Motivation and wellbeing - psych
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is motivation
The conscious or unconscious drive leading the behaviour that individuals initiate direct and maintain
*Observable behaviours
What are motives
They are the desires behind goal directed behaviour
*Motives influence behaviour
What are the sources of motivation
Physiological
Cognitions
Emotional
Social
What is physiological motivation?
The needs for survival that motivate most human behaviour
E.g. sleep, toilet, drink, hunger, etc.
What is cognitions?
Refers to motivation being derived from intellectual challenges due to the intrinsic motivation that they produce
This drive is to satisfy curiosity and explore personal interest
E.g. values, goals, expectations, etc.
What is emotional motivation?
Motivation can stem from trying to avoid pain and seeking happiness
E.g. avoid fear, anger, stress, or strive for happiness and joy
What is social motivation?
The drive to form connections and relationships with the people around us
E.g. peer pressure, conforming, and seeking approval
What are Deci and Ryan’s (1985) 3 types of motivation - SDT?
Amotivation
Extrinsic
Intrinsic
What is amotivation?
It is the lack of intrinsic or extrinsic motivation
Increases when the environment doesn’t allow for behaviour to be performed
What is extrinsic motivation?
Motivation that stems from the desire for external rewards
This motivation is means to an end - meaning that when the reward is earnt, the behaviour ends
E.g. respect, money, awards, social recognition, etc.
What is intrinsic motivation?
Refers to motivation driven by an inner desire for self-actualisation (full potential), arising from achieving a specific goal
This motivation is an end in itself
E.g. self-gratification
What are Deci and Ryan’s (1985) recognised psychological needs for motivation - SDT?
Autonomy
Competency
Relatedness
What is Autonomy?
Refers to how people need to feel in control of their own actions
Satisfying this need improves their wellbeing, leading to increased motivation
What is competency?
The desire to feel capable of mastering new skills and experiencing a sense of achievement
It increases the likelihood that an individual will feel satisfaction from overcoming their obstacles
What is relatedness?
People have a longing to form social connections and be a part of positive relationships
It improves wellbeing
What are the strengths of self-determination theory?
The theory is applicable across cultures and context - the three needs are universal
Intrinsic motivation is a crucial aspect of self-determination theory. It supports the tendency for people to do things that they enjoy, rather than doing things for external rewards
What are the limitations of self-determination theory?
The strong emphasis on autonomy is argued to minimise the influence that external rewards have on motivation
The theory has multiple complex components, it may limit the ability to comprehend and apply (facilitator)
What is the application of self-determination theory?
It is of interest to teachers, employers, and managers, to increase the three psychological needs
This improves self-determination which leads to intrinsic motivation, which then promotes positive wellbeing
What is self-actualisation?
Maslow (1954) created a hierarchy of needs, based on the idea that everyone should reach self-actualisation
It is the ultimate state of being that everyone is trying to attain
It involves reaching one’s full potential and continually seeking growth and knowledge
What are the two types of motivation and needs (Maslow, 1954)?
