Human Anatomy Basics, Overview of the Skeletal System and Its Functions, Anatomy - Integumentary Test , Human Anatomy - Body Tissues, ENDOCRINE QUIZ - ANATOMY, Endocrine System, Anatomy Chapter 16 MATCHING PART 2, Another Structure of the Eye, Struct… Diagram | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Foramen Magnum
Large opening in the skull for spinal cord.
Bifid Vertebrae
Cervical vertebrae with split spinous processes.
Total Bones in Adult Body
206 bones after fusion from childhood.
Ribs in Adult Body
24 ribs, 12 pairs in total.
Fontanels
Soft spots on a baby's skull for growth.
Ethmoid Bone
Single bone located between the eyes.
Atlas Vertebra
C1 vertebra, supports the skull.
Axial Vertebra
C2 vertebra, allows head rotation.
Tendons
Connect muscles to bones, facilitating movement.
Ligaments
Connect bones to other bones, providing stability.
Skeletal System
Parts of the skeletal system include bones, joints, cartilages, and ligaments.
Axial skeleton
One of the two subdivisions of the skeleton.
Appendicular skeleton
One of the two subdivisions of the skeleton.
Functions of the Bones
Support the body, protect soft organs, allow movement via attached muscles, store minerals and fats, and blood cell formation (hematopoiesis).
Protection of soft organs
The skull and vertebrae protect the brain and spinal cord, while the rib cage protects thoracic cavity organs.
Blood cell formation
Also known as hematopoiesis.
Adult skeleton
The adult skeleton has 206 bones.
Osseous tissue
There are two basic types: compact bone and spongy bone.
Compact bone
Dense, smooth, and homogeneous type of osseous tissue.
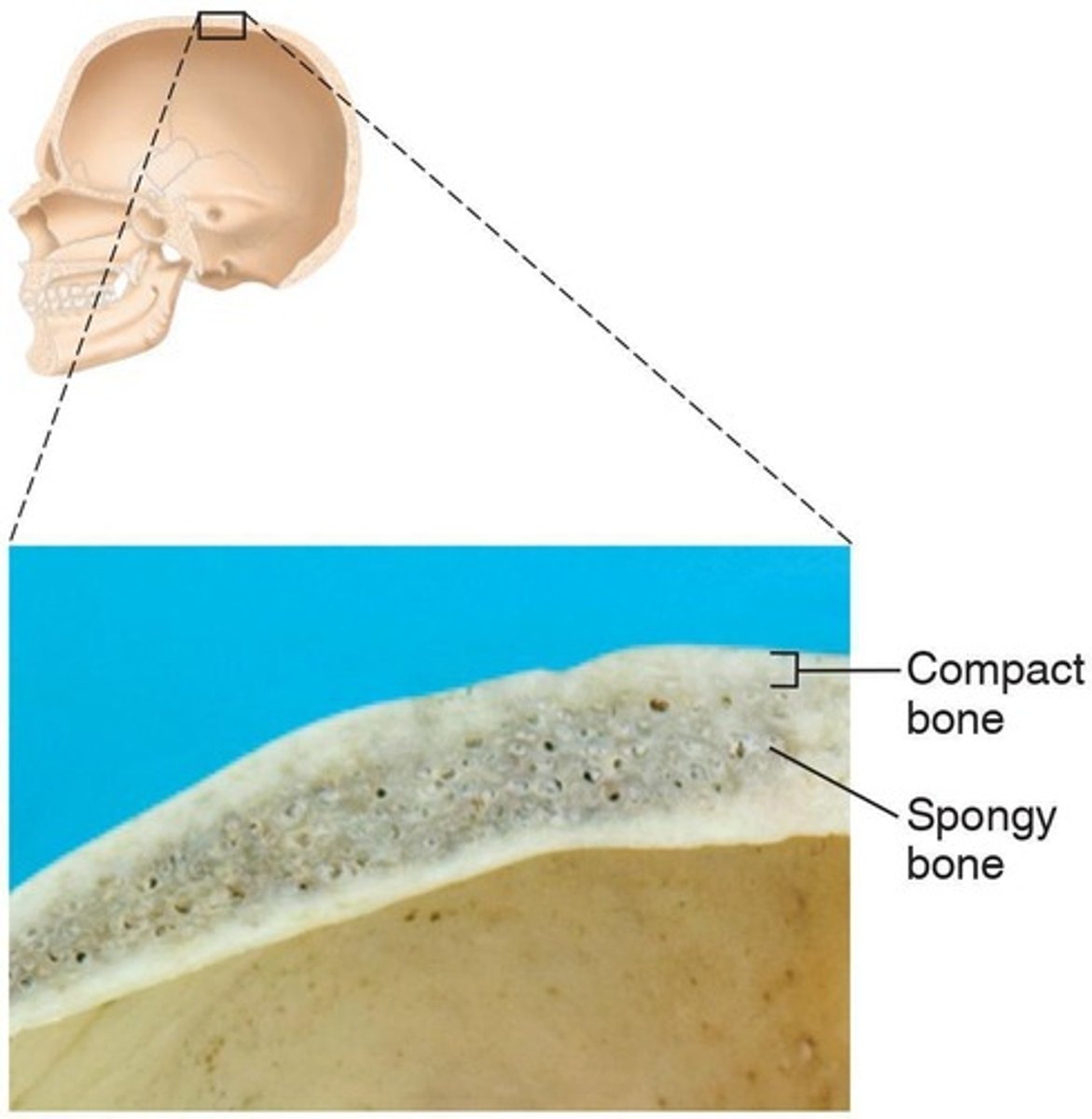
Spongy bone
Contains small needlelike pieces of bone and many open spaces.
Classification of Bones
Bones are classified on the basis of shape into four groups: long, flat, short, and irregular.
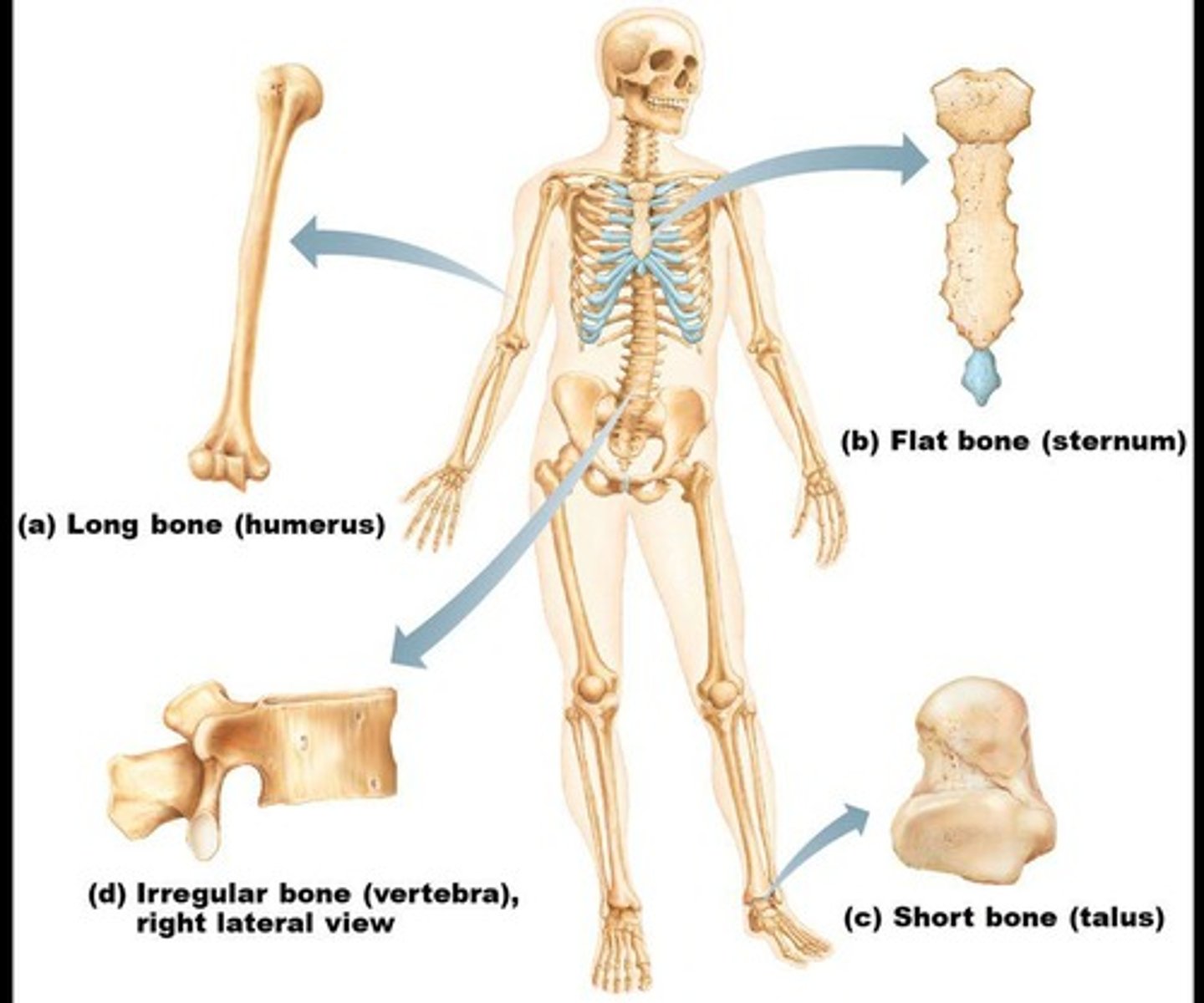
Long bones
Typically longer than they are wide, with a shaft and enlarged ends, containing mostly compact bone.
