QnA - Metals and Non Metals
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
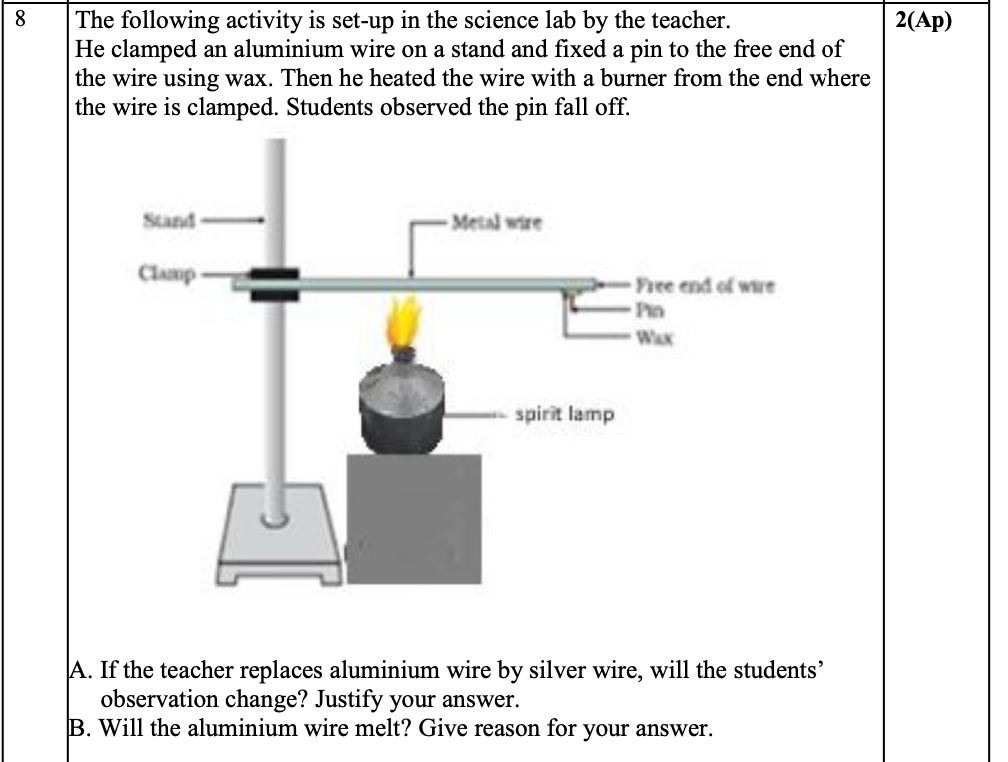
Silver is a better conductor of heat and causes the wax to melt faster
Aluminium wire will not melt due to high melting point , the spirit lamp undergoes incomplete combustion
Copper does not react even with steam
Calcium and magnesium float on water as they form hydroxides.

2Al + 3H₂SO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ +3H₂
Mg + 2HNO₃ → Mg(NO₃)₂ + H₂

Iron is more reactive than copper
Displacement reaction occurs displacing the copper in the iron to form FeSO4
Fe + CuSO₄ → FeSO₄ + Cu

YX₂

Sodium and pottasium
FeO an Fe₂O₃
Iron , nickel , chormiuium , manganese

Due to the oxidation of copper and the formation CuCO₃ and Cu(OH)₂
No we should not , rusting of iron is far more dangerous and causes damage to the structure of the building , oxidation of copper only forms a protective layer around it.
Copper is malleable making it easier to shape into domes. It is more resistant to corrosion.

No we cannot stroe X in water , it will undergo a highly explosive exothermic reaction.
Sodium
NaCl ⇌ Na⁺ + Cl⁻
Obtained by electrolytic refining of their molten chlord
At chathode - Na+ + e- → Na
At anode - 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + e⁻

Sodium - cold water and hot water
Calcium - cold water and hot water
Magnesium - hot water

Nitric acid is. strong oxidising agent. When a metal reacts with nitric acid the hydrogen produced is immediately oxidised to water. Nitric acid gets reduced into nitrogenous oxides.
Zinc oxide can react with both acid and bases to produce salt and water , which makes it an amphoteric.
Due to the presence of free electrons it allows for eletricity to flow through the metal

B is the most reactive
B can displace copper from copper sulphate solution
B - A - C - D

Bubbles is observed showing the formation of hydrogen gas
The solid dissolved into water as both water and salt are formed
No reaction occurs
Brisk Effervescence due to evolution of CO2

Aluminum
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl₃ + 3H₂
2Al + 2NaOH + 2H₂O → 2NaAlO₂ + 3H₂
Thermite reaction occurs , which is highly exothermic
2Al + Fe₂O₃ → Al₂O₃ + 2Fe + Heat

Aluminium has 3 electrons in its outermost shell giving it a valency of 3 , Oxygen has 6 electrons in its outermost shell , hence it would like to receive 2 electrons or in other words has a valency of 2. They combine to form Al₂O₃ (show electron structure)
It is an ionic compound so it will
Ionic compounds are soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents like alcohol and kerosene.
Stronger inter-ionic force of attraction the postive and negative ions and it takes a large amount of energy to break said bonds.

2Cu + O₂ → 2CuO
As they react with both acids and bases. ZnO or Al₂O₃
Na₂O + H₂O → 2NaOH
2Al + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO₂ + 3H₂

It is placed in the middle of reactivity below Zinc and above lead
found as oxides (Fe₂O₃) , sulphides (FeS) or carbonates (FeCO₃)
Feature | Roasting | Calcination |
|---|---|---|
Process | Heating the ore strongly in thepresence of excess air. | Heating the ore strongly inlimited air(or absence of air). |
Ore Type | Generally used forSulphide ores. | Generally used forCarbonate ores. |
Example | $2ZnS + 3O_2 \xrightarrow{\text{Heat}} 2ZnO + 2SO_2$ | $ZnCO_3 \xrightarrow{\text{Heat}} ZnO + CO_2$ |