Immunology: Innate and Adaptive Immunity
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what is innate immunity?
A variety of mechanisms that can prevent infection or eliminate
a pathogen
what type of immunity is present in all individuals at all times?
innate immunity
what type of immunity is the earliest response to infection (minutes/hours)?
innate immunity
what type of immunity recognizes groups of similar pathogens (not-antigen-specific)?
innate immunity
what type of immunity does not increase with repeated exposure to a pathogen (no memory)?
innate immunity
what are examples of innate immuntiy: mechanical barriers?
skin/mucosa
movement of mucus by cilia
what are examples of innate immuntiy: biologically active substances?
Anti-microbial proteins (skin, mucosa)
Cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, TNF and others)
Acute phase proteins: C-reactive protein (CRP) and others
Activation of Complement proteins (Alternative and Lectin Pathways)
what are examples of innate immuntiy: cellular?
Activation of leukocytes (white blood cells):
Macrophages (M)
Neutrophils
Natural killer cells (NK cells)
Mast cells and Basophils
Eosinophils
Dendritic cells (DC)
what are the phagocytic cells that are present in most tissues?
macrophages
macrophages are derived from…?
blood monocytes
what are the major functions of macrophages?
Phagocytosis of microbes and dead cells
Antigen-presentation to T Cells (Discussed later)
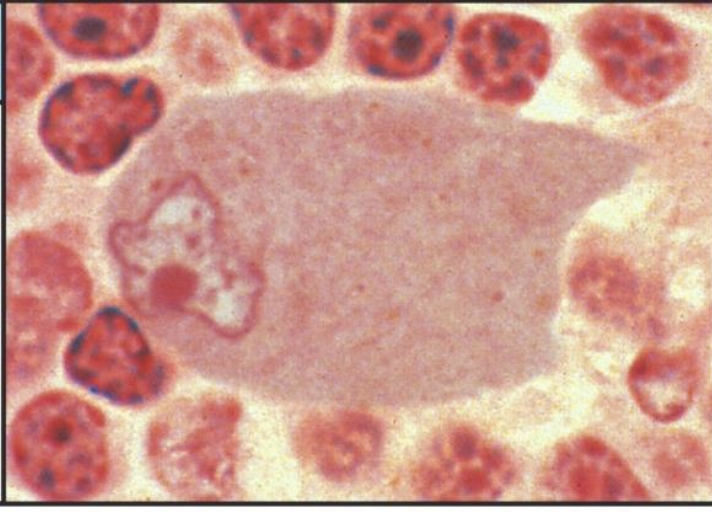
macrophage
what are the phagocytic cells in the blood?
neutrophils (aka polymorphonuclear neutrophils)
what are the major functions of neutrophils?
Neutrophils enter infected tissues to engulf and kill extracellular pathogens, especially bacteria via phagocytosis and cytotoxic mechanisms (also in pus)
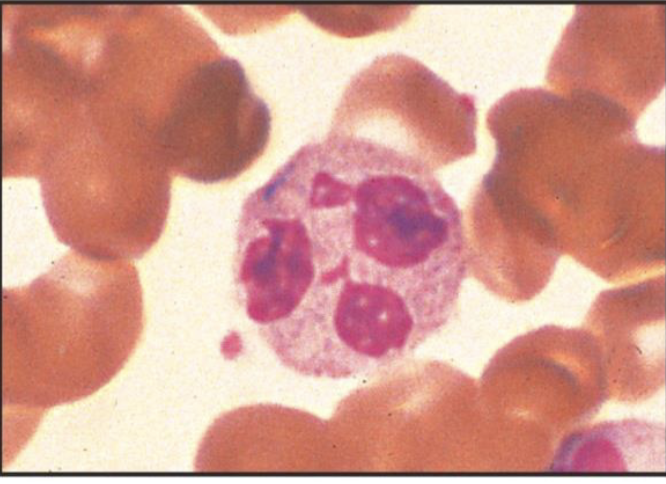
neutrophil
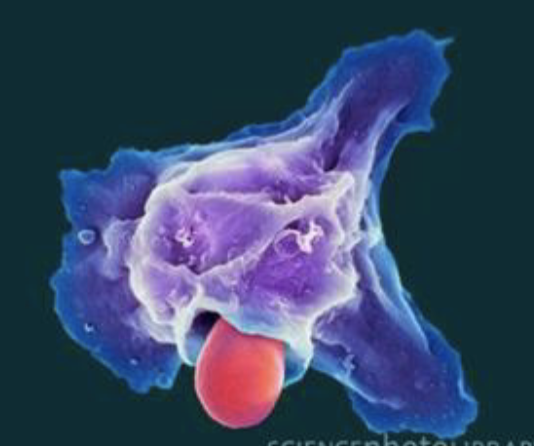
neutrophil eating staphylococcus
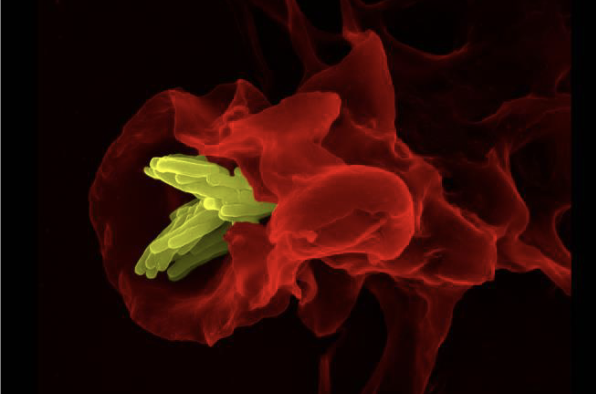
Macrophage eating M. tuberculosis
what are the cytotoxic cells that kill parasites that are too large to be ingested by phagocytes?
