Chapter 19 A Revolution in Politics: The Era of the French Revolution and Napoleon
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Treaty of Paris 1783
The peace treaty that saw Great Britain recognize the independence of the American colonies and granted the Americans control of the western territory from the Appalachians to the Mississippi River.
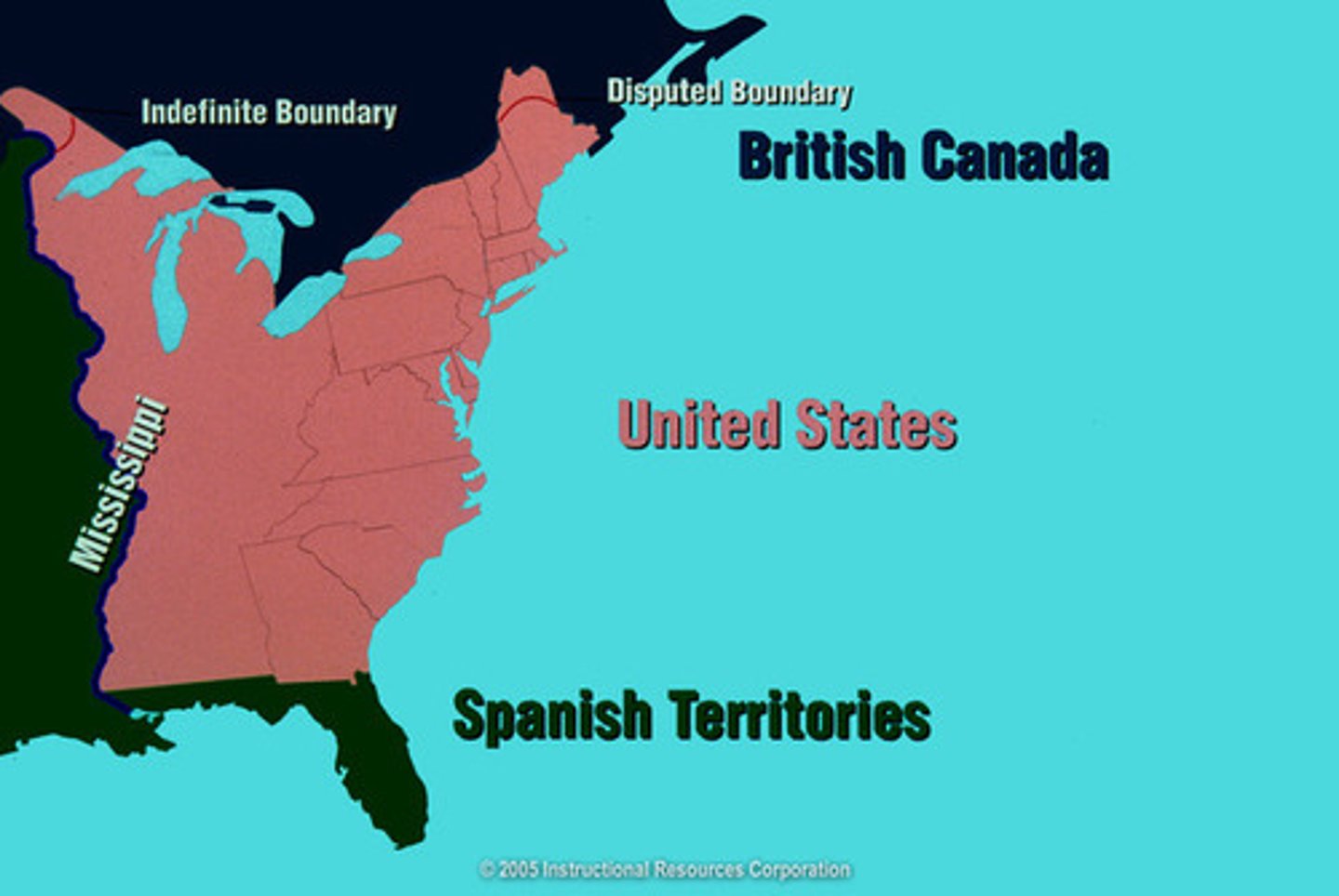
The American Revolutions impact on Europe
Many in Europe saw this event as the embodiment of the ideals of the Enlightenment. Many would push for such ideals and even revolution using the newly formed United States as an example.
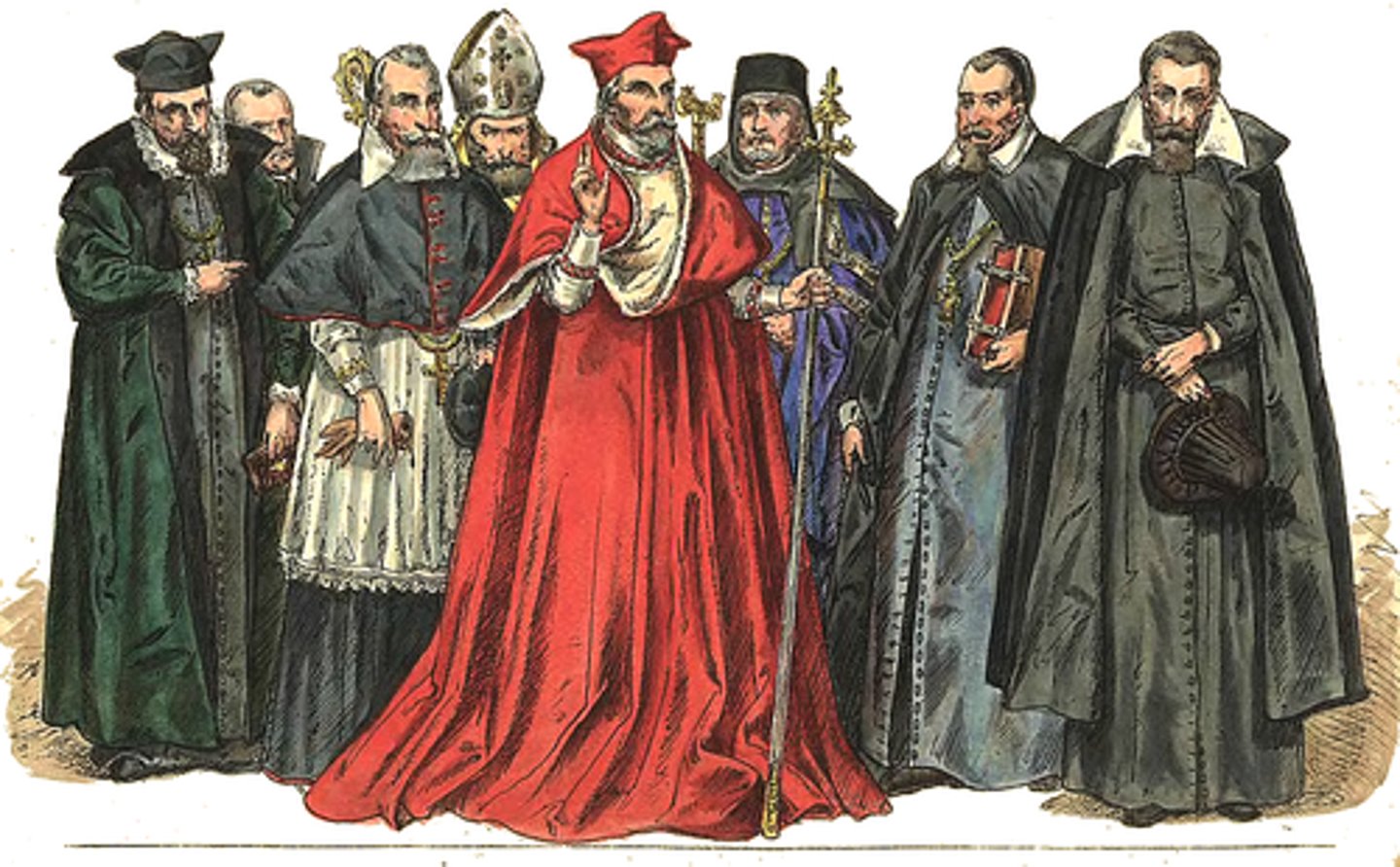
The First Estate
This group numbered around 130,000 in France. This social class was made up of the Clergy. This included the high officials down to the priests and monks. The church was exempt from paying taxes, only paying the state a voluntary amount every 5 years.

