Organic Chemistry 1
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ethanol, esters, carboxylic acids and polymers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the conditions for man-made ethanol production and what is this reaction called?
Hydration - Ethene and steam, 300c, 60-70 atmosphere, phosphoric acid catalyst
100% pure ethanol
What are the conditions for natural ethanol production and what is this reaction called?
Fermentation of sugars - aqueous solution, 30c, zymase enzymes, anaerobic.
15% pure ethanol
Pros and Cons of man-made ethanol
Good access to crude oil - used for spirit burner, solvent, and mixed into petrol, continuous and fast reaction
Not a biofuel - non-renewable resource
Pros and Cons of natural ethanol
Favoured when there is high yield of crops - used for alcoholic drinks, renewable biofuel
Slow process (batch) and slow reaction for zymase to work
Give the equation of the hydration of ethene
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH (CH3CH2OH)
Give the equation of the fermentation of sugars
C6H12O6 (aq) ————> 2C2H5OH (aq) + 2CO2(g) + 2ATP
General formula of alcohol?
CnH2n+1OH
Name the alcohol propane turns into
PropaNOL, C3H8O (CH3CH2CH2OH)
What is the quick test for alcohols?
Acidified potassium dichromate is an oxidising agent, and turns from orange to green as it is being reduced.
What happens when alcohols combust? What does it form?
Carbon dioxide and water
What is the functional group for carboxylic acids?
-COOH
Strong acid vs weak acid
In a strong acid all molecules break down to form H+ ions when added to water/completely dissociate
In a weak acid only a small fraction of molecules break down (reversible reaction) to form H+ ions when added to water
What pH is carboxylic acids?
3-6, acidic (turns blue litmus paper to red)
What do carboxylic acids form when reacted with alkalis
Water and salt
e.g sodium hydroxide + ethanoic acid → sodium ethanoate + water
What do carboxylic acids form when reacted with metals?
Salt and hydrogen
e.g magnesium + methanoic acid → magnesium methanoate + hydrogen
What do carboxylic acids form when reacted with metal carbonates?
Salt, water, and carbon dioxide
e.g calcium carbonate + propanoic acid → calcium propanoate + carbon dioxide + water
What is the molecular and structural formula of ethanoic acid?
Molecular: C2H4O2
Structural: CH3COOH
What is an ester’s functional group?
A molecule that contains -COO- functional group
What are the characteristics of esters?
Volatile compounds with a ‘fruity’ smell
What are esters used in?
Perfumes and food flavourings
How are esters made and what is the catalyst for it?
When an alcohol reacts with carboxylic acid, using drops of concentrated sulphuric acid.
What is the reaction of alcohol and acid reacting together called?
Condensation reaction as a water molecule is lost
Show the reaction of ethanoic acid + ethanol - structural and what it produces
CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH → CH3COOCH2CH3 (ethyl ethanoate)
What is the shortcut for naming/forming esters?
Ethanoic acid (-oate, -CO/OH split)
Ethanol (-yl, -O/H split)
What is a polymer?
A long chain molecule made from many small molecules (monomers) that have joined together.
Alkenes join together to form addition polymers by breaking their double bonds and forming new single bonds that link molecules into a chain
Steps to draw an addition polymer
Redraw monomers so all bonds go up and down
Replace double bond with single bond
Draw longer bonds on each side, add brackets and an n on bottom right corner
How to name a polymer?
alkene → poly(alkene)
Disadvantages of polymers?
Only methods of disposal are:
Burying in landfill - Ugly, uses lots of land, landfill will remain of thousands of years
Incineration - toxic gases released from incomplete combustion, contribute to global warming, but can generate heat/electricity
What is meant by biodegrading?