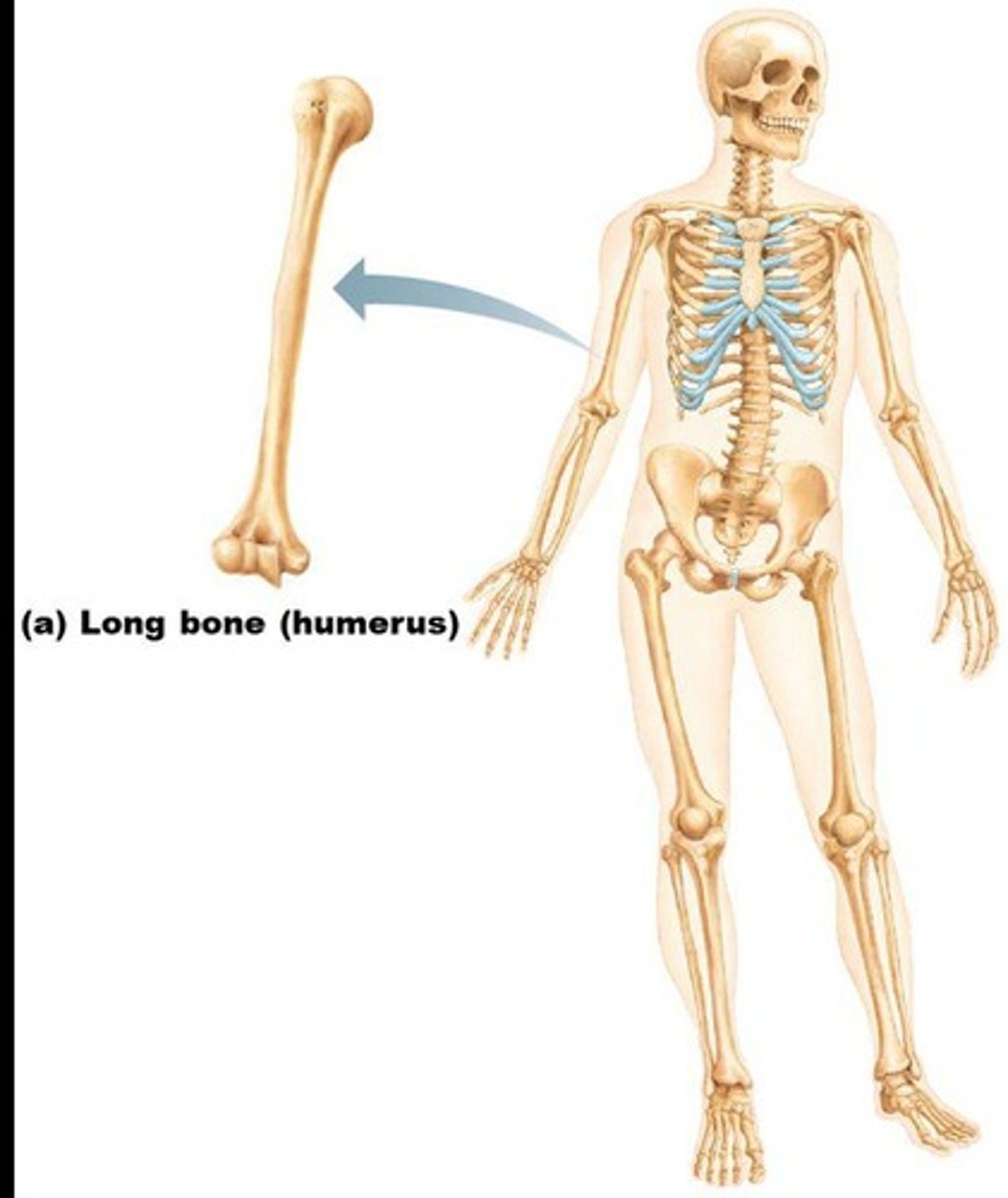
Examples of long bones
Femur and Humerus.
Flat bones
Thin, flattened, and usually curved, with two layers of compact bone sandwiching a layer of spongy bone.
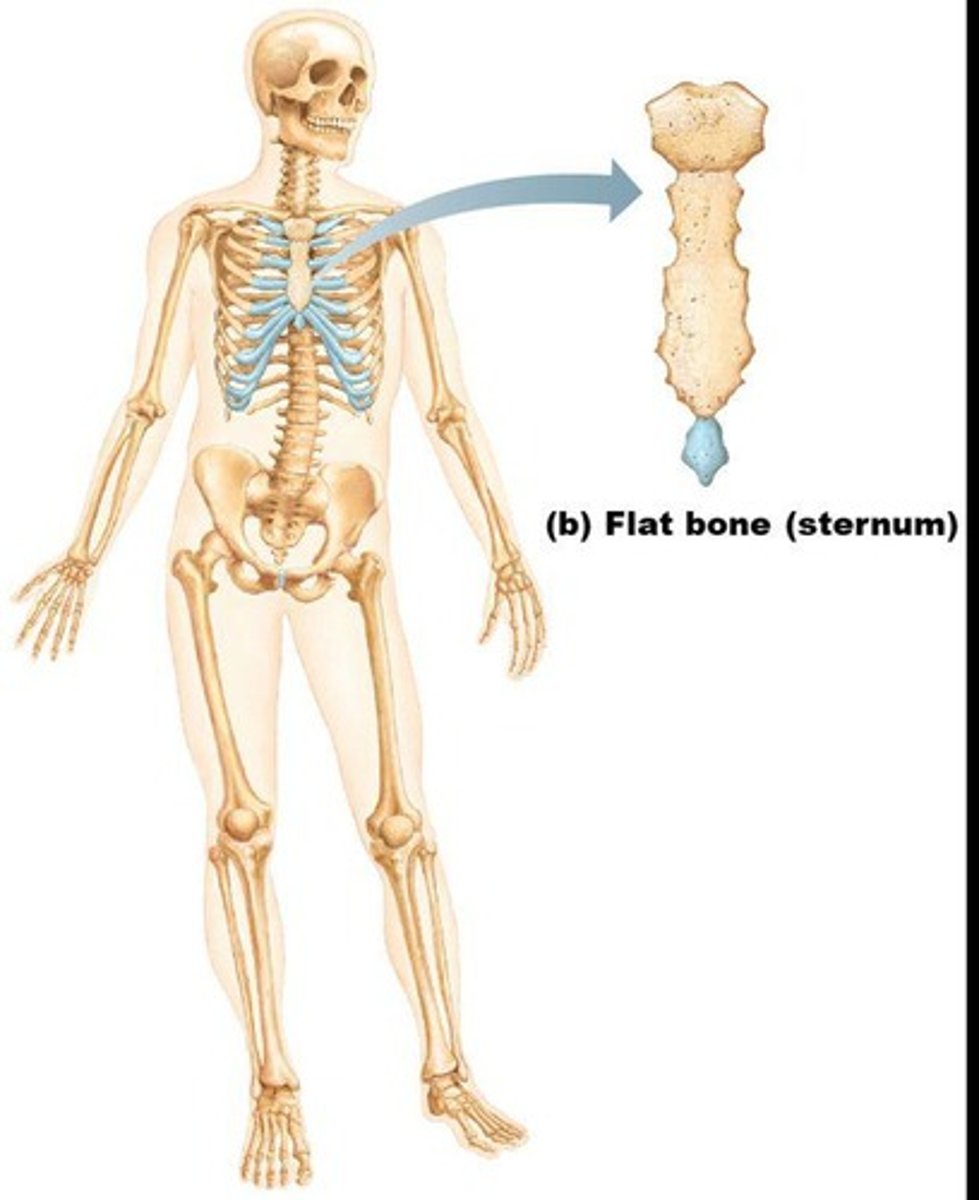
Examples of flat bones
Most bones of the skull, ribs, and sternum.
