Neuro 7: meninges, ventricular system, CSF
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
subarachnoid space
where is CSF found?
periosteal layer (attached to inner surface of cranium)
meningeal layer (adheres to arachnoid mater)
what are the two layers of the dura mater in the cranium?
false (attached to the inner surface of the cranium but not attached to the spinal cord = epidural space)
T/F: the dura mater is always attached to bone
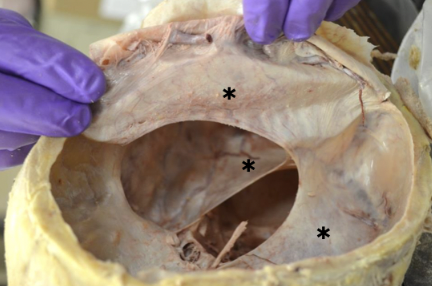
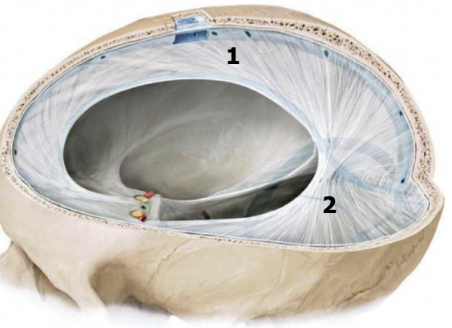
dural reflections/folds
projections of the dura mater that form septa to provide structure support
dural venous sinuses
venous channels between the two layers of the dura mater
internal jugular vein (IJV)
where do the dural venous sinuses drain?
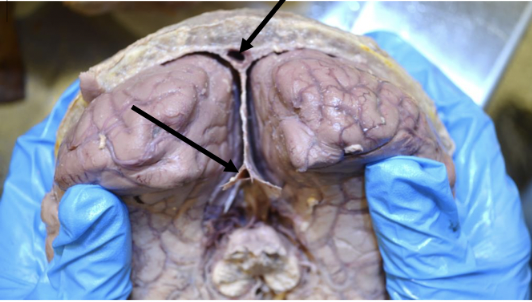
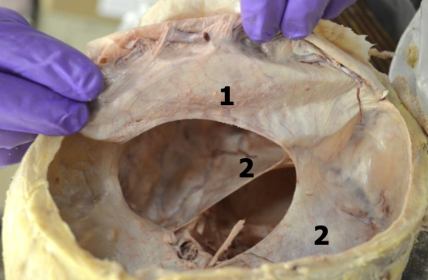
falx cerebri
midline projection located in the longitudinal fissure that separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres; attaches to the crista galli anteriorly
tentorium cerebelli
transverse projection between the occipital lobes and the cerebellum; attaches anteriorly to the clinoid process and laterally to the petrous portion of temporal bone
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
falx cerebelli
median projection between the cerebellar hemispheres
diaphragma sella
projection that forms a roof over the pituitary fossa and has a opening in it for the infundibular stalk of the pituitary gland
