🧠Anatomy - Blood Supply to the Brain
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
internal carotid a
branch of common carotid artery → ophthalmic artery, anterior cerebral artery, middle cerebral artery, posterior communicating artery
anterior cerebral a
supplies frontal, parietal, temporal lobes and frontal pole NOT occipital lobe
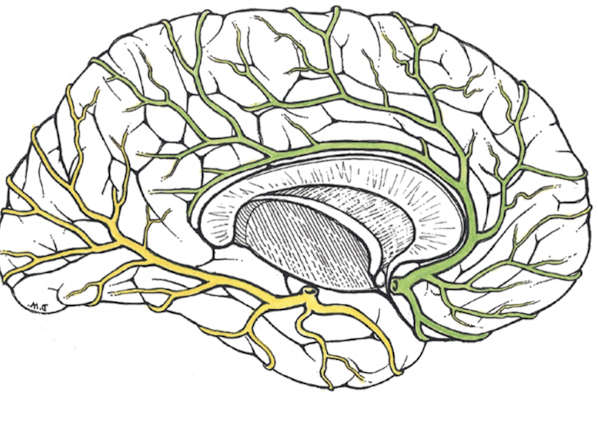
anterior communicating a
connects two anterior cerebral arteries
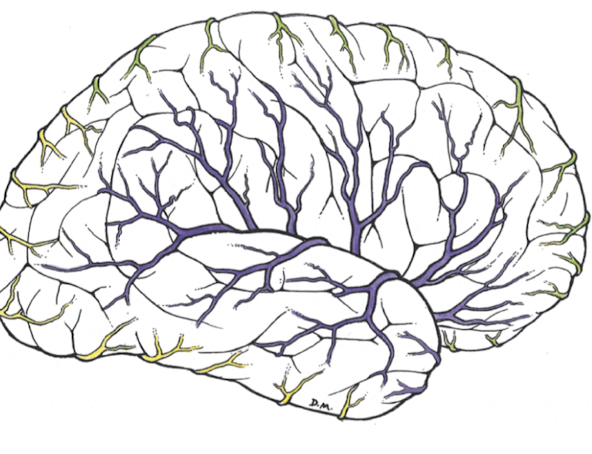
middle cerebral artery
continuation of internal carotid, supplies most of lateral surface of cerebral hemispheres (frontal, parietal, temporal)
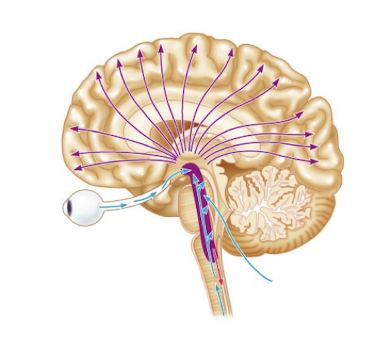
ophthalmic a
