3.10.2 electrophilic substitution
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
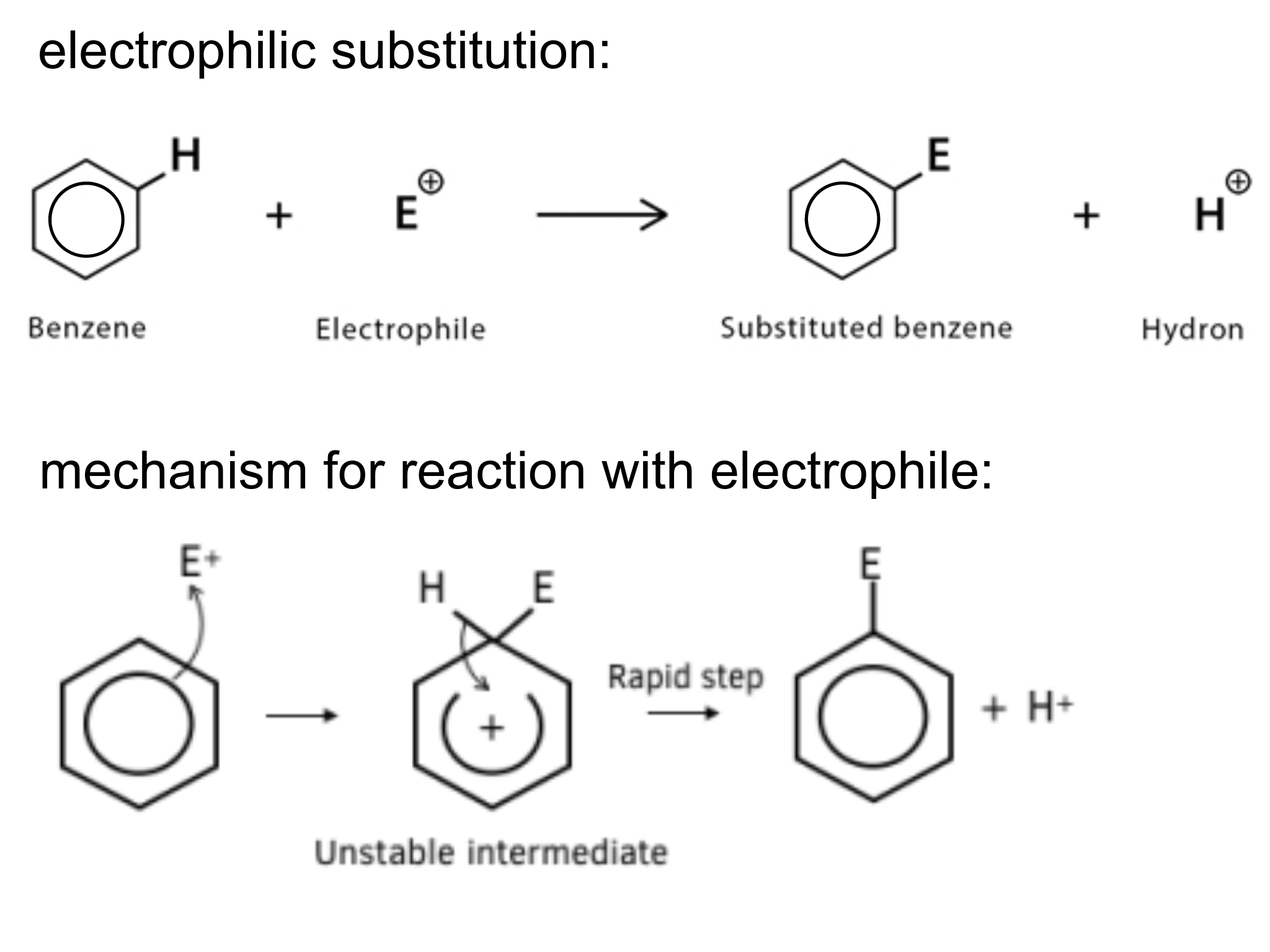
what happens when benzene undergoes electrophilic mono-substitution?