The Second Estate
This group numbered around 350,000 people in France. This social class was composed of the nations nobility. They were exempt from taxes. This group had 2 parts, the Nobles of the Sword and Nobles of the Robe.

Nobles of the Sword
This part of French royalty had claim to their status by being descendants of the original medieval nobility. Many in this group although privileged, often were not very wealthy.

Nobles of the Robe
This part of French royalty had claim to their status from office holding. This let those of common birth have a pathway to attain noble rank. They often dominated the royal law courts and important administrative offices.

The Third Estate
This part of French society was made up of commoners and made up the great majority of France. This group had a wide variety within its ranks, from the lowest peasant to skilled artisans and business owners. Made up of the poorest of society, this group paid nearly 100% of the nations taxes.

Bourgeoisie
This was the middle class in France. It consisted of roughly 8 percent of the country. This group often included merchants, industrialists, bankers and lawyers.

The Old Order
The term used to describe the system in France that held the roles in society to the rigid system of estates and ranks in society rather that merit or ability.

The Estates General
This group consisted of representatives of the three estates in French society. It was called out of desperation right before the French Revolution to try and fix Frances financial problems. The previous time they met was back in 1614. The First and Second Estates often voted together to block or overrule the interests of the Third Estate.
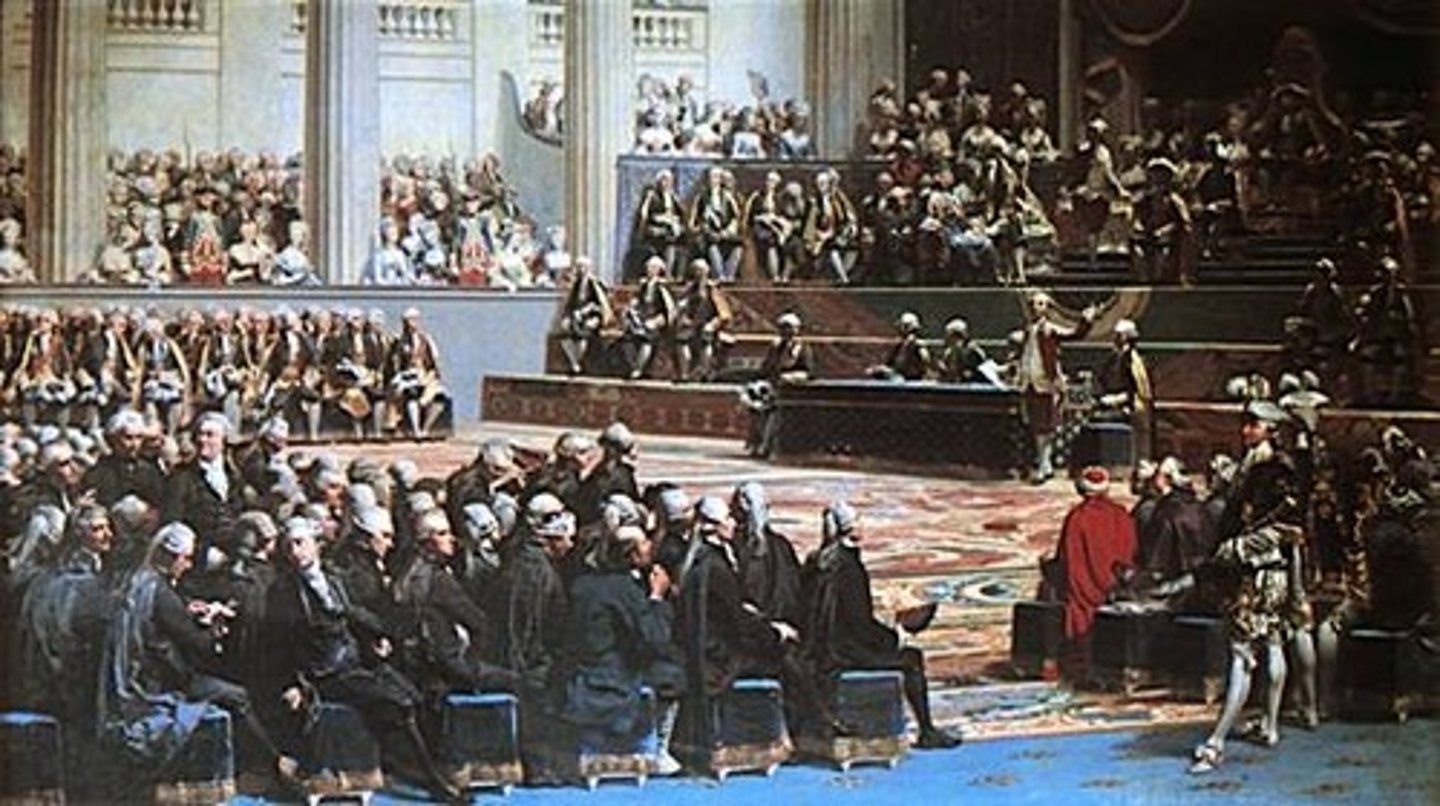

The Tennis Court Oath
A meeting of the Third Estate on June 20, 1789 that took place after they were locked out of the normal meeting place to work on a new constitution for France.

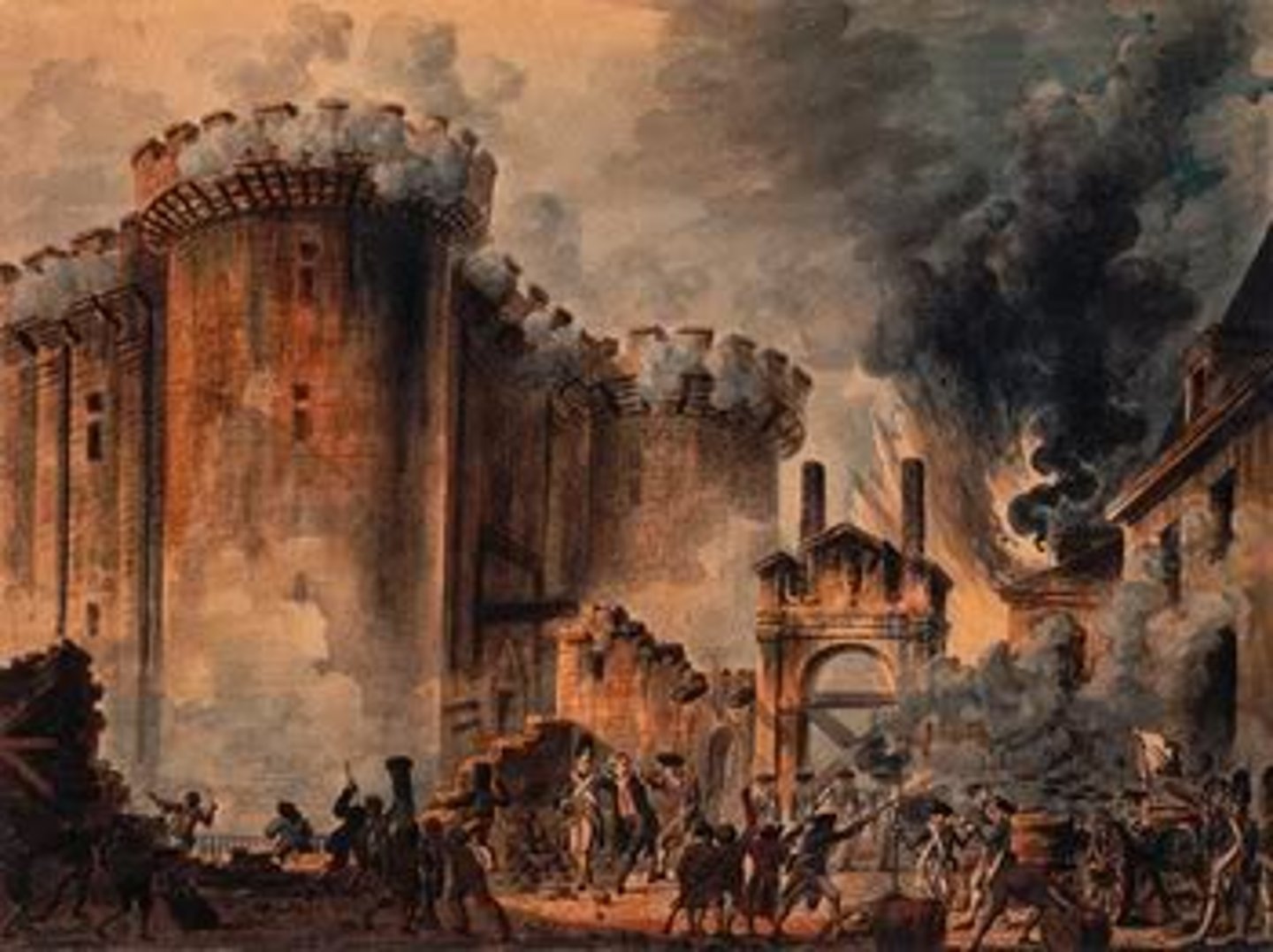
The Bastille
The storming and capture of this infamous political prison was a large symbolic victory for the rebels in their attack on the French government. Its loss showed the monarchy no longer held control of the country or the army.

The Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen
A charter in the early part of the French Revolution that reflected the ideals of the major philosophes of the French Enlightenment and the American Declaration of Independence.

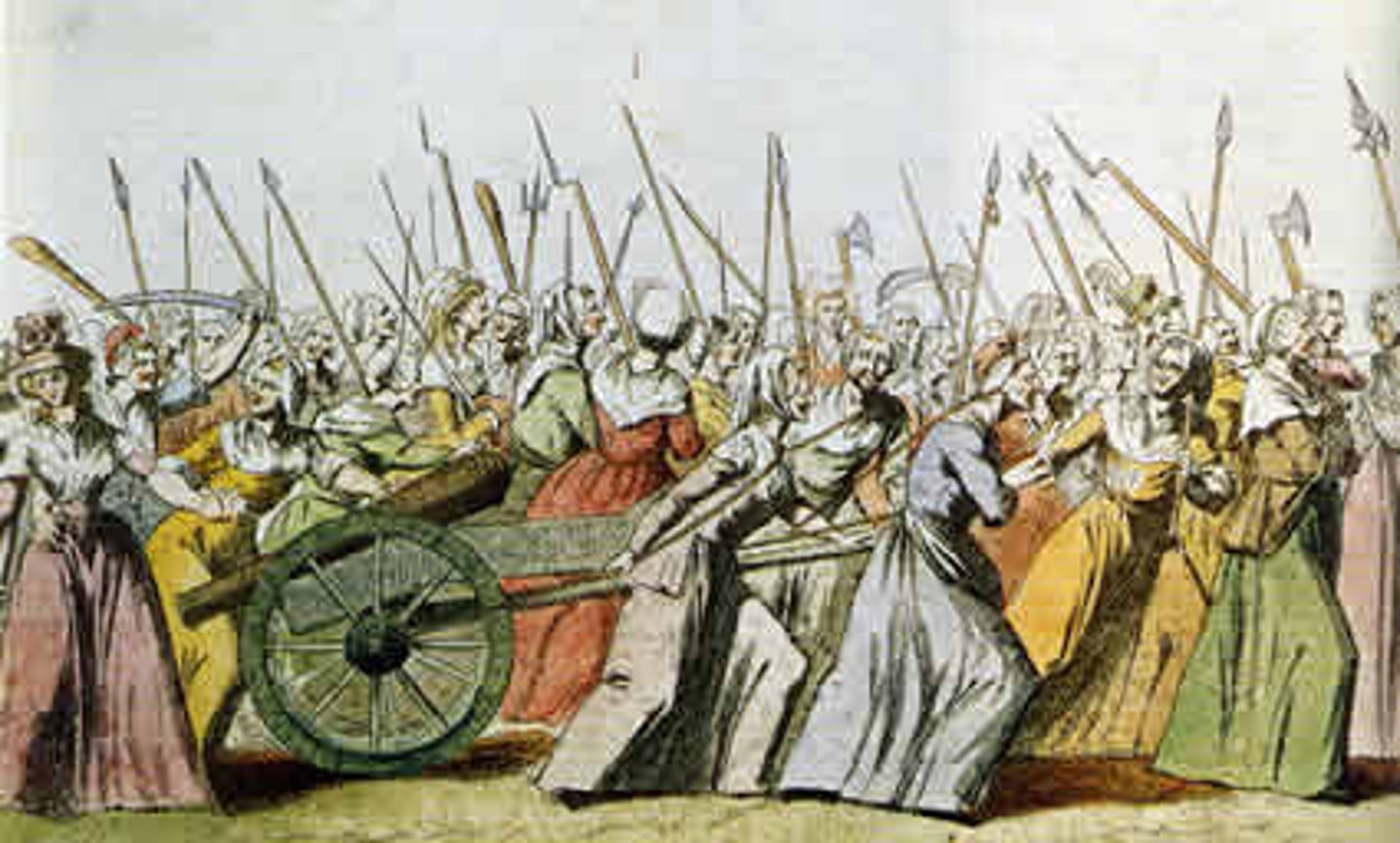
Women's March to Versailles
A large group of French women walked to the King's palace to plead for better conditions and bread for their starving children. It ended with the King being brought back to Paris as a virtual prisoner.