supplies eye and other structures of orbit, enters orbit through optic canal; travels with optic nerve (CN II)
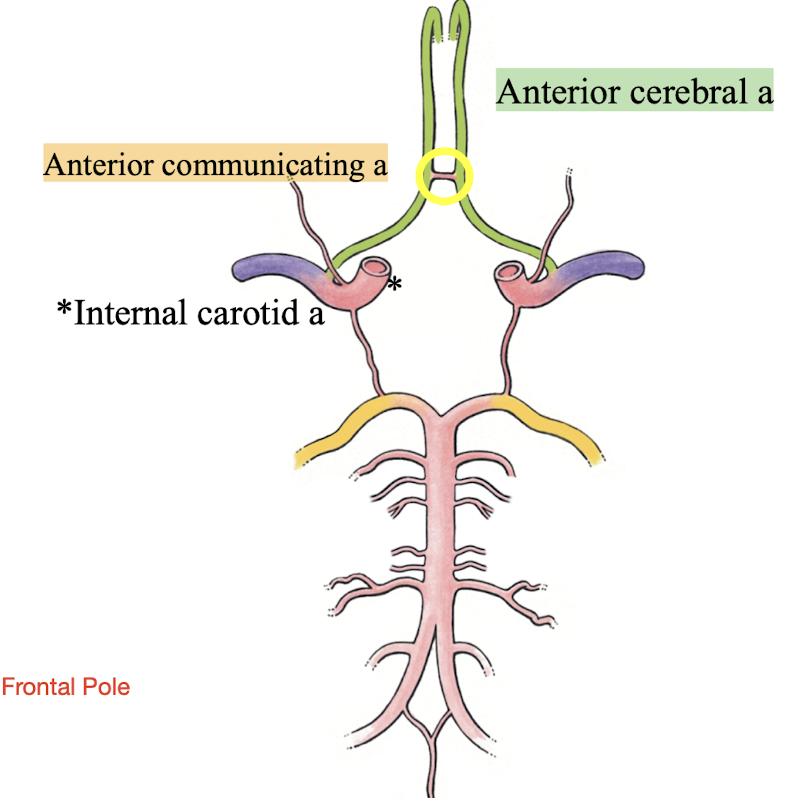
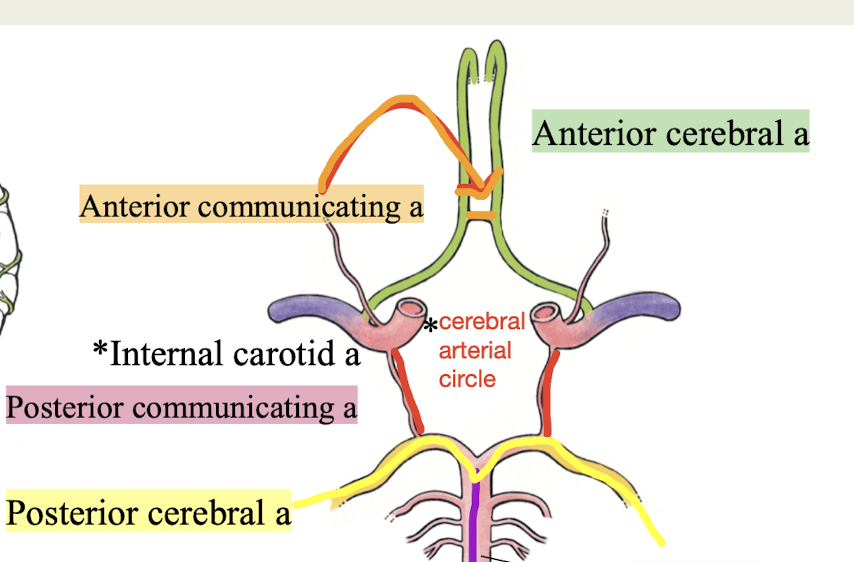
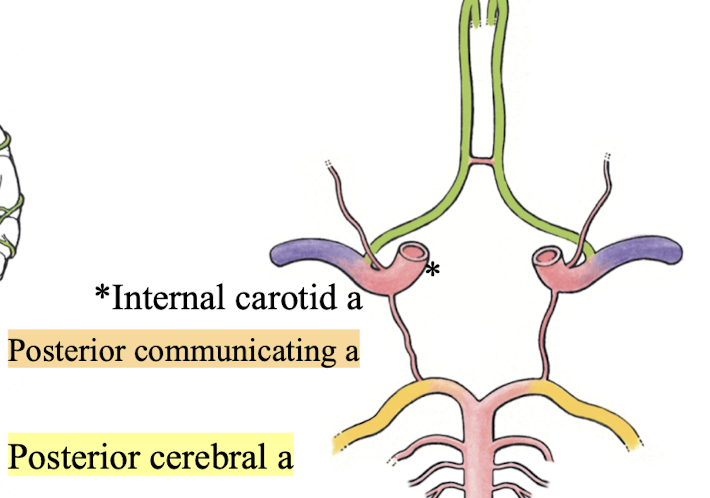
Cerebral Arterial Circle (Circle of Willis)
a. Internal carotid aa (2)
b. Anterior cerebral aa (2)
c. Anterior communicating a (1)
d. Posterior communicating a (2)
e. Posterior cerebral aa (2)
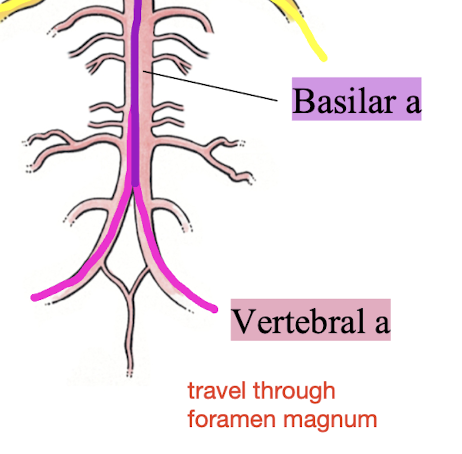
vertebral a
branch from subclavian artery → travels through transverse foramina of cervical vertebrae → foramen magnum → forms basilar a, posterior cerebral a, posterior communicating a
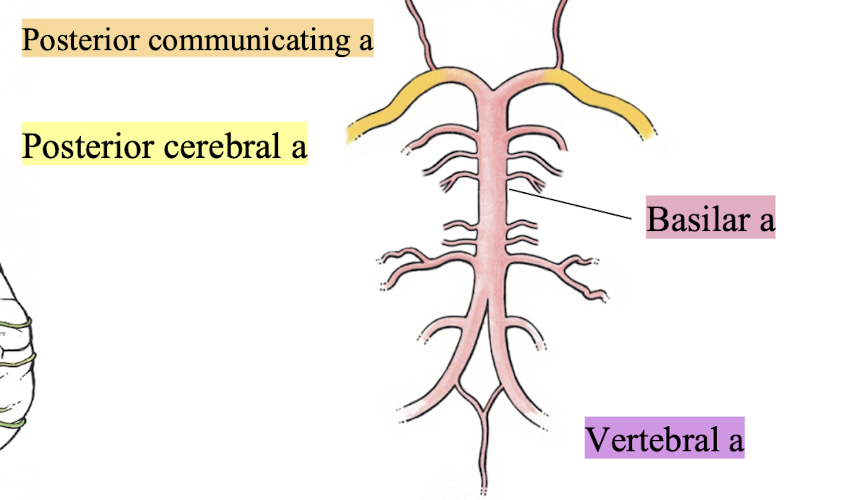
basilar a
the left and right vertebral arteries form the _______