eosinophils
what are the major functions of eosionphils?
Eosinophils enter infected tissues from the blood
Killing of antibody-coated parasites via release of substances that are toxic to helminths
Eosinophils are especially important in…?
allergy, severe asthma, eczema (atopicdermatitis)
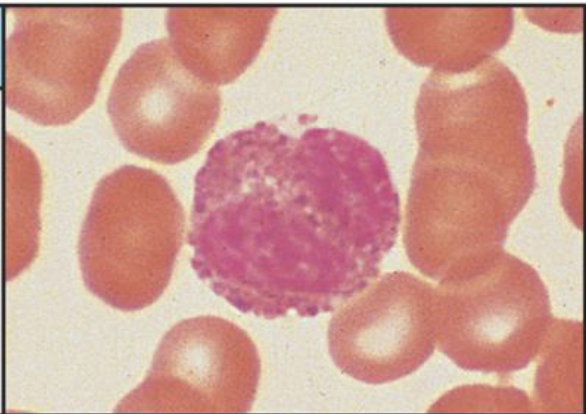
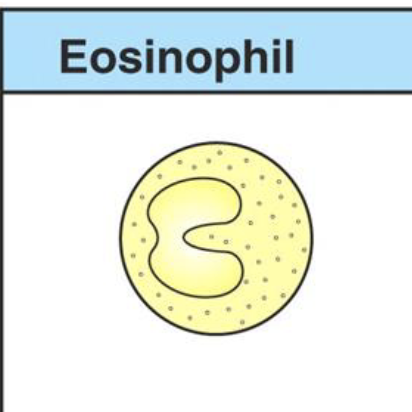
what cells are involved in responses to parasites and allergy?
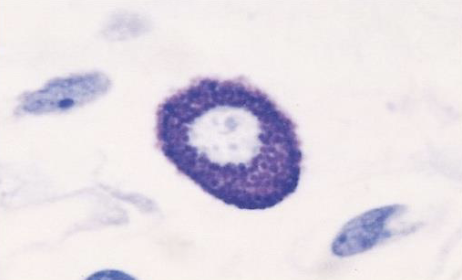
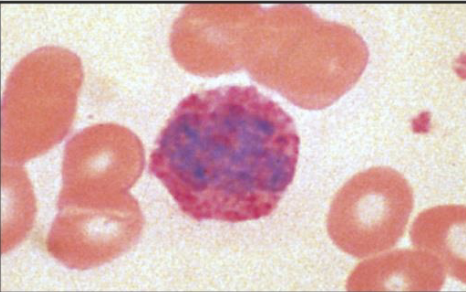
mast cells and basophils
where are mast cells found?
in connective tissues throughout the body
where are basophils found?
in blood and have similar function as mast cells
what are major functions of mast cells and basophils?
Release of granules containing histamine etc.
Especially import for helminths
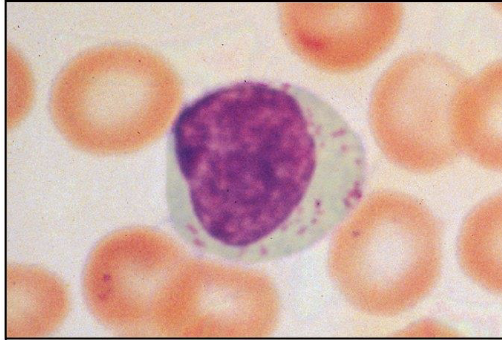
what cells remove tumor cells and infected cells?
natural killer cells
what are major functions of natural killer?