catalyst generates electrophile with + charge
an electron pair from delocalised ring is donated to electrophile
ring is partially destroyed
electrophile is substituted onto the benzene ring, removing a hydrogen ion and restoring the ring
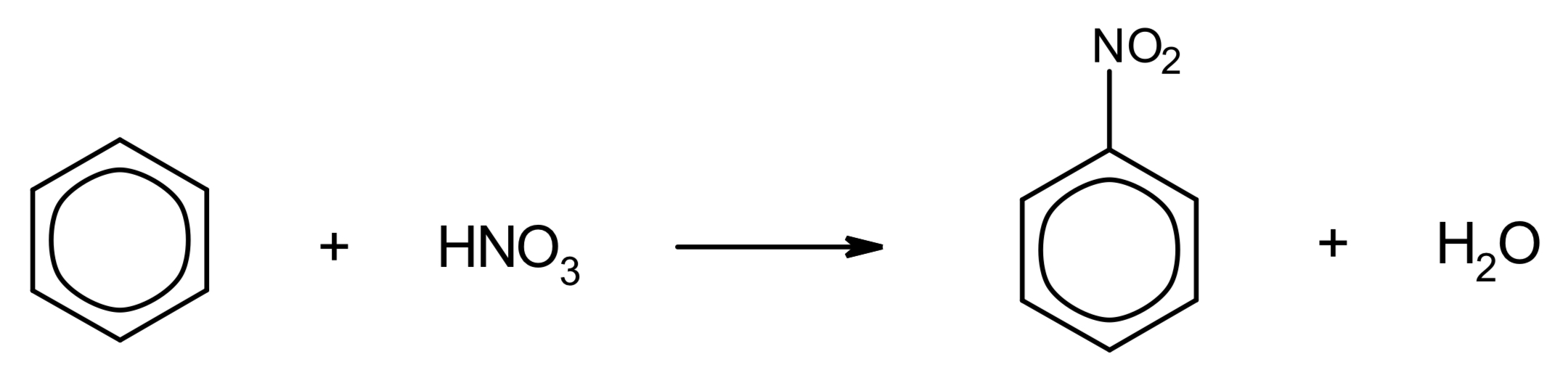
what happens when benzene undergoes nitration?
give the overall equation.
nitronium ion electrophile generated
H atom on benzene is substituted for nitronium ion
benzene + HNO3 → nitrobenzene + H2O
H2SO4 above arrow
why is nitration an important step in synthesis?
produces nitrobenzene and aromatic amines from benzene
nitrobenzene used in the manufacture of explosives, pesticides, dyes and pharmaceuticals
aromatic amines used in the manufacture/making of dyes, surfactants/fabric softeners, detergents and hair conditioners
what are the conditions for nitration?
conc H2SO4 and conc HNO3 to generate NO2+ electrophile
H2SO4 is the catalyst, HNO3 acts as base when generating electrophile
temperature 50 - 55°C
why shouldn’t nitration be carried out at a temperature higher than the required reaction temperature?
reaction must be a mono-substitution
only one substitution must occur for the production of aromatic amines
at temperatures higher than 50 - 55°C, multiple substitutions/more nitrations can occur
why shouldn’t nitration be carried out at room temperature?
a relatively high activation energy is required to form the unstable intermediate with a partially broken delocalised ring
reaction would be slow at room temp
in nitration, how is the H2SO4 used as a catalyst?
it generates the electrophile, the nitronium ion, from nitric acid
HNO3 + 2 H2SO4 → NO2+ + 2 HSO4- + H3O+
in nitration, how is the H2SO4 catalyst regenerated?