posterior cerebral a
terminal branch of basilar a; supplies inferior aspect of temporal and occipital lobes, occipital pole
posterior communicating a
connects ipsilateral internal carotid a to posterior cerebral a
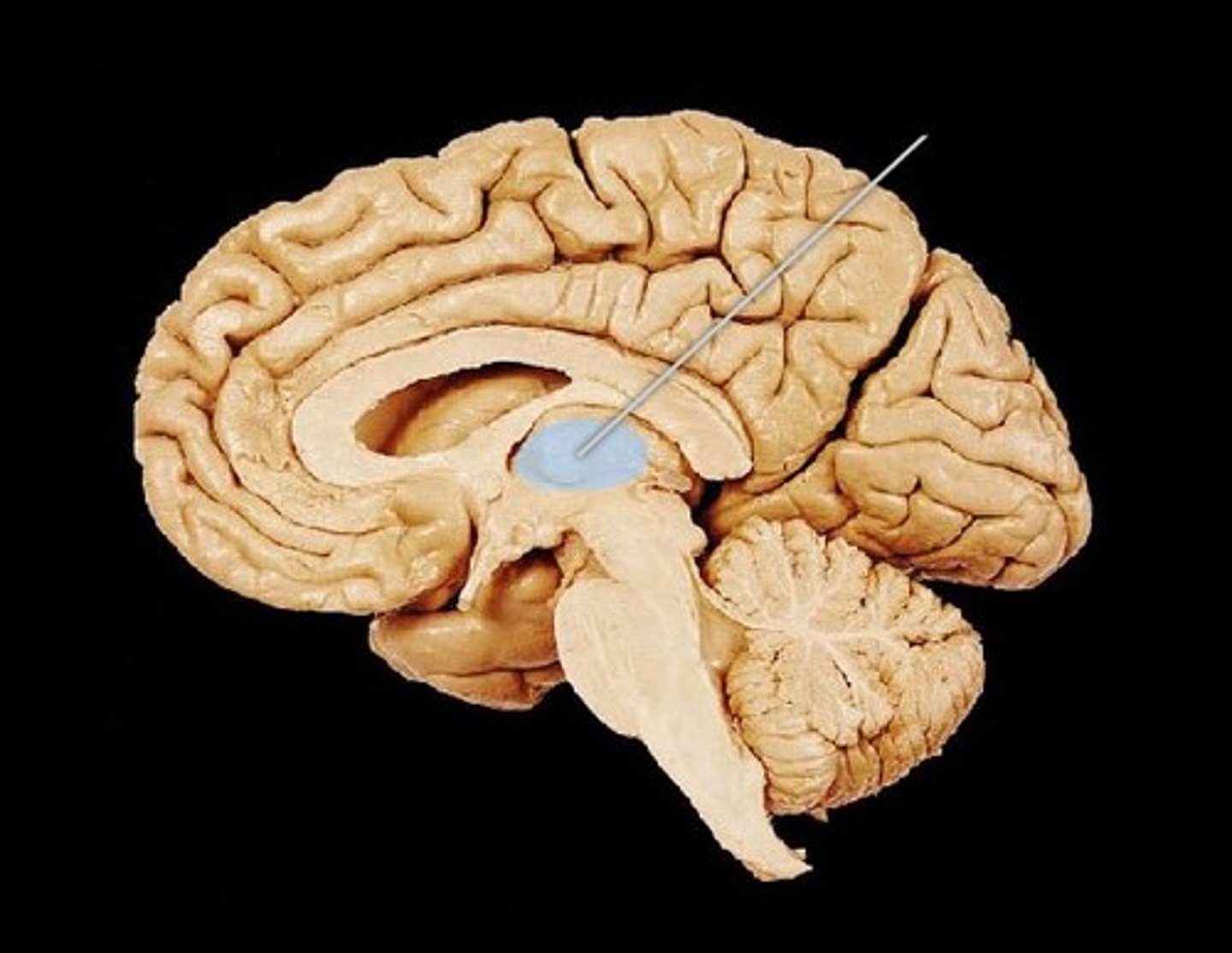
Diencephalon
What structure includes thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus and surrounds the third ventricle?
Thalamus
sensory relay center: information sorted and edited
Mediates sensation, motor activity, cortical arousal, memory
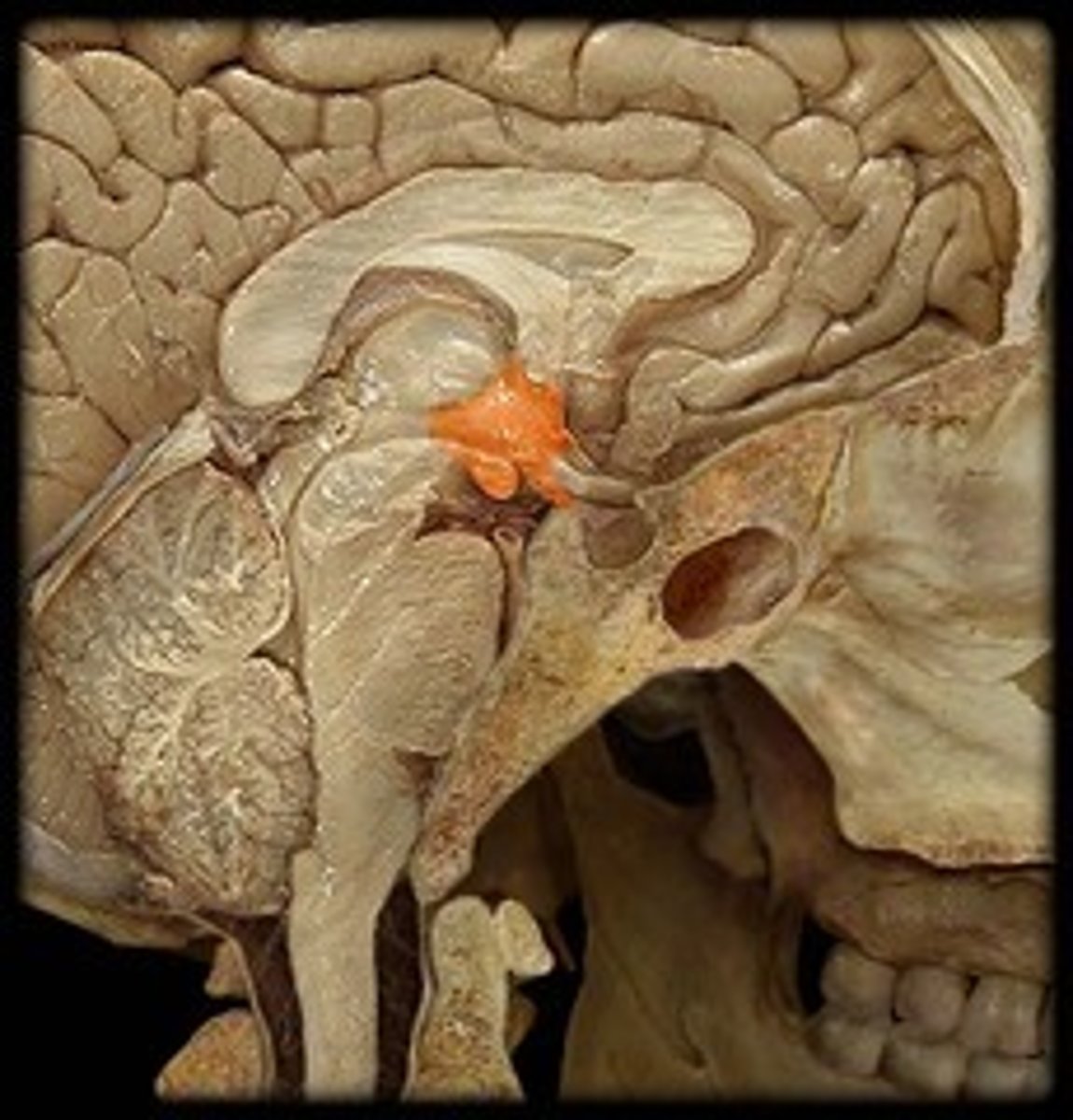
hypothalamus
-autonomic control center (HR, BP, respiration, GI movement, gland secretion)
-center for emotional response and behavior (pleasure, pain, rage, fear, sex drive)
