Seedless Vascular Plants
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What are the major groups of seedless vascular plants?
Horse tails
Club mosses
Whisk ferns
Ferns
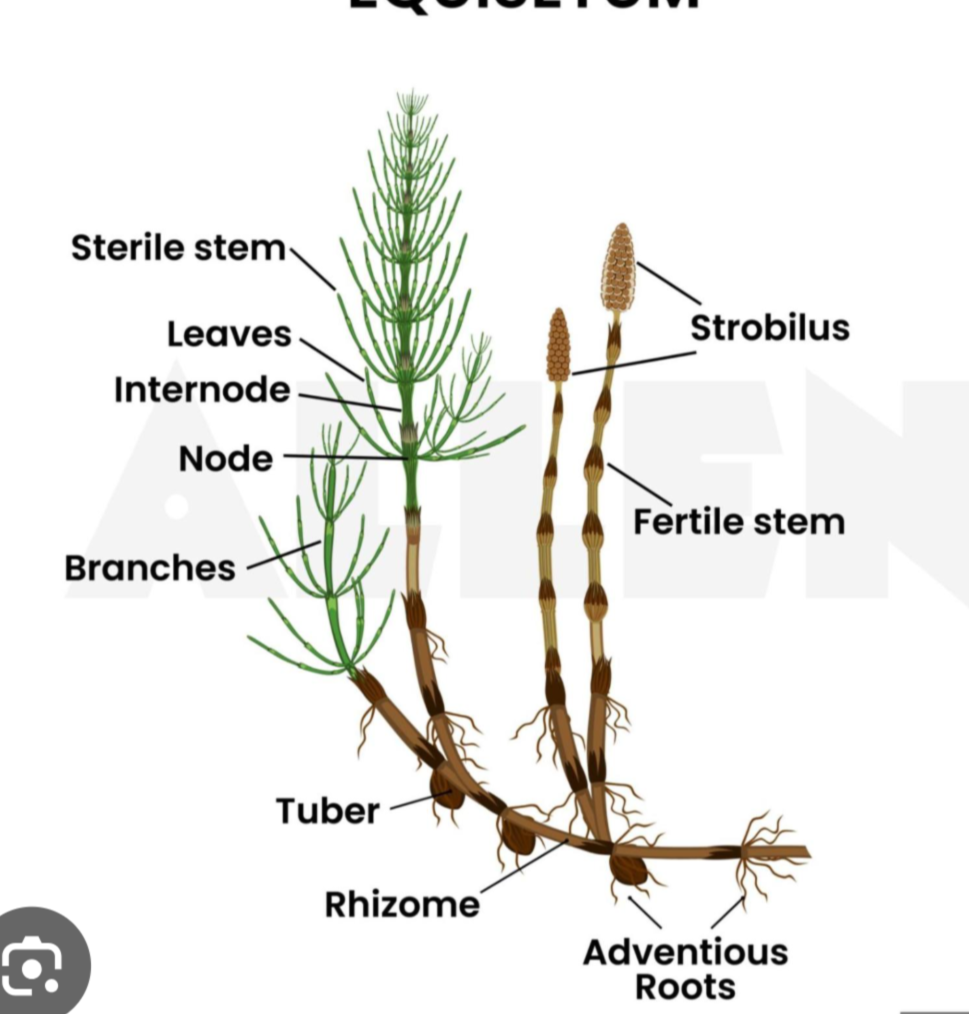
What are equisetum?
Horse tails
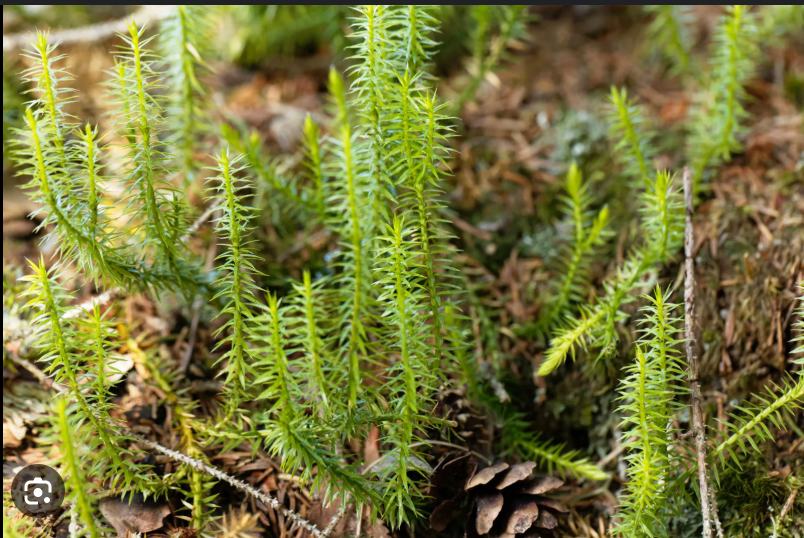

What are lycophytes?