Deficiency needs
Growth needs
What are deficiency needs (Maslow 1954)
They are basic needs that people are motivated to fulfil due to their absence.
Important for survival
Motivation decreases as each need is met
E.g. hungry, but eats food - need fulfilled
What are growth needs (Maslow, 1954)
They are needs that once met act as the motivation to continue fulfilling them
Develops a unique personality, leads to happiness, motivation increases as the need is met
E.g. graduating and inspired to reach your full potential
What was Maslow’s 1954 first hierarchy of needs
Physiological needs
Safety needs
Love and belonginess
Esteem needs
Self-actualisation
*don’t reference pyramid for exam
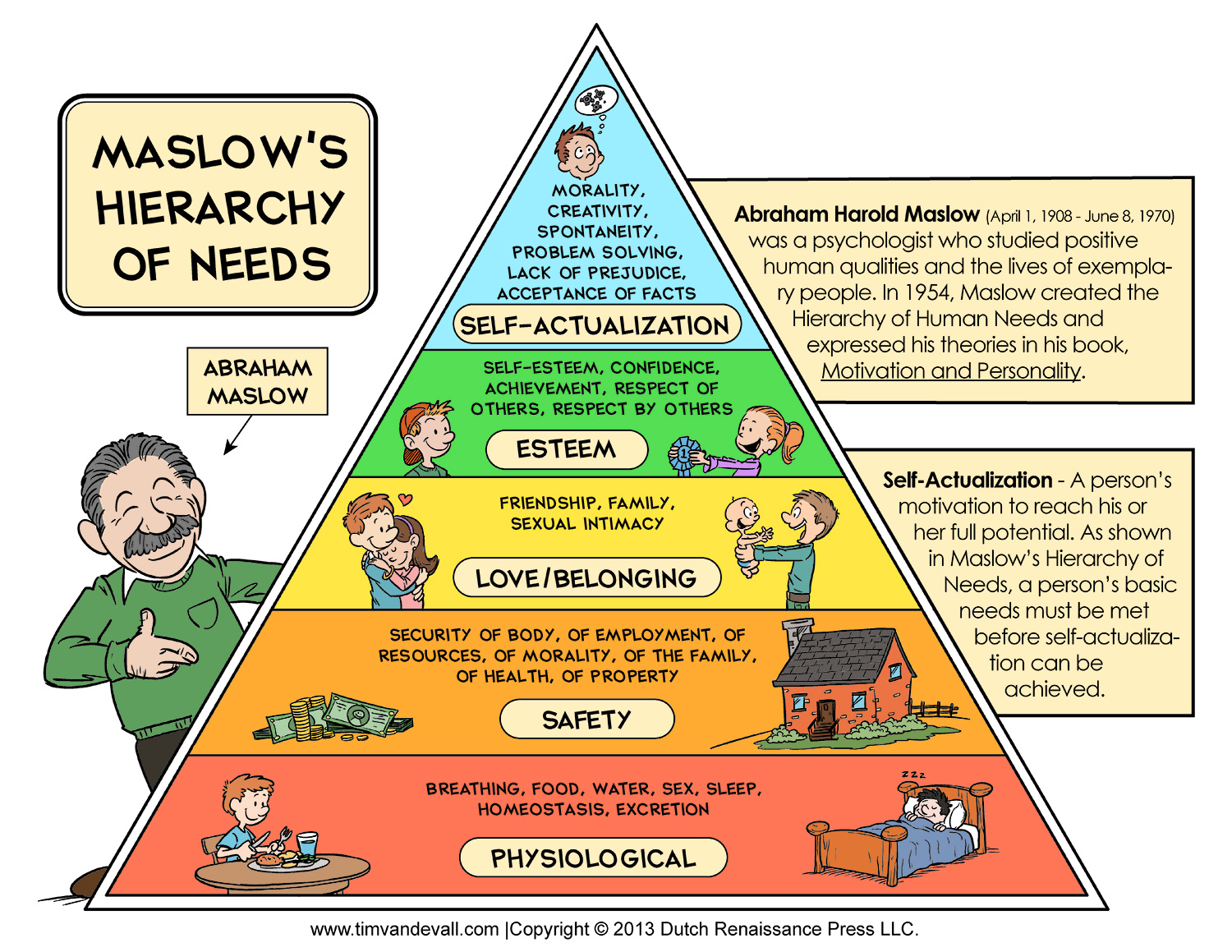
What was Maslow’s revised 1970 hierarchy of needs?
Physiological needs
Safety needs
Love and belonginess
Esteem needs
Cognitive needs
Aesthetic needs
Self-actualisation
Transcendence needs
What are the deficiency needs?
Physiological needs
Safety needs
Love and belonginess
Esteem needs
What are physiological needs?
Basic biological requirements that provide energy, physical contentment, and health
E.g. food, water, shelter, etc.
What are safety needs?
Involves both physical and emotional safety.
When these needs are not met, it causes anxiety and a lack of confidence in the environment
E.g. order, stability, free from threat, etc.
What is love and belonginess?
Incorporates both receiving love and giving love
A lack of love and belonging can result in isolation and loneliness
E.g. feeling worthy of love, affection, etc.
What are esteem needs?
There are two components:
Self esteem: desire for achievement, confidence, and freedom
Respect from others: recognition, attention, and appreciation from others
What are the growth needs?
Cognitive needs
Aesthetic needs
Self-actualisation
Transcendence needs
What are cognitive needs?
Gaining knowledge and understanding through the senses, personal experiences, and mental activity
A curiosity to understand
Philosophy and theology
What are aesthetic needs?
The appreciation for anything beautiful (the things around us). It contributes to a positive wellbeing
Not reaching this level can cause a sense of discomfort
What is self-actualisation?
It refers to how each person has their own way of reaching a feeling of self-realisation, self-fulfillment, and self-actualisation
It increases as people are autonomous
Peaks and troughs are normal here
Restlessness and discontentment are barriers to reaching self-actualisation
What are Transcendence needs?
Going beyond the limits of human experience. The deeper meaning found is then used to help humanity, rather than focusing on the self.
What are the strengths of Maslow’s (1954, 1970) theory?
The theory focused on healthy human psychological development, which was uncommon at the time
The theory was supported by a meta-analysis conducted by Alexander and colleagues (1991, et all). Results from 42 studies revealed that transcendental meditation (variant of yoga) was associated with significant progress toward self-actualisation
What are the limitations of Maslow’s (1954, 1970) theory?
The sample was small and purposefully selected by Maslow. It lacked objectivity as he used subjective measures only
The hierarchical categorisation of needs oversimplifies complex human behaviour. Other theorists have argued that this is not the most suitable structure for human needs.
The pyramid shape was not created by Maslow, but has become popular, it is not reflective of human behaviour and life’s obstacles
What is the application of Maslow’s (1954, 1970) theory?