diaphragma sella
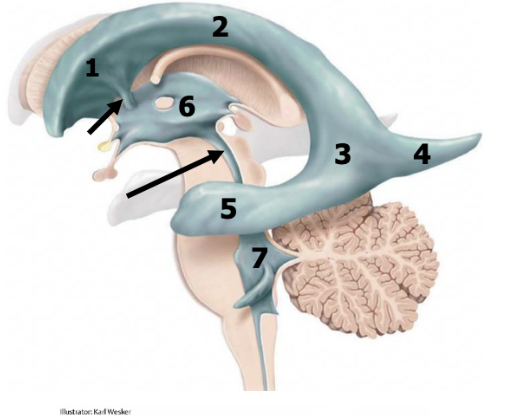
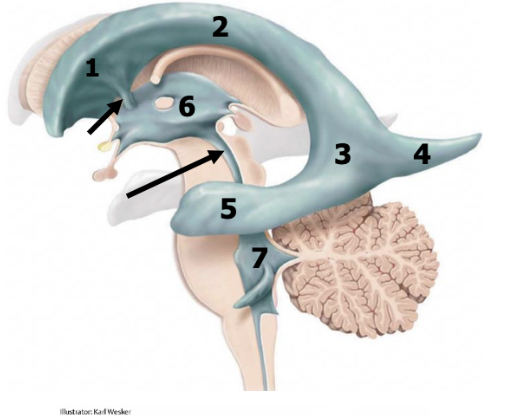
black arrow
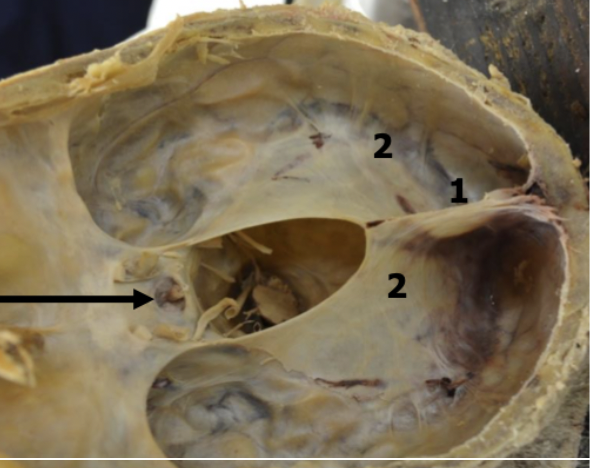
arachnoid trabeculae
thin CT septa on the inner surface of the arachnoid that attach to the pia mater
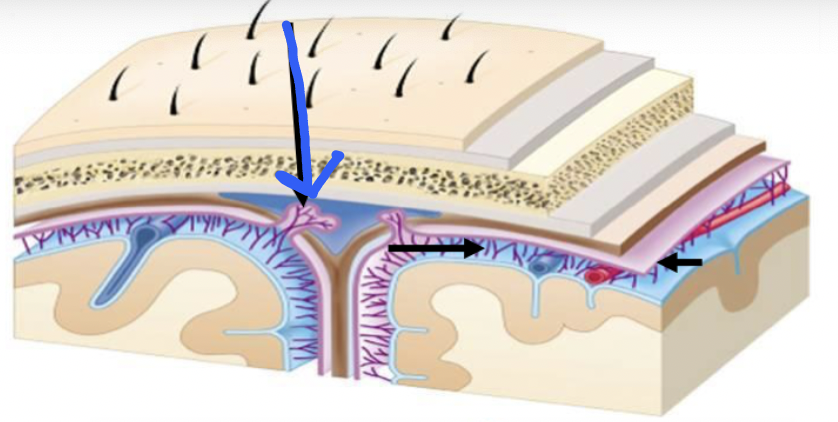
arachnoid granulations
mushroom-shaped structures that project through the dura into the dural venous sinuses; function as one-way valves to transfer CSF
arachnoid trabeculae
black arrows
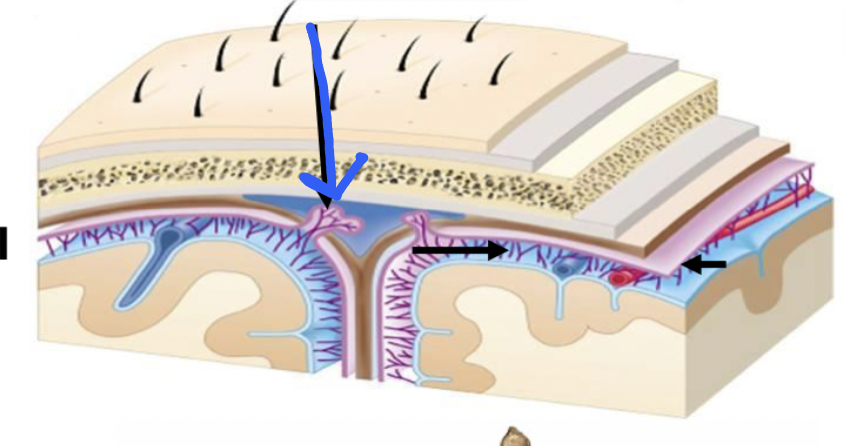
arachnoid granulations
blue arrow
filum terminale externum
fibrous bands that connects the dura mater to the coccyx in the spinal cord
lumbar cistern
formed by the subarachnoid space from the conus medullaris to the second sacral vertebra; location of a spinal tap
denticulate ligaments
fibrous bands that attach from the pia mater to the arachnoid mater in the spinal cord
filum terminale internum
pia mater extension that attaches to the dural sac at the tip of the conus medullaris
middle meningeal
primary arterial supply to the meninges
meningeal branches from opthalmic artery
ethmoidal arteries
additional blood supply to the anterior cranial fossa besides the middle meningeal artery
ascending pharyngeal artery
occipital artery
vertebral artery
additional blood supply to the posterior cranial fossa besides the middle meningeal artery
all three branches of trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular)
what innervates the anterior and middle fossa?