-regulates body temperature (sweat, shiver, fever), food and water intake, regulate sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythms), endocrine control (controls pituitary hormone secretion)
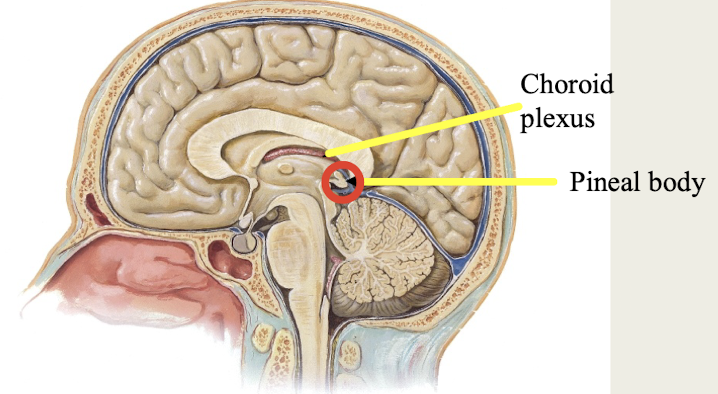
Epithalamus
What brain region includes:
a. Choroid plexus: makes CSF
b. Pineal body (gland): produces melatonin
Cerebellum
Responsible for subconscious control, smooth, coordinated movement, receives information from cerebral cortex about intended movement, receives information from rest of body, helps maintain posture and equilibrium
Vermis
What structure connects the two cerebellar hemispheres?
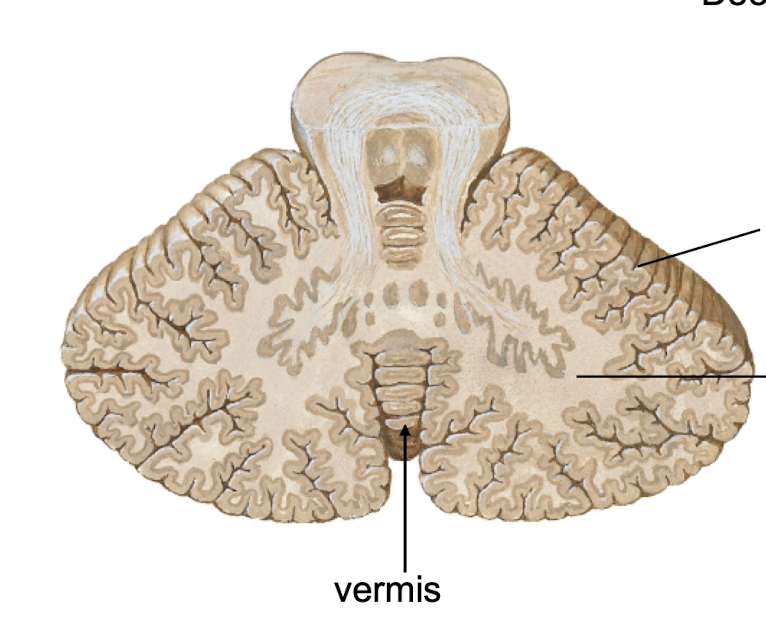
Folia
What are the parallel ridges of cerebellum?
