Fundamentals of Microbiology
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 1 (1/13-1/15)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are microbes?
Any single-celled living creature too small to see (Bacteria, archaea, yeast, viruses)
What are the three laws of microbiology
Microbes are…very small, everywhere, they rule
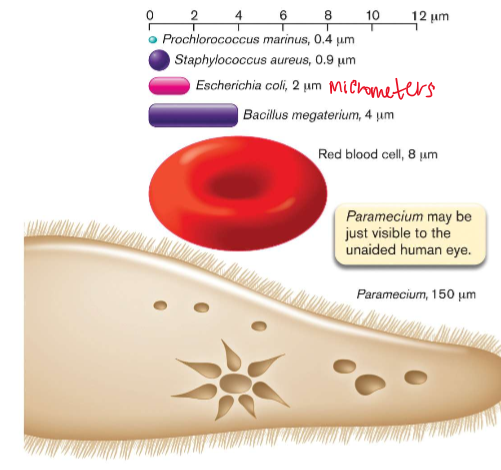
What is the average size of microbes?
Microbes range in size
0.4 micrometers (Prochlorococcus marinus) - 150 micrometers (Paramecium)
(Human hair is 50 micrometers)
Largest bacterial cells
Thiomargarita namibiensis
Thiomaragarita magnifica
How do microbes constitute biomass?
Equal to amount of carbon produced by plants, 10x all nitrogen and phosphorous produced by plants (Microbes fix nitrogen)
Where are microbes found?
Everywhere! Food, surfaces, soil, water, air, below ground
How many bacterial species are on our fingertips?
Around 150!
How do microbes help us?
Microbes help us digest food and fight off pathogens, etc.
What are extremophiles?
Microbes that can survive/thrive in extreme environments (Temp, pressure, pH, etc.), but not all microbes can
What is the morphology of bacterial cells? Is it a good predictor of evolutionary relationships?
Very limited (Three shapes: coccus, bacillus, spirillum)
No, distantly related species could look similar (Practice tree reading)
Shape: Coccus
Sphere
Shape: Bacillus
Rod
Shape: Spirillum
Spiral
What are the trade-offs in bacterial shape?
Fastest for swimming, easiest to make, best for maneuverability
What are the advantages of small bacterial cells.
Higher surface area/volume ratio (Exchange nutrients, remove waste), faster growth (less energy), easier movement (diffusion)
The movement in large cells?
Requires energy (vesicle trafficking)
Prokaryotic cell is the same size as mitochondria
What is the lower limit of microbial cell size?
All living things has to have chromosomes and proteins (minimum 300 genes) around 0.02 micrometeres
What does the name of this microbe tell us about its shape and function: Deinococcus radiodurans
Shape: Sphere (Coccus)
Function: Survive high levels of radiation (Repairs shattered DNA)
What does the name of this microbe tell us about its shape and function: Bacillus infernus
Shape: Rod (Bacillus)
Function: Survive harsh-like conditions (2 miles deep, no light, oxygen, high pressure, high temperature)
What does their biomass, persistence, and metabolic diversity tell us about microbes?
The unique role they play in running the planet (Nutrient cycles)
Microbes fix Nitrogen (Nitrogen → ammonium → nitrite/nitrate →plants)
Prochlorococcus marinus
Size: 0.4 micrometers
Shape: Coccus (Sphere)
One of the smallest bacteria
2nd abundant bacteria in ocean (Over 1 trillion, more in warmer areas)
Responsible for 20% of the Oxygen we breathe
What percentage of life history is microbial only?
90%
What are the roles of microbes in health and food?
Health: Leads to infectious diseases, obesity
Food: Fermentation processes