Physical Activity for Wellness and Interventions
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What term can be defined as any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires an expenditure of energy?
Physical activity
Physical Activity
Any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditure
What has been identified as the fourth leading risk factor for global mortality (e.g. 6% of deaths)?
Physical inactivity (e.g. lack of physical activity)
True or False: Physical activity is more than just exercise, it includes any movement one does.
True
Exercise
Planned, structured, and repetitive movement intended to improve or maintain physical fitness
What perspective highly values physical fitness and activity?
Fitness ethic
Fitness Ethic
A perspective that highly values physical fitness and activity
What does fitness ethic assist with?
Prevention of disease and injury
Examples of Fitness Ethic
The Olympics
Presidents Council on Physical Fitness and Sports
United States National Health Objectives
What does cardiorespiratory fitness include?
Aerobic endurance exercises
What does household physical fitness include?
Instrumental activities of daily living that require movement
What term can be defined as how the heart and lungs sustain physical activity?
Endurance
Endurance
How the heart and lungs sustain physical activity
What term can be defined as the standard unit of measure that estimates the amount of oxygen used by the body during physical activity?
Metabolic equivalent
Metabolic Equivalent
The standard unit of measure that estimates the amount of oxygen used by the body during physical activity
3 Barriers to Physical Activity
1. Time
2. Place
3. Access
Personal Barriers to Physical Activity
Time (e.g. school, work)
Self-esteem (e.g. body image)
Life roles (e.g. caregiving)
Social influences (e.g. friends, family)
Energy
Motivation
Fear of injury
Skill
Resources
Weather conditions
Travel
Family obligations
Aging
Solutions to a Lack of Time for Physical Activity
Monitor daily activities for one week
Identify at least three 30-minute time slots for physical activity
Add physical activity to daily routine (e.g. walk, bike, exercise)
Organize activities around physical activity (e.g. park far away)
Select activities that require minimal time (e.g. climbing stairs)
What can a negative body image hinder?
Physical activity
Solutions to Social Influences for Physical Activity
Explain interest in physical activity to friends and family
Ask friends and family to support efforts
Invite friend and family to exercise with you
Plan social activities involving exercise (e.g. pickle ball)
Develop new friendships with physically active people
Join a physical activity group (e.g. YMCA, hiking club)
Solutions to a Lack of Energy for Physical Activity
Schedule physical activity around energetic times of the day
Convince yourself that physical activity will increase energy
Solutions to a Lack of Motivation for Physical Activity
Plan ahead (e.g. write in on the calendar)
Make physical activity a regular part of daily schedule
Invite a friend to exercise with you on a regular basis
Join or start an exercise group or class
Solutions to a Fear of Injury from Physical Activity
Learn how to warm up and cool down to prevent injury
Exercise appropriately considering age, fitness, skill, and health
Choose activities involving minimum risk (e.g. low impact)
Solutions to a Lack of Skill for Physical Activity
Select activities requiring no new skills (e.g. walking, jogging)
Take a class to develop new skills (e.g. zumba, kickboxing)
Solutions to a Lack of Resources for Physical Activity
Select activities that require minimal facilities or equipment
Identify inexpensive, convenient resources in community
Join a program (e.g. park and recreation, worksite)
What forms of physical activity are available in any weather condition?