H+ lost from benzene reacts with the hydrogen sulfate ion
H+ + HSO4- → H2SO4
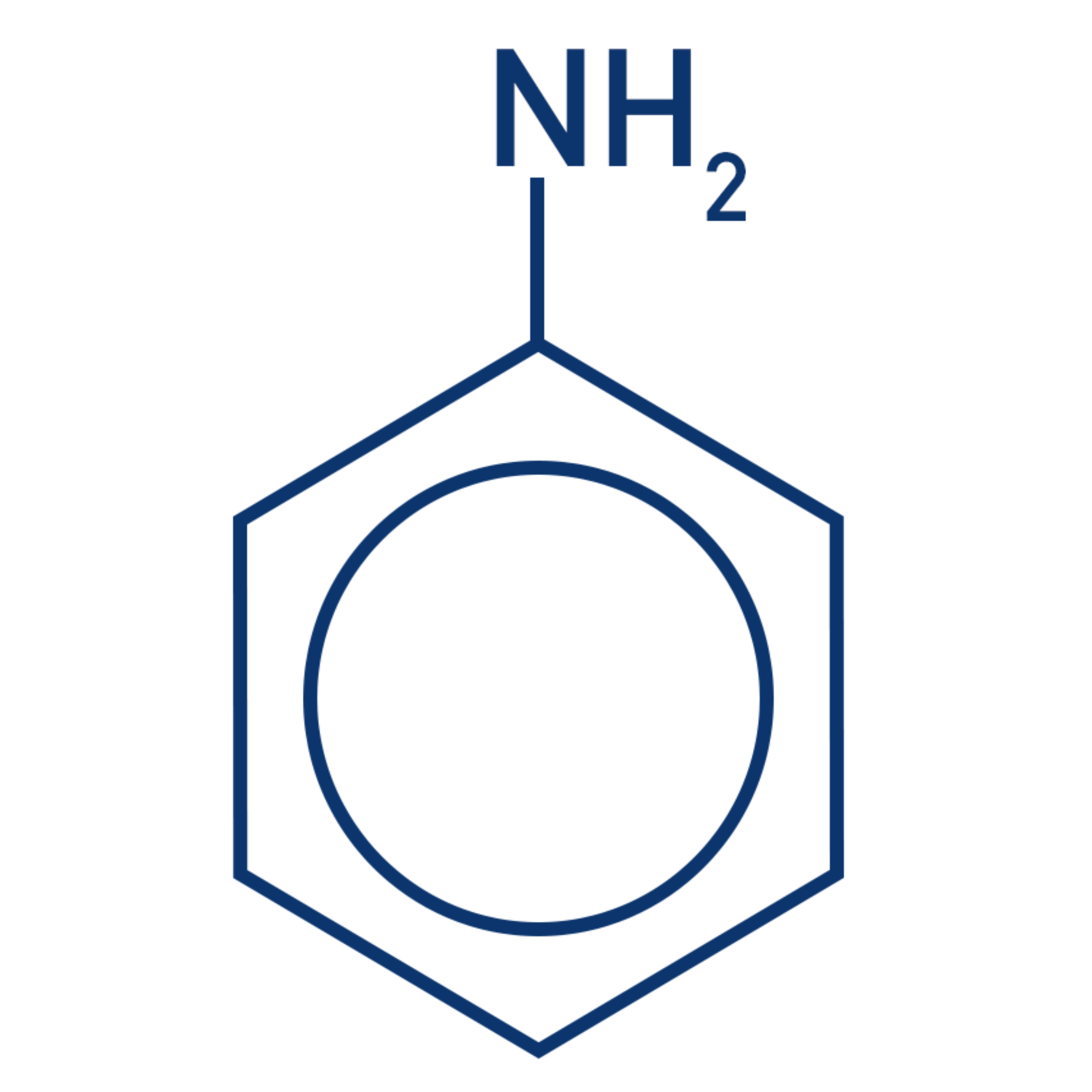
why is phenylamime a weak base?