Break down of polymers by microorganisms
Why aren’t polymers biodegradable
CHEMICALLY INERT, so not biodegradable
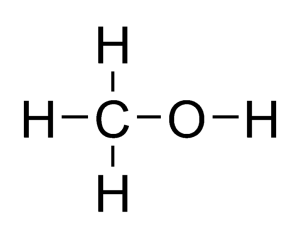
What is the molecular and displayed formula of methanol
CH4O, CH3OH
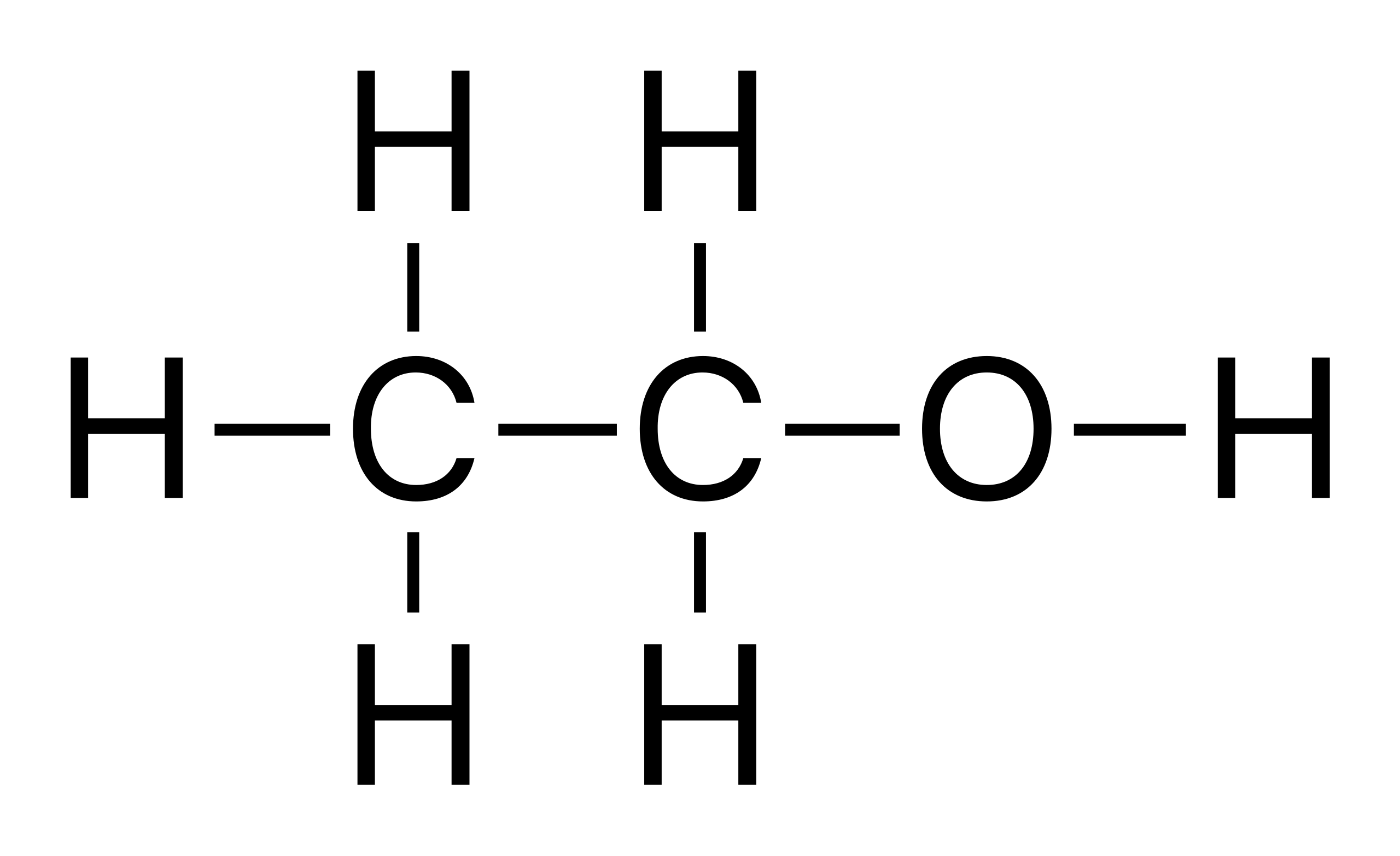
What is the molecular and displayed formula of ethanol
C2H6O, CH3CH2OH
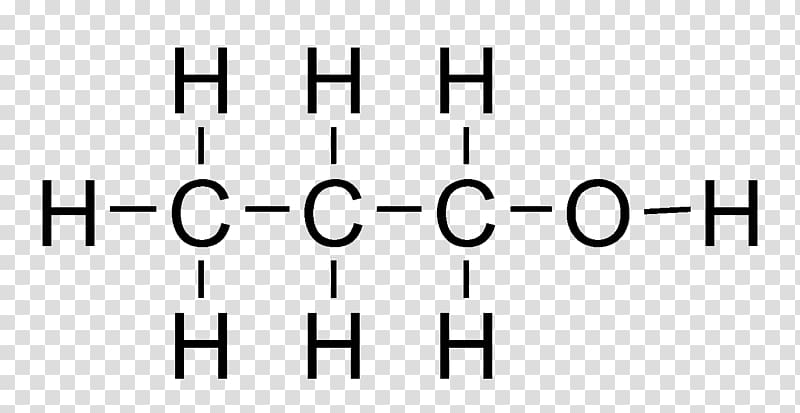
What is the molecular and displayed formula of propanol
C3H8O, CH3CH2CH2OH
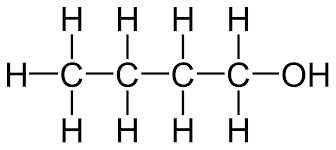
What is the molecular and displayed formula of butanol
C4H10O, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
