CHAPTER 15 AMP2
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
The word root angio- means Blank______.
The cardiovascular system includes the heart and blood vessels.
The heart is located in the Blank______ and is Blank______ to the diaphragm.
The covering that encloses the heart is called the
pericardium
What is the skeleton of the heart?
The three layers of the heart, in the correct order from superficial to deep, are
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
How many hollow chambers are found in the heart?
What are the upper, thin walled chambers of the heart?
Myocardium
What organ is housed within the thoracic cavity?
The heart, and the proximal ends of the large blood vessels to which it attaches, are enclosed in a membranous sac called the Blank______.
The heart can be divided into left and right sides and each side has Blank______ chambers.
The thick-walled inferior chambers of the heart that pump blood into the arteries are called
ventricles
Choose all features of the atria of the heart.
They are thin-walled.
They receive blood returning to the heart.
They are the upper chambers of the heart.
The heart is housed within the mediastinum and rests on the , a muscle.
diaphragm
A blood cell is traveling in the inferior vena cava and approaches the heart. Rank the following structures in the order in which the cell encounters them, starting with the first one at the top.
RT atrium, RT ventricle, lungs, RT atrium, Rt ventricle
What are the ventricles?
The thicker-walled, inferior chambers of the heart
What are the upper, thin walled chambers of the heart?
left and right atrium
The heart has a skeleton.
The heart has rings of fibrous tissue that give it its shape and provide attachment points for the valves and muscle fibers. This is referred to as the "fibrous skeleton" of the heart.
The heart is composed of (number) hollow chambers.
4
What is the name of the main vessels that supply the heart tissue with blood?
Which of the following describes the path of a blood cell from the superior vena cava as it makes its way through the heart?
right atrium --> right ventricle --> pulmonary artery --> lung --> pulmonary vein --> left atrium --> left ventricle --> aorta
During the heart's operation, when the atria contract, the ventricles are Blank______; when the ventricles contract the atria are Blank______.
relaxation, relaxation
The thick-walled inferior chambers of the heart that pump blood into the arteries are called
ventricles
What are some characteristics of cardiac muscle fibers?
branching, connected to intercalated disc
Choose all features of the atria of the heart.
They receive blood returning to the heart.
They are the upper chambers of the heart.
They are thin-walled.
The sinoatrial node is a mass of specialized noncontractile cells located just beneath the epicardium in the ____atrium near the opening of the superior ____ _____ .
right atrium, superior vena cava
When electrodes are placed on the skin and electrical changes in the myocardium are recorded on an instrument, a reading called a(n)____ can be obtained.
ECG, electrocardiogram
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
They supply the heart tissues with oxygenated blood.
Heart sounds are generated when blood vibrates the wall of the heart due to the Blank______ of the valves.
closing
What happens after the ventricles of the heart complete their contraction?
All four chambers of the heart relax for a brief interval.
The opening and closing of the heart valves is associated with Blank______.
changes in chamber pressure
Branching cells that are uninucleate and striated are typical of _______ muscle fibers.
cardiac
The portion of the cardiac conduction system located in the right atrium near the opening of the superior vena cava is the .
Sinoatrial node
What does an electrocardiogram record?
The electrical changes in the myocardium
How can the human circulatory system be described?
What causes the lubb-dubb sound of a heartbeat, as heard through a stethoscope?
The vibrations in heart tissue as blood flow is slowed when valves close
The rise and fall of blood _______ in the heart chambers is the cause of the opening and closing of heart valves.
pressure
Arterioles differ from the large arteries that leave the heart, because they are Blank______.
finner and branched
Cardiac muscle cells can contract as a unit because adjacent cells are connected by Blank______.
intercalated discs
What is the tunica interna?
The inner lining of a blood vessel's wall composed of simple squamous epithelium
Where is the cardiac center located?
in the medulla oblongata
The blood vessels in a human form a(n) Blank______ circuit through which blood circulates.
closed
Which of the following are directly affected by vasodilation and vasoconstriction?
Blood flow
Blood pressure
As arteries branch or subdivide, they give rise to smaller vessels called Blank______.
arterioles
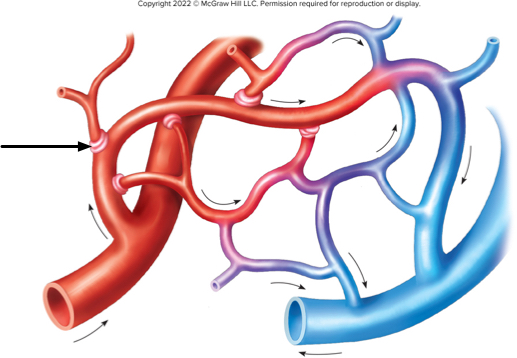
On this diagram of a small capillary bed, what is the arrow pointing to?