lone pair on N is (partially) delocalised / spread into ring
so lone pair is less available to accept H+
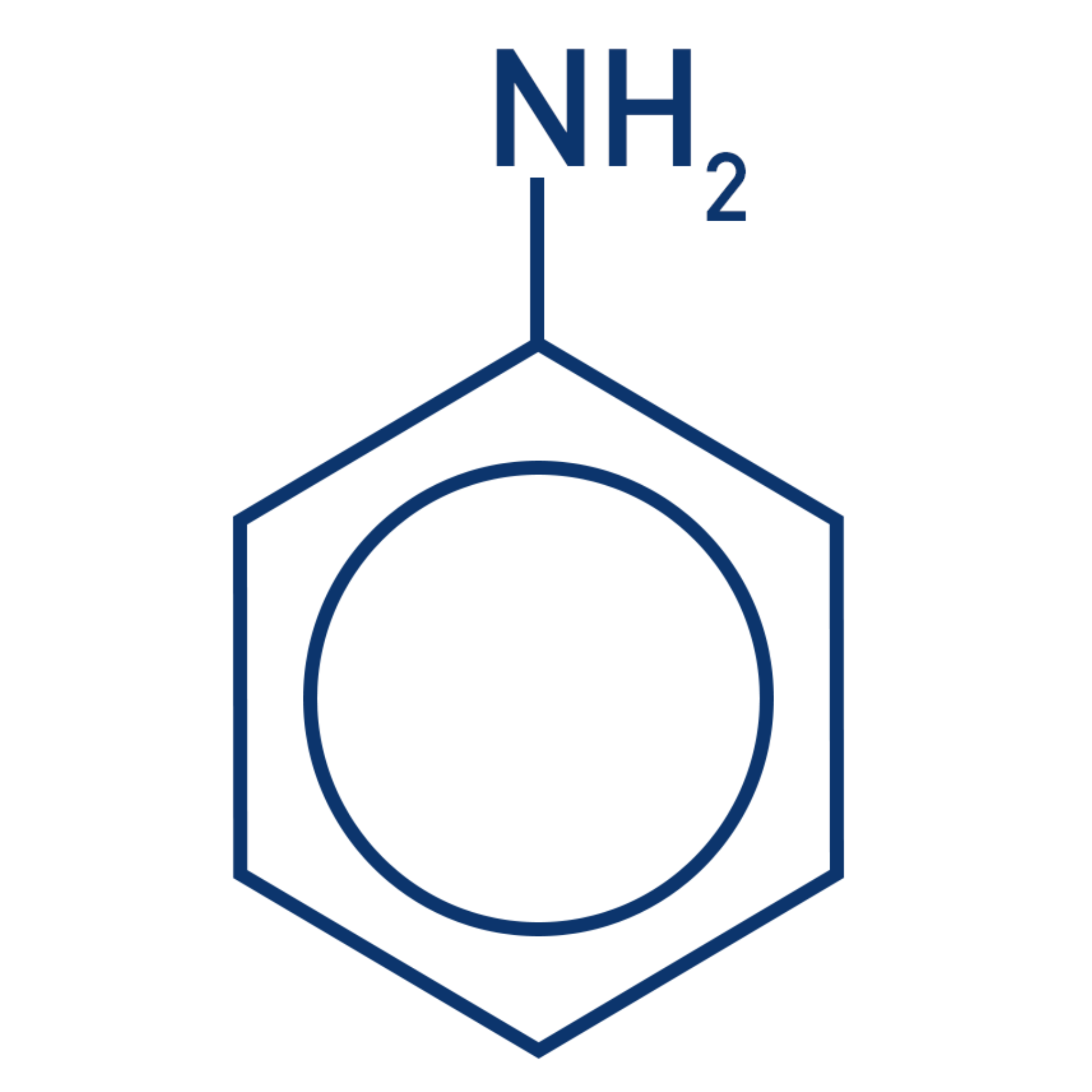
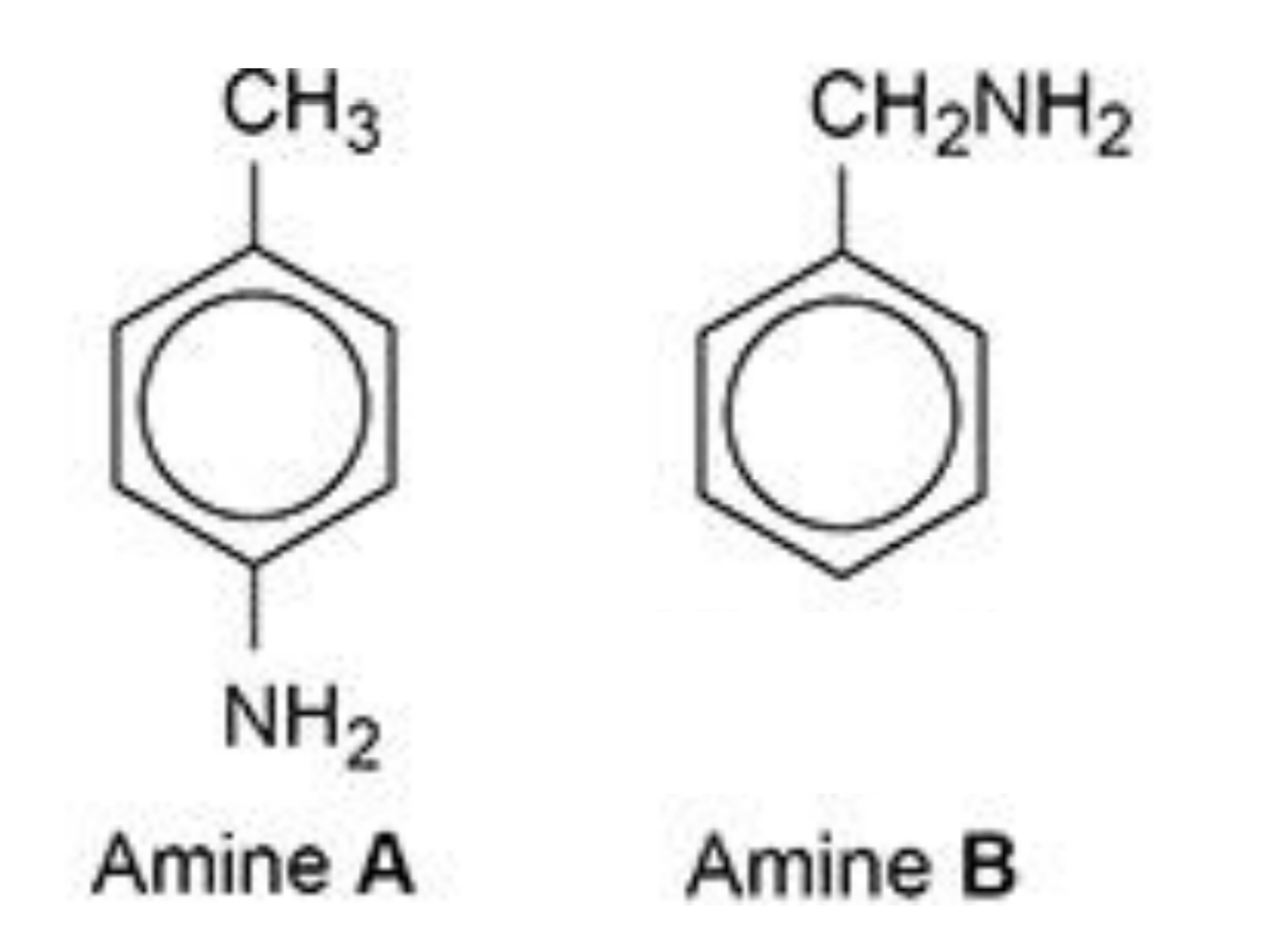
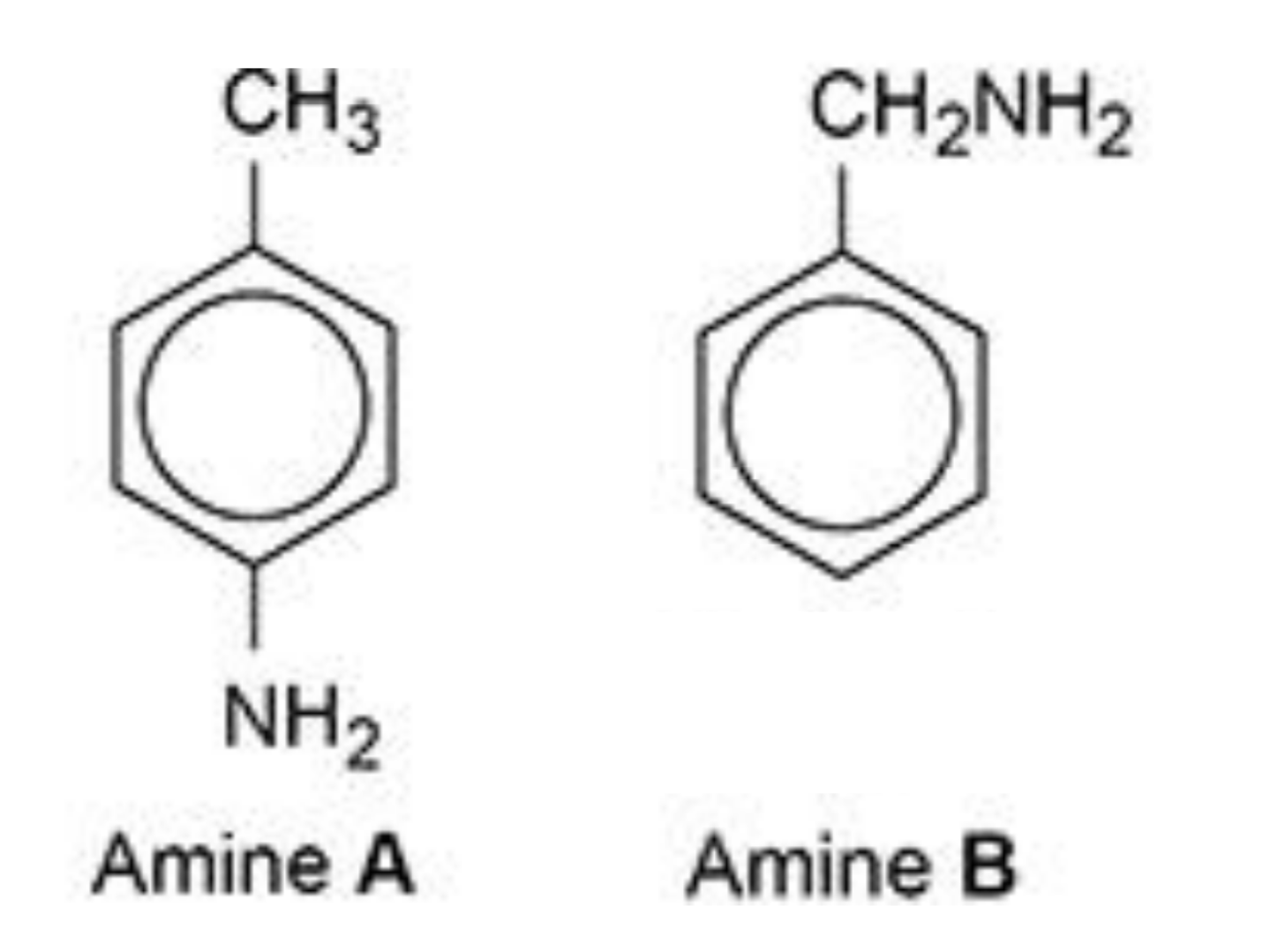