*analogous to gyrus of cerebrum
Cerebellum
_______ needs info on equilibrium, info from proprioceptors on current movements of limbs, neck, trunk, info from cerebral cortex on intended movements
gray matter (external) → white matter → deep gray matter
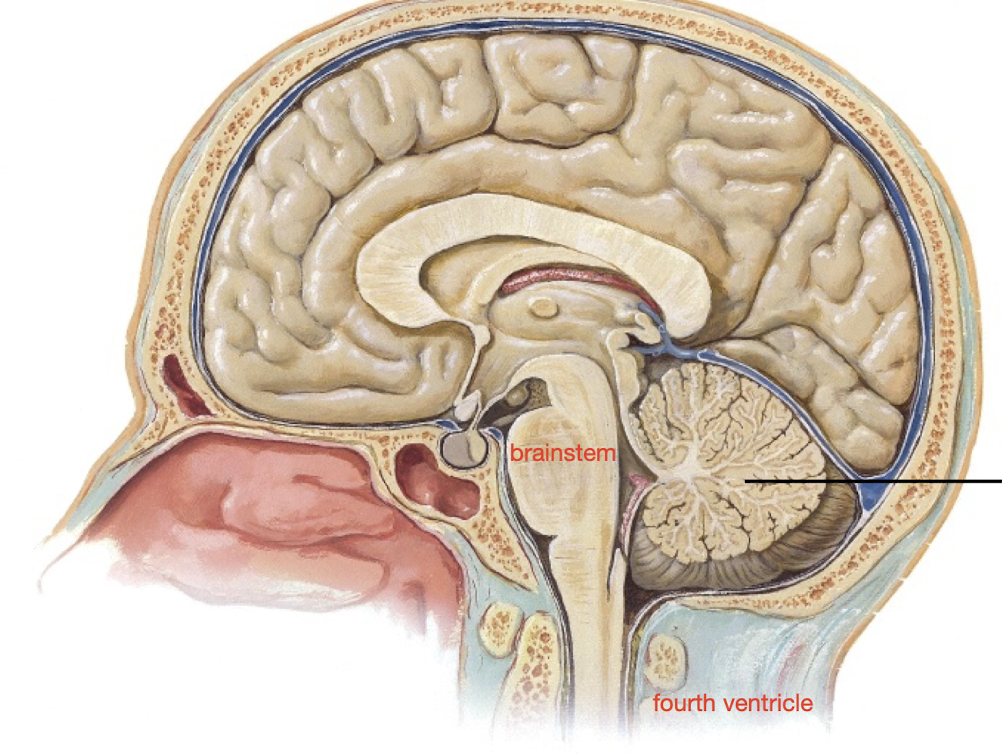
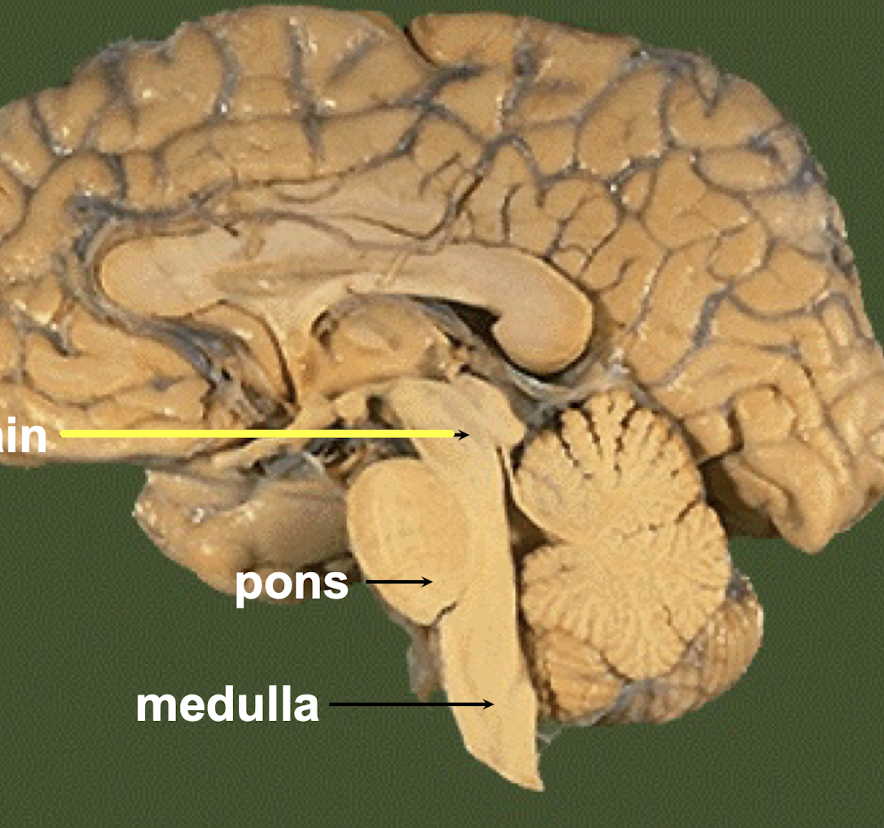
Brainstem
includes midbrain, pons, medulla
