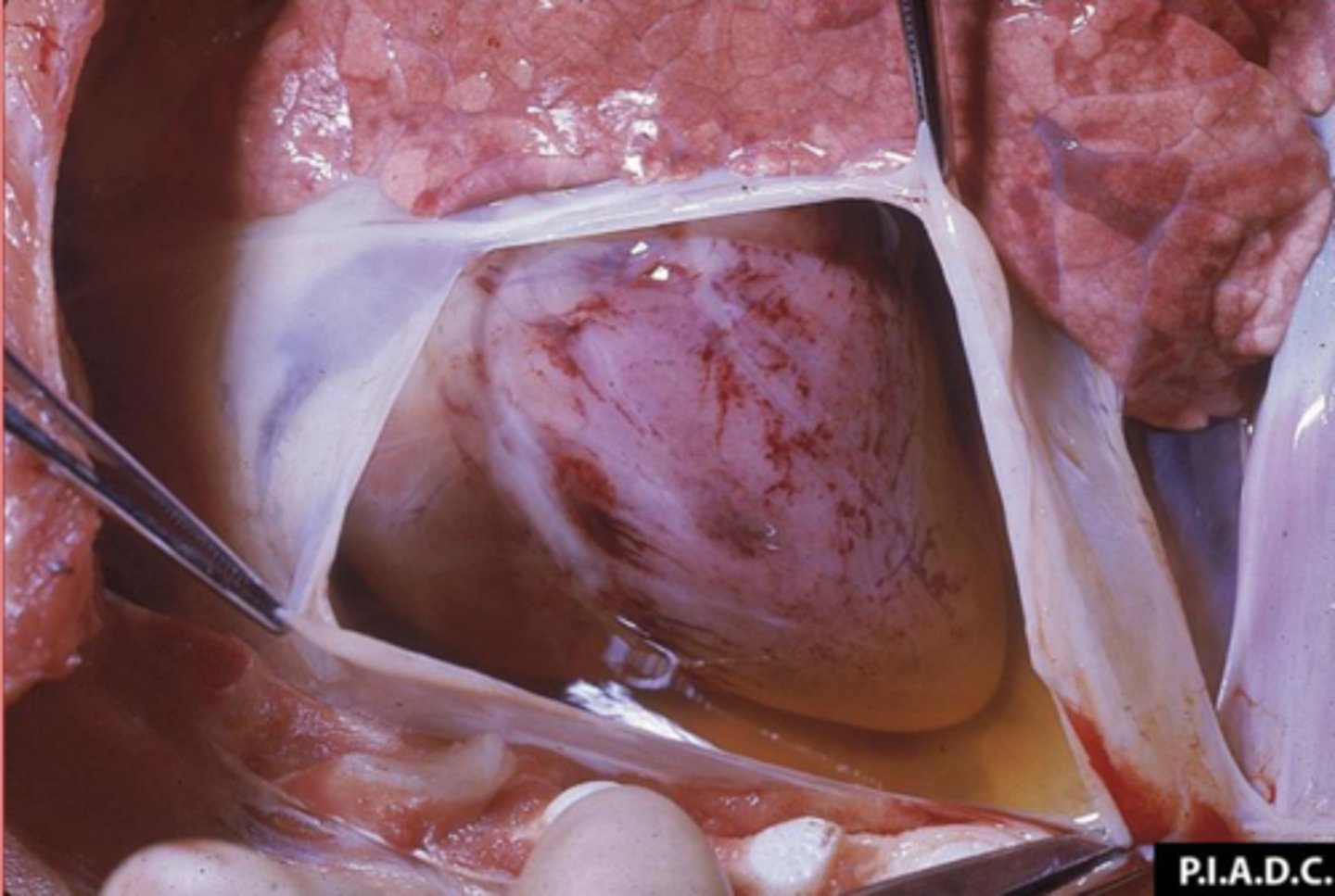
hydropericardium
What is this called?
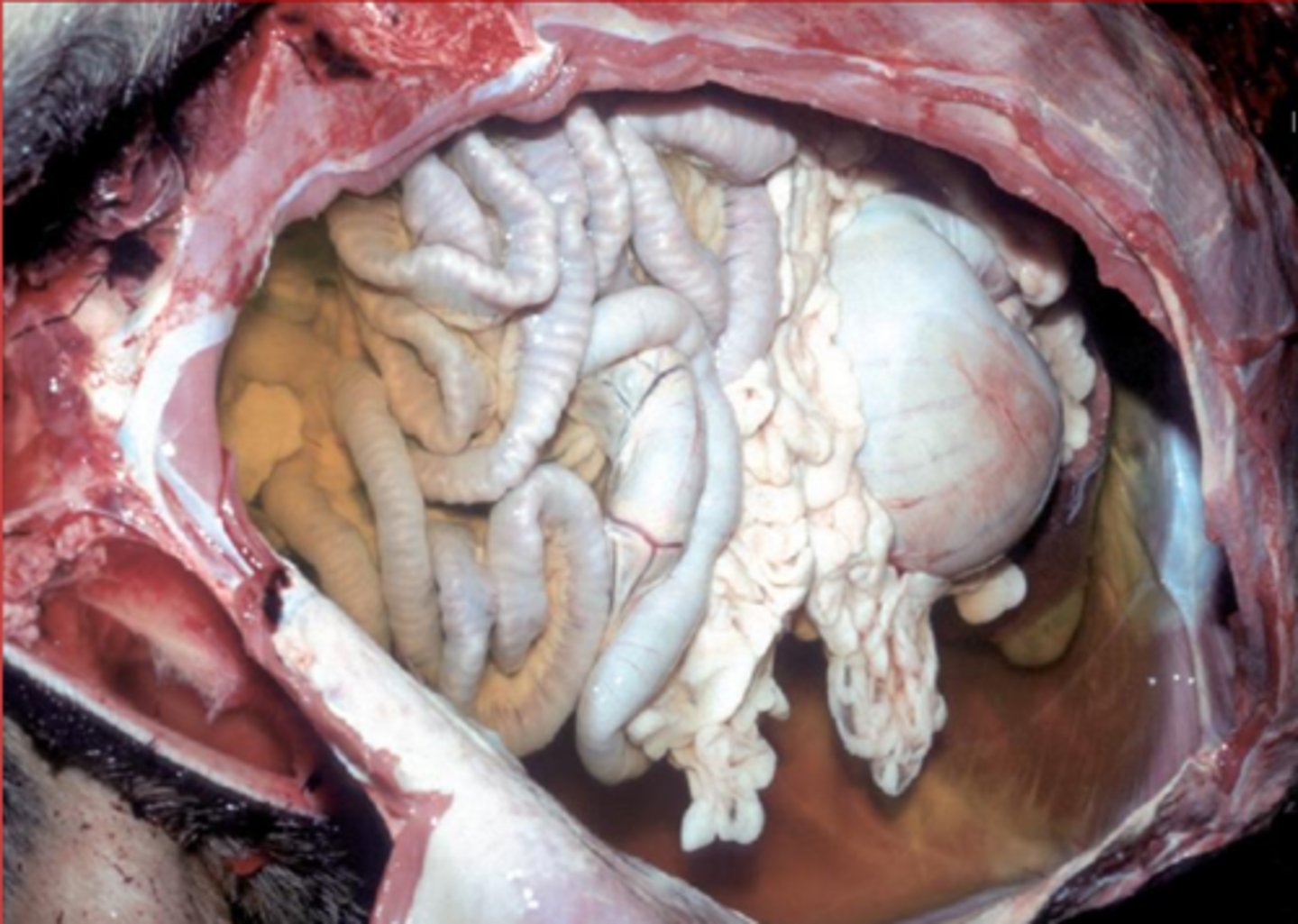
ascites
what is this called?
pulmonary edema
What is this specifically?