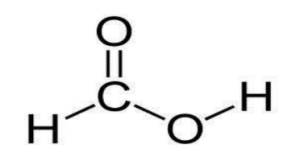
What is the molecular, structural, and displayed formula of methanoic acid
CH2O2, HCOOH
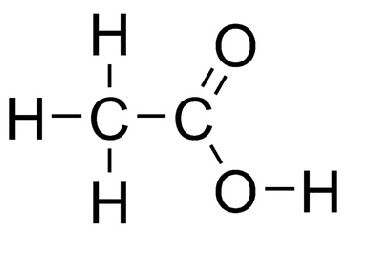
What is the molecular, structural, and displayed formula of ethanoic acid
C2H3O2, CH3COOH
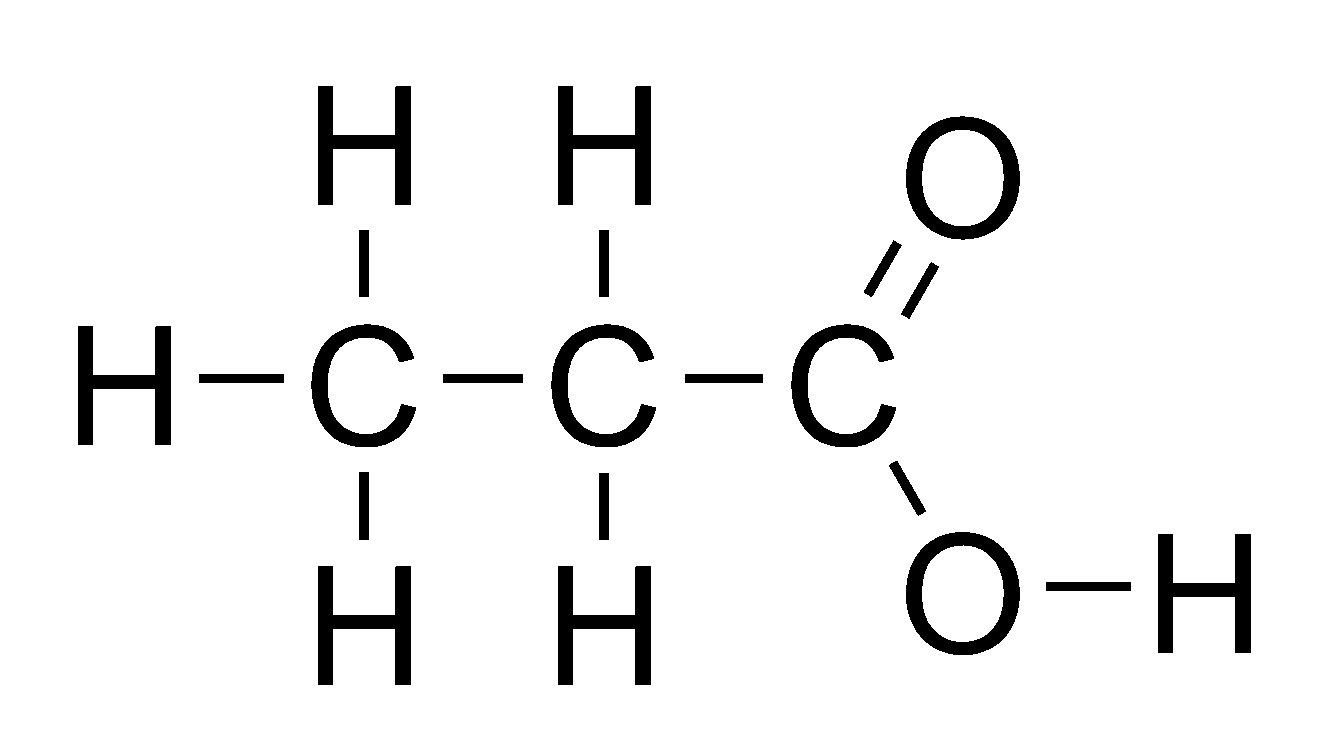
What is the molecular, structural, and displayed formula of propanoic acid
C3H6O2, CH3CH2COOH
What is the molecular, structural, and displayed formula of butanoic acid
C4H8O2, CH3CH2CH2COOH
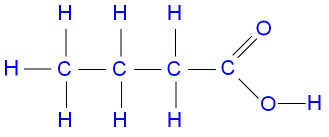
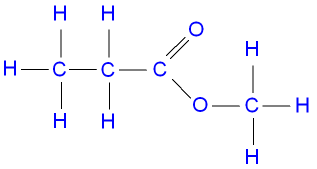
Ester of methyl propanoate structural