why is amine B a stronger base than amine A?
amine B:
positive inductive effect / alkyl group is electron-releasing
so lone pair on N is more available to donate to H+
amine A:
lone pair on N is partially delocalised / spread into ring
so lone pair is less available to donate to H+
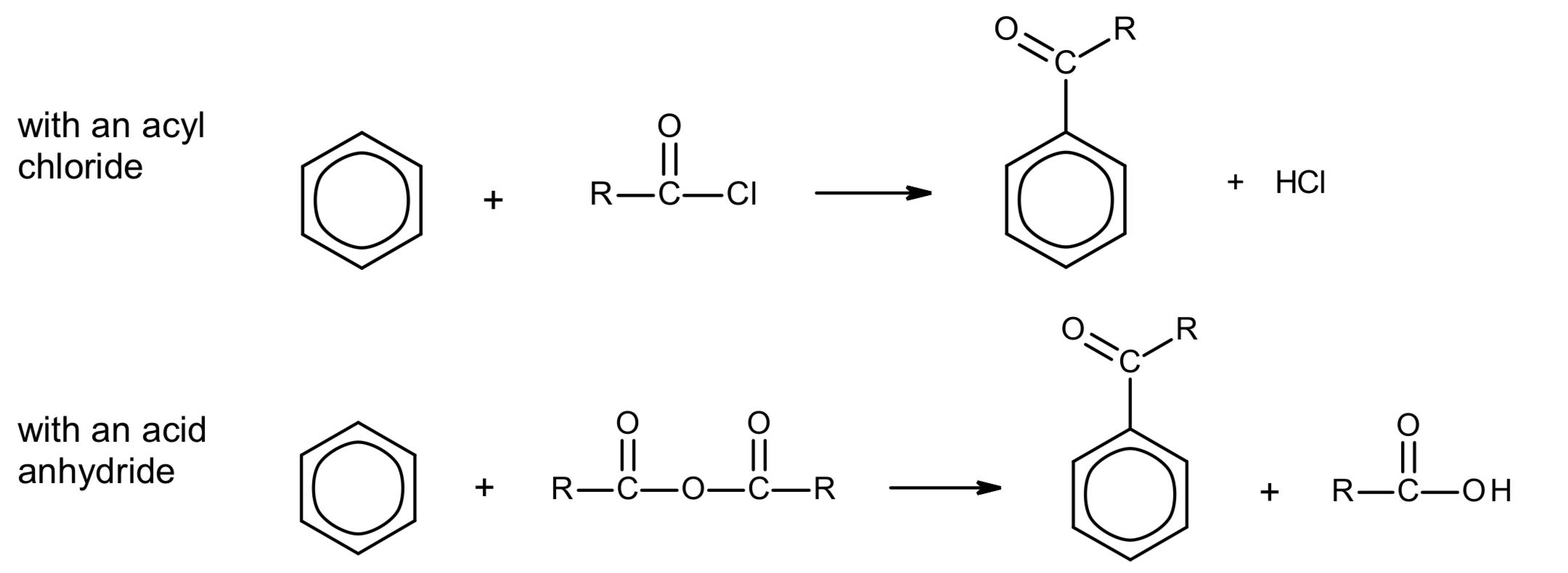
what happens when benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation?
