Respiration flash arc tidal volume ERV
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
Tidal Volume (TV)
the amount of air you move into or out of your lungs during a single respiratory cycle under resting conditions
2
New cards
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
the amount of air that your can voluntarily expel after you have completed a normal, quiet respiratory cycle
3
New cards
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
the amount of air that you can breathe in over and above the tidal volume
4
New cards
Inspiratory Capacity (IC)
the amount of air that you can draw into your lungs after you have completed a quiet respiratory cycle
5
New cards
Vital Capacity (VC)
the maximum amount of air that you can move into or out of your lungs in a single respiratory cycle
6
New cards
Residual Volume (RV)
the amount of air that remains in your lungs even after a maximal inhalation
7
New cards
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
the total volume of your lungs
8
New cards
anatomic dead space
the volume of air filling the parts of the respiratory tract where gas exchange does not occur (150mL)
9
New cards
TV+ERV equals
expiratory capacity
10
New cards
TV+IRV equals
inspiratory capacity
11
New cards
IRV+TV+ERV equals
vital capacity
12
New cards
VC+RV equals
total lung capacity
13
New cards
500mL in, 500mL out equals
tidal volume
14
New cards
these muscles are used during normal inspiration
external intercostals
diaphragm
diaphragm
15
New cards
muscles used during forced exhalation
internal intercostals
external and internal obliques
rectus abdominus
external and internal obliques
rectus abdominus
16
New cards
muscles used during forced inhalation
sternocleidomastoid
pectoralis minor
pectoralis minor
17
New cards
TLC calculation
TLC = FRC + IC
\
(Total lung capacity = functional residual volume + inspiration capacity )
\
(Total lung capacity = functional residual volume + inspiration capacity )
18
New cards
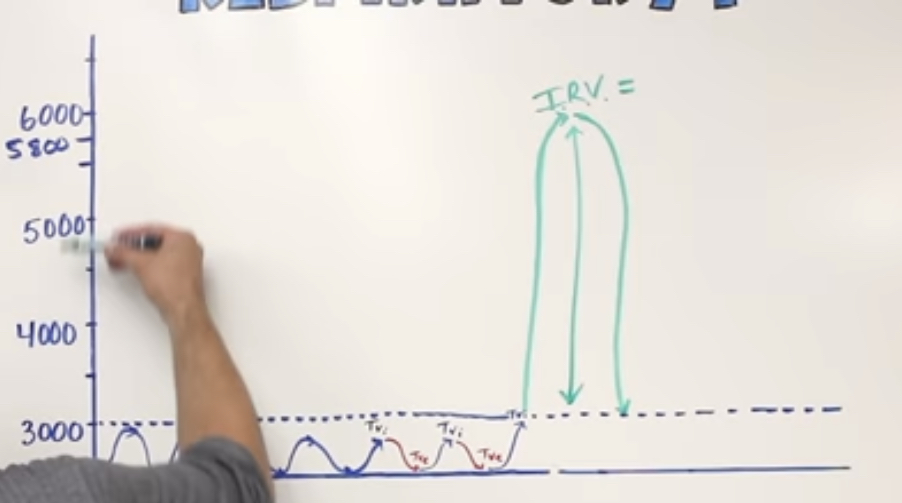
(Inspired volume) 6000-3000(tidal volume) = 3000