dorsal roots of C2-C3
what innervates the posterior fossa?
tentorial nerve from ophthalmic CN V1
what innervates the tentorium cerebelli?
sympathetic from superior cervical ganglion (autonomic fibers)
what innervates the vessels of the dura
recurrent meningeal nerve
what innervates the spinal dura in every level?
ependymal cells
what cells line the ventricles?
choroid plexus
vascularized cuboidal epithelial cells with microvilli
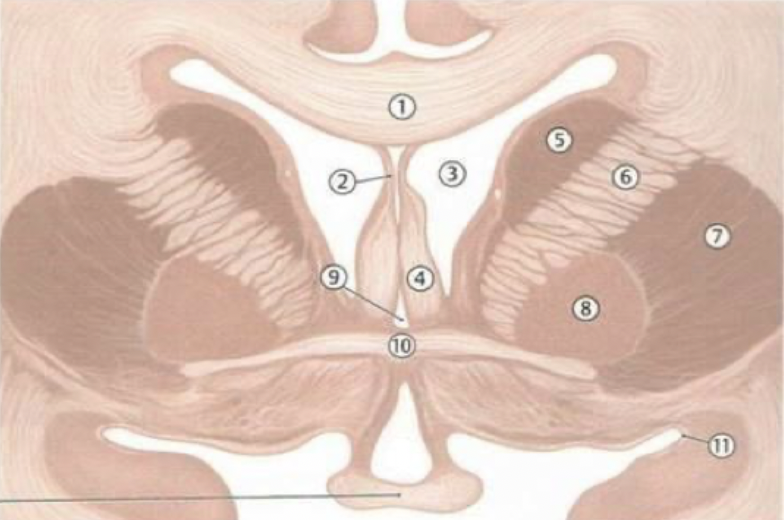
anterior/frontal horn of lateral ventricles
1
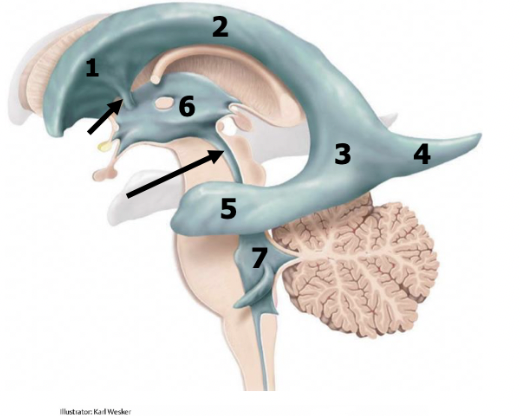