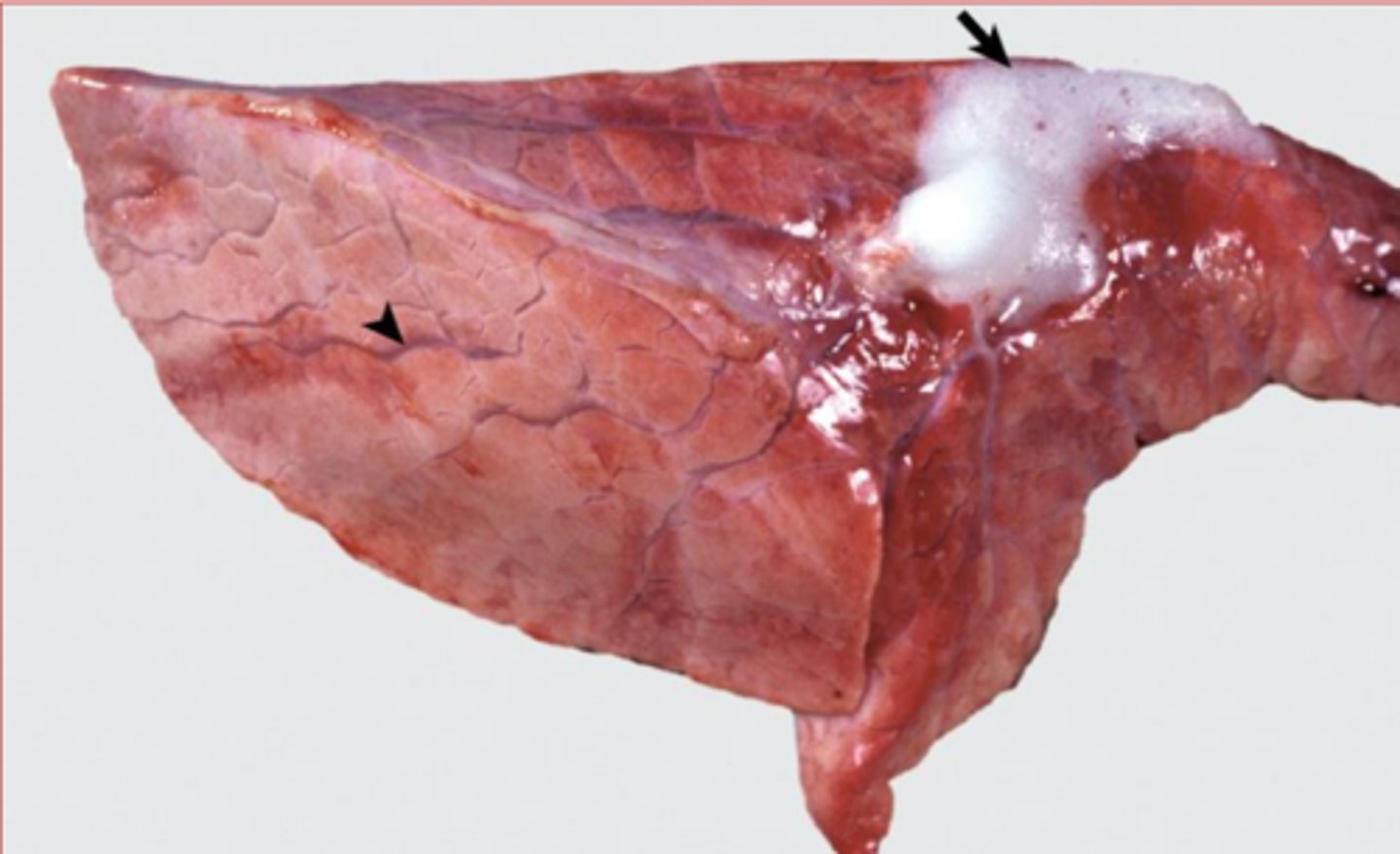
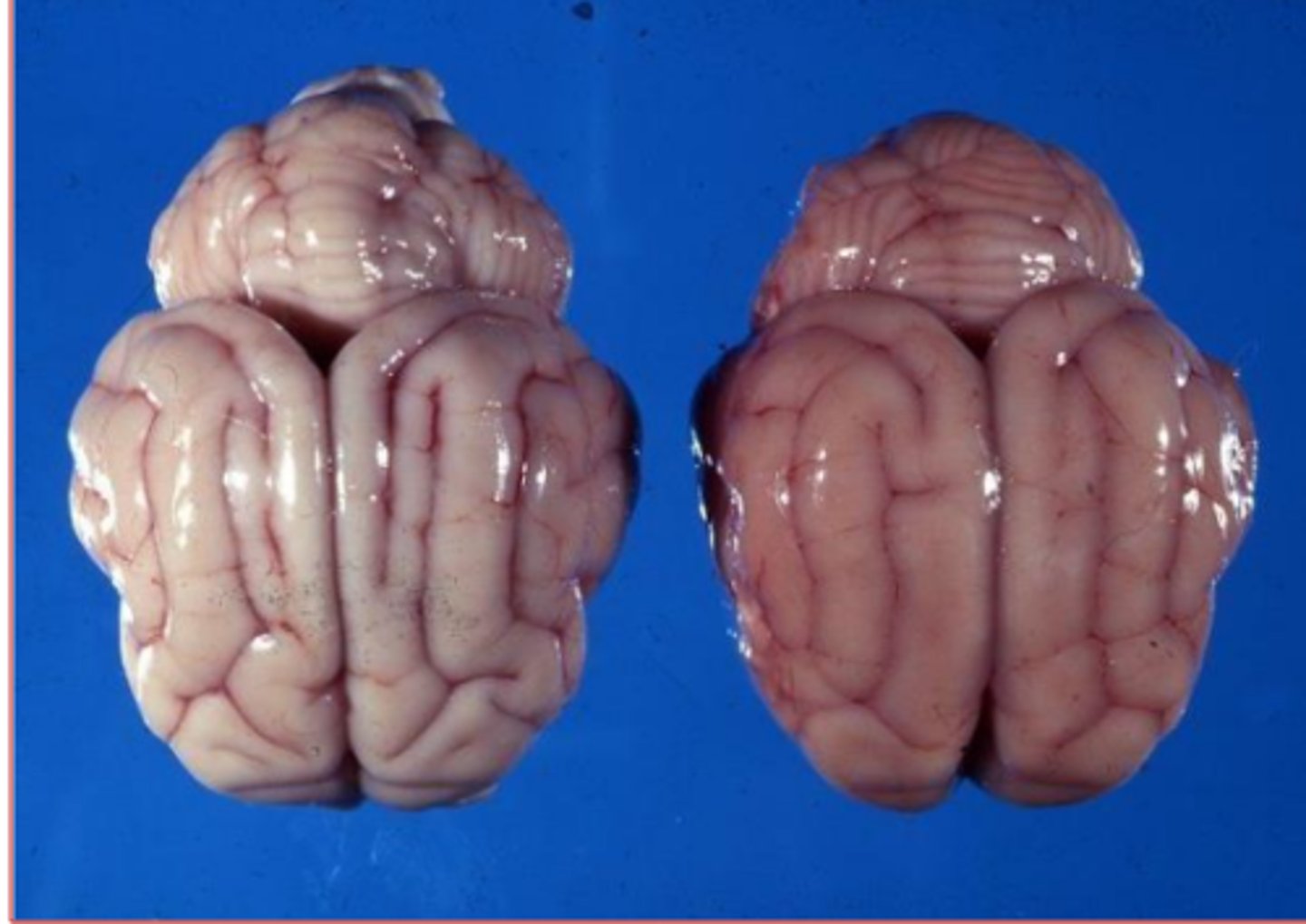
cerebral edema, flat/wide gyri, narrow sulci
What does the brain on the right have here? It's subtle but how can you tell?