Microscopic, thin-walled vessels that connect the smallest arterioles to the smallest venules are called
capillaries
What is filtration as it occurs in capillaries?
The forced movement of compounds through a membrane via hydrostatic pressure
What are venules?
the smallest veins
The nervous system can trigger vasoconstriction and vasodilation of arteries. What effect does this have?
It influences blood flow and blood pressure.
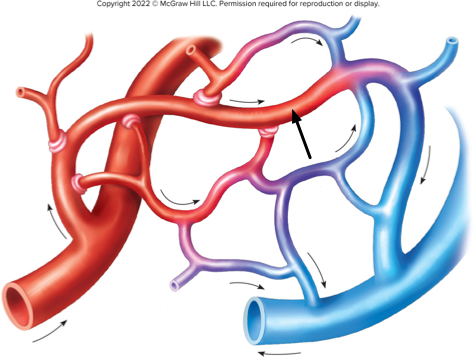
On this diagram of a capillary network, the arrow points to a metarteriole forming a(n)
arteriovenous shunt
The force exerted by the blood against the inner walls of vessels is called
blood pressure
What is the smallest-diameter blood vessel?
What process, that occurs in capillaries, is described as the movement of molecules across a membrane under the influence of hydrostatic pressure?
filtration
Microscopic vessels that are continuations of capillaries and merge to eventually form veins are called
venule
Blood pressure is reported as two numbers. The _________ pressure is the maximum blood pressure reading attained during ventricular contraction.
systolic
What is the definition of blood pressure?
The force blood exerts against the blood vessel
The volume of blood ejected from the heart with each contraction is called the Blank______.
The smallest-diameter blood vessels are the
capillaries
Blood pressure can be determined by Blank______.
What factors contribute to venous return to the heart?
Skeletal muscle contractions
Vein vasoconstriction
Pressure changes during breathing
The central venous pressure represents the pressure in the Blank______.
What is systolic pressure?
The maximum pressure achieved in the arteries during ventricular systole
An average-weight male at rest ejects about 70 ml of blood with each ventricular contraction. This is known as the .
stroke volume
Why does the body need skeletal muscle contraction, pressure changes during breathing, and vasoconstriction to move blood through the veins?
Which circuit supplies body tissues with oxygenated blood and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart?
THE SYSTEMIC CIRCIT
The pressure in the right atrium is also called the central Blank______ pressure.
The major vessel that originates at the left ventricle is the
aorta
What is stroke volume?
Three major arteries originate from the aortic arch. They are the _____ trunk, the left common ____artery, and the left _____ artery
brachiocephalic trunk, the left common carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery
In the systemic circuit, freshly oxygenated blood from the _____ventricle is pushed into the aorta to travel out to the body and then to return via veins to the _____ atrium.
left ventricle, right atrium
Once it passes between the clavicle and the first rib, the subclavian artery is called the Blank______ artery.
What is the origin of the aorta?
left ventricle
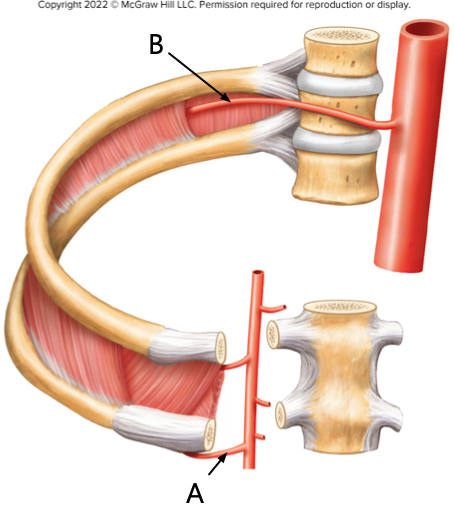
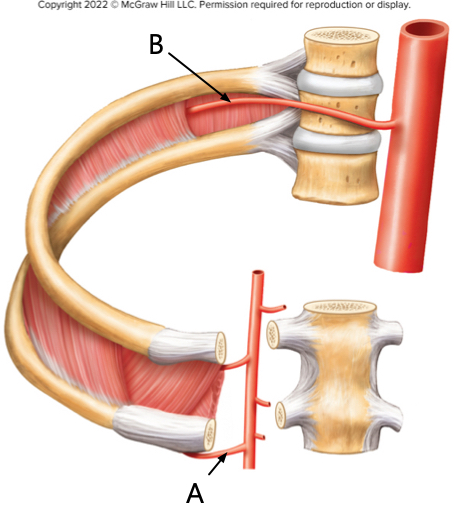
This diagram focuses on arteries that supply the thoracic wall. The artery indicated by arrow A is the Blank______ intercostal artery; the artery indicated by arrow B is the Blank______ intercostal artery.