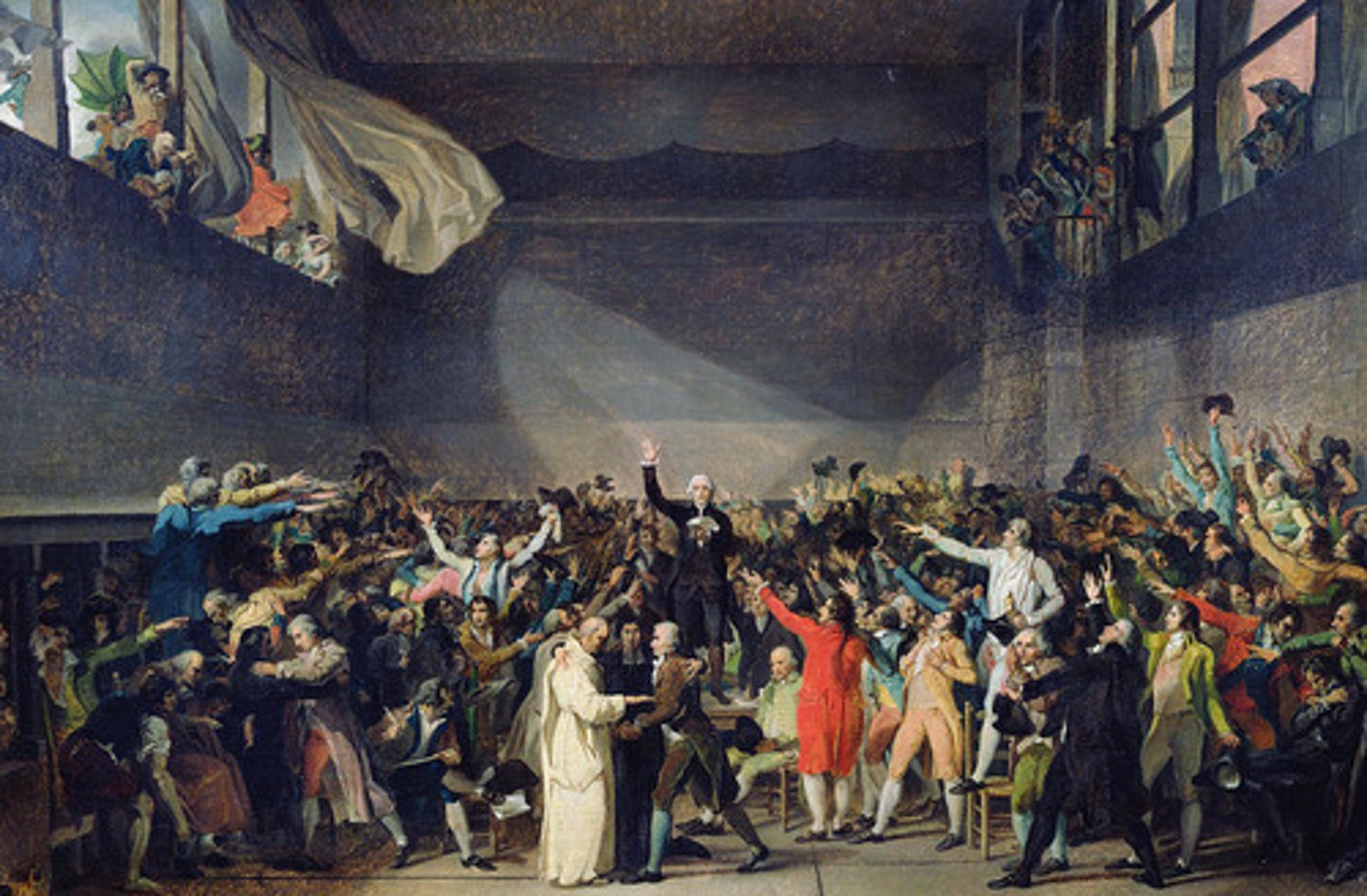
The National Assembly
This would become the new basis for the French government in the early French revolution and would work on a constitution and new government to replace royal power. It would be made up of many who where members of the Third Estate.
Jacobins
This group of more radical deputies had more revolutionary ideas on how to solve France's problems than the fairly conservative National Assemblies early approaches to the crisis.
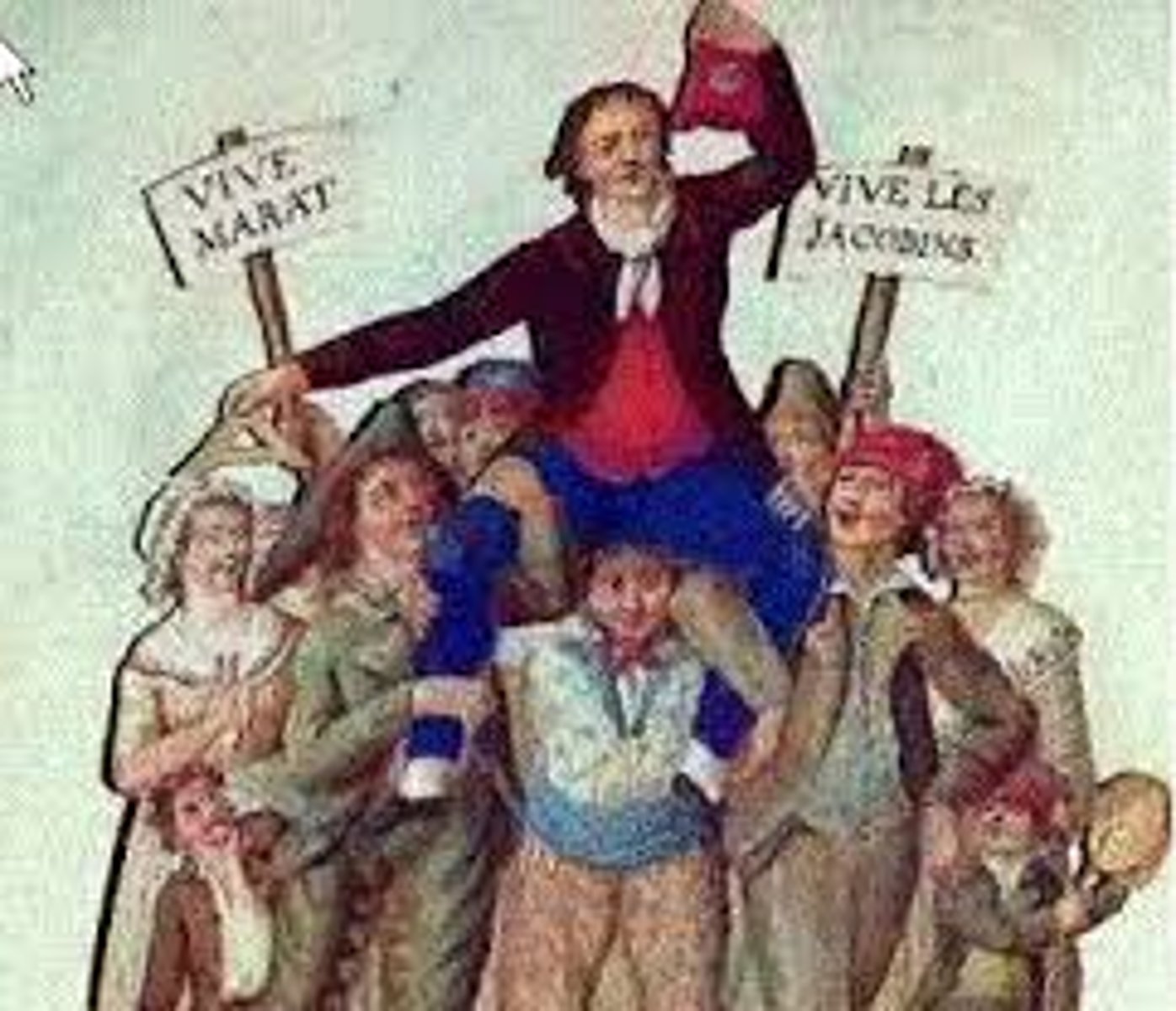

