Astrocytes and Microglia: Roles in CNS Support and Immune Response
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What are the primary functions of astrocytes?
Astrocytes transport nutrients from blood vessels to neurons and oligodendrocytes, regulate tissue water content, direct the formation of the blood-brain barrier, and support neuronal signal transduction.
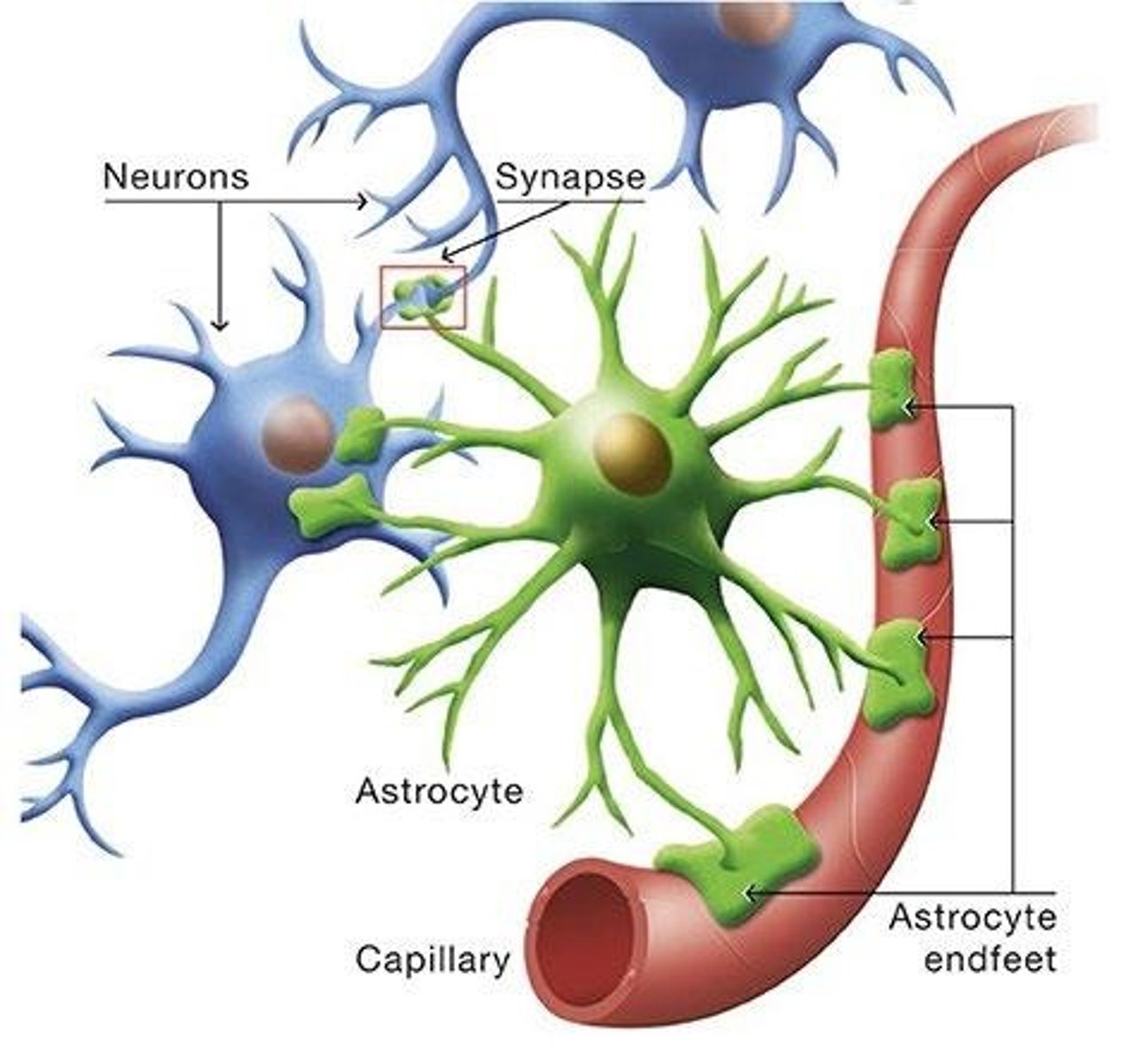
What is astrocytosis?
Astrocytosis refers to the proliferation of astrocytes in response to injury in the central nervous system, often leading to the formation of scar tissue.
What are the characteristics of activated microglia?