Indoor cycling or swimming
Aerobic dance
Calisthenics
Stair climbing
Rope skipping
Mall walking
Dancing
Gymnasium games
Solutions to Physical Activity in Traveling
Put exercise equipment in suitcase (e.g. jump rope)
Walk the halls and climb the stairs in hotels
Stay in places with swimming pools or exercise facilities
Join gyms with mobile memberships (e.g. YMCA, YWCA)
Visit the local shopping mall and walk for half an hour or more
Load phone with favorite aerobic exercise music
Solutions to Family Roles and Obligations for Physical Activity
Trade babysitting time
Exercise with kids (e.g. go for a walk together, play tag)
Use equipment while kids are playing or sleeping
Try to exercise when the kids are not around (e.g. school)
Solutions to Aging for Physical Activity
Look upon retirement as an opportunity to become active
Spend time gardening, walking the dog, playing with children
Make great walking partners
Learn a new skill (e.g. ballroom or square dancing, swimming)
Make regular physical activity a part of every day
Go for a walk every morning or every evening before dinner
Ride an exercycle while reading a favorite book or magazine
Environmental Barriers to Physical Activity
Accessibility (e.g. walking paths, cycling trails, rec facilities)
Support system (e.g. family, friends, pets, community)
Legislation (e.g. campaigns, policies, procedures)
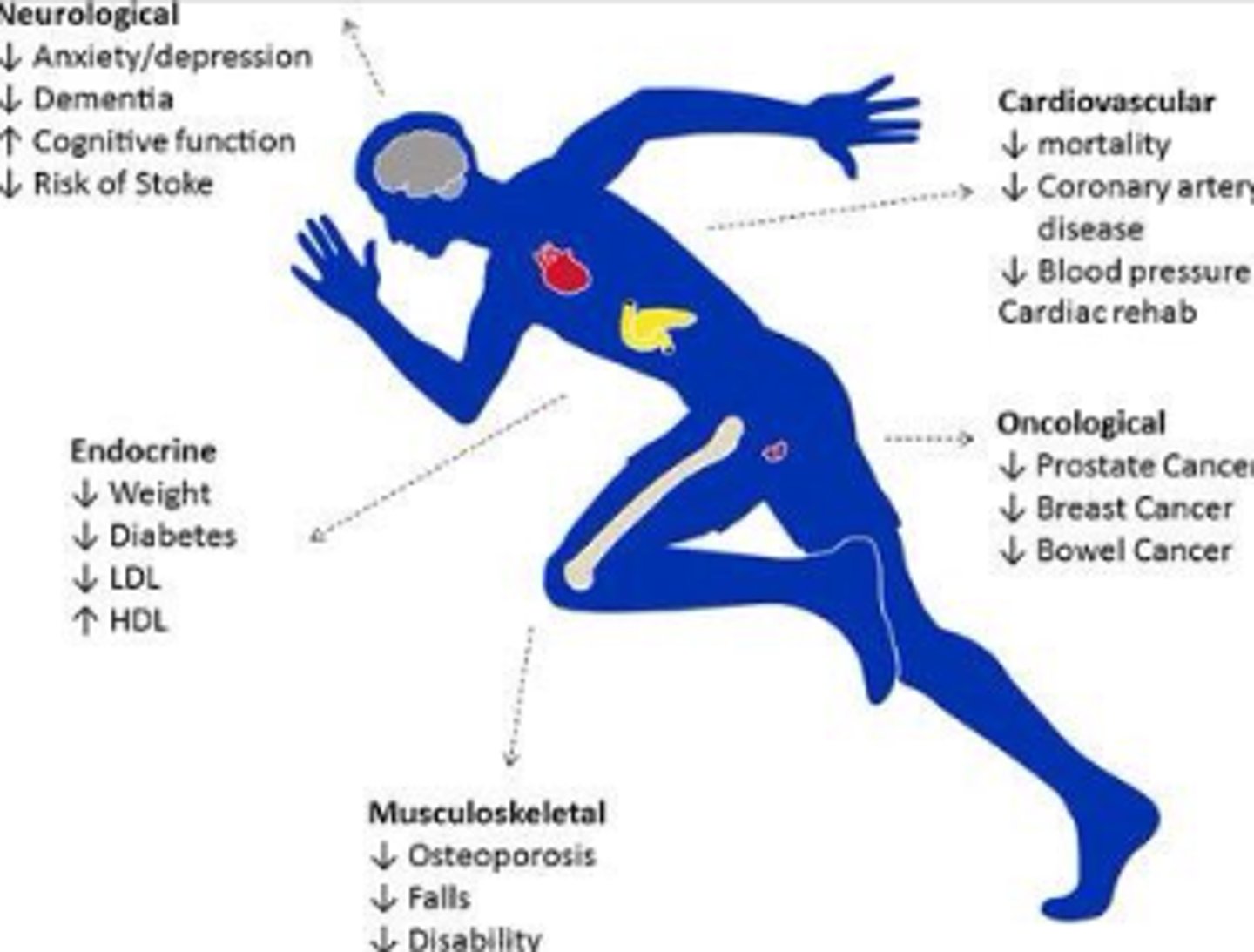
Benefits of Physical Activity
Prevention of chronic diseases (e.g. heart disease, diabetes)
Reduction of body fat around the abdomen
Decreases blood pressure
Maintenance of muscles and bone density
Controls weight
Reduction of stress, anxiety, and depression
What is the aim of Active People Healthy Nation?