Short bones
Generally cube-shaped, containing mostly spongy bone with an outer layer of compact bone.
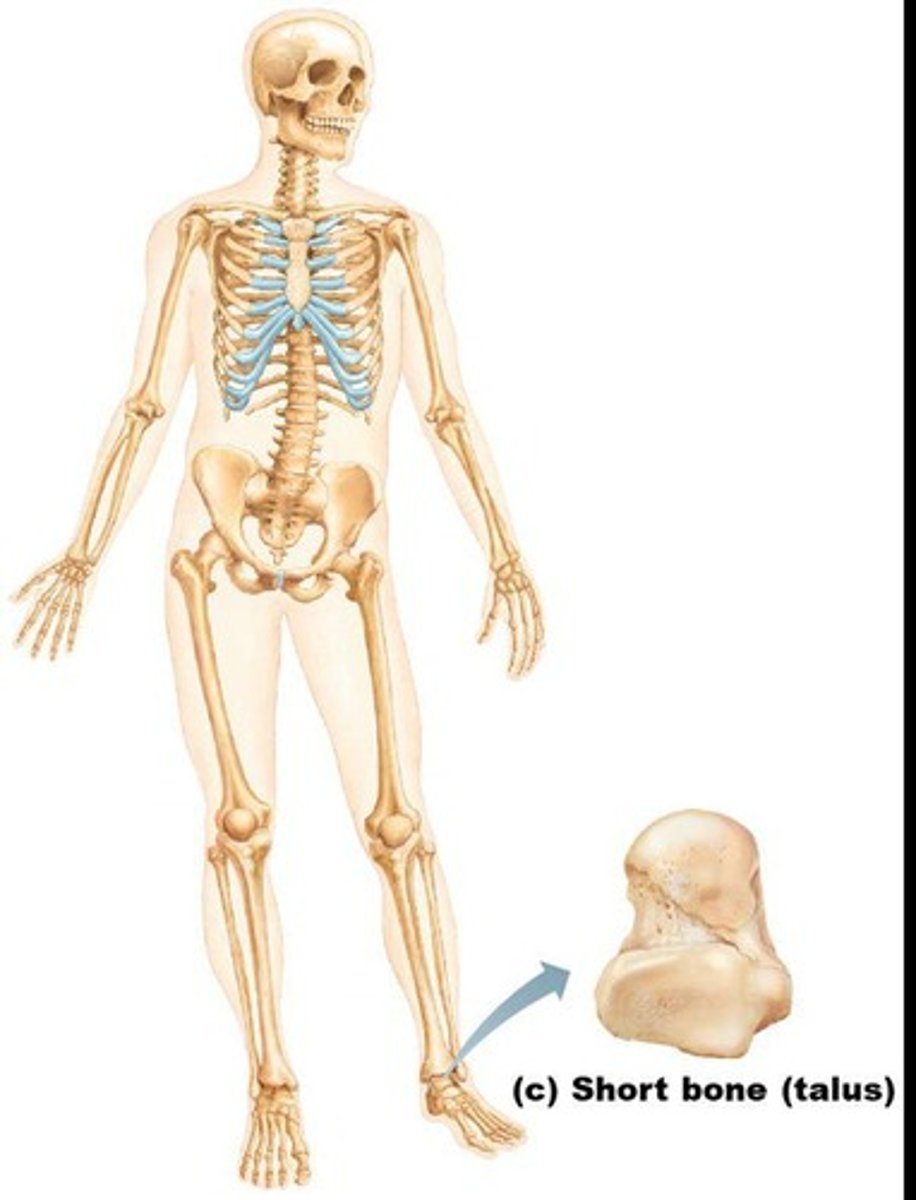
Examples of short bones
Carpals (wrist bones) and tarsals (ankle bones).
Irregular bones
Have irregular shapes and do not fit into other bone classification categories.
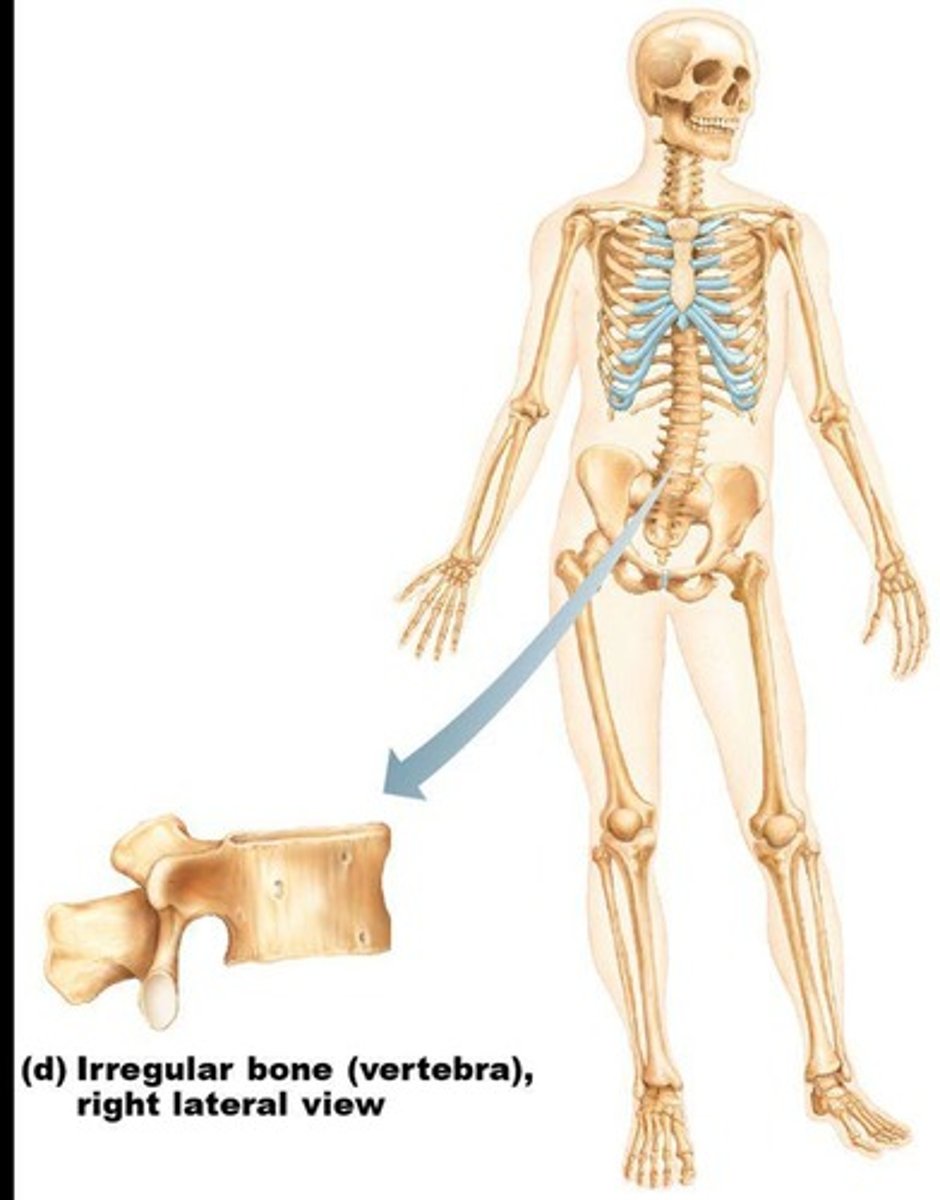
Examples of irregular bones
Vertebrae and hip bones.