body of lateral ventricles
2
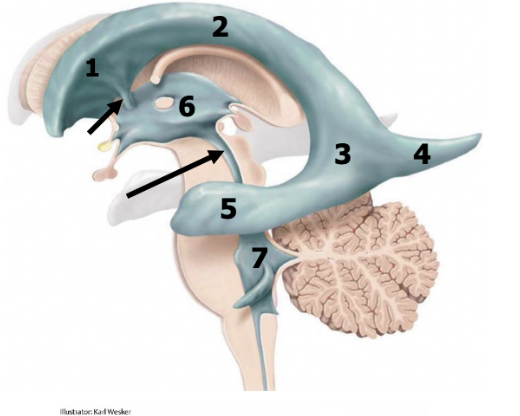
atrium
3
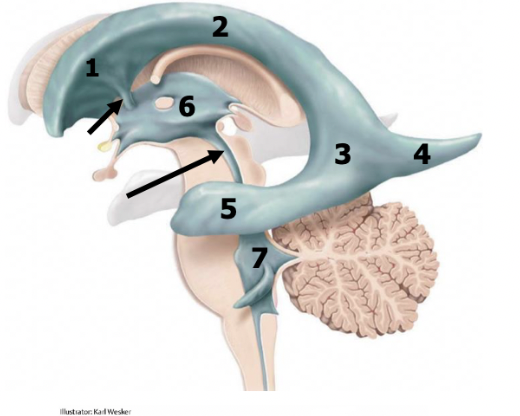
posterior/occipital horn (occipital lobe)
4
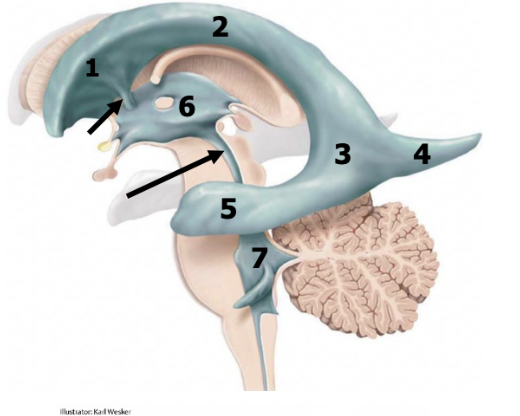
inferior/temporal horn (temporal lobe)
5
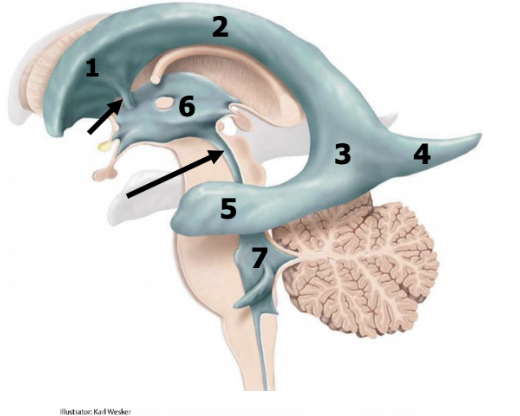
2 interventricular foramens
red arrow
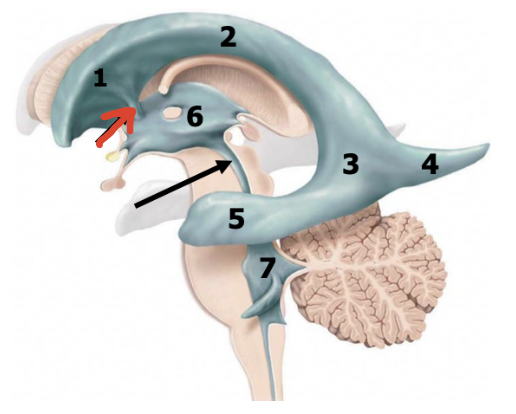
third ventricle (diencephalon)
6
cerebral aqueduct
black arrow
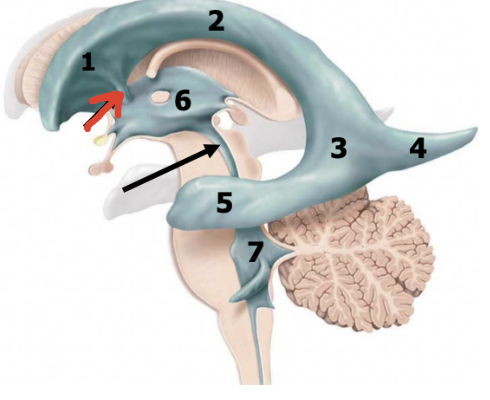
fourth ventricle (pons and medulla)
7
corpus callosum
1
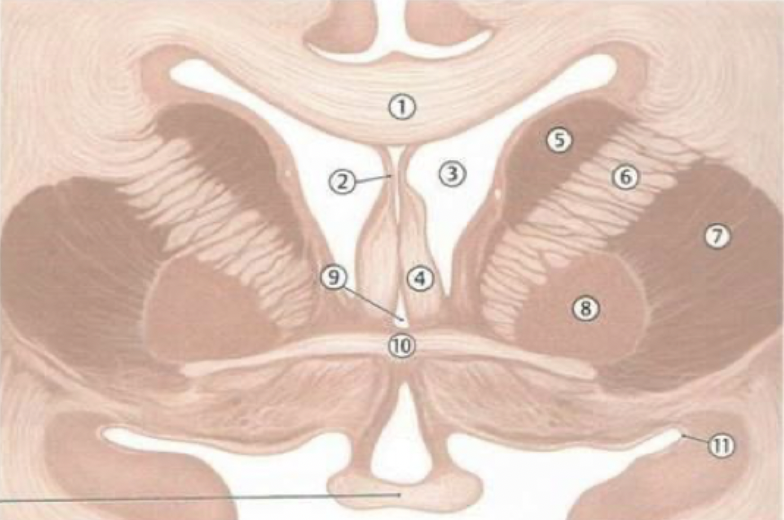