Maslow’s theory provides the framework to educational programs around the world - physiological needs are required before other needs can be met (e.g. recess and lunch)
What is subjective wellbeing - Diener 1984 ?
A mixture of negative and positive measures and overall emotional and cognitive assessment of life that is personal to the individual
It is based on the personal experiences of an individual and therefore ‘subjective’ for each person
What are the three main components that make up the concept of subjective wellbeing - Diener 1984
Life satisfaction
Affective balance (positive)
Affective balance (negative)
What is life satisfaction?
Refers to the overall assessment a person makes of their life and their own life experiences
It is influenced by feeling an overall positive affect of mood, usually influenced by those closest to you
These global judgements are the ‘cognitive’ measures of wellbeing
What is affective balance?
It encompasses all the moods, emotions, and feelings that an individual experiences. The moods and emotions make up the ‘emotional’ measure of wellbeing
Positive affect = pleasant emotions
Negative affect = unpleasant emotions
People experience positive and negative affect and attempt to enhance their lives by reducing negative affect and increasing positive affect
A global judgement of happiness is continuously assessed by people comparing their negative affect with positive affect
What makes up subjective wellbeing?
Life satisfaction + affective balance = subjective wellbeing
What are the strengths of Diener’s 1984 theory?
The theory has cultural universality and can be applied across cultures and contexts
The theory is comprehensive and holistic (focuses on the good)
What are the limitations of Diener’s 1984 theory?
External factors are not considered in the theory
E.g. finances, work conditions, relationships, and cultural influences
The theory relies on self-reporting, which can produce bias when participants give answers in order to be socially desirable
What is the application of Diener’s 1984 theory?
The effectiveness of public health initiatives and policies are positively influenced by the knowledge of subjective wellbeing - includes a longitudinal study
What is the PWB
The psychological wellbeing scale - designed by Ryff based on her theory of psychological wellbeing
What are the components of the 6 factor model of wellbeing - Ryff 1989
Autonomy
Environmental mastery
Personal growth
Positive relations with others
Purpose in life
Self-acceptance
What is autonomy?
Refers to individuals seeking personal evaluation from within themselves using their own standards and the ability to make their own decisions using free will
What is the dimension of autonomy?
High autonomy = they are independent and able to make their own choices based on self-accepted moral principles, rather than feeling pressured to conform to social norms
Low autonomy = they are highly concerned by what society thinks of them and is easily pressured to conform to social norms, making decisions based on the opinions of others.
What is environmental mastery?
Rather than accepting things for how they are, especially when they are not desirable, it involves manipulating the surroundings to best suit personal needs - a feeling of being able to influence others
What is the dimension of environmental mastery?
High environmental mastery = they feel confident in manipulating their environment, manages complicated tasks, and makes the most of situations they find themselves in
Low environmental mastery = they feel unable to manipulate their surroundings, finds complex tasks overwhelming, and feel little control over their external environment
What is personal growth?
Utilising past and present experiences, allowing one to continually develop as a person and experience new things
What are the dimensions of personal growth?
High personal growth = they have a sense of continual development and self-improvement, welcomes new experiences, and reflects upon them to increase knowledge
Weak personal growth = they feel a sense of stagnation due to a lack of personal improvement, is unmotivated to try to better themselves, finds life boring, and feels unable to shift this mindset
What is positive relations with others?
Refers to how individuals who self-actualise find importance in forming genuine relationships with other people and also in guiding the younger generations.
Such individuals believe in the significance of forming empathetic connections with others
What are the dimensions of positive relations with others?
Strong positive relations = they understand that relationships involve a balance of give and take, are empathetic, affectionate, and caring, and can participate in trusting relationships
Weak positive relations = unwilling to make compromises in relationships, has difficulties caring for others and forming intimate and trusting human connections
What is purpose in life?
Refers to how meaning in life evolves over time and requires the individual to continually re-evaluate its intentionality and direction
What is the dimension of purpose in life?
Strong purpose in life = believes the past and present life is meaningful, sets life goals to follow and has a sense of direction
Weak purpose in life = feels that life lacks purpose
What is self-acceptance?
An individuals acknowledgement of their personal strengths, weaknesses, and past decisions and behaviours
What are the dimensions of self-acceptance?
High acceptance = accepting of good and bad personal characteristics, has high self-esteem, and has a positive view of the life they have lived
Low acceptance = concerned by certain parts of their character, has low self-esteem, and is disappointed in their past life
What are the strengths of Ryff’s 1989 theory?
Ryff’s model encompasses multiple dimensions, unlike other wellbeing models (Diener 1984)
Ryff created a PWB survey that allowed empirical evidence to be collected. It had high reliability and validity
What are the limitations of Ryff’s 1989 theory?
Additional everyday factors that affect wellbeing are not accounted for
E.g. Economic and social factors
Does not account for negative affect (random)
E.g. adversity, hardships (breakup), etc.
What is the application of Ryff’s 1989 theory?
There is a relationship between optimal sleep duration and psychological wellbeing