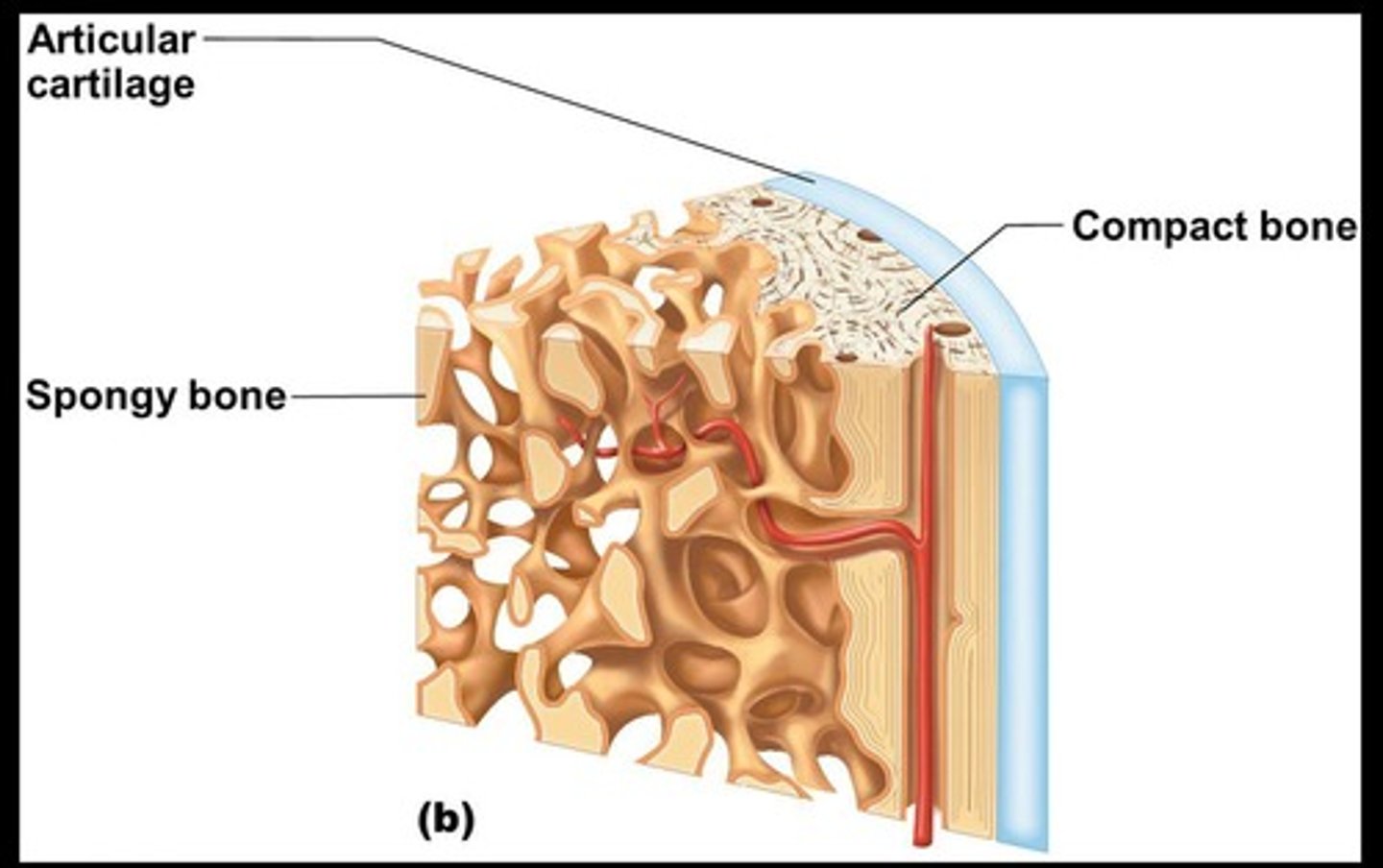
Long bone anatomy
Includes the diaphysis (shaft) and periosteum.
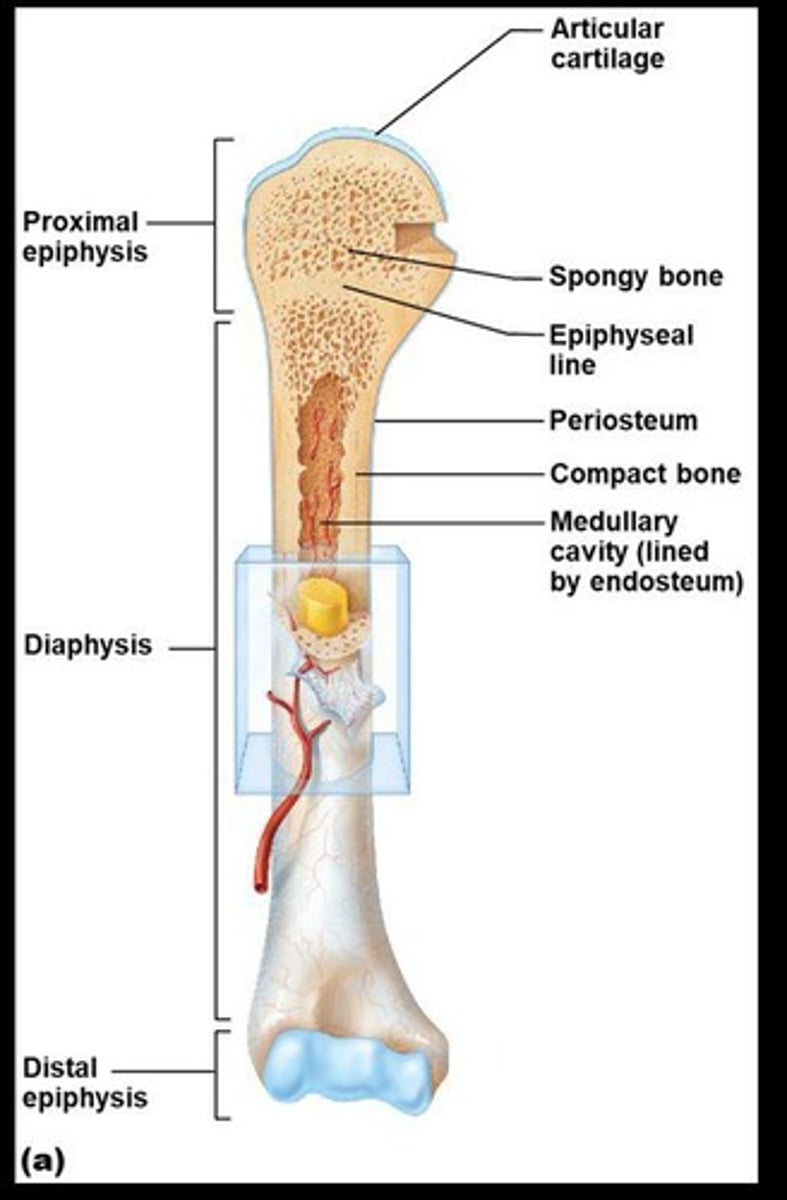
Diaphysis
Makes up most of the bone's length and is composed of compact bone.