septum pellucidum
2
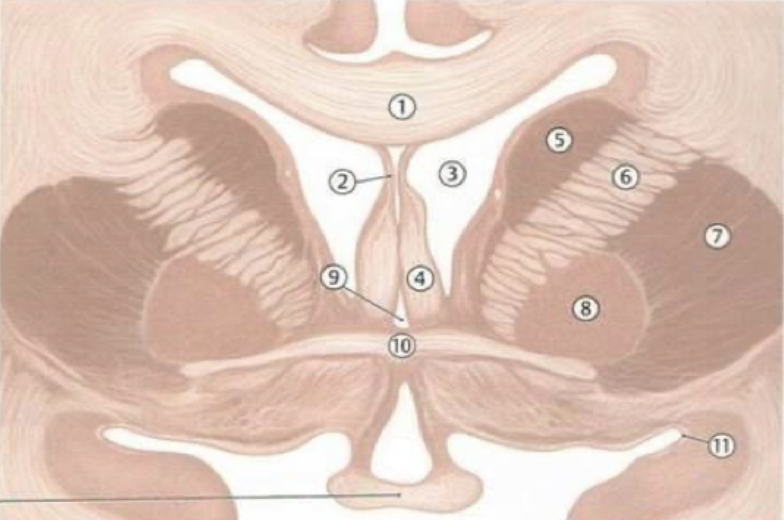
fornix
4
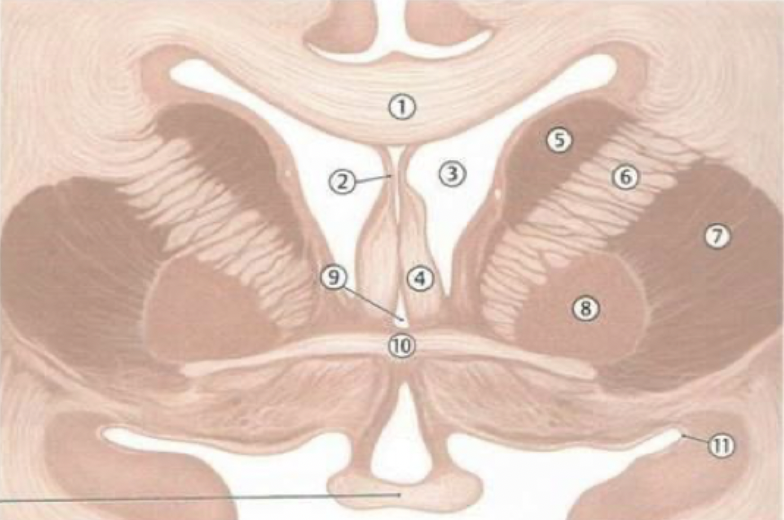
lateral ventricles
3
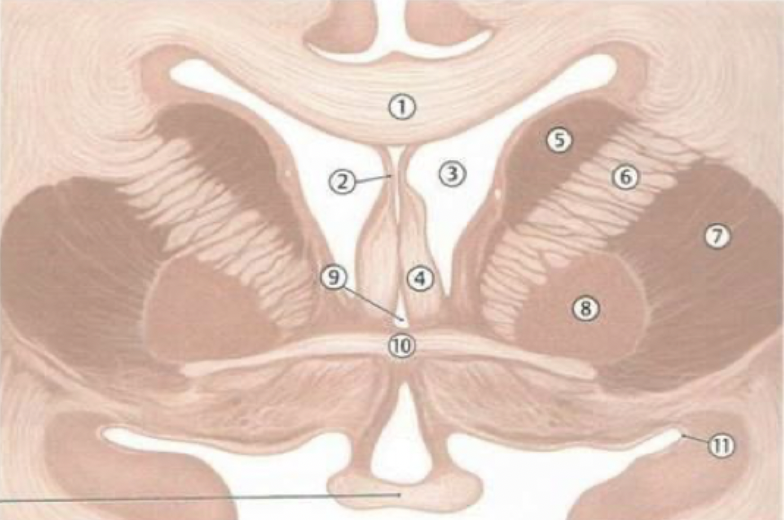
caudate nucleus
5
thalamus
red arrow
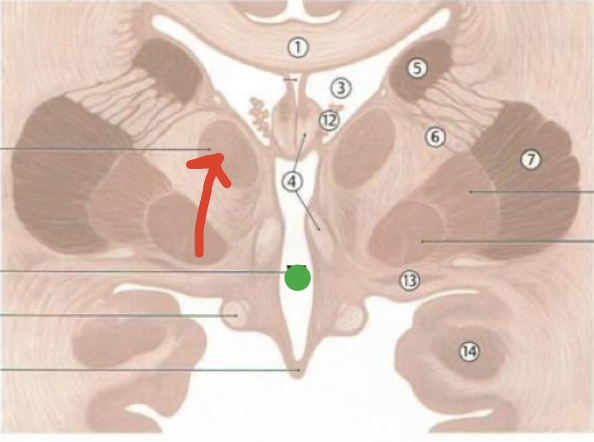
third ventricle
green dot
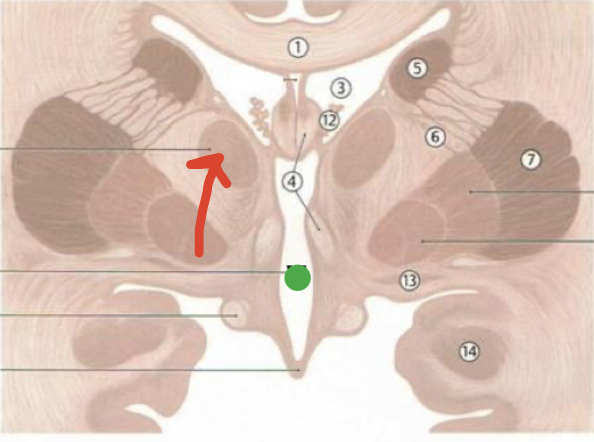
corpus callosum
1
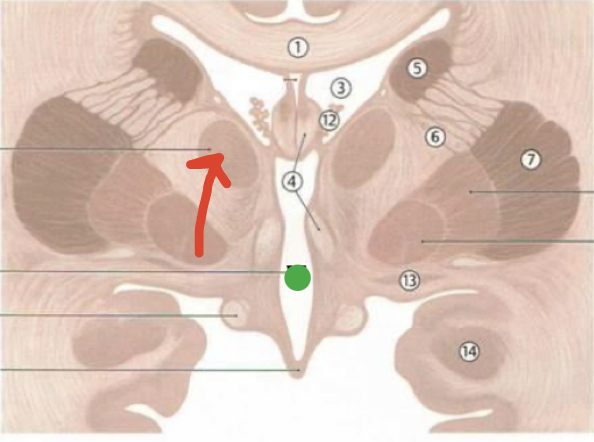
lateral ventricles
3
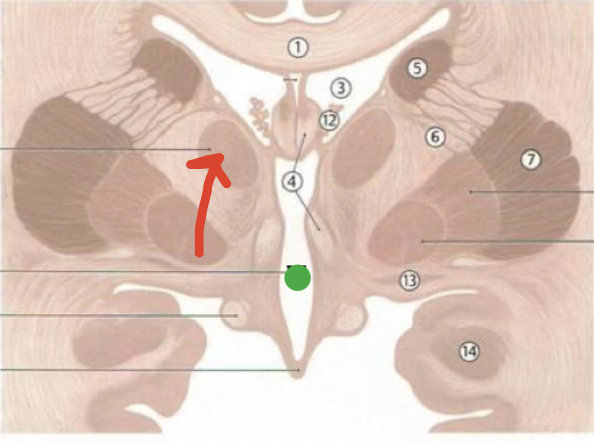
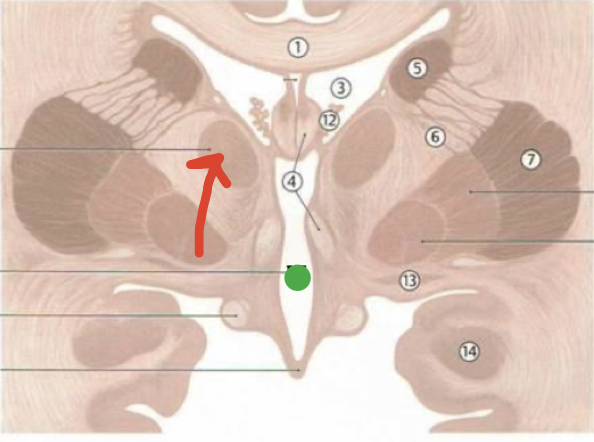
fornix
4
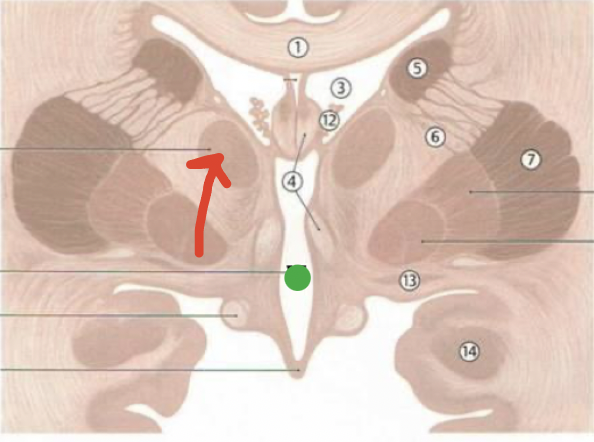
choroid plexus
12
one
how many third ventricles?