→the passageway for fiber tracts between cerebrum, spinal cord
→Produces rigid programmed automatic behavior needed for survival
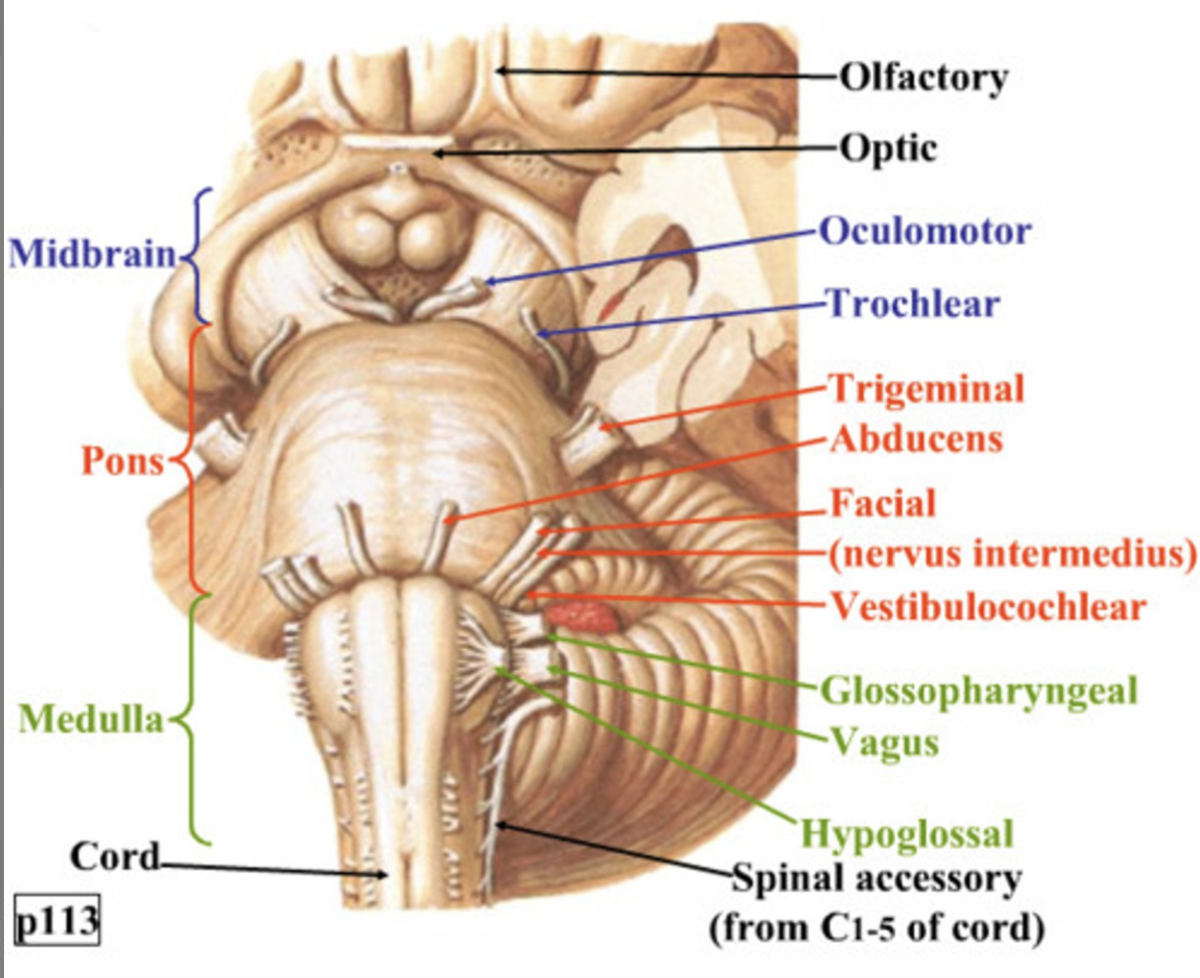
→CN III-XII attach here
Midbrain
What part of brainstem is the visual reflex center, auditory reflex center, initiates sympathetic motor pathways, carries instructions from cerebellum to cerebral cortex
has periaqueductal gray matter that connects to autonomic fight or flight