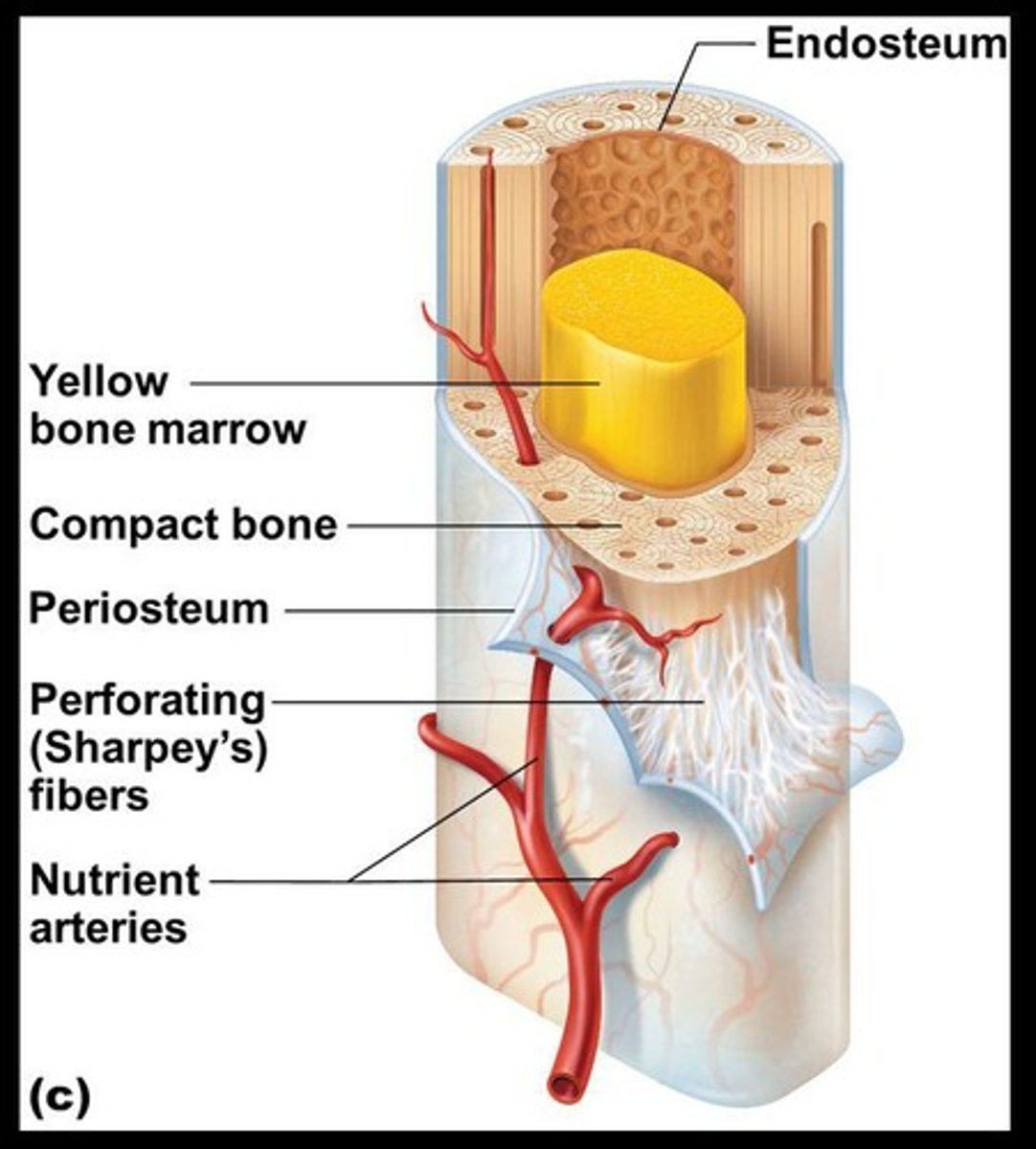
Periosteum
The outside covering of the diaphysis, a fibrous connective tissue membrane.
Perforating (Sharpey's) fibers
Secure the periosteum to the underlying bone.
Epiphysis
Composed mostly of spongy bone enclosed by thin layer of compact bone.
Articular cartilage
Covers the external surface of the epiphyses, made of hyaline cartilage, and decreases friction at joint surfaces.
Epiphyseal line
Remnant of the epiphyseal plate seen in adult bones.
Epiphyseal plate
Flat plate of hyaline cartilage seen in young, growing bone that causes lengthwise growth of a long bone.
Endosteum
Lines the inner surface of the shaft and is made of connective tissue.
Medullary cavity
Cavity inside the shaft that contains yellow marrow (mostly fat) in adults and red marrow for blood cell formation until age 6 or 7.
Bone markings
Sites of attachments for muscles, tendons, and ligaments, and passages for nerves and blood vessels.
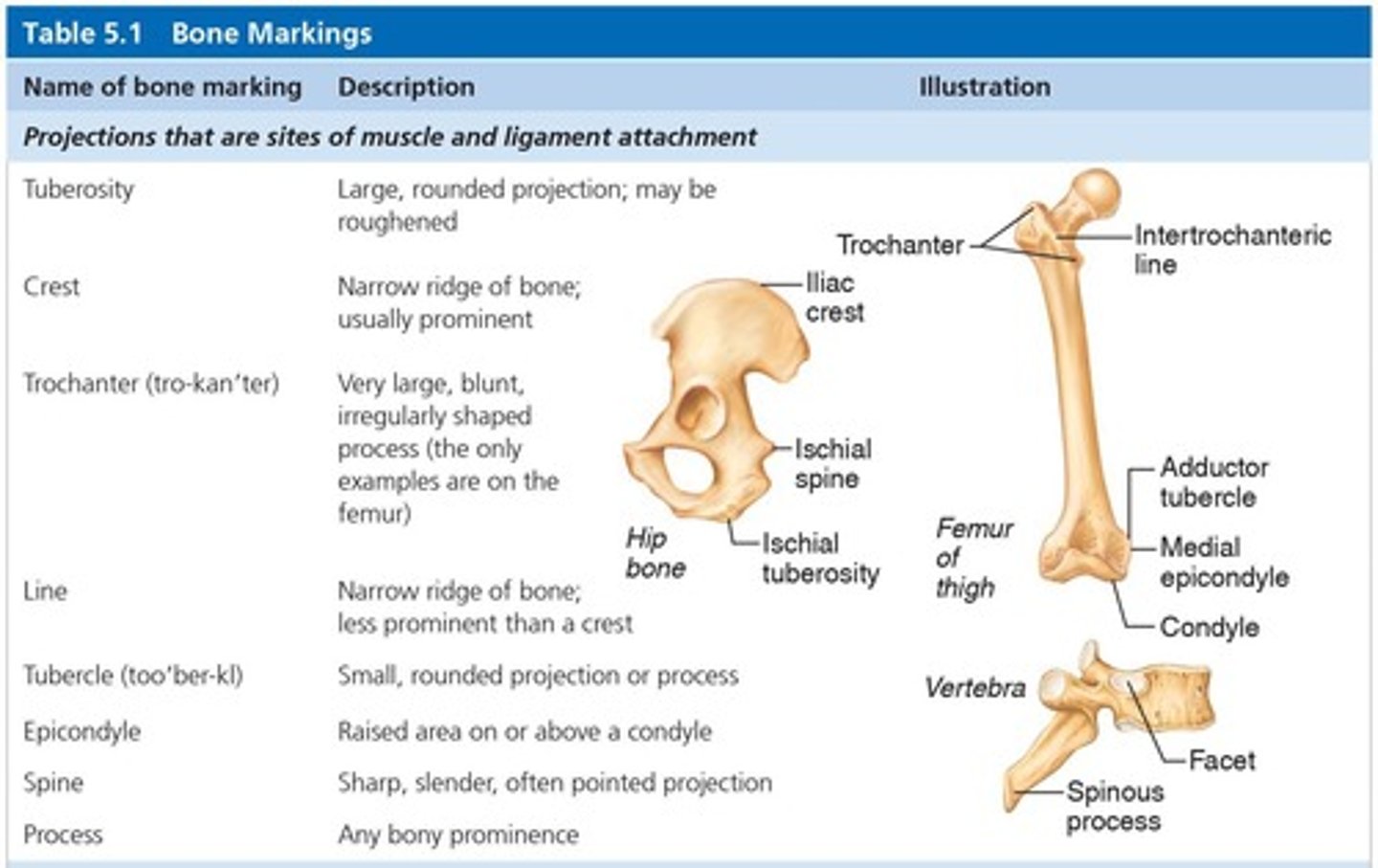
Projections or processes
Grow out from the bone surface, with all projections beginning with 'T'.
