1.2.2 Makeup of Muscle & 1.2.5 Joints in Motion
1/7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
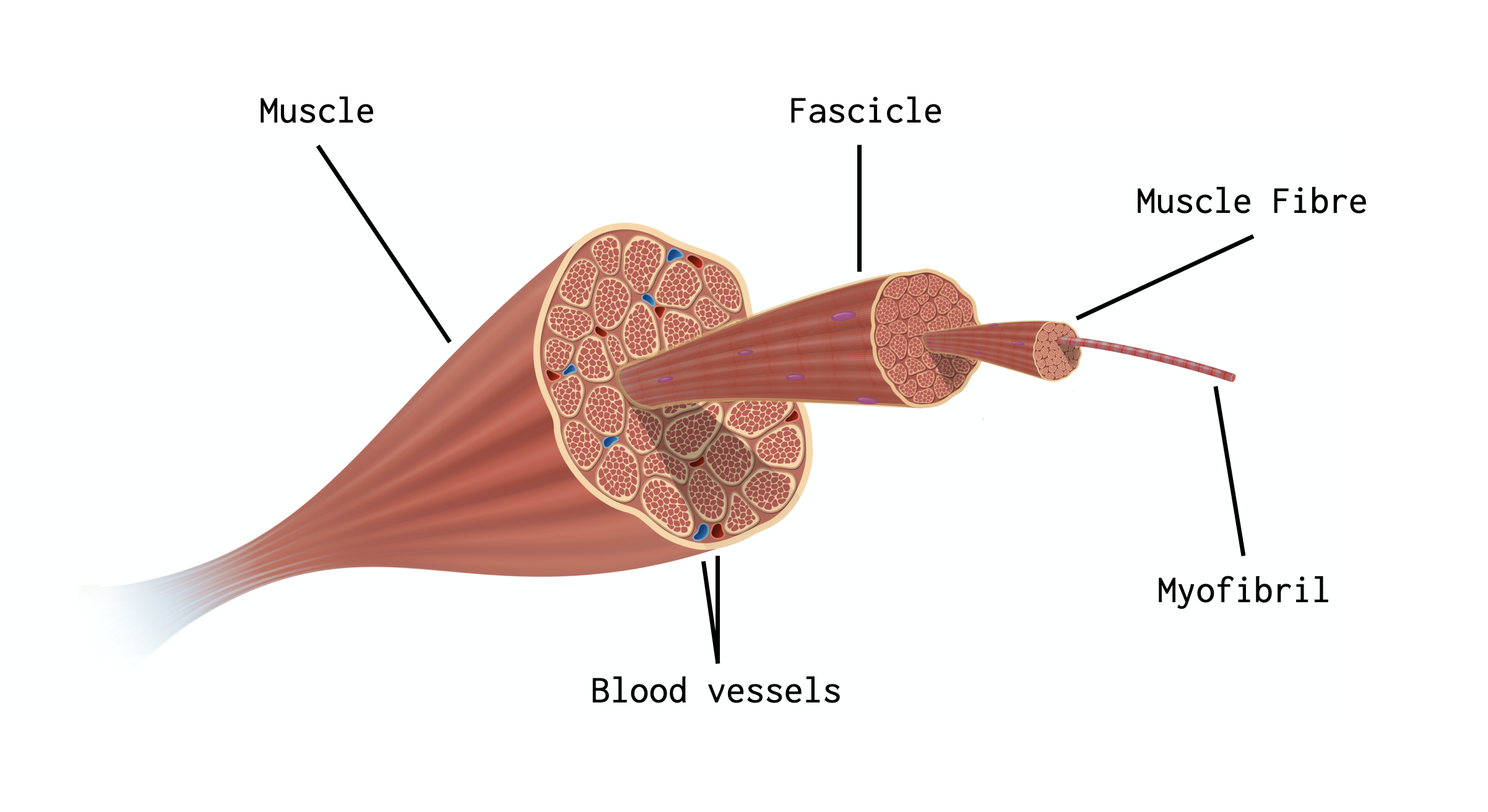
Muscle>Fasicle>Muscle Fiber>Myofibril
Epimysium covers muscle, Perimysium covers fasicle, Endomysium covers muscle fibers.
6 Muscle Rules
Muscles must have at least 2 attachments and must cross at least one joint
Muscles always “pull” and get shorter
The attachment that moves is known as the insertion; the attachment that remains stationary is known as the origin
Muscles that decrease the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as flexors; Muscles that increase the angle are known as extensors
Muscles work in opposing pairs
Muscle striations point towards the attachments and show the direction of the pull.
Sprains, Strains, Tears
Sprain: injury to ligament (connects bone to bone) due to overstretching
Strain: injury to tendon/muscle due to overstretching
Tear: serious injury when ligament/tendon is torn apart
7 classification categories of muscle names
Shape (for ex., trapezius)
Size (for ex., gluteus maximus)
Location (for ex., frontalis)
Direction of fibers (for ex., Obicularis Oculi)
Action (for ex., Flexor Carpi Ulnaris)
Origin+Insertion (for ex., Brachioradialis)
Number of attachment points (for ex., Biceps Brachii)
Types of Joints
Fibrous Joints: Fixed/immobile joint. Mostly made of cartilage
Cartilaginous Joints: Joint with some motion. Made of hyaline cartilage
Synovial Joints: Most common joint. Movable joint with fluid in between bones.
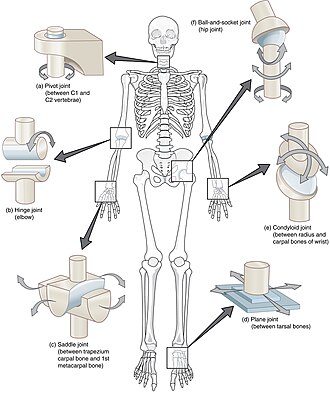
Types of Synovial Joints
Hinge Joint: Bends/straightens. Flexion/extension
Saddle Joint: Back and Forth, side to ride, no rotation
Ball and Socket Joint: Forwards/backwards, sideways, with rotation
Condyloid Joint: Up/down and side to side
Plane Joint: Gliding motion between 2 flat/slightly curved bones
Pivot Joint: Limited rotation around an axis
Types of Range of Motion Movements
Rotation: turns on a single axis
Circumduction: circular motion (makes a cone)
Elevation: moves up
Depression: moves down
Flexion: decrease angle (bending)
Extension: increase angle (straighten)
Abduction: moves away from midline
Adduction: moves towards the midline
Plantar flexion: toes down
Dorsiflexion: toes up
Types of Cartilage
Articular (Hyaline): Cushion joints, protect bone, supports weight. Found on ends of bone condyles
Elastic: Provides structural support. Found in the ear, nose, and epiglottis
Fibrocartilage: For shock absorption. Found in between vertebrae and in pelvis.
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that provides shape and support to various body parts and cushions bones (allowing for movement and flexibility).