Can kill some virus-infected cells and some tumor cells via cytotoxic mechanisms
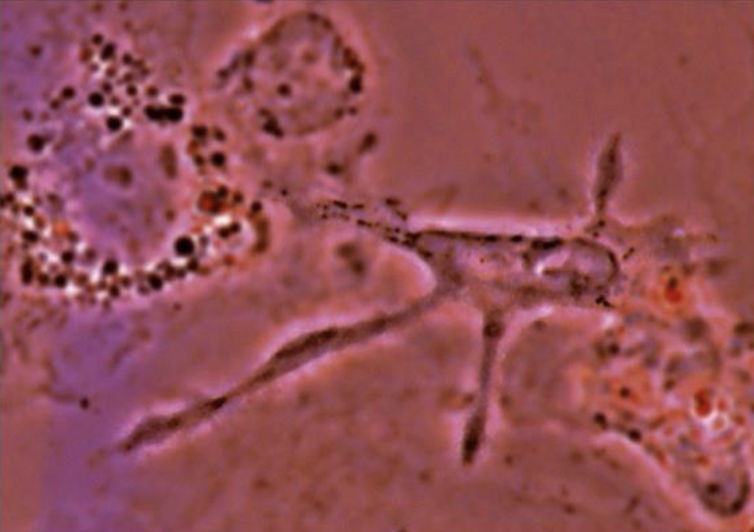
what are the major functions of dendritic cells?
Secrete cytokines that activate innate responses (Il-1, IL-6, TNF)
Antigen presentation to T cells
dendritic cells are referred to as ______ of the immune response
sentries
Dendritic cells (DC) are found in tissues and function to…?
detect infection and elicit innate and adaptive responses
HOW DOES THE BODY DETECT INFECTION?
Innate receptors recognize non-self structures that are
essential elements of pathogens
Innate immune cells have receptors for pathogens. These receptors are called ….?
pattern recognition receptors (PRR)
pattern recognition receptors (PRR) recognize structures called
pathogen associated molecular pattern (PAMP)
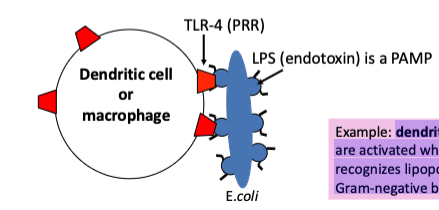
what’s an example of pattern recognition receptors (PRR) and pathogen associated molecular pattern (PAMP)?
dendritic cells and macrophages are activated when TLR-4 (toll-like receptor 4) recognizes lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from
Gram-negative bacteria.
how many pattern recgoition receptors do we know of?
a few dozen
When innate responses are not enough, dendritic cells (DC) elicit _________ responses
adaptive
WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF A MICROBE WAS ABLE TO AVOID PRR DETECTION?
If a microbe avoids pattern recognition receptor (PRR) detection, it may evade the innate immune response, potentially leading to unchecked infection and increased virulence
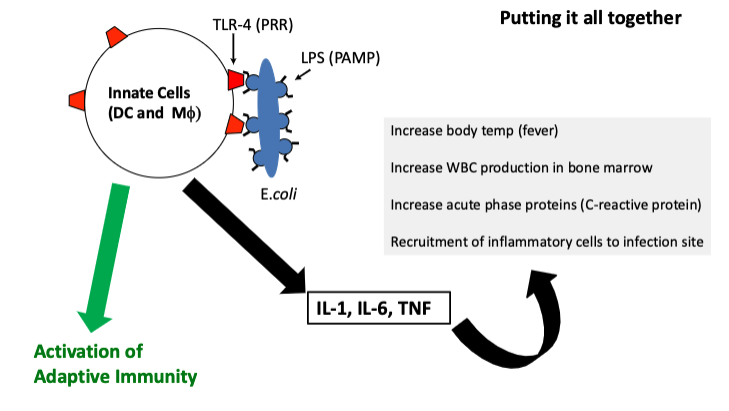
walk through this diagram
what is adaptive (acquired) immunity?