Depressions or cavities
Indentations, with all depressions beginning with 'F' (except facet).
Trabeculae
Small, needlelike pieces of bone that compose spongy bone.
Lacunae
Cavities in bone matrix that house osteocytes.
Lamellae
Concentric circles of lacunae situated around the central (Haversian) canal.
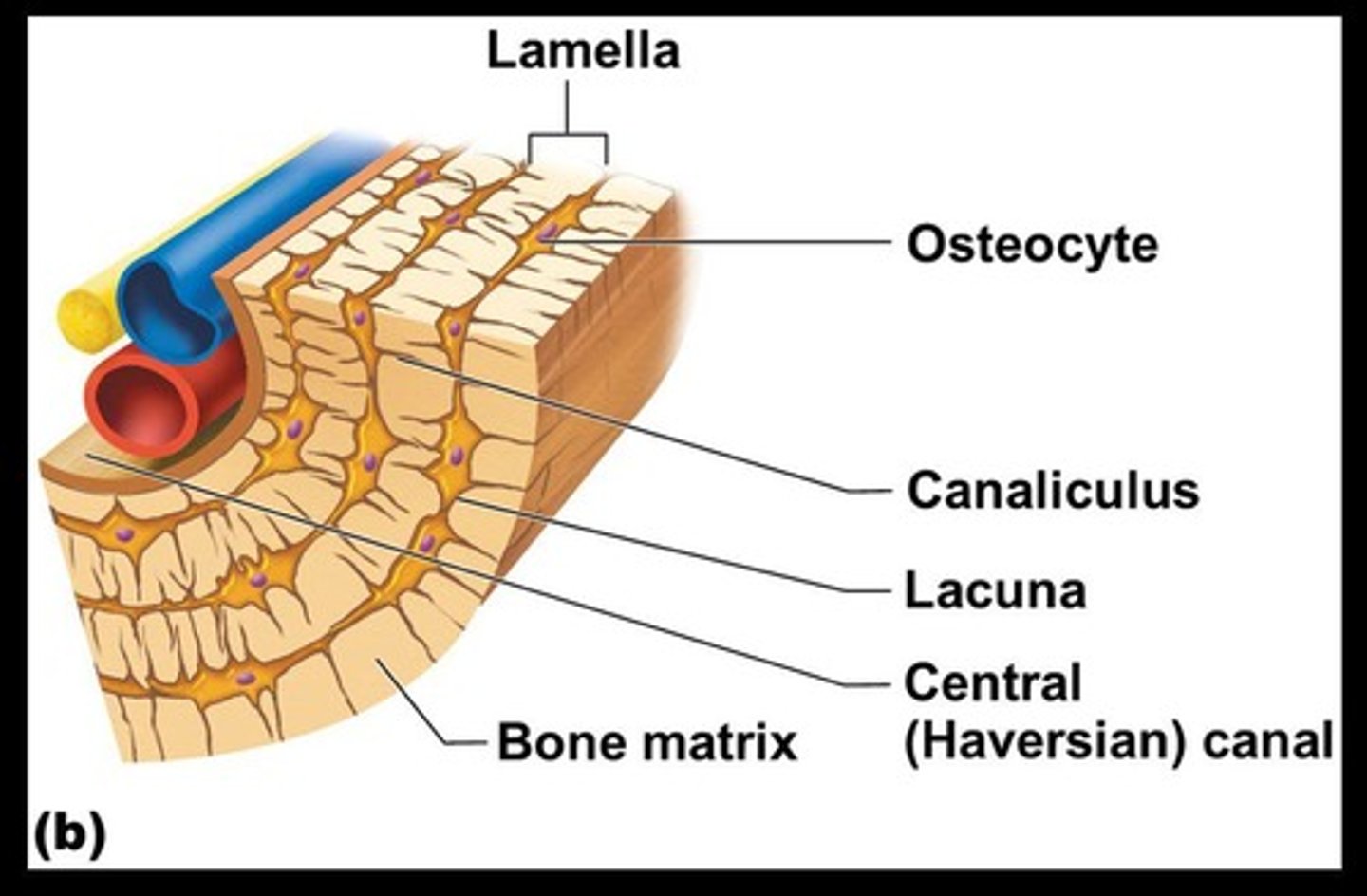
Central (Haversian) canal
Opening in the center of an osteon that runs lengthwise through bone and carries blood vessels and nerves.
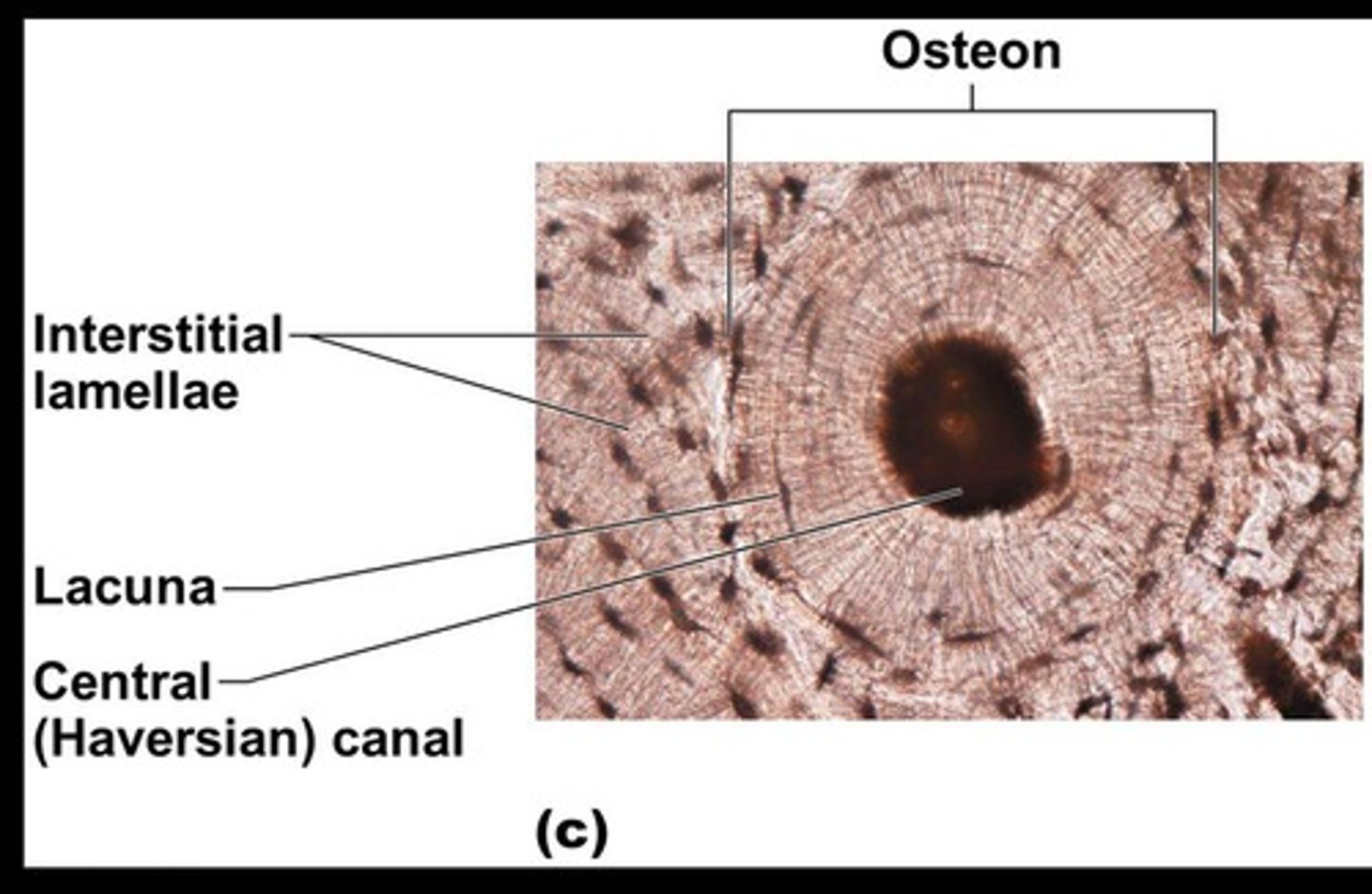
Osteon (Haversian system)
A unit of bone containing central canal and matrix rings, serving as the structural and functional unit of compact bone.