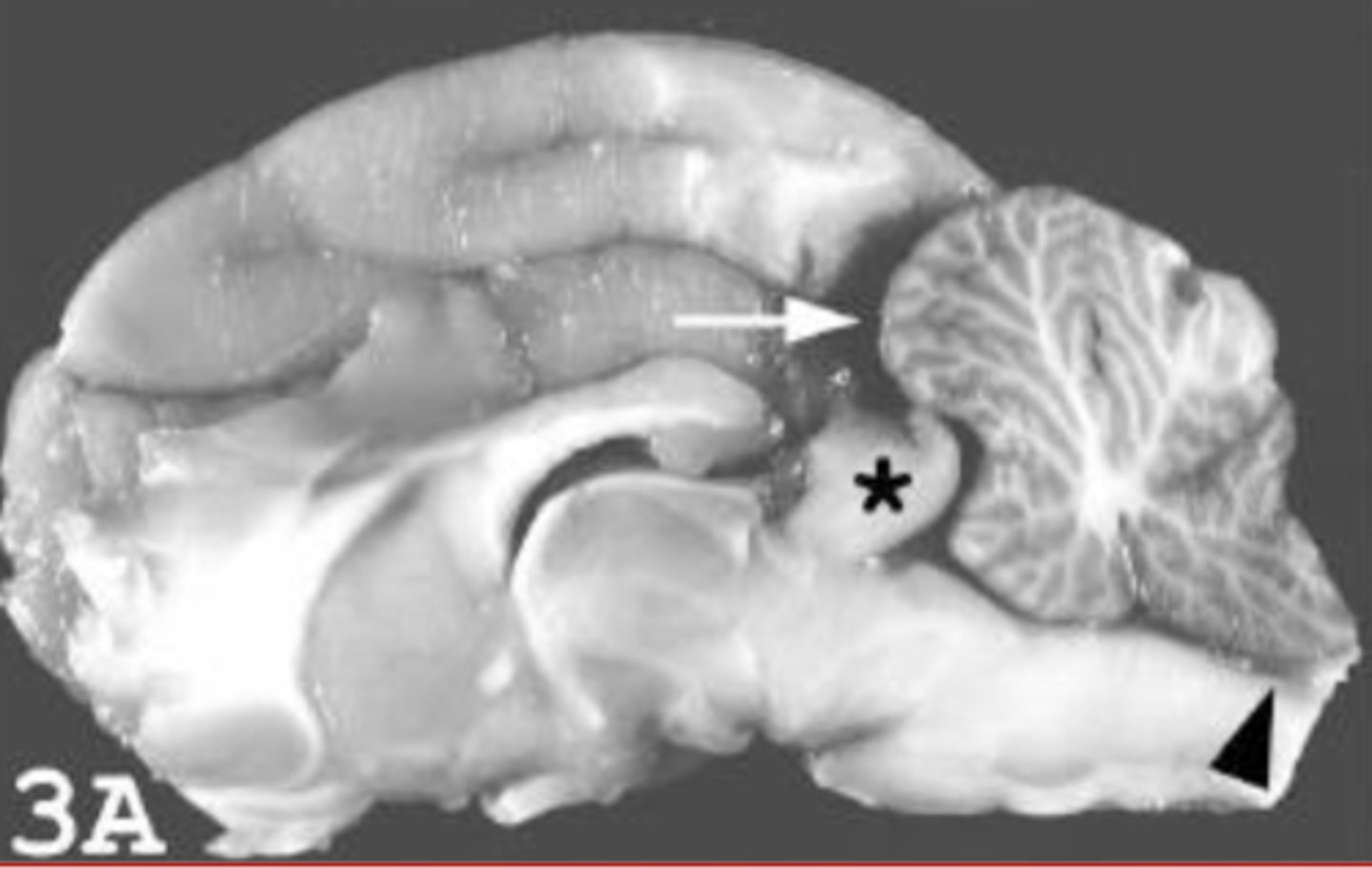
cerebral edema, foramental herniation
Whats up with this brain? (general issue and thing at the *)
Slightly granular, clear to eosinophilic, amorphous, interstitial
infiltrate/material
describe edema histological appearance
increased protesin, dilution of the proteins with fluid, fibrin, hemorrhage, empty space
on histology, edema may look more eosinophilic due to _________... but could also have reduced eosinophilia due to ________________
and you may also see ______ or __________ or just ___________
dilation
in edema, you may see [dilation/compression] of lymphatic vessels
perivascular edema (white space by veins)
what is this?