substantia nigra
What part of the midbrain influences activity of basal ganglia?
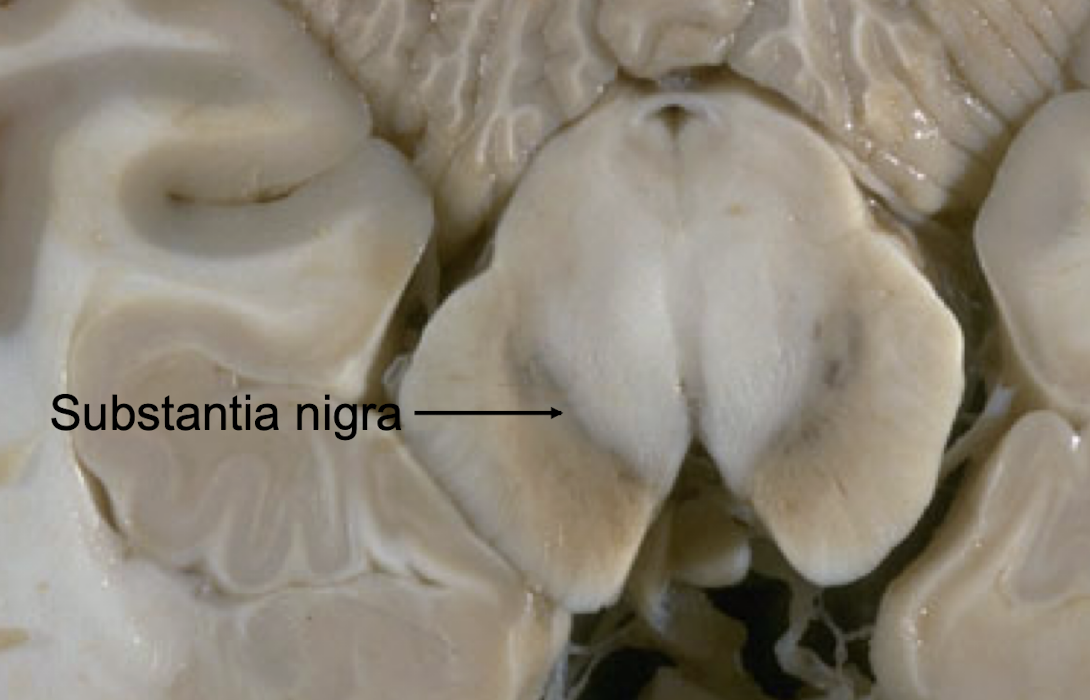
Midbrain
CN III (oculomotor) and IV (trochlear) are associated with the ____
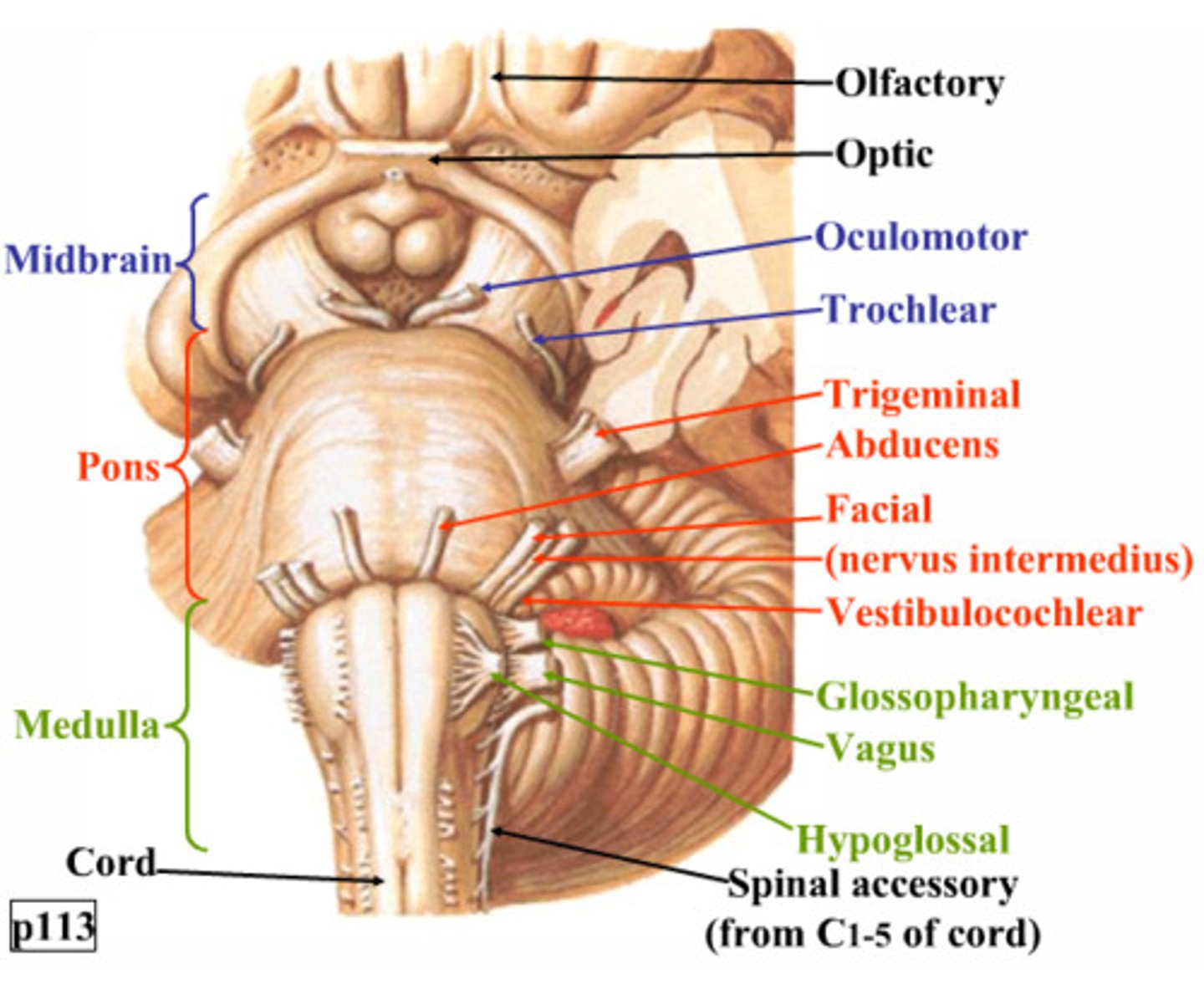
Pons
What part of the brainstem carries tracts between higher brain and spinal cord; and between motor cortex and cerebellum?