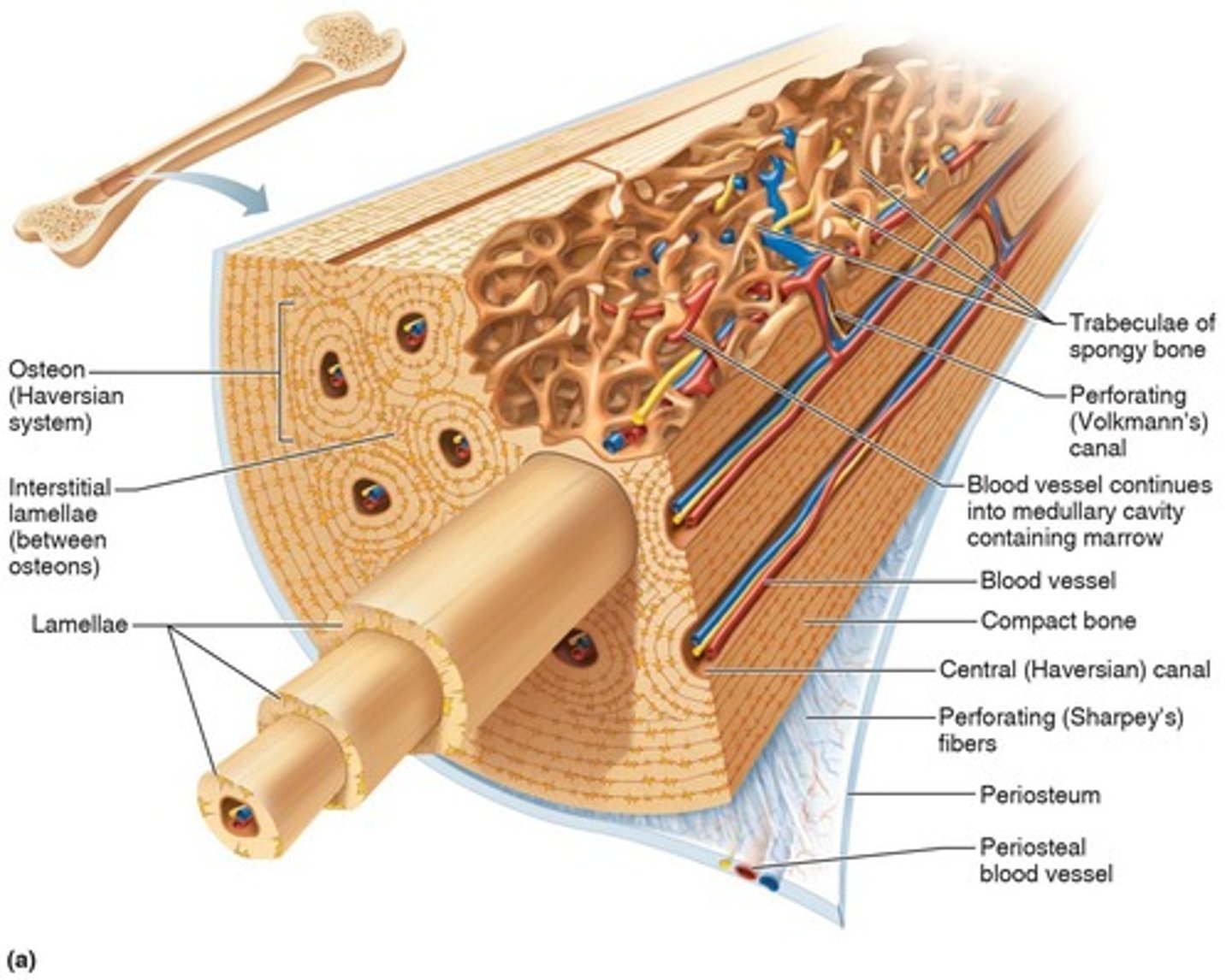
Canaliculi
Tiny canals that radiate from the central canal to lacunae, forming a transport system connecting all bone cells to a nutrient supply.
Perforating (Volkmann's) canal
Canal perpendicular to the central canal that carries blood vessels and nerves.
Bone
Relatively lightweight and resists tension and other forces.
Organic parts of bone
Collagen fibers that make bone flexible and have great tensile strength (stretch without breaking).
Calcium salts in bone
Deposited in the bone to make it hard and resist compression.
Ossification
The process of bone formation.

Hyaline cartilage models
The structures on which ossification occurs.
Phases of long bone growth
Involves two major phases.
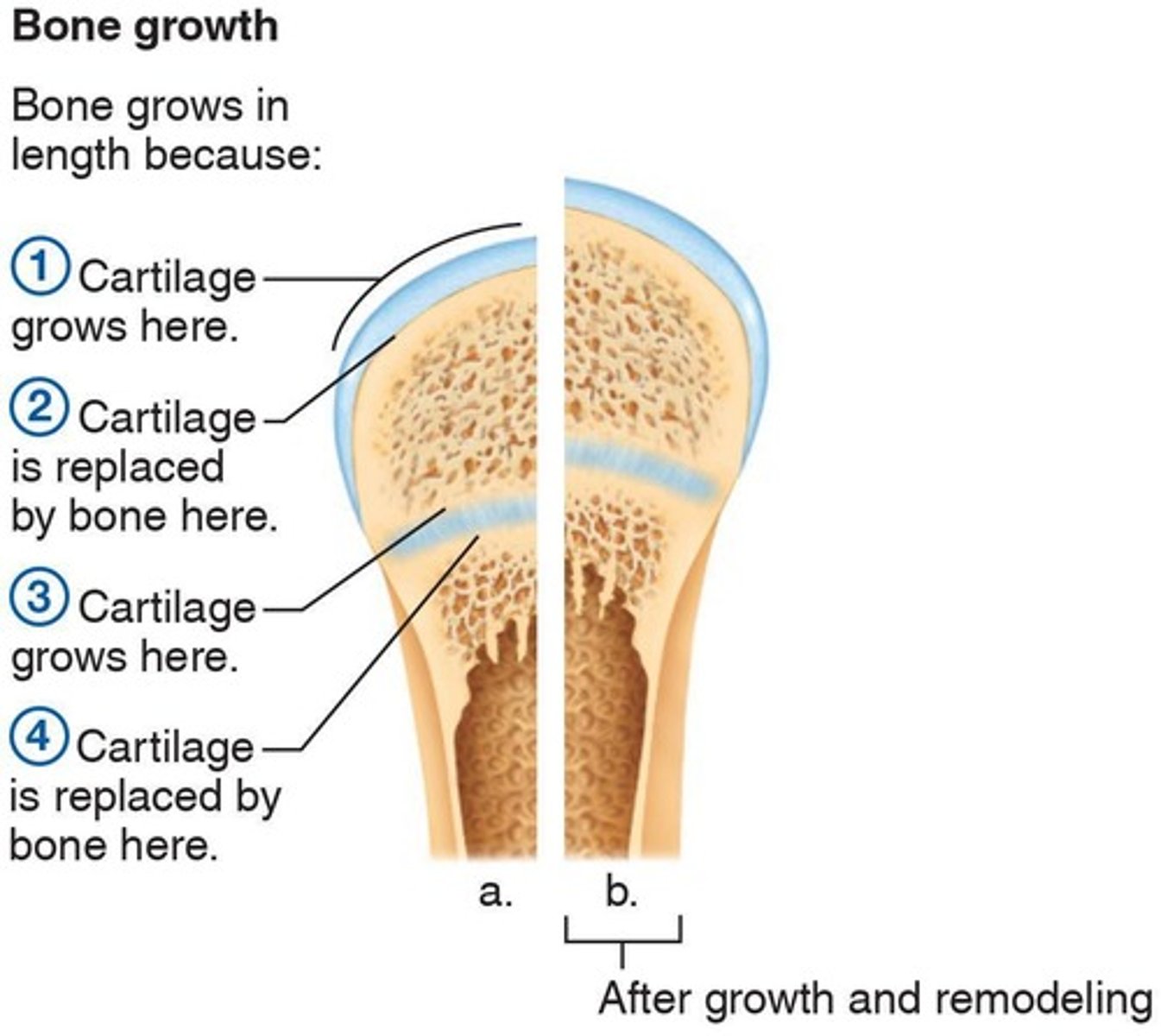
Osteoblasts
Bone-forming cells that cover the hyaline cartilage model with bone matrix in an embryo.