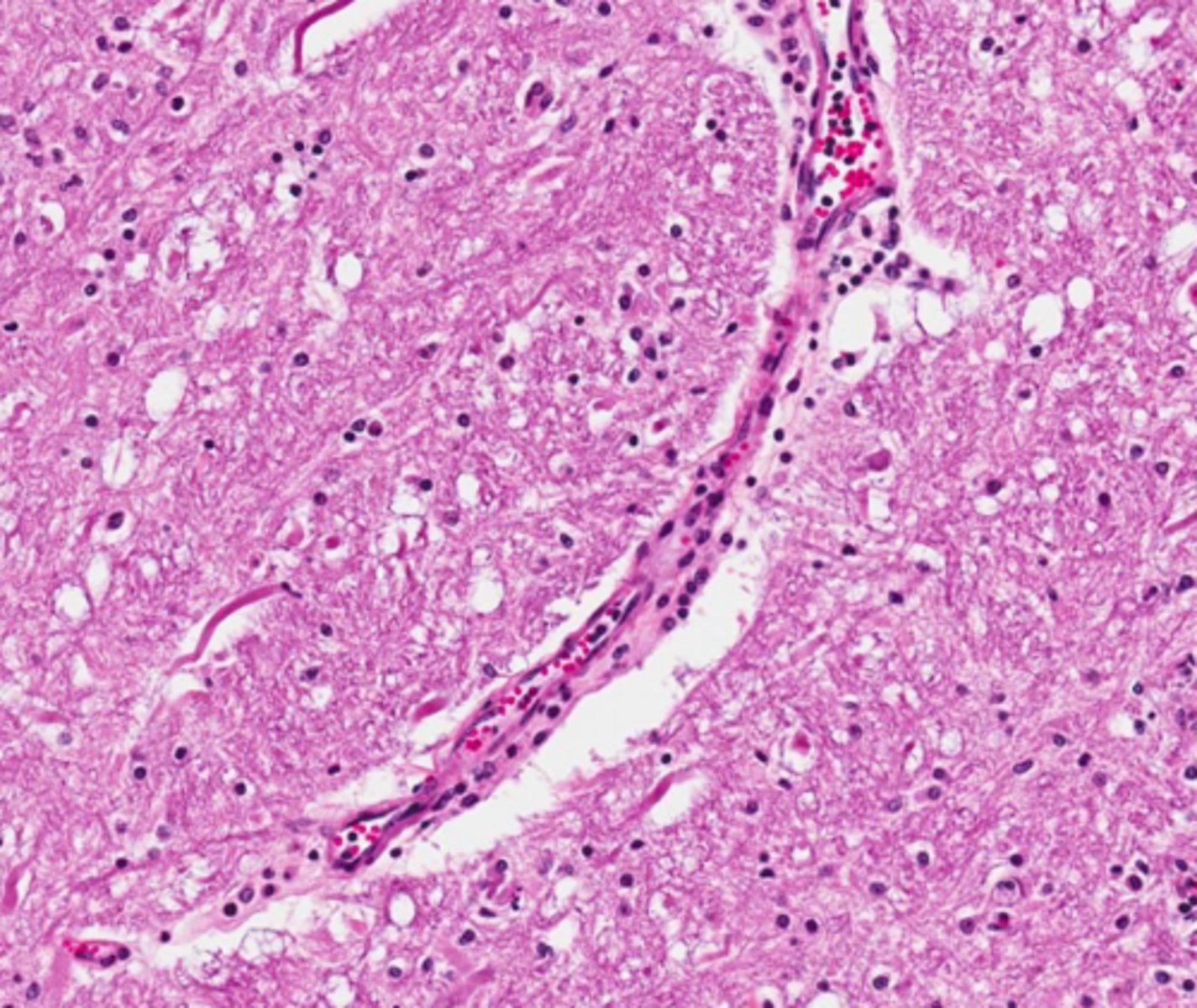
nope, so. much. white space.
Is this normal?
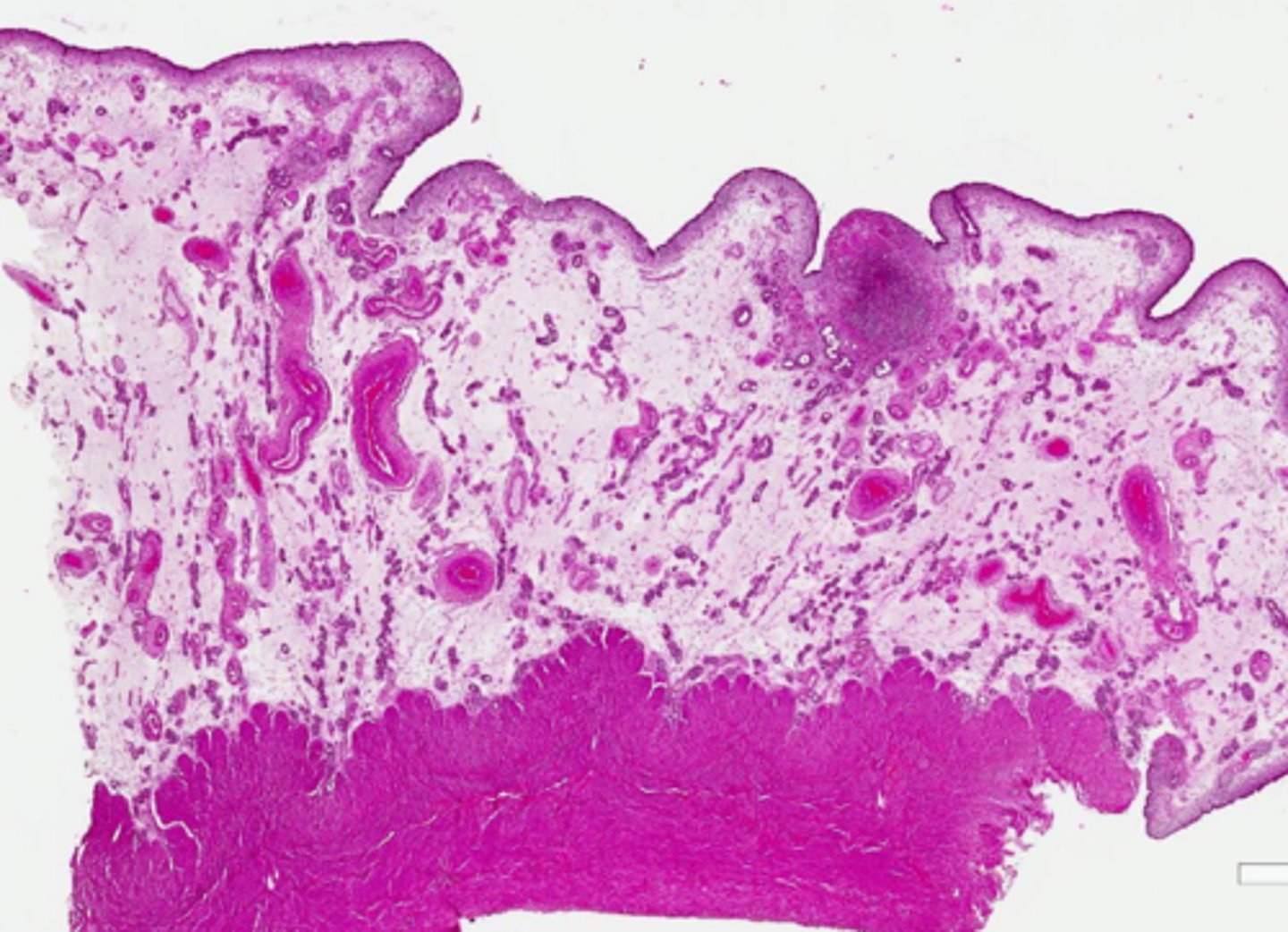
effusion
____________: Accumulation of excessive fluid in tissues of a body cavity secondary to escape of fluid from the blood vessels or lymphatics into the tissues or a body cavity
cell and protein pure
what does it mean if effusion is classified as "pure transudate"
intermediate levels of cell and protein
what does it mean if effusion is classified as "modified/protein rich transudate"
cell and protein rich
what does it mean if effusion is classified as exudate?
imbalanced hydrostatic/oncotic forces; decreased oncotic pressure
Pure transudate fluid has passed through a vascular wall as a result of _______________ and ____________________;
usually what is the more specific reason?