Activated microglia are mobile, ameboid, phagocytic cells that present antigens, release inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-1 and TNF), and produce nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species.
What triggers microglial activation?
Microglial activation is triggered by Damage Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPS), Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPS), and interferon.
What is the role of microglia in the central nervous system?
Microglia act as the immune cells of the central nervous system, involved in phagocytosis and inflammatory responses.
What are foamy gitter cells?
Foamy gitter cells are a form of phagocytic microglia that have accumulated lipids and appear foamy under a microscope.
What is the significance of the blood-brain barrier?
The blood-brain barrier is crucial for protecting the brain from harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients to pass through.
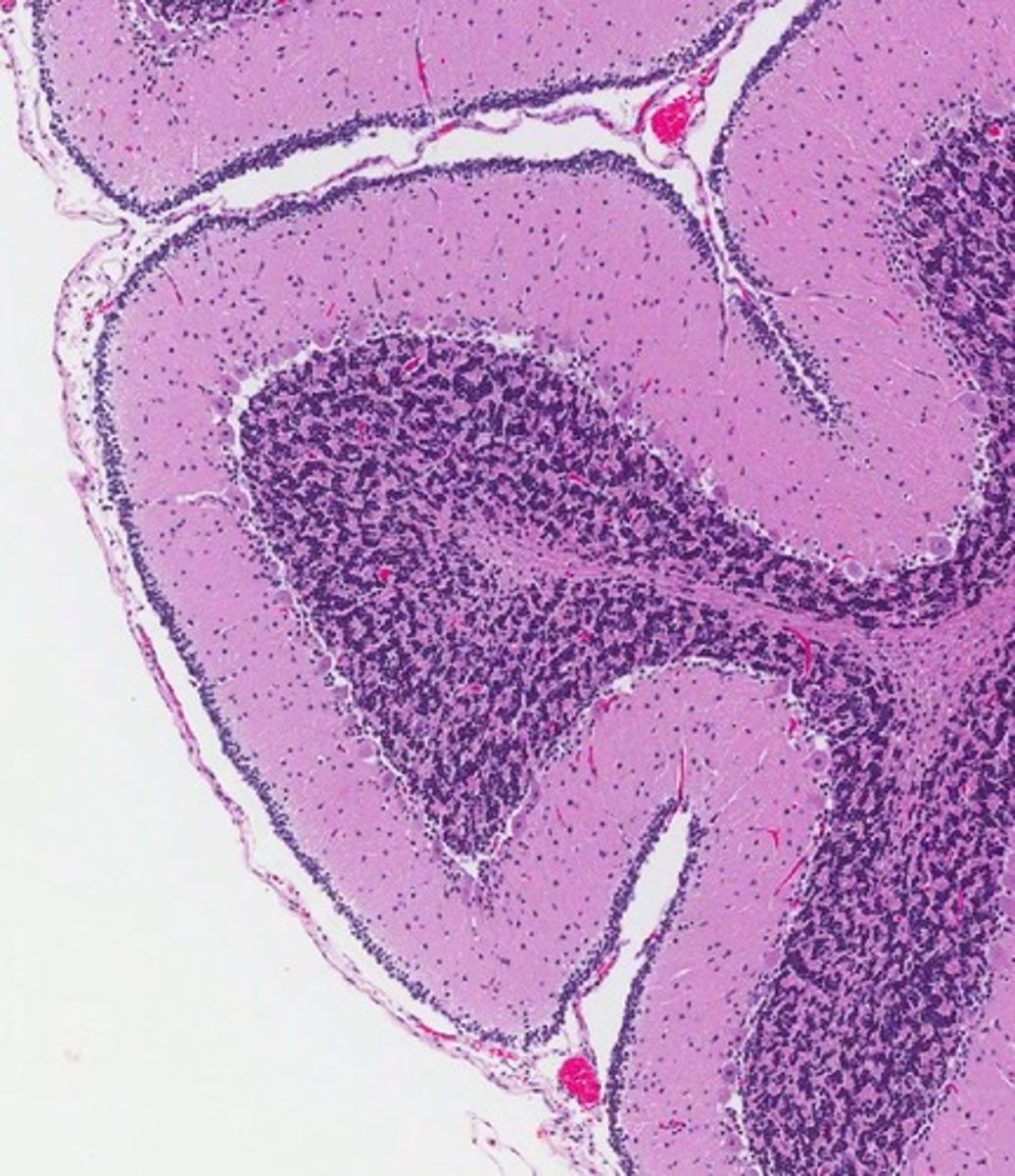
What are the layers of the neonatal cerebellum mentioned in the notes?