Help Americans become more physically active by 2027 to improve their overall health and quality of life and to reduce healthcare costs
What is the aim of Coordinated Approach To Child Health (CATCH)?
Promote physical activity and healthy food choices and prevent tobacco use in schools
What is the aim of Bounce at University of Houston?
Reduce obesity related chronic illness in underserved communities (e.g. African American, Latino) and increase children's self-esteem
What is the aim of Adolescent Health: Think, Act, Grow® (TAG)?
Promote activities that support physical, social, emotional, and mental health for teens
What is the most frequently used model in physical activity research?
Transtheoretical Model of Change
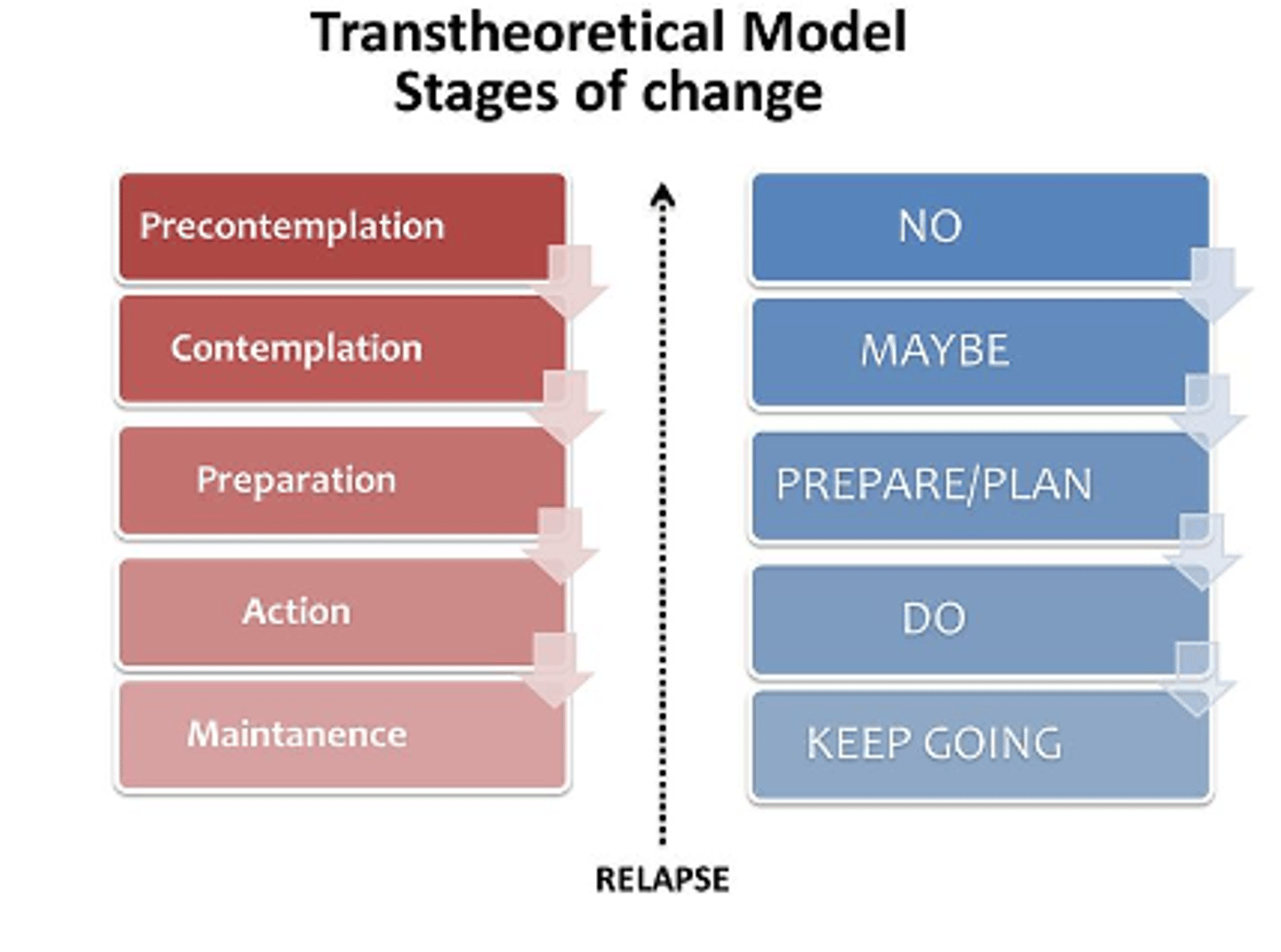
How does the Transtheoretical Model of Change view change?