Club mosses
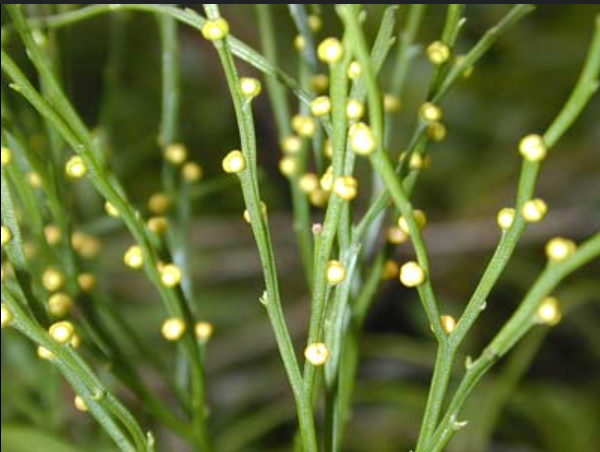

What are Psilotum?
Whisk ferns
When did seedless vascular plants dominate the landscape?
350 mya
What type of significance do Seedless vascular plants have?
Horticultural
Ecological
How do seedless vascular plants have ecological significance?
The brake fern removes Arsenic from water and soil
They form mutualistic relationships
What are other uses of seedless vascular plants?
Fiddleheads are one of the few edible parts of a fern—ostrich fern
What is the leaf of a fern called?
The frond which has leaflets and subleaflets
Example of world wide problem fern?
Lydogium
Example of a mutualistic relationship fern?
Water fern Azolla with cyanobacteria
What are the two apical meristems of vascular plants?
root and shoot
What are the three tissue systems of vascular plants?
Dermal
Vascular
Ground
What primary meristem is for dermal tissue system?
Protoderm
What primary meristem is for ground tissue system?
Ground meristem
What primary meristem is for vascular tissue system?
Procambium
What do vessel elements have that tracheids lack?
perforation plates
What are microphylls?
Simple leaves with one vein down the middle
What are megaphylls?
Leaves with branched veins
What is independent in seedless vascular plants?
Both the gametophyte and sporophyte at maturity
What were the three most important phyla of seedless vascular plants the devonian period?
Rhyniophyta
Zosterophyllophyta
Trimerophytophyta
What is homospory?
The production of only one type of haploid spore
Can result in separate male and female gameotphytes or bisexual depending on the species
What is heterospory?
The production of two types of spores in two different kinds of sporangia
Microspores—produced in microsporangia
Megaspores—produced in megasporangia
Why is heterospory important?
It is the precursor to seeds and pollen
In the production of sperm and eggs, seedless vascular plants are similar to
bryophytes in having both __
Antheridia and archegonia
The sporophyte-gametophyte relationship in seedless vascular plants differ from
both bryophytes and seed plants
In seedless vascular plants, what is larger the sporophyte or gameotphyte
Sporophyte
Rhyniophytes, zosterophytes, and trimerophytes all had __-
branching photoysnthetic stem systems without roots or leaves and underground rhizomes
What was the key transitionary feature of seedless vascular plants
Tracheids
What are the two phyla of living seedless vascular plants
Lycopodiophyta (lycophytes)
Monilophyta
The first phyla of living seedless vascular plants (lycopodiophyta or lycophytes) contain what
Lycopodiacea (club mosses)
Selaginellacea (spike mosses)
Isoetacea (quillworts)
The second phyla of living seedless vascular plants (monilophyta) contains what
Psilotopsida (whisk ferns)
Marattiopsida (small group of tropical ferns)
Polypodiopsida (true ferns)
Equisetopsida (horsetails)
How do modern lycophytes compare to extinct lycophytes
Modern lycophytes are small herbaceous plants while ancient lycophytes dominated moist tropical forests during the Carboniferous period
All lycophytes have ___
Microphylls—single leaf vein
Which lycophytes are heterosporous and which are homosporous?