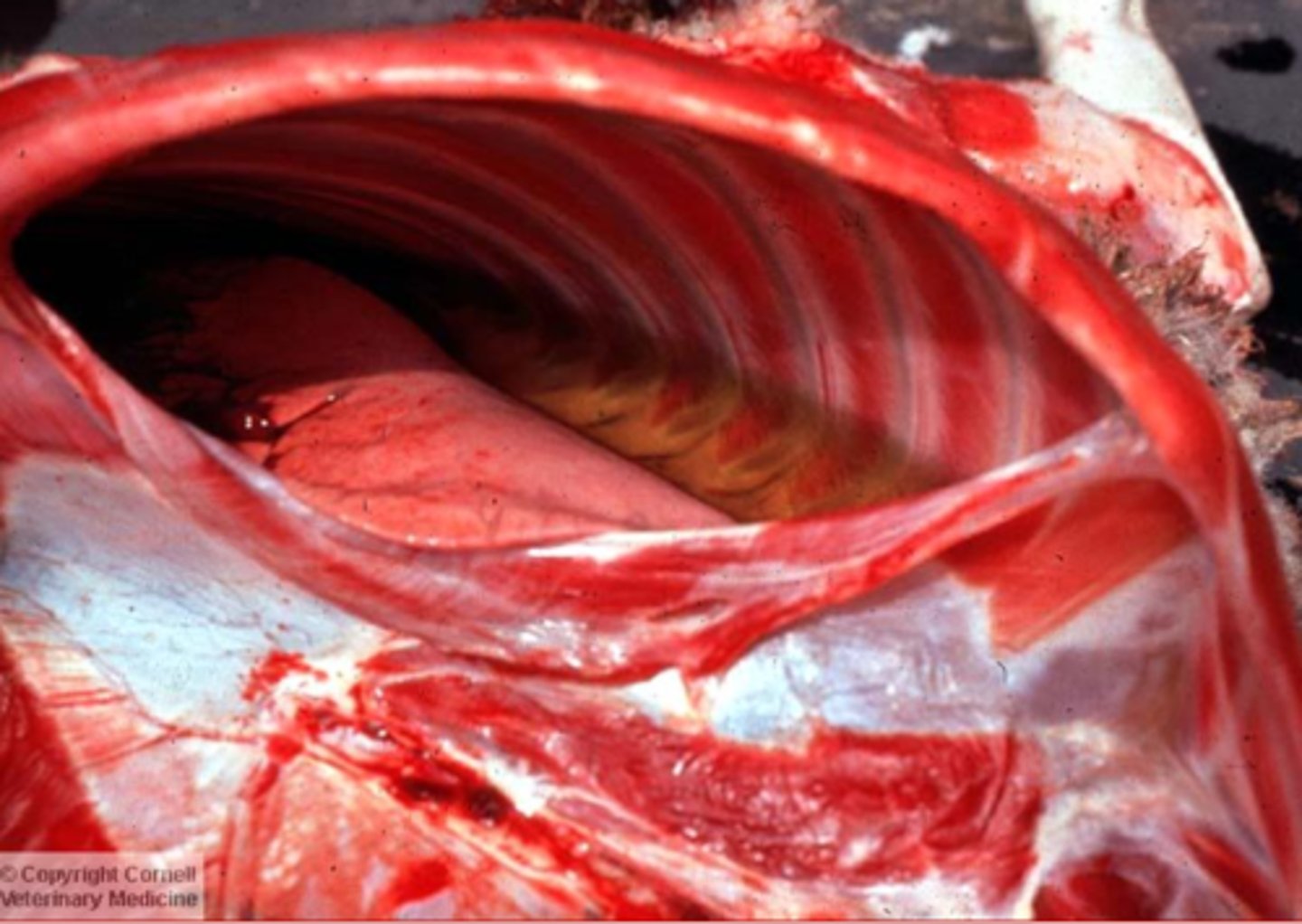
few, low, low (mostly albumin)
in pure transudate... describe:
cells?
specific gravity?
protein?
pure transudate
what type of effusion typically goes with hypoalbuminemia?
hepatic, renal, gastrointestinal disease
what may be some causes of hypoalbuminemia?
pure transudate
what type of pleural effusion is this?
increased hydrostatic pressure, or increased vascular permeability
What general issue typically causes modified/protein rich transudate?
fluid leakage from lymphatic or blood vessel
what specific mechanism causes modified/protein rich transudate?
cardiac disease, liver disease, neoplasia, vascular damage, organ strangulation
What specific diseases can cause modified/protein rich transudate
modified/protein rich transudate
this is the body cavity of an animal with FIP; what type of effusion is this?
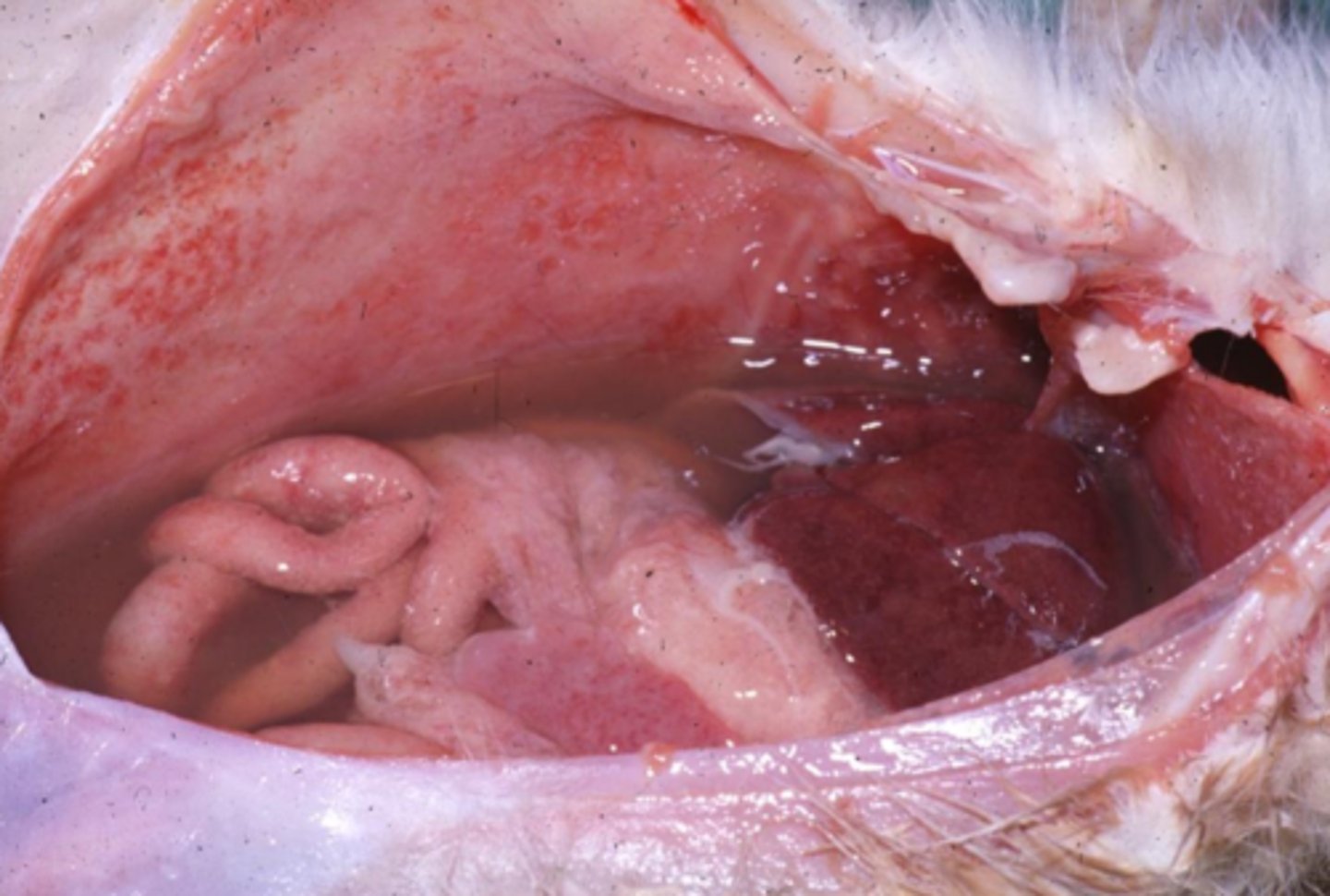
increased vascular permeability caused by inflammation
exudates develop due to ______________________________
high,
cellular,
high
Describe exudates:
protein concentration?