2
how many lateral ventricles
third ventricle
where is the largest choroid plexus?
lateral ventricles
interventricular foramen (foramen of munro)
third ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
fourth ventricle
subarachnoid space
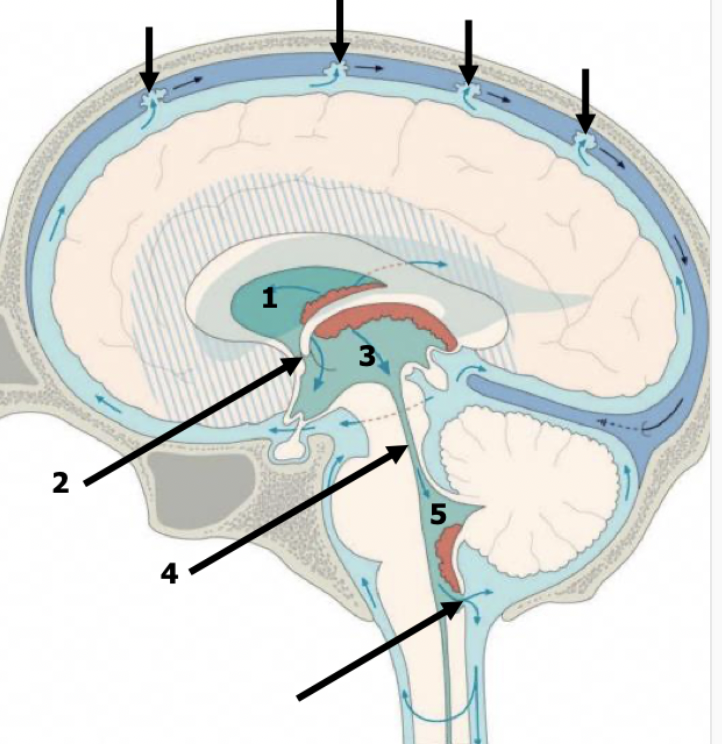
describe the flow of CSF
tight junctions (active transport only)
what kind of junctions between the cells in the blood brain barrier
rupture of middle meningeal artery due to fracture of the temporal lobe
most common cause of epidural hematoma?
kids
epidural hematomas are more common in?
subdural
hematoma between the dura and arachnoid
rupture of bridging veins (as it leaves the subarachnoid space to enter the dura)
what is the most common cause of subdural hematomas?
elderly (brain atrophy from aging and alcohol)
subdural hematomas are more common in ?
head trauma
rupture of intracranial aneurysm (non-traumatic)
most common cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage
arachnoid villa cells
where do meningiomas usually start?
cranial cavity (90% vs. 9% in spinal cord)
where are meningiomas most commonly found?