Lycopodiacea (club mosses)—homosporous
Selaginellacea (spike mosses)—heterosporous
Isoetacea (Quillworts)—heterosporous
What is a strobilus>
A reproductive structure that consists of sporophylls at the end of aerial branches
What is a sporophyll?
A specialized leaf-like organ that bears spore producing structures (sporangia)
Where are sporangia found on sporophylls
On the upper surface
In heterosporous members, the gametophyte development is ___
endosporic
What is endospory?
Gametophyte development takes place MOSTLY inside the spore wall
Homospores are __
exosporic
Psilotopsida (whisk ferns) consists of what two orders?
Both homosporous
Ophioglossales
Psilotales
The psilotales include which two living genera?
Tmesipteris
Psilotum (whisk ferns)
What is an epiphyte?
A plant that grows on another plant but is not parasitic?
How do Tmesipteris grow?
As epiphytes
What are enations?
Leaf-like structures that are different from leaves as they lack vascular tissue
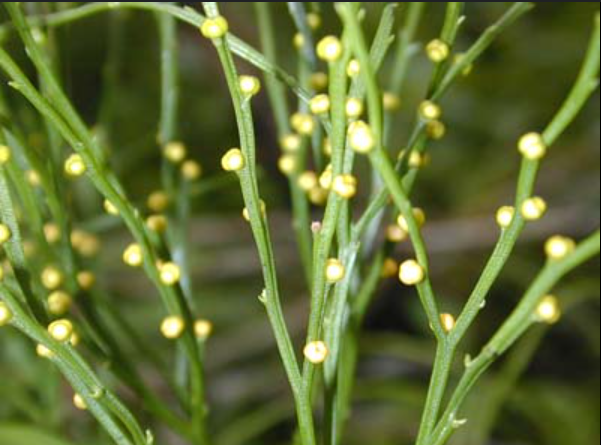

How do psilotum (whisk ferns) grow?
Lack true roots and have enations instead of leaves. Homosporous and bisexual gametophytes that are small underground structures
The leaves/fronds of Polypodiopsida are ___
Megaphylls
Most ferns are __
Homosporous
Where do the sporangia of Polypodiopsida occur?
On the lower surface of the leaves
What is a fiddlehead?
The young fern megaphylls that arise from an underground stem termed a rhizome
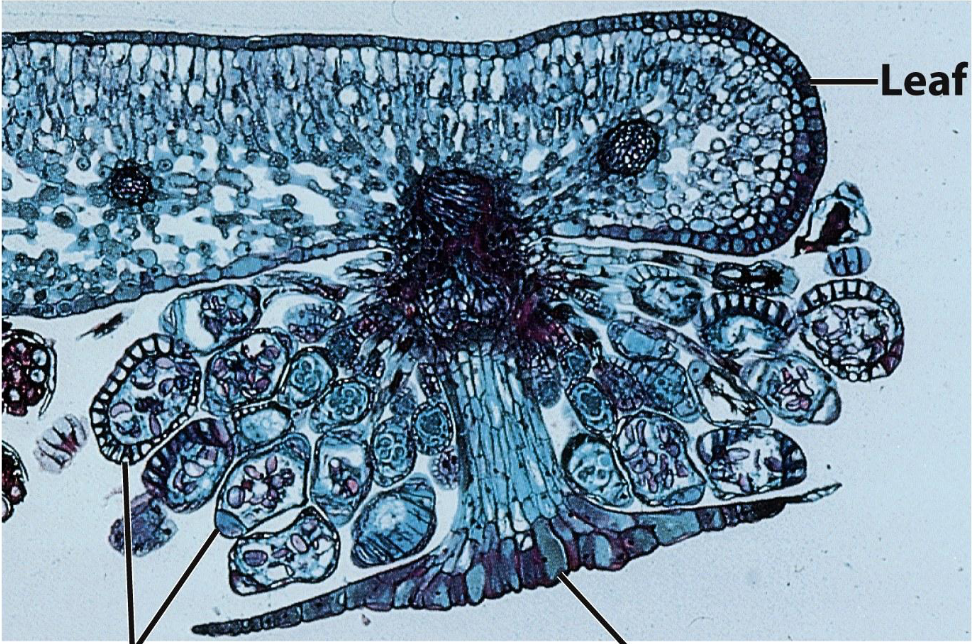
What is this?