Sans-Culottes
This group would steer the French revolution in much more drastic and violent directions. This group, 'without fancy clothes' would see to the arrest and execution of thousands.

Girondins
The group in the National Convention that wanted to keep the king alive and were fearful of the mobs in Paris and what the country was turning into.
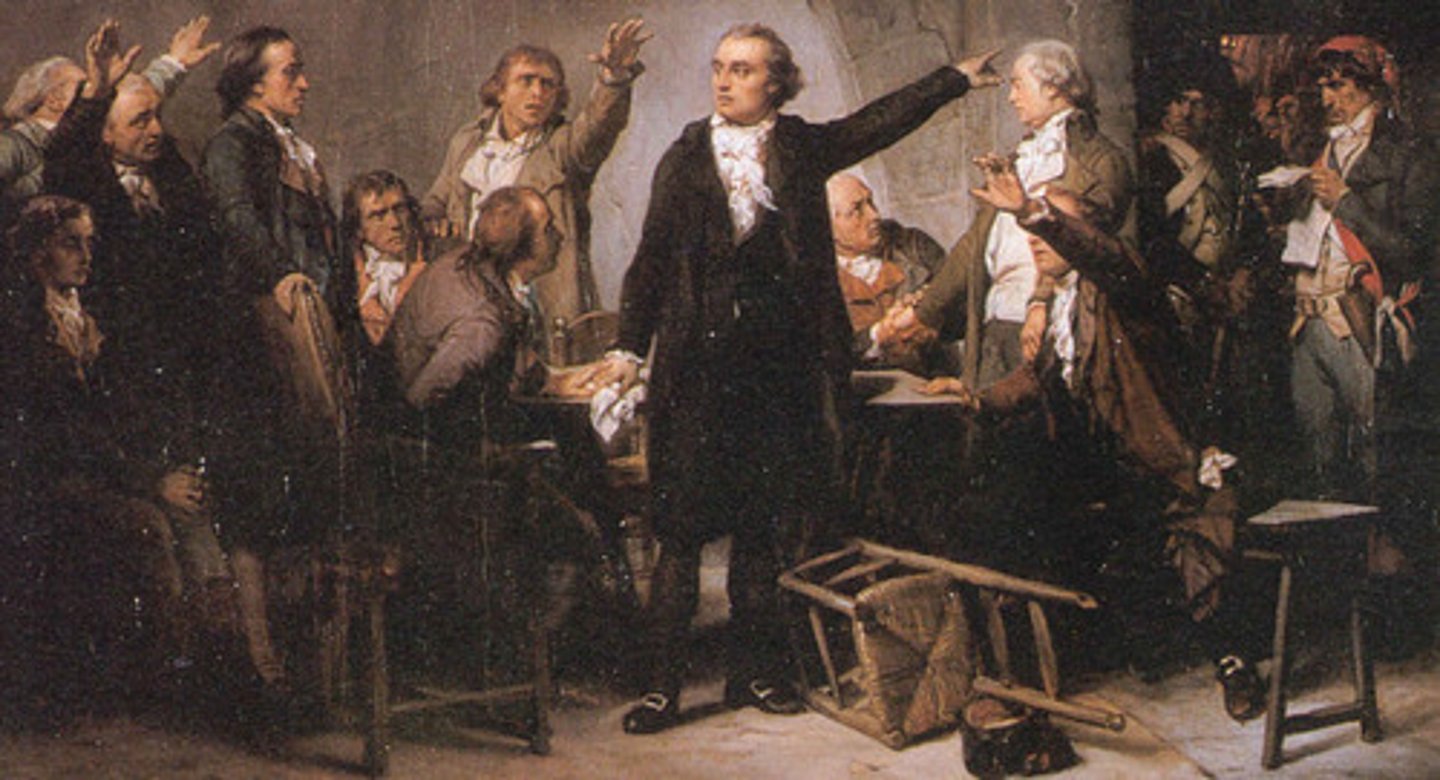