Medullary cavity
The space opened up when the enclosed cartilage is covered by bone and digested away.
Articular cartilages
One of the two regions in a long bone where cartilage is retained by birth.
Epiphyseal plates
The second region in a long bone where cartilage is retained by birth.
Appositional growth
The process by which bones grow in width.
Hormones controlling bone growth
Growth hormone and sex hormones.
Factors affecting bone remodeling
Calcium ion level in the blood and the pull of gravity and muscles on the skeleton.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Released when calcium ion levels in blood are low, activating osteoclasts.
Hypercalcemia
High blood calcium levels that prompt calcium storage to bones by osteoblasts.
Fracture
A break in a bone.
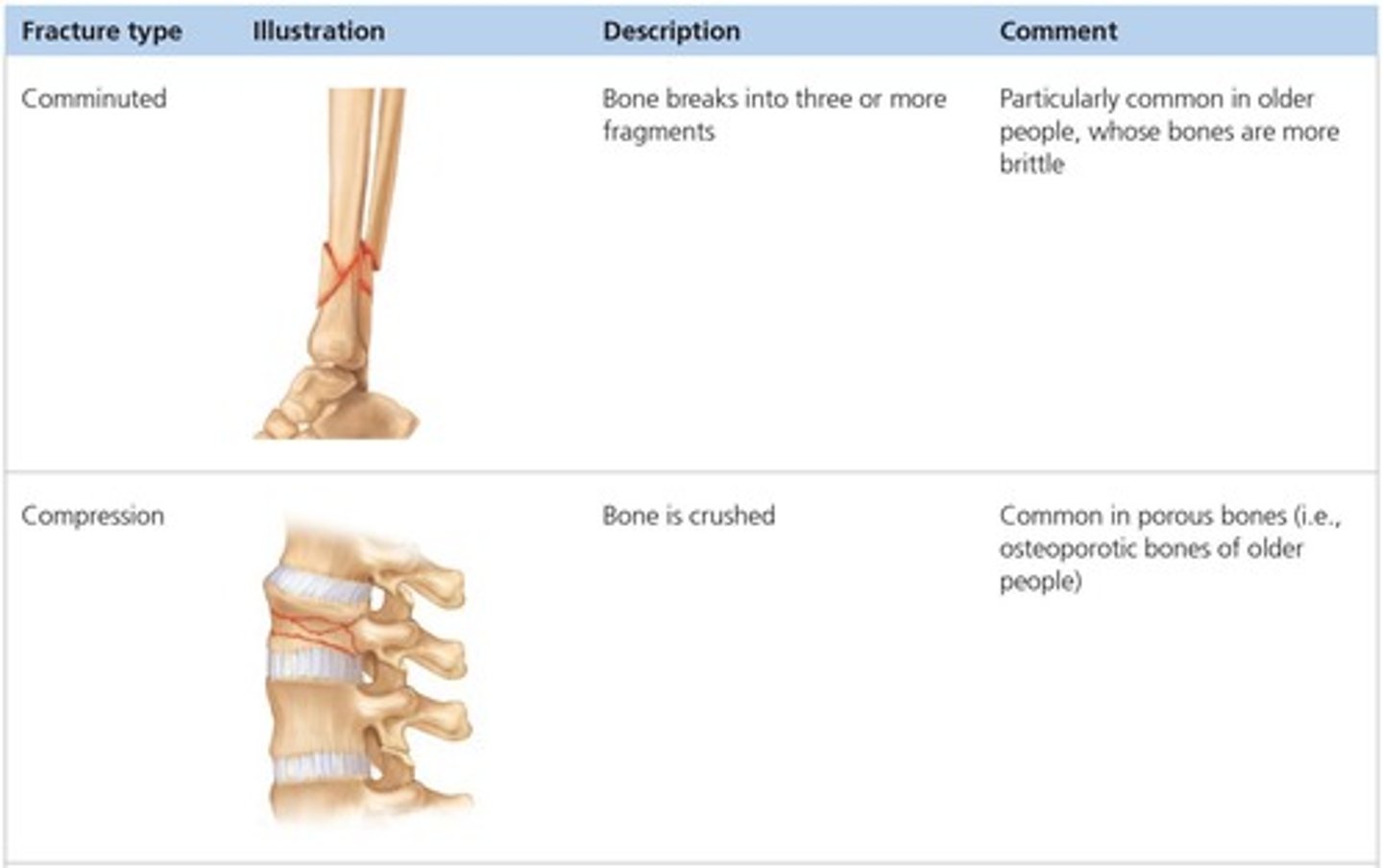
Closed (simple) fracture
A break that does not penetrate the skin.
Open (compound) fracture
A broken bone that penetrates through the skin.
Reduction and immobilization
The treatment for bone fractures.
Closed reduction
Bones are manually coaxed into position by physician's hands.
Open reduction
Bones are secured with pins or wires during surgery.
Healing time for fractures
6-8 weeks.
Hematoma
Blood-filled swelling, or bruise, formed during the repair of bone fractures.
Fibrocartilage callus
A structure that forms during bone fracture repair, consisting of cartilage matrix, bony matrix, and collagen fibers that splint the broken bone.
Bony callus
Replaces the fibrocartilage callus during the repair of bone fractures, formed by the migration of osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Bone remodeling
The process that occurs in response to mechanical stresses during the healing of a bone fracture.
Axial Skeleton
Forms the longitudinal axis of the body and is divided into three parts: skull, vertebral column, and bony thorax.
Cranium bones
Bones that enclose the brain.
Facial bones
Bones that hold the eyes in anterior position and allow facial muscles to express feelings.
Sutures
Immovable joints that join the bones of the skull.
Mandible
The only bone in the skull that is attached by a freely movable joint.
Frontal bone
One of the eight cranial bones that protect the brain.
Occipital bone
One of the eight cranial bones that protect the brain.
Ethmoid bone
One of the eight cranial bones that protect the brain.
Sphenoid bone
One of the eight cranial bones that protect the brain.
Parietal bones
A pair of cranial bones that protect the brain.
Temporal bones
A pair of cranial bones that protect the brain.
Maxillae
A pair of facial bones.
Palatine bones
A pair of facial bones.
Lacrimal bones
A pair of facial bones.
Zygomatic bones
A pair of facial bones.
Nasal bones
A pair of facial bones.
Vomer bone
A single facial bone.
Inferior nasal conchae
A pair of facial bones.
Paranasal sinuses
Hollow portions of bones surrounding the nasal cavity that lighten the skull and amplify sounds made as we speak.
Hyoid bone
The only bone that does not articulate with another bone, serving as a movable base for the tongue and aiding in swallowing and speech.
Vertebral column
Provides axial support, extending from the skull to the pelvis, consisting of 26 vertebral bones separated by intervertebral discs.
Cervical vertebrae
Seven vertebrae located in the neck.
Thoracic vertebrae
Twelve vertebrae located in the chest region.
Lumbar vertebrae
Five vertebrae associated with the lower back.
Sacrum
Formed by the fusion of five vertebrae.