plcy 581
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
cross sectional data
collects information from multiple different subjects at a single point in time
longitudinal data
panel data
pooled cross section data
a type of data that combines multiple cross-sectional datasets gathered at different times, allowing for comparisons across time and subjects.
time series data
Data collected at successive points in time
meta data
Data that provides information about other data, helping to organize, manage, and utilize the primary dataset.
intercept surveys
surveys conducted at a specific point in time to assess respondents' immediate reactions or behaviors.
household surveys
Surveys conducted to gather data on the characteristics, behaviors, and opinions of households.
Group self-administered surveys
Surveys where a group of participants complete questionnaires independently, usually in a designated setting. This method allows for anonymity and convenience in gathering responses.
Web surveys
Surveys conducted via the internet to collect information from respondents.
Establishment surveys
Surveys conducted to collect data from businesses or organizations, focusing on their operations, employment, and economic characteristics.
r-squared
variation in the dependent variable predicted or explained by all independent variables combined
internal validity
A measure of how well a study's evidence supports a claim about cause and effect
external validity
The extent to which the results of a study can be generalized beyond specific conditions of the study
primary research
Research that involves the collection of original data directly from subjects or experiments
context-dependent mediation
A psychological phenomenon where the effect of a treatment or condition on an outcome varies depending on the context in which it occurs.
belmont report
respect for persons, beneficence, justice
secondary research
Research that involves the synthesis and analysis of existing data or literature without collecting new data directly.
normative question
a value judgment expressing an opinion about what should or ought to be
positive question
a factual inquiry seeking to understand reality or gather evidence without subjective judgment.
first condition for causal interference
Cause must precede its anticipated effect in time.
second condition for causal interference
Variation in the cause must correlate with variation in the effect
third condition for causal interference
Researcher must rule out all other plausible explanations for the hypothesized cause and effect relationship
counterfactual
A scenario that indicates what would have occurred in the absence of the causal factor.
average treatment effect
The average difference in outcomes between units receiving the treatment and those who do not, reflecting the overall impact of the treatment.
theory
generates a testable hypothesis and identifies key variable
moderator variable
a variable that affects the strength or direction of the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
intervening variables
variables that mediate the relationship between independent and dependent variables, explaining how or why the effect occurs.
control variables
variables that are kept constant to accurately measure the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
unit of analysis
Objects or things described by variables in a model
logic models
Communicate underlying theory or set of assumptions, visual representation of relationship, links in a chain of reasoning
FINERMAPS
Feasible • Interesting • Novel • Ethical • Relevant • Manageable • Appropriate • Potential value and publish ability • Systematic
basic model
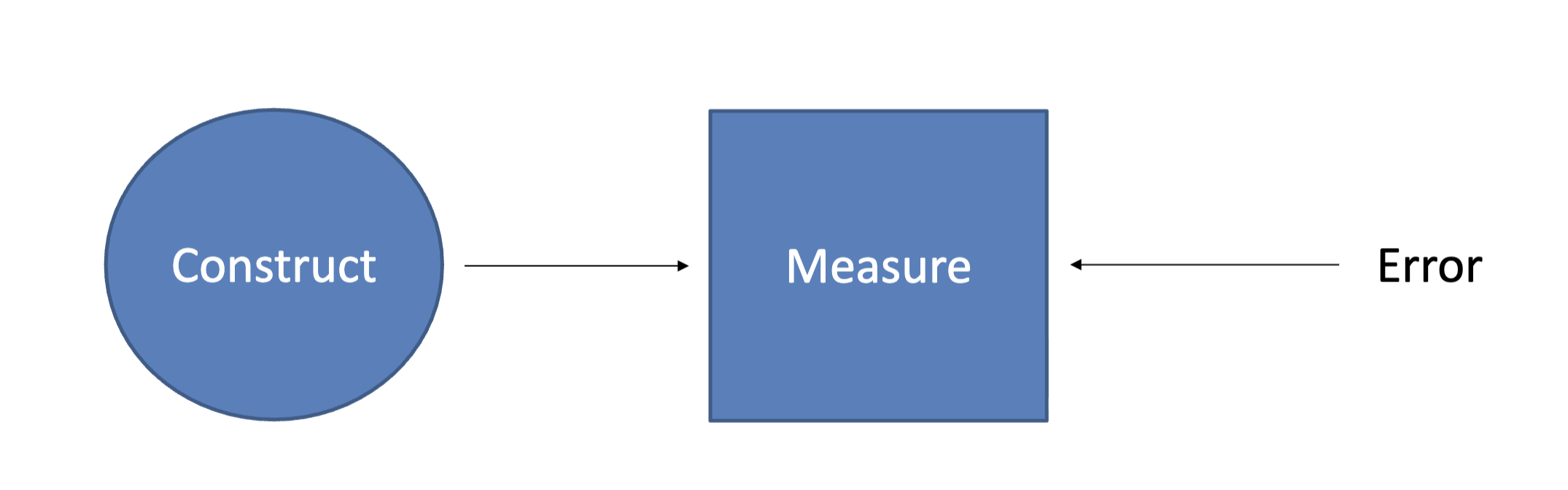
conceptualization
The process of defining and clarifying concepts or ideas in a way that provides a foundation for research or practice.