What type of debris?
Specific gravity?
bacteria and other microorganisms
If there is a septic exudate, what is found in it?
bile, urine, pancreatic enzymes
if there is a non septic but infectious/inflammatory exudate... what is found in it?
exudate
what kind of effusion in this perotineal effusion?
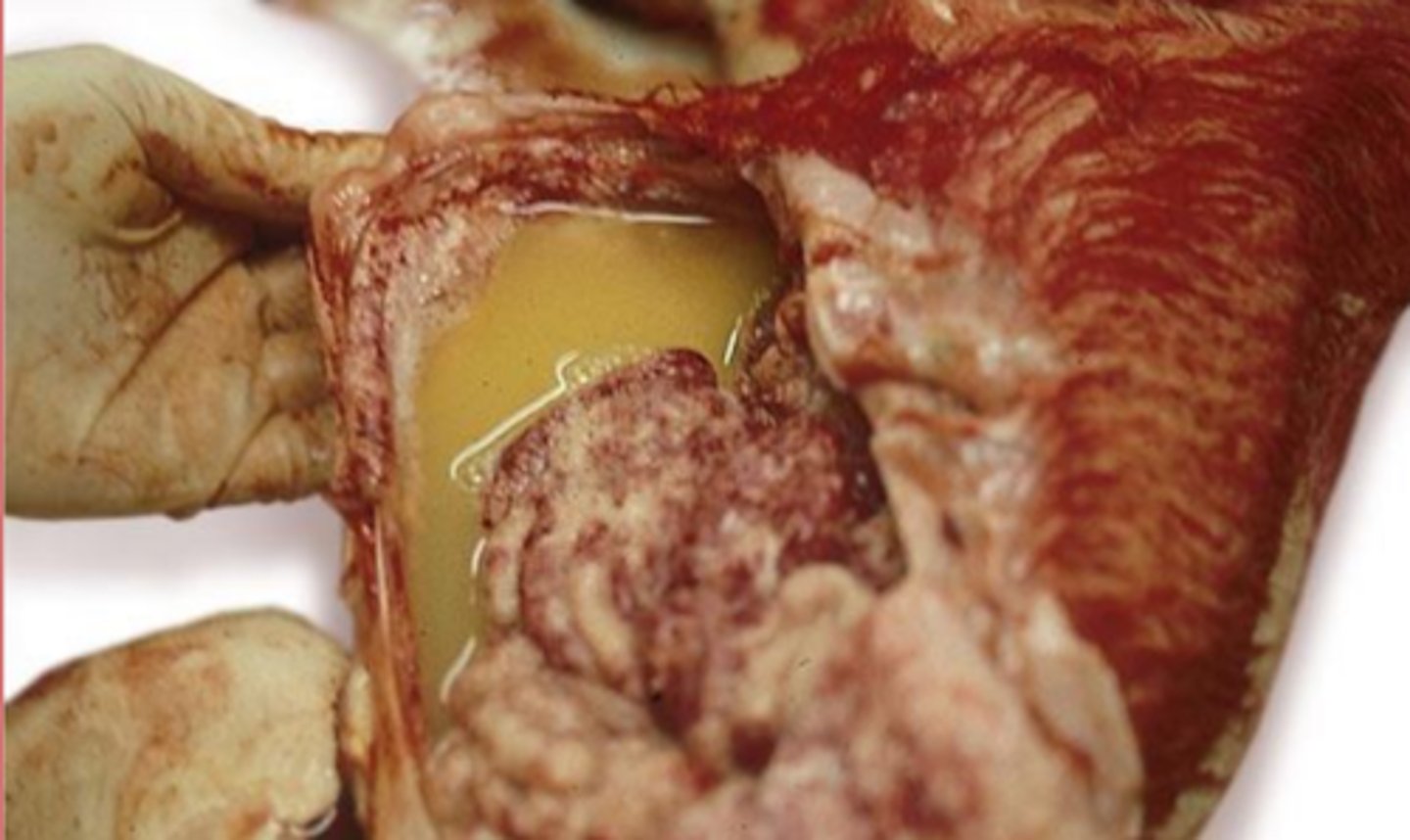
exudate
what kind of effusion?
