Financial Accounting 1 chapter 1,2,3 review
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
External Users
Shareholders, Lenders, External Auditors, Nonmanagerial Employees, Regulators (People outside the company)
Internal Users
Purchasing managers, Human resource managers, Production managers, Research and development managers, Marketing managers
(People inside the company that use accounting info to make decisions for the company)
3 Factors of Fraud Triangle
Oppurtunity
Rationalization
Pressure
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
The set of accounting rules and practices used in the United States to prepare financial statements.
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
FASB sets GAAP, was given authory by SEC and works closely with them
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
Issues International Financial Reporting Standards(IFRS).
• Standards identify preferred accounting practices.
• Standards are similar to, but sometimes different from U.S. GAAP.
General Principles
the assumptions, concepts, and guidelines for preparing financial statements.
Specific Principles
detailed rules used in reporting business transactions and events.
Measurement Principle (Cost principle)
Accounting information is based on actual cost. Actual cost is considered objective.
Revenue Recognition Principle
1. Recognize revenue when goods or services are provided to customers and
2. at an amount expected to be
received from the customer.
Expense Recognition Principle (Matching Principle)
A company has to record its expenses when incurred to generate the revenue reported
Full Disclosure Principle
A company reports the details behind financial statements that would impact users’ decisions in the notes to the financial statements (includes information about assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, pending lawsuits, and incomplete transactions)
Going-Concern Assumption
The business is presumed to continue operating instead of being closed or sold
Monetary Unit Assumption
Transactions and events are expressed in monetary, or money, units
Time Period Assumption
The life of a company can be divided into time periods, such as months and years
Business Entity Assumption
A business is accounted for separately from other business entities, including its owner
Cost-Benefit Constraint
Only information with benefits of disclosure greater than the cost need to be disclosed
Materiality Constraint
Only information that would influence the decisions of a reasonable person need to be disclosed
The accounting equation
Assets=liabilities+ equity

Assets
Resources a company owns or controls that are expected to carry future benefit
Liabilities
Creditors’ claims on assets; claims reflect obligations to transfer assets or provide products or services to others
Owners Capital (Equity 1/4)
Owner investments are inflows of cash and other net assets from owner contributions; increases equity (Credit)
Revenues (Equity 2/4)
Total amount of money business earns from completing sales or services in a period of time; increases equity (Credit)
Owner Withdrawals (Equity 3/4)
Outflows of cash and other assets to owners for personal use; decrease equity (Debit)
Expenses (Equity 4/4)
Cost of assets or services used to earn revenues; decreases equity (Debit)
Equity
Owner’s claim on assets; assets- liabilities; also called net assets or residual equity (Equity is made up of 4 parts; Owners capital, Revenues, Owner Withdrawals, Expenses)
Income Statement
Describes a company’s revenue and expenses and computes net income or loss over a period of time (First financial statement)

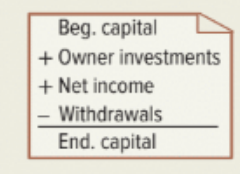
Statement of Owner’s equity
Explains changes in owner’s equity from owner investments, net income (or loss), and any withdrawals over a period of time (2nd financial Statement)
Balance Sheet
Describes a company’s financial Position (Types and amounts of assets, liabilities, and equity) at a single specific point in time (3rd financial statement)
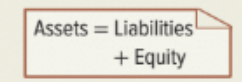
Statement of Cash Flows
Identifies cash inflows (receipts) and cash outflows (payments) over a period of time

Return on assets (ROA)
Net income divided by the average total assets invested
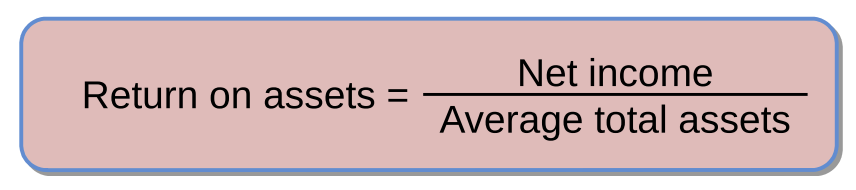
Accrual basis
Revenues are recorded when products or services are delivered, and records expenses when incurred; most companies use this and is compliant with GAAP
Cash basis
Revenues are recorded when cash is received and expenses are recorded when cash is paid (barely used; only some small companies use it; not compliant with GAAP)
depreciation
Instead of expensing the cost of a plant asset (equipment, building, cars, etc.) in the year it is purchased we allocate, or spread out, the cost over their expected useful lives
Straight line depreciation formula

Unearned revenue
Cash received in advance of providing products or services
Accrued expense
costs incurred in a period that are both unpaid and unrecorded
Accrued revenue
revenues earned in a period that are both unrecorded and not yet received in cash or other assets
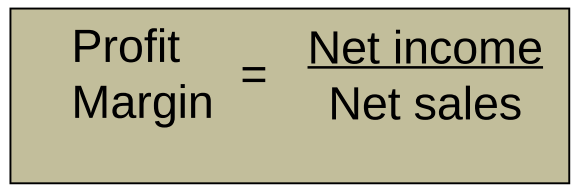
Profit margin
The profit margin ratio measures the company’s net income to net sales