give the overall equation.
acylium ion electrophile generated
H atom on benzene is substituted for acyl group
benzene + acyl chloride → phenylketone + HCl, e.g.
benzene + ethanoyl chloride → phenylethanone + HCl
exception: benzene + methanoyl choride → benzenealdehyde + HCl
benzene + acid anhydride → phenylketone + carboxylic acid
AlCl3 above arrow
why are Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions important steps in synthesis?
produces aromatic ketones (phenylketones), which are commonly used in industrial production of:
dyes
pharmaceuticals
explosives
fragrances
reaction increases C chain length
what are the conditions for Friedel-Crafts acylation?
anhydrous
AlCl3 (halogen carrier catalyst)
heat under reflux
in Friedel-Crafts acylation, how is AlCl3 used as a halogen-carrier catalyst?
it generates the electrophile, an acylium, from the acyl chloride or acid anhydride
in Friedel-Crafts acylation, how is the halogen-carrier catalyst regenerated?
the H+ ion lost from the benzene ring reacts with the AlCl4- to reform the AlCl3 catalyst
H+ + AlCl4- → AlCl3 + HCl
what happens when benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
give the overall equation.
alkyl ion electrophile generated
H atom on benzene is substituted for alkyl group
benzene + haloalkane → alkylbenzene + HCl, e.g.
benzene + chloromethane → methylbenzene + HCl
AlCl3 above arrow
why are Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions important steps in synthesis?
reaction increases C chain length
in Friedel-Crafts alkylation, how is AlCl3 used as a halogen-carier catalyst?
it generates the electrophile, a carbocation, from the haloalkane
haloalkane + AlCl3 → alkyl ion + AlCl4-
e.g. CH3Cl + AlCl3 → CH3+ + AlCl4-
in Friedel-Crafts alkylation, how is the halogen-carrier catalyst regenerated?
the H+ ion lost from the benzene ring reacts with the AlCl4- to reform the AlCl3 catalyst
H+ + AlCl4- → AlCl3 + HCl
what effect does adding an alkyl group have on benzene?
the ring becomes more reactive, so further alkylations are likely to occur
-
electrophilic substitution reactions happen faster if benzene has an alkyl group
alkyl group is electron-releasing / has positive inductive effect / increases electron density of benzene ring
so electrophiles will be more attracted / benzene ring will be a better nucleophile
how does benzene react with bromine?
bromonium ion electrophile generated
H atom on benzene substituted for Br
benzene + Br2 → bromobenzene + HBr
FeBr3 or AlCl3 above arrow
what are the conditions for the bromination of benzene?
room temp and pressure
anhydrous FeBr3 or AlBr3 - halogen carrier catalyst
can be formed by adding metallic Fe or Al to reaction mixture
for the bromination of benzene:
give an equation to show how the halogen-carrier catalyst generates the electrophile
give an equation to show how the halogen-carrier catalyst is regenerated
Br2 + AlBr3 → Br+ + AlBr4-
H+ + AlBr4- → AlBr3 + HBr