Defenses mediated by the clonal expansion and differentiation
of antigen-specific lymphocytes (B cells and T cells)
IF YOU ARE VACCINATED TODAY FOR EBOLA, WILL
YOU BE PROTECTED TOMORROW?
no. it takes time (12-18 days to a month depending on the infection)
what type of immunity requires sensitization by antigen (Ag)?
adaptive (acquired) immunity
what is an antigen?
“Antigen” is what we call the foreign substance (usually a microbe) that is recognized by lymphocytes
what type of immunity develops over days/weeks?
adaptive (acquired) immunity
what type of immunity has a response that is antigen-specific?
adaptive (acquired) immunity
what type of immunity results in immunological memory?
adaptive (acquired) immunity
adaptive immune response can be classified as:
humoral immunity
cell-mediated immunity (CMI)
what is humoral immunity?
mediated by antigen-specific antibodies produced by activated B lymphocytes (B cells)
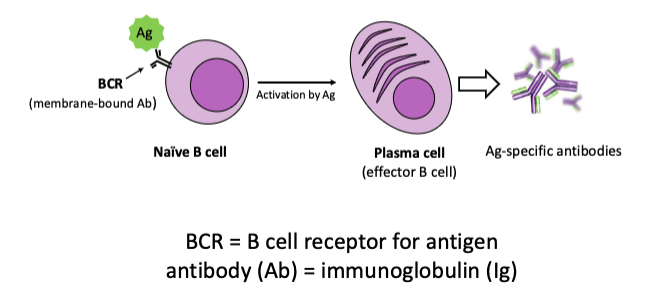
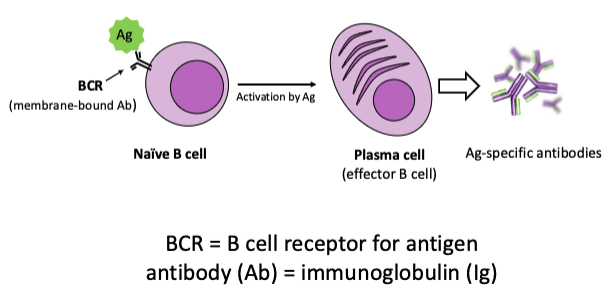
what type of immunity is this?
humoral immunity
what is cell-mediated immunity (CMI)?
mediated primarily by antigen-specific T lymphocytes (T cells)
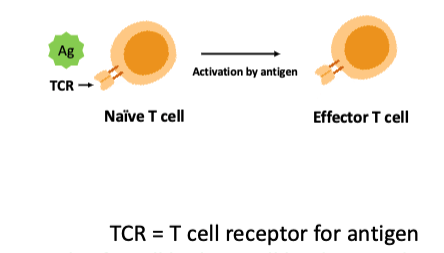
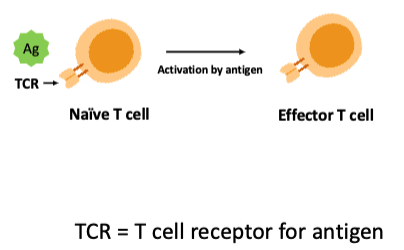
what type of immunity is this?
cell-mediated immunity (CMI)
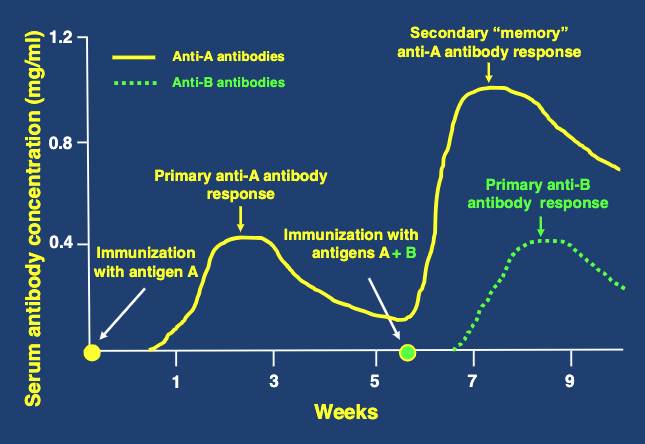
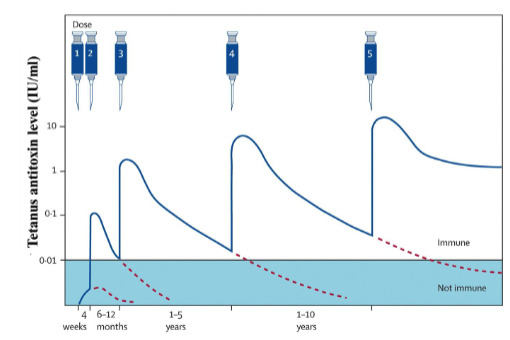
prime-boost antibody response to tetanus vaccination
what is the central paradigm of immunology?
clonal selection
Antigen-specific lymphocytes develop _______of exposure to antigen
before and independent
Antigen binds ________ and activates these cells to proliferate and form greatly expanded clones of antigen-specific ______ lymphocytes and ______ lymphocytes.
pre-existing antigen-specific lymphocytes
effector, memory
what is clonal deletion?
