Chapter 42 | Circulation and Gas Exchange
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Circulation
Transport of materials/substances that will be transported in & out of the body and throughout the body
Circulation of materials through
Direct diffusion
Gastrovascular cavity
Circulatory system with specialized structures
Heart
A pump that moves materials throughout the entire body
Vessels
Tubes that materials are transported through
Interstitial fluid
Fluid that surrounds cells and are in spaces found between cells
Circulatory fluid
Fluid that circulates and transports materials throughout the body
Materials transported through the blood
O2 as intake & CO2 as out take
Wastes to be eliminated
Nutrients
Signaling molecules
Immune cells & molecules
Open circulatory system
Found in arthropods: A circulatory system in which fluid called hemolymph bathes the tissues and organs directly and there is no distinction between the circulating fluid and the interstitial fluid. A tubular heart pumps the hemolymph through large vessels to the rest of the cells found in the coelom, eventually returning to the heart
Closed circulatory system
All vertebrates and some invertebrates: A circulatory system in which blood is confined to vessels and is kept separate from the interstitial fluid. The heart pumps fluid to vessels that infiltrate the organs and deliver materials to all cells, eventually returning to the heart
Cardiovascular system
The circulatory system found in vertebrae (majority of Chordata phylum)
Arteries
Vessels that move away from the heart. Has thick smooth muscle layers that undergo peristaltic contractions
Capillaries
Connect the arteries, and form capillary beds consisting of several tubes that infiltrate the organs
Veins
Vessels moving blood toward the heart
Has a very thin smooth muscle layer with no significant contractions
Contains valves to prevent backflow
Surrounding skeletal muscles help move blood
Single circulation
Occurs in all fish
Blood flows in a single loop:
Heart - 2 chambers; atria & ventricle
Blood moves from the heart through arteries to the capillary beds, then back through veins to the heart
No separation between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood
Double circulation
Occurs in amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals
Two separate circulatory circuits
Pulmocutaneous/Pulmonary Circuit: Carries blood to the lungs (or lungs and skin in amphibians) for oxygenation
Systemic Circuit: Delivers oxygenated blood to the rest of the body
Blood passes through the heart twice: once for oxygenation and once for distribution throughout the body
Pulmocutaneous circulation
Occurs in amphibians (e.g., frogs, salamanders, some reptiles)
Heart: 3 chambers (2 atria, 1 ventricle)
Blood flow:
Veins bring oxygen-poor blood to the right atrium
Blood moves from the right atrium to the ventricle (no separation between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood)
Blood is pumped to the lungs and skin for gas exchange and oxygenation
Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium, moves to the ventricle, and is pumped into the systemic circuit to supply the rest of the body with oxygen
Pulmonary circulation
Occurs in mammals
Heart: 4 chambers (2 atria, 2 ventricles)
Blood flow:
Right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary circuit → lungs → left atrium → left ventricle → arteries → systemic circuit
Order of blood flow through the 4 chambers of the heart
Vena cava → Right atrium —(AV / tricuspid valve)→ Right ventricle —(Semilunar valve)→ pulmonary artery → Lungs → Pulmonary veins → Left atrium —(AV / bicuspid valve)→ Left ventricle —(Semilunar / aortic valve)→ Aorta → Systemic circuit
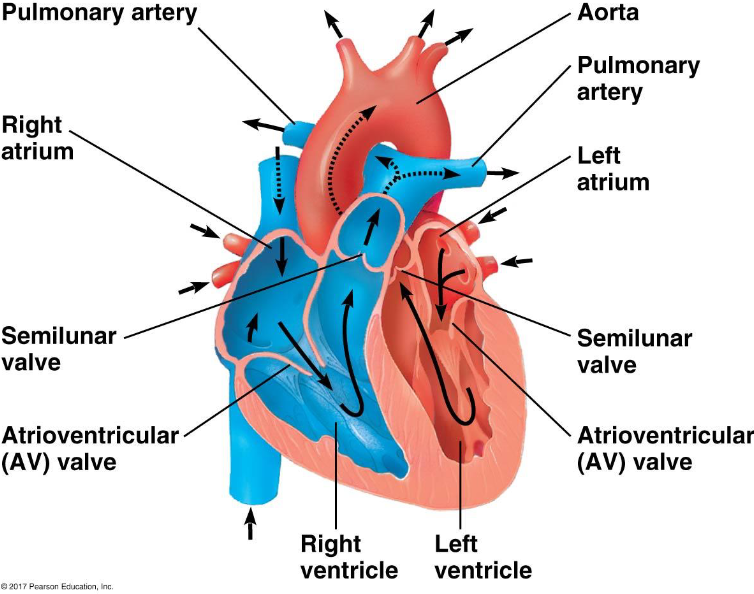
Chambers of the heart
Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body
Right Ventricle: Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation
Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the body
Cardiac cycle
Heart fills with blood:
Atrial + ventricular diastole
Blood from the atria flows into the ventricles:
Atrial systole
Ventricular diastole
Semilunar valve closed, AV valve open
Blood flows to pulmonary or systemic circuit:
Ventricular systole
Atrial diastole
Semilunar valves open, AV valves closed
Heartbeat
Relaxation (diastole) and contraction (systole) of the heart
Control of heartbeat
Sinoatrial (SA) node sends electrical signal that causes the atria to contract first. The signal relays through ventricles to cause them to contract
Sinoatrial node
The heart's natural pacemaker, generating electrical signals that trigger heart contractions. It causes atrial contraction and sends signals to the ventricles, influencing heart rate. Is autorhythmic but is highly influenced by the nervous and endocrine system
Atrioventricular node
A region where electrical impulses are delayed for ~0.1s before spreading to both ventricles and causing them to contract
Cardiac output
The volume of blood pumped per minute by each ventricle of the heart (mL / min). Obtained by multiplying stroke volume by heart rate
Blood volume
Total about of blood found in the circulatory system
Stroke volume
Specific amount of blood that leaves the ventricles per heartbeat (mL / beat)
Heart rate
beats / min
Insufficient cardiac output
Heart failure
Blood pressure
Measures how much pressure it takes to push Hg through a tube. Is measured in the arm
During systole, maximum pressure is on the artery (systolic pressure)
During diastole (diastolic pressure)
Is high in arteries and low in veins
Arteries & Veins
Made of 3 layers of cells:
Interior layer of epithelial cells, the endothelium
Smooth muscle surrounding the endothelium
Connective tissue surrounding smooth muscle to hold cells together
Path of blood flow through vessels
Heart → arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins → heart