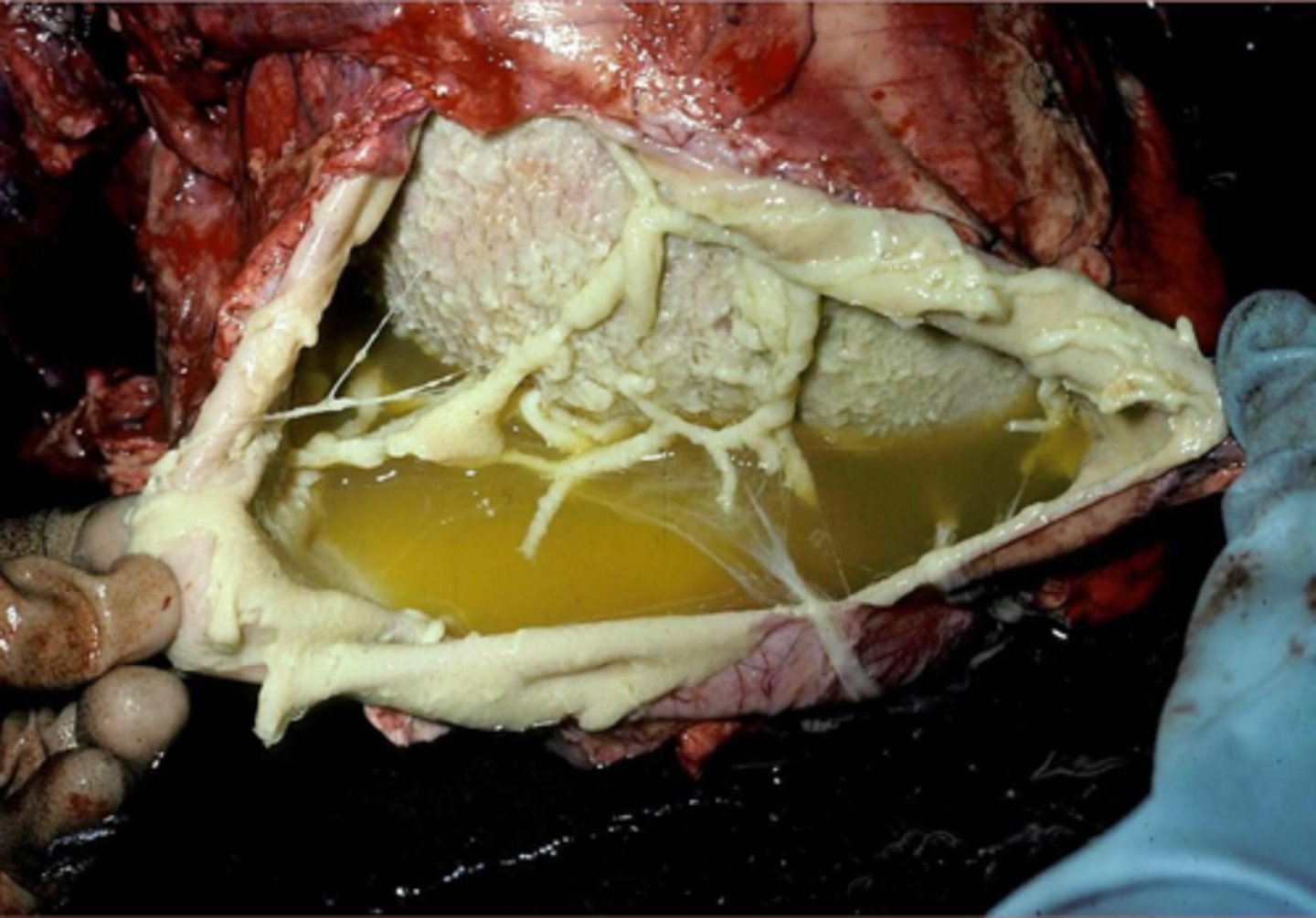
chylous effusion
effusion Composed of lymph and emulsified fat extracted from chyme by the lacteals
milky white/creamy pink
what color is chylous effusion?
obstruction of outflow of chyle from thoracic duct into vena cava
what causes chylous effusion?
thorax
where does chylous effusion usually occur?
chylous effusion
what is this?
increased microvascular permeability
increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure
decreased intravascular osmotic pressure
decreased lymphatic drainage
what are the four major mechanisms of edema? (KNOW THESE she said)
vasodilation, increased microvascular permeability
What is the initial microvascular reaction to inflammatory or immunologic stimuli
histamine, bradykinin, leukotrienes, substance P -> cytokines
what are the mediators of increased microvascular permeability?
inflammation, neovascularization, anaphylaxis, toxins, clotting abnormalities, metabolic abnormalities
what are the causes for increased microvascular permeability?
false; passive is more common
true/false: increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure can be active or passive but active is the more common form.
hyperemia
what is active Increased Intravascular Hydrostatic Pressure called?
congestion
what is passive Increased Intravascular Hydrostatic Pressure called?
arteriolar dilation
active Increased Intravascular Hydrostatic Pressure results from increased flow of blood into the microvasculature and is often associated with ___________________
decreased blood REMOVAL by venous dilation
passive increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure results from increased blood in tissues resulting from passive venous engorgement... this is usually associated with _________________
filtration, fluid absorption back into vessels
What is the end result of Increased Intravascular Hydrostatic Pressure?
increase __________ and reduced or reversed ___________
right sided heart failure (portal hypertension), left sided heart failure (pulmonary hypertension), generalized heart failure, fluid overload (iatrogenic or renal disease)
causes for increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure can be either generalized or localized... what are some generalized examples?
local inflammation, trauma (insect bites), venous obstruction
causes for increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure can be either generalized or localized... what are some localized examples?
congestive heart failure
______________: Inability to adequately empty the venous reservoirs
reduced cardiac output
What is the general result of congestive heart failure once there is loss of cardiac pumping efficiency
lungs and thoracic cavity
where are the effects of left sided heart failure seens?
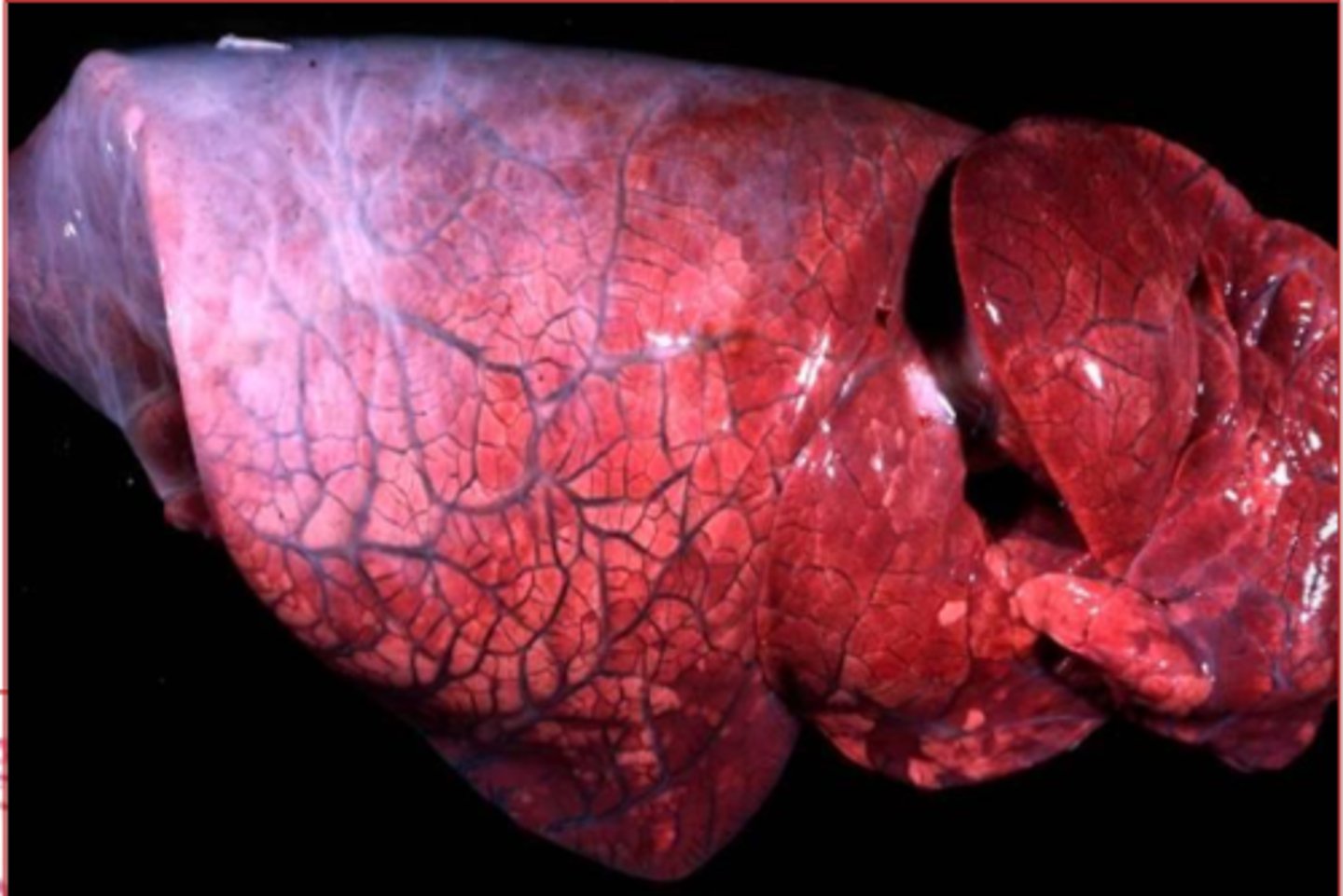
chronic pulmonary congestion
What is this?