dimension
A measurable extent of a concept or framework that can be analyzed or observed.
proxy
A variable or indicator used to represent or estimate another variable that is difficult to measure directly.
operationalization
The process of defining how a concept will be measured or quantified in research, providing specific procedures to collect data.
protocol
A formal set of rules or procedures that outline the steps to be followed in conducting research
Face validity
Content validity
The degree to which a test or measure represents all aspects of the concept being studied, ensuring that it covers the entire domain of the construct.
concurrent validity
predictive validity
convergent validity
discriminant validity
construct validity
snowball probability
A sampling technique where existing participants recruit future subjects from among their acquaintances, commonly used in studies with hard-to-reach populations.
nomological
response rate
(contact rate X cooperation rate)
non-response bias
A type of bias that occurs when certain participants do not respond to a survey or study
standard error
A measure of the variability or dispersion of a sample statistic, often used to quantify the uncertainty associated with a sample estimate.
Systematic sampling
A sampling method where samples are selected from a larger population according to a random starting point and a fixed, periodic interval.
Stratified sampling
A method of sampling where the population is divided into distinct subgroups or strata, and samples are taken from each stratum to ensure representation within the overall sample.
Disproportionate sampling
A sampling method where strata are selected in unequal proportions, often used to emphasize certain subgroups within the population.
Multi-stage sampling
A sampling technique that combines two or more sampling methods. It involves selecting groups or clusters, and then sampling within those selected groups.
cluster sampling
A sampling method where the population is divided into clusters, usually geographically, and a random sample of these clusters is selected for analysis.
microdata
Data that contains individual-level information about respondents or subjects from a larger dataset
aggregate data
Data that is collected and presented in summary form, often used for statistical analysis and reporting.
multilevel data
Data collected at multiple levels of analysis, often used in hierarchical modeling to examine relationships across different units.
panel data
A type of data collected from the same subjects over multiple time periods, allowing for analysis of changes over time.
a
constant/Predicted value of the dependent variable when all
independent variables are 0
Multicollinearity
A situation in regression analysis where two or more independent variables are highly correlated, making it difficult to isolate their individual effects on the dependent variable.
Dummy variables
Variables used in regression analysis to represent categorical data, allowing for inclusion of qualitative predictors.
Interaction term
Allows you to test whether the effect of one variable on the dependent variable depends on the level of another variable
Endogeneity
when a predictor (independent) variable is correlated with the error term
Exogenity
the condition where an independent variable is uncorrelated with the error term, ensuring unbiased estimates in regression analysis.
Internal validity
the extent to which a study accurately establishes a causal relationship between variables, free from confounding factors.
External validity
the degree to which the results of a study can be generalized to, or have relevance for settings, people, times, and measures beyond the study itself.
Reverse causation
is when the outcome appears to happen before the exposure
Spurious correlation
where two variables appear to be causally related, but this
relationship is actually due to a third, unaccounted for variable