As a dynamic process
Interventions to Promote Physical Activity for Children Under 6
Allow them to be active naturally (e.g. play)
Aim to keep them moving for 3 hours a day
Limit time when they're just sitting around (e.g. sitting around)
Interventions to Promote Physical Activity for Children 6-17 Years
Aerobic (60+ minutes of moderate-vigorous intensity, 3x/week)
Muscle strengthening (60+ minutes, 3x/week)
Bone strengthening, resistance (60+ minutes, 3x/week)
Participate in age-appropriate and enjoyable activities
Physical Education in Comprehensive School Physical Activity Programs
An academic subject characterized by a planned, sequential K-12 curriculum that is based on the national standards for physical education
What is the aim of physical education in schools?
Increase level of physical activity
Improve grades and standardized test scores
Stay on-task in the classroom
Does increased time spent in physical education negatively affect students’ academic achievement; yes or no?
No
What does physical education provide?
Cognitive content and instruction designed to develop motor skills, knowledge, and behaviors for physical activity and physical fitness that can be maintained for a lifetime
Forms of Physical Activity in School
Physical education
Recess
Classroom physical activity
Physical activity before and after school
Recess
A regularly scheduled period in the school day for physical activity and play that is monitored by trained staff or volunteers
What are students encouraged to do during recess?
Be physically active and engaged with their peers in activities of their choice, at all grade levels, kindergarten through 12th grade
Benefits of Recess
Increase level of physical activity
Improve memory, attention, and concentration
Help children stay on-task in the classroom
Reduce disruptive behavior in the classroom
Improve social and emotional development (e.g. sharing)
Classroom Physical Activity
Any physical activity done in the classroom, taking place at any time in one or several brief periods during the school day
What does classroom physical activity include?
Integrating physical activity into academic instruction as well as providing breaks from instruction specifically designed for physical activity
True or False: Classroom physical activity should be offered in addition to physical education and recess and at all school levels (elementary, middle, high school).
True
Benefits of Classroom Physical Activity
Improve concentration and ability to stay on-task
Reduce disruptive behavior in the classroom (e.g. fidgeting)
Improve motivation and engagement in the learning process
Help to improve their academic performance
Increase their amount of daily physical activity
What does physical activity before and after school include?
Walking or biking to and from school programs
Physical activity clubs
Intramural programs (e.g. sports organized by the school)
Interscholastic sports (e.g. sports between schools)
Physical activity in before and after-school extended day
How much exercise should adolescents get each day?
At least 60 minutes of varied, moderate-to-vigorous intensity exercise
Why should exercise for adolescents be varied?
To strengthen their heart, bones, and muscles
Exercises to Strengthen the Heart
Brisk walking
Cycling
Swimming
Exercises to Strengthen the Bones
Running
Jumping rope
Playing basketball
Exercises to Strengthen the Muscles
Lifting weights
Yoga
What does daily physical activity improve?
Health
Fitness
Quality of life
Benefits of Daily Physical Activity for Children
Improve grades
Increase self-confidence
Reduce stress
What is poor physical fitness in early adulthood linked to?