fluid buildup in the body
right sided heart failure leads to _______________---
left sided failure or pulmonary hypertension
right sided heart failure can occur secondarily to _______ or _______________
hydrostatic pressure, venous congestion
liver, abdominal cavity (hydrothorax rare but in cats), periphery and subcutis
systemic lesions that lead to right sided heart failure typically are because of increased ________________ due to _________________
and can cause secondary lesions in the "systemic circulation" which includes _____________________ (4)
Hepatic Chronic Passive Congestion
____________________: congestion of the sinusoids and vessels in the liver; leading to nutmeg liver
congested vessels and sinusoids around central veins
describe what hepatic chronic passive congestion looks like on histology
nutmeg liver/hepatic chronic passive congestion
what is this?
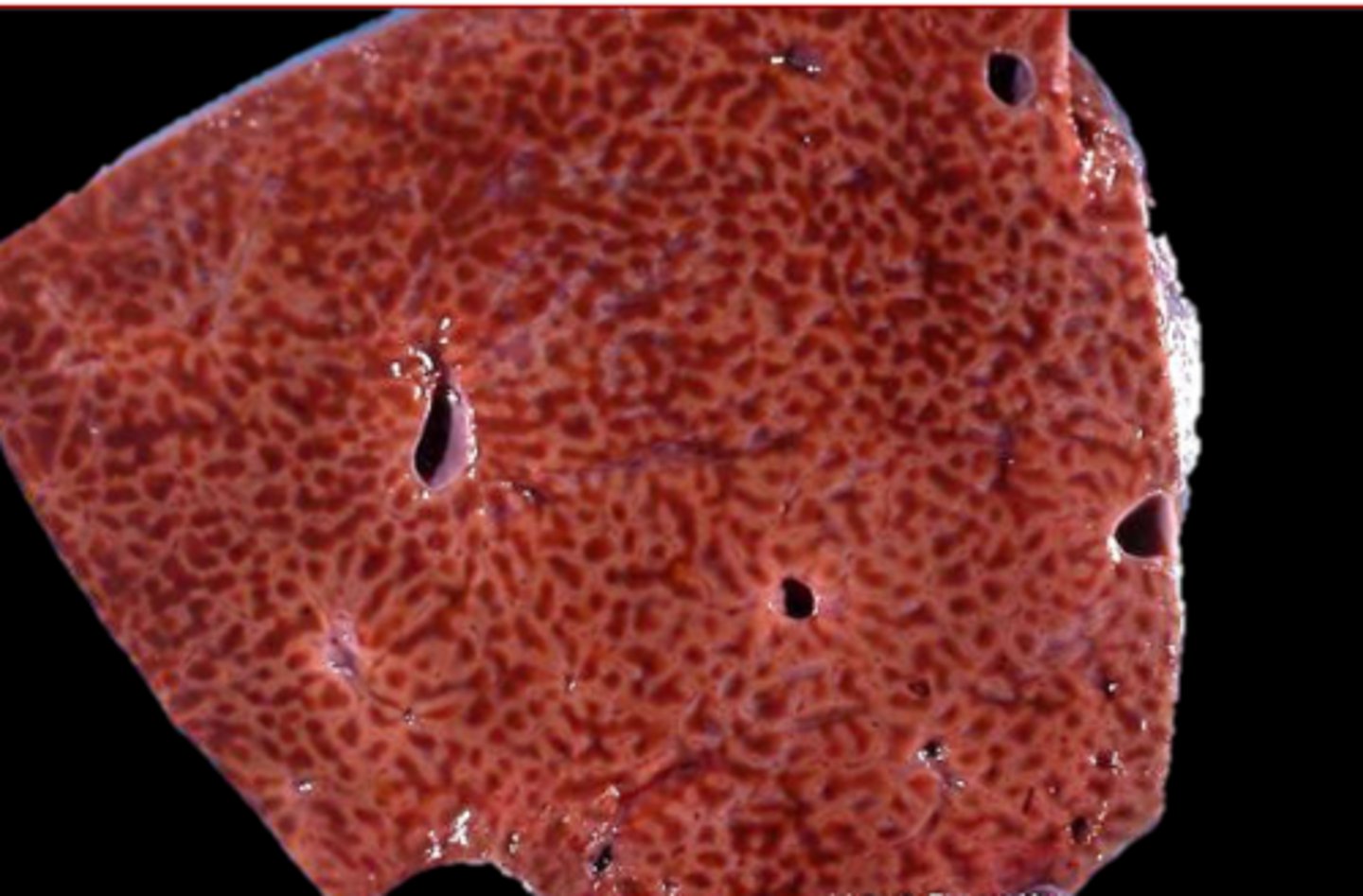
renal hypoperfusion, activation of RAAP (promoting more water retension), exacerbates fluid overload
congestive heart failure leads to generalized edema which in turn reduces the circulating plasma volume... What does this lower plasma volume lead to?
decreased ALBUMIN (really just plasma protein conc but mostly albumin)
what causes decreased intravascular osmotic pressure generally?
fluid filtration, absorption, generalized edema
decreased intravascular osmotic pressure leads to increased __________ and decreased ______________ generally ending in ___________________-
starvation, malnutrition, cachexia, chronic liver disease
hypoproteinemia that leads to decreased intravascular osmotic pressure can be due to decreased production by ____________ (4)
heavy parasitism*, severe burns, protein-losing enteropathy, protein-losing nephropathy
hypoproteinemia that leads to decreased intravascular osmotic pressure can also be due to increased loss due to ___________ (4)
haemonchus contortus/barber pole worm
which parasite is found in the abomasum of ruminants and feeds on blood causing sever anemia, hypoproteinemia, and decreased intravascular osmotic pressure leading to bottle jow
ostertagia (O. ostertagia in cows, Teladorsagia circumcinta in sheep/goats)
what reddish-brown worms can be found in the abomasum of ruminants that will expand and destroy glands and cause "leaky tight junctions", destroying the integrity of the mucosa
protein-losing gastroenteropathy and brisket edema
ostertagiosis tends to lead to __________ and ____________________