Surveying Measurements and Angle Correction
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering surveying measurements, angle adjustments, and triangulation techniques.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Azimuth (Z)
Measured clockwise from true north (0°); Ranges from 0°– 360°.
Bearing
Always given as an acute angle (<90°); Uses compass directions: e.g., N30°E or S75°W.
Traverse Adjustment
Used to close polygon loops for location/path surveys.
Angle Correction Rule
Angle opposite longer side gets smaller; Angle opposite shorter side gets larger.
Length Correction Rule (Proportional)
Distribute corrections in proportion to segment lengths.
Compass Rule
Used to distribute coordinate (Δx, Δy) corrections proportionally.
Bowditch Rule
Same as Compass Rule; Assumes equal precision in angle and distance measurements.
Triangulation / Intersection
Used when you can measure angles but not distances. Uses ASA (Angle-Side-Angle): Two angles and the included side known.
Resection
Used to find unknown location from known points; SAS (Side-Angle-Side): Two sides and included angle known.
Mixture Case (SSA)
Two sides and an angle not between them; Can result in ambiguous cases (2 possible solutions).
Leveling
Process of determining height differences between points; Based on optical leveling and backsight/foresight measurements.
Interior angles
(n-2) x 180
Exterior angles:
(n+2) x 180
Deflection angles (full circle):
2π
Sum of given angles
interior angles traverse - the total of all interior angles of a polygon
correction per angle
misclosure / polygon sides
azimuth to bearing
the conversion from a clockwise angle measured from true north to a direction expressed in the format of degrees east or west of north.
law of sines
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
total linear misclosure
like taking the magnitude
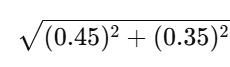
relative precision
total distance / total misclosure
systematic error
a consistent error that occurs in measurements, often due to faulty equipment or an incorrect measuring process, leading to biased results.
random error
an unpredictable error that occurs due to various factors such as environmental changes or human variability, affecting the precision of measurements.