Increased mortality (20%)
Benefits of Daily Physical Activity for Early Adulthood
Reduce obesity and co-morbid conditions linked to obesity
Reduce likelihood of cognitive decline
Reduce early onset of certain chronic diseases and mortality
Improve mental focus for education, learning new skills, trades
Benefits of Daily Physical Activity for Middle Adulthood
Reduce risk for chronic diseases (e.g. high blood pressure)
Increase energy
Improve mood
Promote better sleep
How much exercise should middle-aged adults get a week?
150 minutes of moderate intensity
75 minutes of vigorous exercise
10 minutes of aerobic exercise
How many muscle strengthening activities should middle-aged adults do a week?
2 or more
What is the loss of strength and stamina attributed to aging caused by?
Reduced physical activity
Does inactivity increase or decrease with age?
Increase
By what age do about one in three men and one in two women engage in no physical activity at all?
75
What are the most popular forms of physical activity among adults aged 65 years and older?
Walking
Gardening
Yard work
What does regular physical activity in adults aged 65 years and older help maintain?
Ability to live independently
What is a key component of a healthy lifestyle?
Regular physical activity
What is regular physical activity related to?
Social support from family and friends
What does regular physical activity improve?
Stamina
Muscle strength
Mood and feelings of well-being
Bones, muscles, and joints
Joint swelling and pain
What does regular physical activity reduce the risk of?
Falling
Fracturing bones
Dying from chronic diseases
Blood pressure
Symptoms of anxiety and depression
Interventions Aimed at Adults for Physical Activity
Community-based physical activity programs
Encourage safe places for walking in any weather
Ensure facilities accommodate participation in physical activity
Provide transportation to physical activity programs
Incorporate physical activity into daily lives
Plan community physical activities
Are people with disabilities more or less likely to engage in regular moderate physical activity than people without disabilities?
Less, despite them having similar needs to promote their health and prevent unnecessary disease
What should people with disabilities do before beginning a program of physical activity to which they are unaccustomed to?
Consult a physician
What intensity of exercise is emphasized for people with disabilities? Why?
Moderate to vary activities and meet individual needs, preferences, and life circumstances
Interventions Aimed at People Living with Disabilities
Adaptive sports and fitness programs