A is anterior, B is posterior
Place the branches of the aortic arch in the correct order in which they originate, starting with the most proximal branch at the top
Brachiocephalic trunk
left common carotid artery
left subclavian artery
Choose the main divisions of the subclavian artery that supply the brain, head, and neck.
Thyrocervical artery
Costocervical artery
Vertebral artery
Blood moves from the subclavian artery to the Blank______ artery.
axillary ARTERY
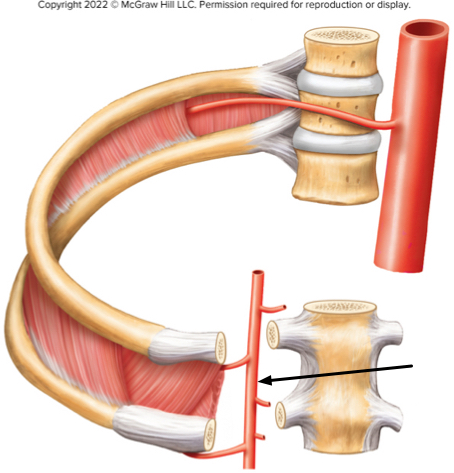
In the figure of the thoracic wall, what artery is the arrow indicating?
The internal thoracic artery
The ______arteries arise from the abdominal aorta and provide blood supply to the pelvic organs, the gluteal region and the lower limbs.
common iliac ateries
The structures in the neck, head and brain receive blood supply from branches of the ______artery and the ____carotid artery
subclavian artery and common caratid artery
What is the destination of the blood in the superior vena cava?
right atrium
Which circuit supplies body tissues with oxygenated blood and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart?
The systemic circuit
The Blank______ veins drain blood from the face, scalp and superficial regions of the neck.
The subclavian artery becomes the _____ artery after it passes between the clavicle and first rib.
axillary
This diagram focuses on arteries that supply the thoracic wall. The artery indicated by arrow A is the Blank______ intercostal artery; the artery indicated by arrow B is the Blank______ intercostal artery.
A- anterior, B- posterior
Which of the following are supplied by the common iliac arteries?
Pelvic organs
Lower limb
Gluteal region
The brachial veins are formed by the merger of the Blank______.
ulnar and radial veins
The abdominal and thoracic walls are drained by tributaries of two major veins: the _______ vain and ____vain
Azygos vein and brachiocephalic vein
The external jugular vein drains directly into what vessel?
The subclavian vein
Once it passes between the clavicle and the first rib, the subclavian artery is called the Blank______ artery.
axillary
What is the function of the hepatic portal system?
To deliver nutrients absorbed from stomach and intestines to the liver
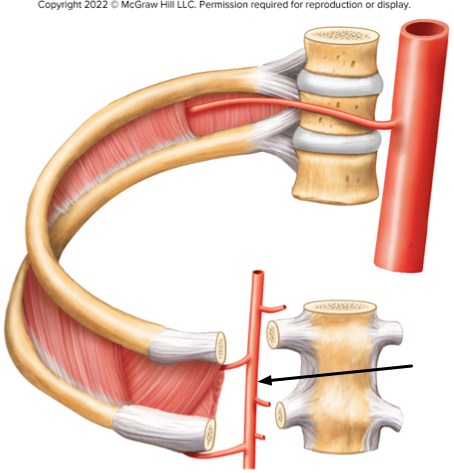
In the figure of the thoracic wall, what artery is the arrow indicating?
The internal thoracic artery
Place the veins in the order that blood would flow through them on the way back to the heart, starting with the vein farthest from the heart at the top.
ANTERIOR TIBIAL VEINS
POPLITEAL VEIN
FEMORAL VEIN
EXTERNAL ILIAC VEIN
the raidal and ulnar vein join to form the?
brachial vein
As the cardiovascular system ages, systolic blood pressure increases.
The Blank______ veins drain blood from the face, scalp and superficial regions of the neck.
external jugular
Blood from the spleen, stomach, and intestines drain into which vessel?
The hepatic portal vein
At the level of the knee, the anterior and posterior tibial veins form a single trunk called the vein.
popliteal vein