Unit 5 AP Human Geo Vocab (copy)
1/23
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Agriculture
the purposeful cultivation of plants or raising of animals to produce goods for survival
Mediterranean Agriculture
an agricultural practice that consists of growing hardy trees and shrubs and raising sheep and goats
Subsistence Agriculture
an agricultural practice that provides crops or livestock to feed one's family and close community using fewer mechanical resources and more people to care for the crops and livestock
Commercial Agriculture
an agricultural practice that focuses on producing crops and raising animals for the market for others to purchase
Intensive Agriculture
an agricultural practice in which farmers expend a great deal of effort to produce as much yield as possible from an area of land
Plantation Agriculture
a type of large-scale commercial farming of one particular crop grown for markets often distant from the plantation
Market Gardening
a type of gardening that produces fruits, vegetables, and flowers and typically serves a specific market or urban area
Mixed Crop and Livestock Farming
a type of farming in which both crops and livestock are raised for profit
Extensive Agriculture
an agricultural practice with relatively few inputs and little investment in labor and capital that results in relatively low outputs
Shifting Cultivation/Slash and burn
the agricultural practice of growing crops or grazing animals on a piece of land for a year or two, then abandoning that land when the nutrients have been depleted from the soil and moving to a new piece of land where the process is repeated
Pastoral Nomadism
a type of agriculture based on people moving their domesticated animals seasonally or as needed to allow the best grazing
Domestication
the deliberate effort to grow plants and raise animals, making plants and animals adapt to human demands and using selective breeding to develop desirable characteristics
Fertile Crescent
a hearth in Southwest Asia that forms an arc from the eastern Mediterranean coast up into what is now western Turkey and then south and east along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers to western parts of modern Iran
Columbian Exchange
the exchange of goals and ideas between the Americans, Europe, and Africa that began after Christopher Columbus landed in the Americas
First Agricultural Revolution
the shift from foraging for food to farming about 11,000 years ago, marking the beginning of agriculture
Second Agricultural Revolution
a change in farming practices, marked by new tools and techniques, that diffused from Britain and the Low Countries starting in the early 18th century
Third Agricultural Revolution/Green Revolution
movement beginning in the 1950s and 1960s (till now) in which scientists used knowledge of genetics to develop new high-yield strains of grain crops and new technology
Grain Farming
the cultivation and harvesting of cereal crops, which are essential for human consumption and animal feed
Livestock ranching
a form of agriculture focused on the raising of livestock for meat, wool, milk, and other animal products, typically on large tracts of land
Clustered settlement
settlements where a number of families live in close proximity to each other with fields surrounding the collection of houses and farm buildings
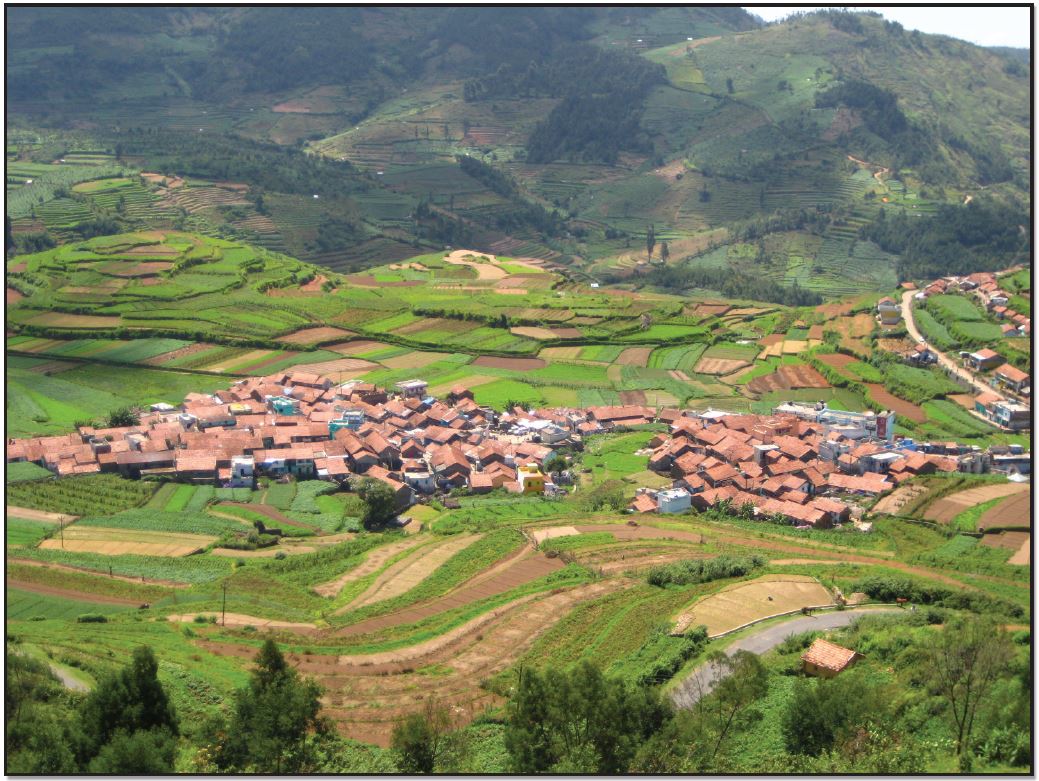

Dispersed settlement
a type of settlement pattern where households are spread out over a large area, often with individual farms and fields, rather than clustered together.

Metes and bounds
originated in England and marks the boundaries of a property according to its surrounding landmarks
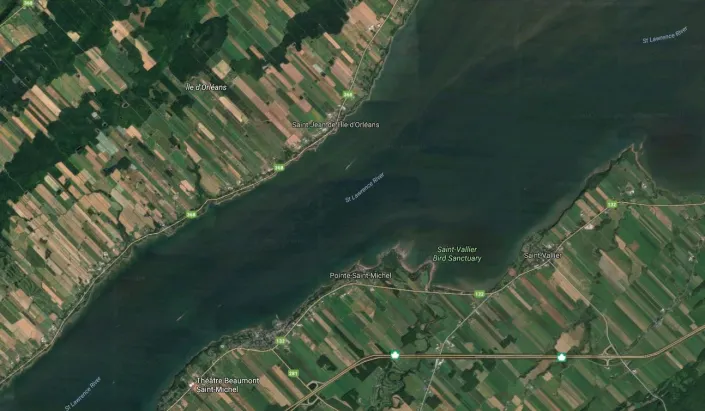
Long lot system
Primarily used in areas settled by the French, particularly in parts of Canada and Louisiana. Each long lot typically ran perpendicular to a body of water

Township and range
a method of land surveying used in the United States, established by the Land Ordinance of 1785 (US government)