Conducive environments and facilities for physical activity
Ensure that people with disabilities are involved at all stages
Provide daily physical education classes
Incorporate physical activity into daily lives
How can moderate intensity exercise be obtained for people with disabilities?
In longer sessions (e.g. 30-40 minutes of wheeling oneself in a wheelchair) or in shorter sessions of more strenuous activities (e.g. 20 minutes of wheelchair basketball)
Physical Activity Assessments
Activity diary (e.g. record of physical activity)
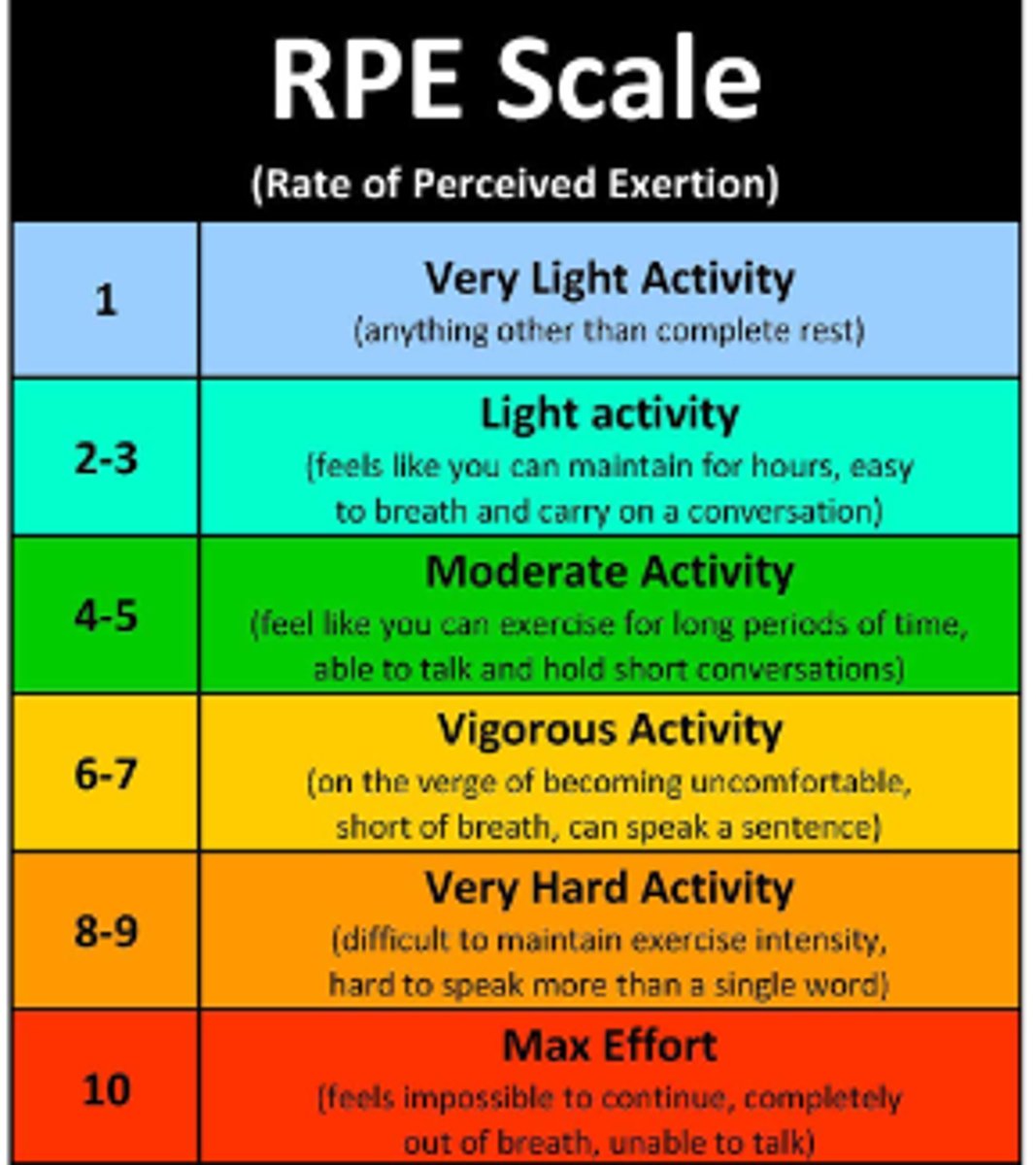
Borg Scale Rating of Perceived Exertion (e.g. level of fatigue)
International Physical Activity Questionnaire
Pedometer
Population based surveys of the environment (e.g. checklist)
Borg Scale Rating of Perceived Exertion
An assessment that examines physical activity through heart rate, respiration rate, sweat, and muscle fatigue
Physical Activity Questionnaire for Young and Middle-Aged Adults (15-64 years)
An assessment used to measure physical activity and reduced sedentary behavior
Pedometer
An assessment that counts steps acting as both a motivational and accountability tool
Walkability Checklist
An assessment that determines how feasible it is to walk to resources in a specific community (e.g. asks about sidewalks, ease of crossing streets, and safety for all ages)
Bikeability Checklist
An assessment that determines how feasible it is to bike within a specific community (e.g. asks about safety when sharing the road and crossing intersections)
What role do occupational therapists play in the promotion of physical activity?
Motivation
Time management
Modification (e.g. down grade, upgrade)
Progress
Tier 1 Interventions for the Promotion of Physical Activity in Children
Consultations with schools regarding physical activity
Development of programs for movement, nutrition, and routine
Diversity training for teachers and students to reduce bullying
Tier 2 Interventions for the Promotion of Physical Activity in Children
Focus on social and recreational activities
Promote healthy eating
Incorporate movement based activities
Provide a safe and stress-free environment
Tier 3 Interventions for the Promotion of Physical Activity in Children
Educational assessment focused on health and wellbeing
Motivation to change a health behavior
Investment of family and individual time to make a change
National Goals for Obesity Prevention and Occupational Therapy
Make physical activity an integral and routine part of life
Promote physical activity through play
Transform messages about physical activity and nutrition
Develop workshops that educate through physical activity