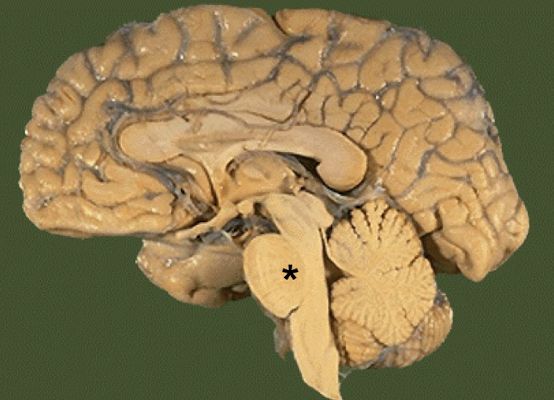
Pons
V (facial), VI (abducens), VII (facial) are associated with the _____
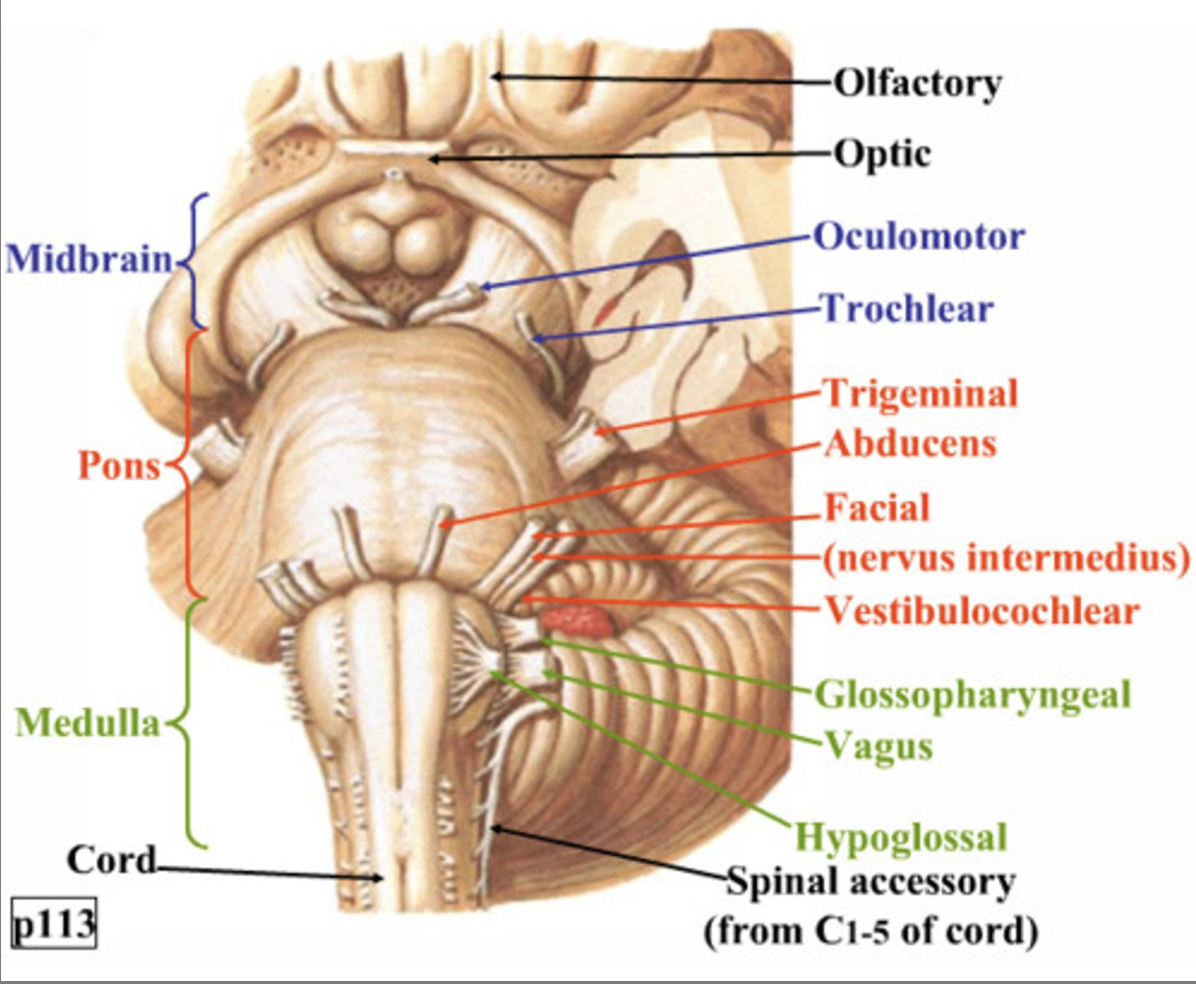
Medulla
What part of the brainstem maintains homeostasis and has cardiovascular center, respiratory center, sensory relay?
→Continuous with spinal cord at foramen magnum
→Carries info between higher brain centers and spinal cord
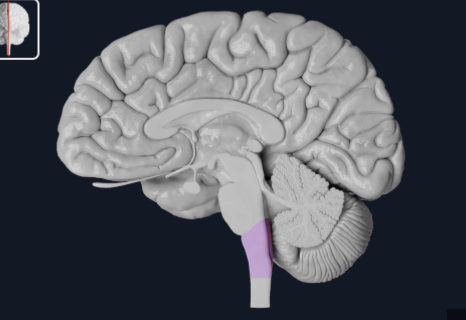
Medulla
CN VIII (vestibulocochlear), IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (accessory), XII (hypoglossal) are associated with the _______
Limbic system
Which functional brain system is widespread throughout forebrain (between encephalon and telencephalon) containing:
→Emotional brain; involved in controlling emotion and memory
→Processes fear and sympathetic response to fear.
Reticular formation
What functional brain system is found throughout brainstem, maintains arousal of whole brain, has RAS (reticular activating system)
→Motor component: controls coarse skeletal muscle movement
→Visceral component: regulates visceral motor function
RAS
What system within the reticular formation of the brainstem mediates alertness of cerebral cortex, filters sensory inputs, and helps prevent sensory overload?