Mountain
The group in the National Convention, because of the incline in the seats were they were in the building, that favored executing the King of France for treason. This group won out, the king lost his head on January 21, 1793.
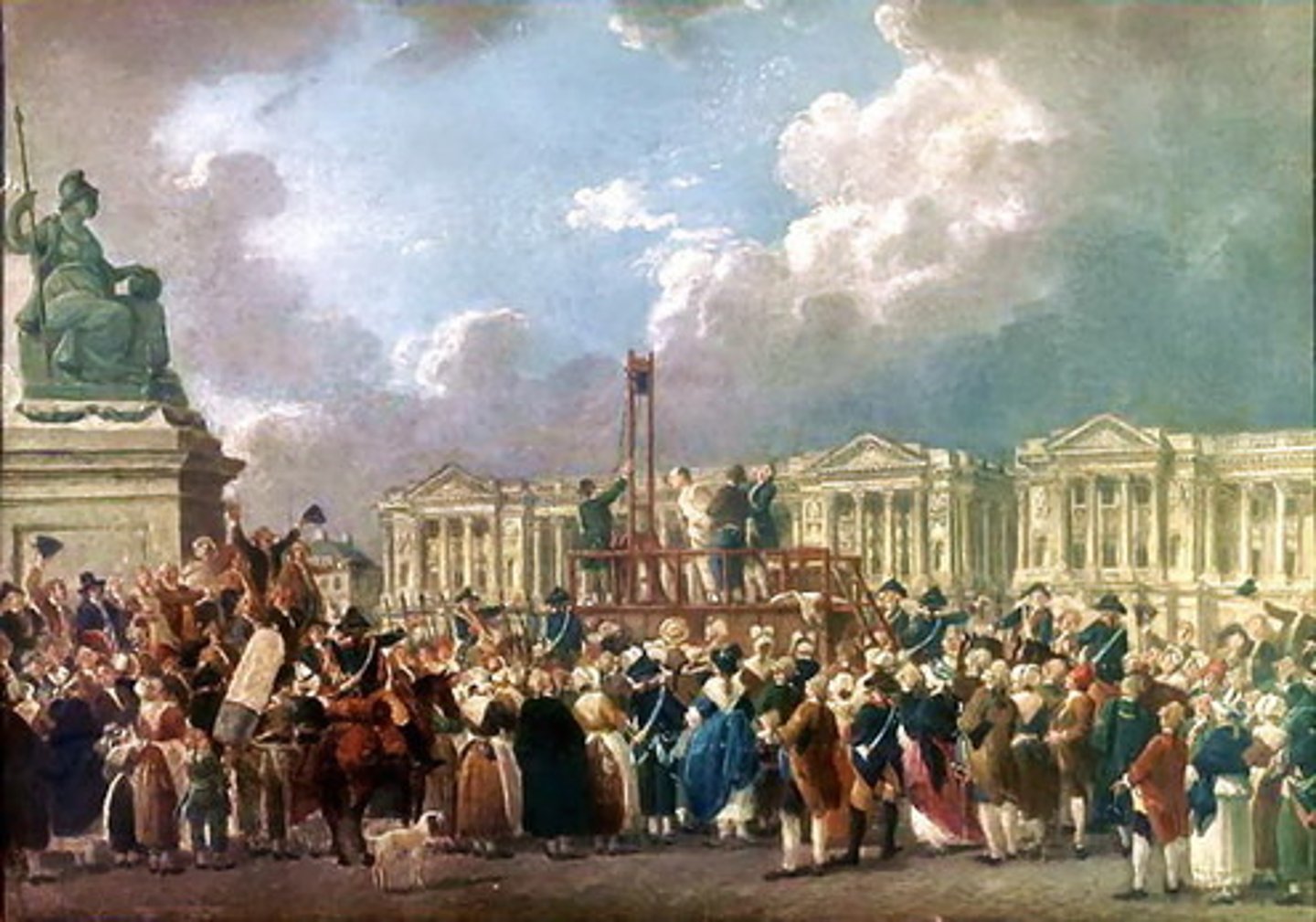

Maximilien Robespierre
He was a dominant figure in the Committee of Public Safety and would oversee many executions during the Reign of Terror. He would eventually be put to death himself by those in the revolutionary government who grew to fear him.