The layers of the neonatal cerebellum include the External Granular Cell Layer, Molecular Layer, Purkinje Cell Layer, and Internal Granular Cell Layer.
What staining method is used to visualize astrocyte processes?
H&E staining is used, with astrocyte processes appearing brown due to GFAP expression.
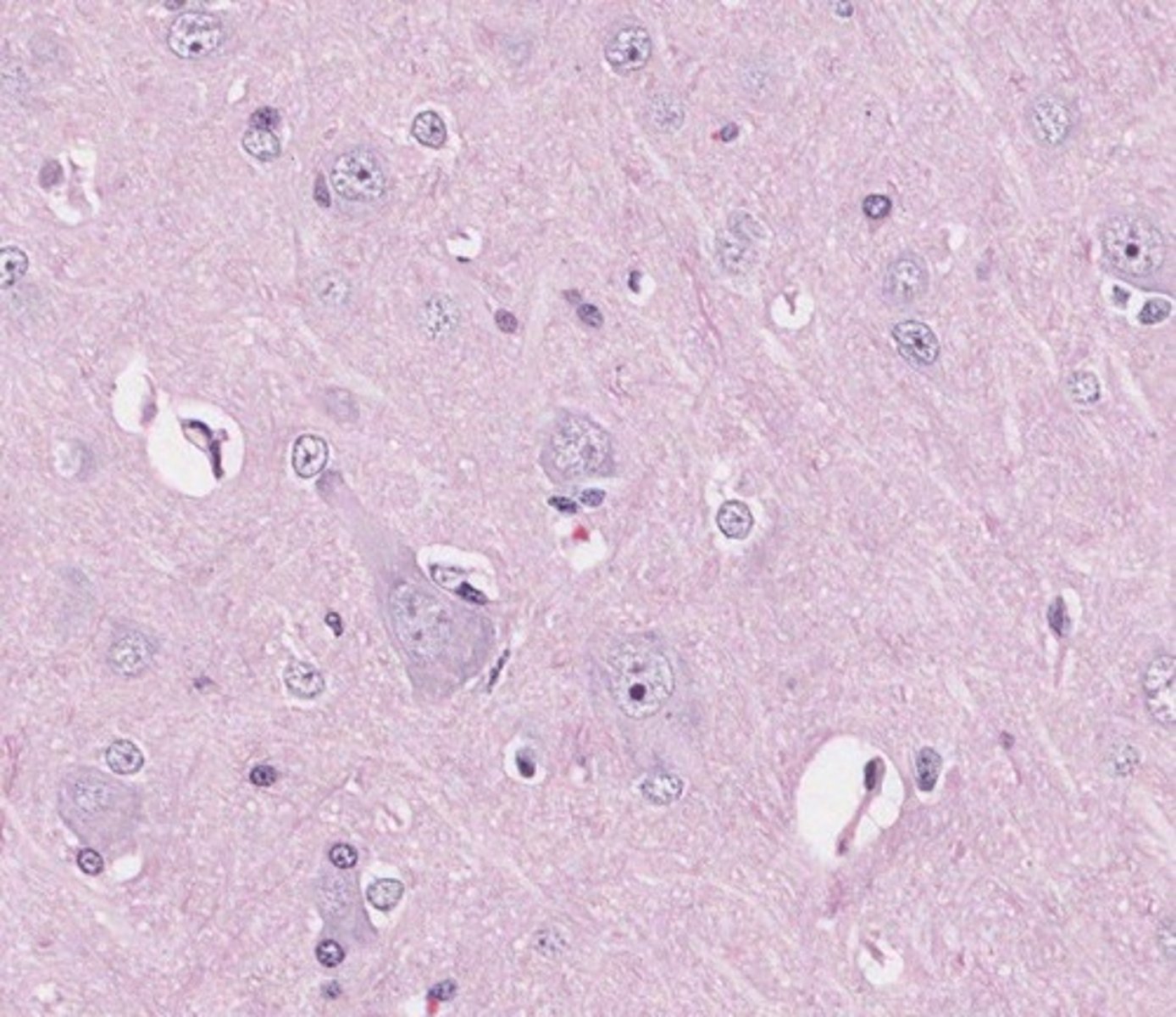
What is the role of astrocytes in the development of the central nervous system?
Astrocytes provide a scaffold for development, supporting the growth and organization of neurons.