Lymphocytes that are specific for “self-antigens” are eliminated
Each lymphocyte clone has receptors that recognize…?
one specific antigen
what is clonal selection?
Proliferation and differentiation to produce effector cells and memory cells (both T and B cells)
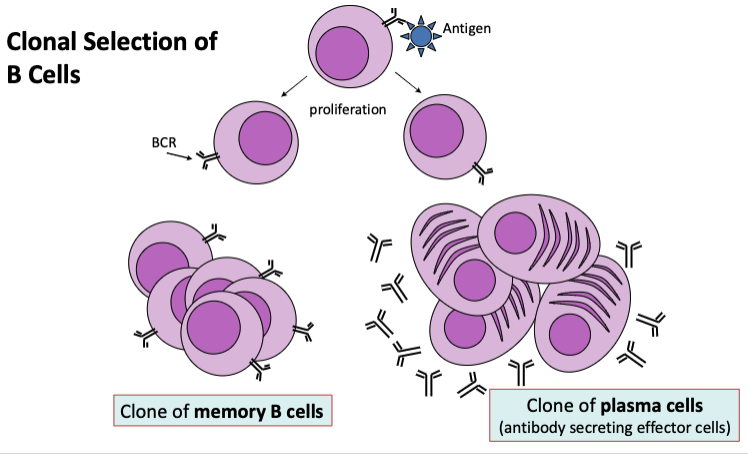
what are the primary lymphoid organs? (where B and T cells develop in absence of antigens)
Bone Marrow (B cell development)
Thymus (T cell development)
what are the secondary lymphoid organs? (where B and T cells go and wait for exposure)
Adenoid
Tonsil
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Peyer’s patches
what does it mean that antibody responses are polyclonal?
Polyclonal antibody responses involve the production of multiple antibody types by different B cell clones, each targeting the same antigen.
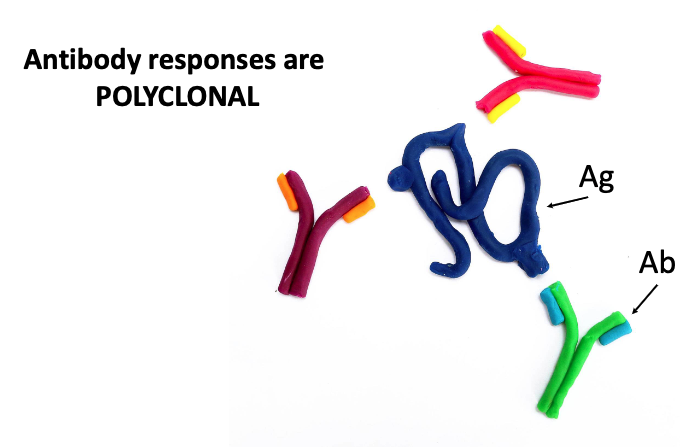
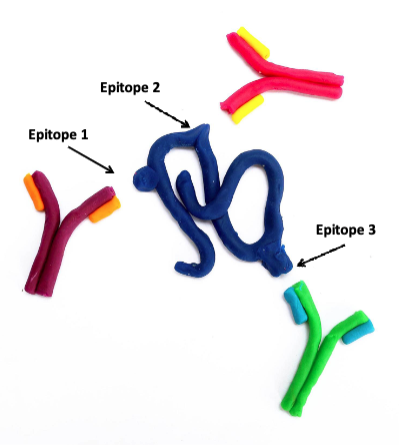
what does it mean that antibody binds to an epitope?
An antibody binds specifically to a distinct part of an antigen known as an epitope

what is this called?
Ag-Ab complex (immune complex)
do u have lymphocytes (both B and T cells) that have antigen-specific receptors for tetanus toxin?
yes
do you have serum antibodies specific for tetanus toxin?
yes (because we’ve been vaccinated)
do u have lymphocytes (both B and T cells) that have antigen-specific receptors for Ebola toxin?
yes
do you have serum antibodies specific for Ebola virus?
no (because you need exposure to antigen)