Committee of Public Safety
This was a revolutionary body used to carry out the Reign of Terror. It's purpose was to instill fear and destroy those who would oppose the goals of the revolution. Royals, former revolutionaries, peasants, and innocents would all be it's victims.

De-Christianization
This was the attempt to rid France of the influences of the Catholic Church in France. It involved the removing of religious names from streets, the looting of churches and even replacing the calendar.

Napoleon Bonaparte
A popular general that was able to take advantage of the turmoil in the French government and seize power. He would say 'he was the revolution' and would work to preserve the positive parts of it but at the same time would rule France as a military dictator.

Code Napoleon (Napoleonic Code)
A major overhaul of the French legal system that took hundreds of different legal systems and laws and put them into a coherent system. This new Civil Code protected many of the gains of the revolution but would be a setback to the rights of women.

Prefects
These were the often hand picked government officials, that replaced the intendants and local nobles, that would oversee local government affairs and make sure they were in step with the wishes of the central government.

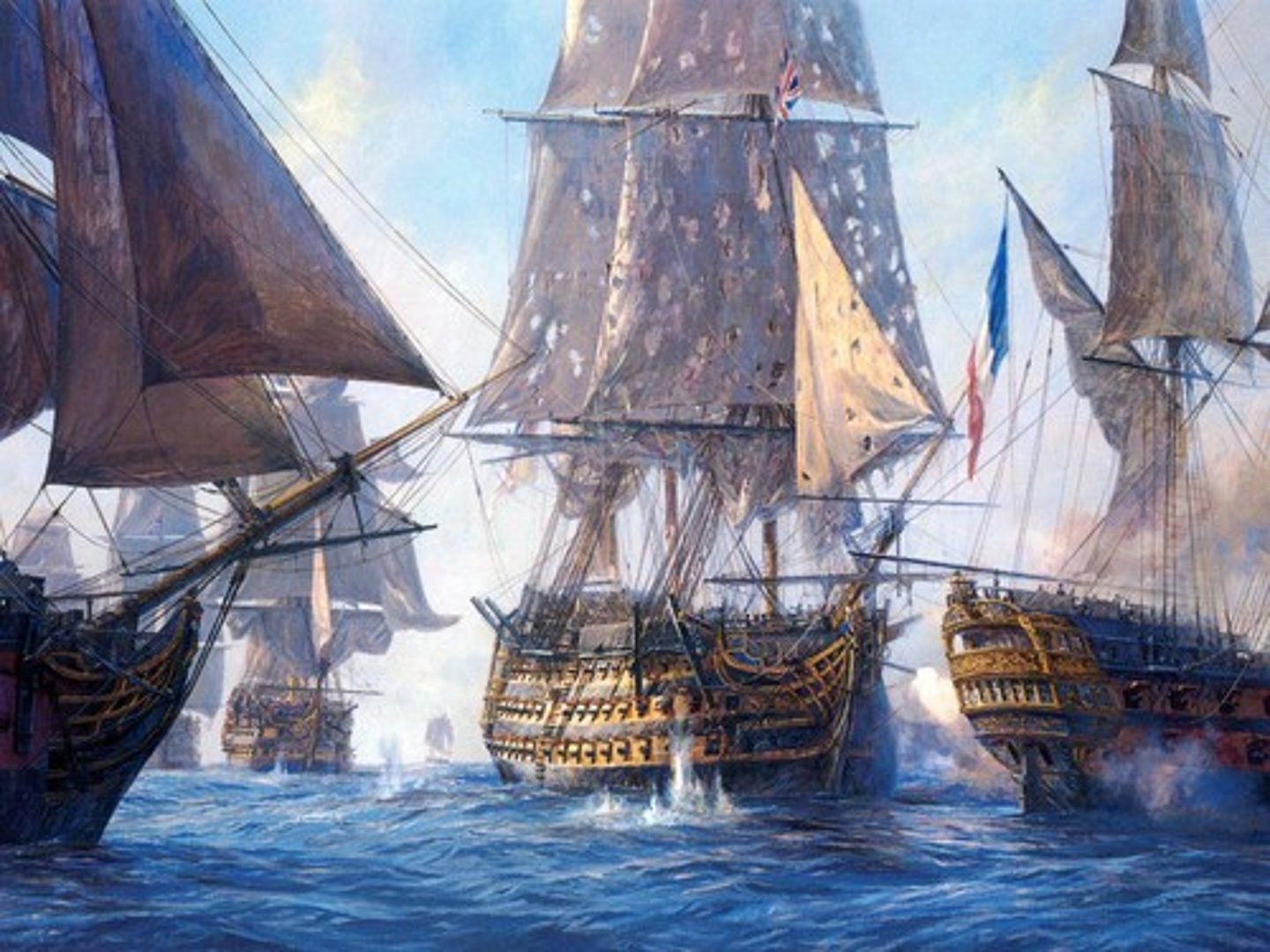
Trafalgar
A major naval battle and defeat for the combined French and Spanish ships. It showed that the English would keep control of the seas and would remain safe from French invasion.

Continental System
This was a system developed by France to try and lock out the British from European markets in an attempt to ruin them financially. It was a major failure.

Nationalism
The solidarity felt by a people of the same nation, who speak the same language and often religion. It was a force that contributed to countries eventually fighting back and defeating the armies of Napoleon.

Battle of Waterloo
The final major battle and defeat of Napoleon in 1815. After this he would be exiled to the small island of Saint Helena and later die in 1821.