A fern sorus
What is an indusium?
The upside down umbrella structure of fern sori that holds the sporangia
How do the archegonia and antheridia of ferns grow?
Both antheridia and archegonia produce on the same thallus (bisexual) but mature at different times to prevent self-fertilization
Some species are unisexual
What is an annulus?
A thickened ridge of cells along the back of fern sporangia which aids in spore dispersal
What is sporopollenin?
A substance found in plant spore cell walls to prevent cellular damage
What is a prothallus?
The gametophyte of ferns
What is a rhizome?
horizontal underground plant stem that can produce both shoots and roots
What type of sporous are the water ferns of polypodsidia
heterosporous
What are trichomes?
Extensions of epidermal cells that look like egg beaters
Equistium (horse tails) may be
the oldest survivng genus of plants on earth
What type of sporous is Equistium?
Homosporous
Equisetum are made up of what?
Sporangia are clustered into umbrella-like structures sporangiophores that are grouped together into strobilus
What are the characteristics of the spores of Equisetum?
Spores are wrapped with elongated structures called elaters that uncoil as it matures and dries releasing the spores. Each spore becomes a bisexual gameotphyte photosynthetic
What two tissue types is vacular tissue composed of?
Xylem and phloem
What does xylem carry and to where?
water up through the plant
What does phloem carry and to where?
Carries photosynthate down through the plant
Where can you find vascular tissue in ferns?
In the rhizomes, stem, and leaves
Is there vascular tissue in the fern prothallus/gametophyte?
No; it is green so photosynthetic and thin so no space for vascular tissue
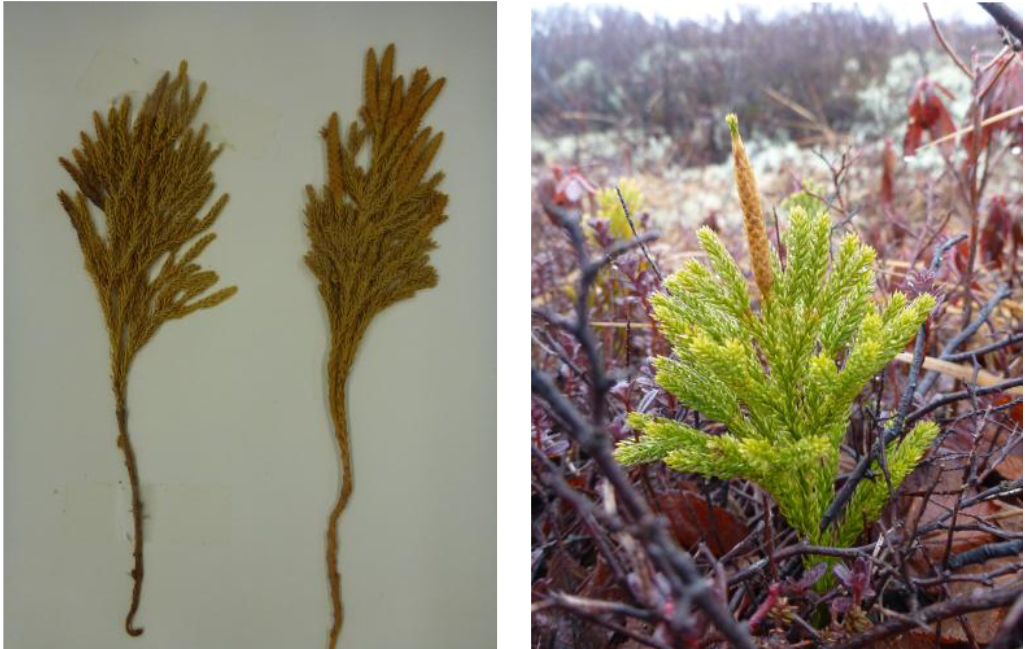

Identify?
Lycopodiacae
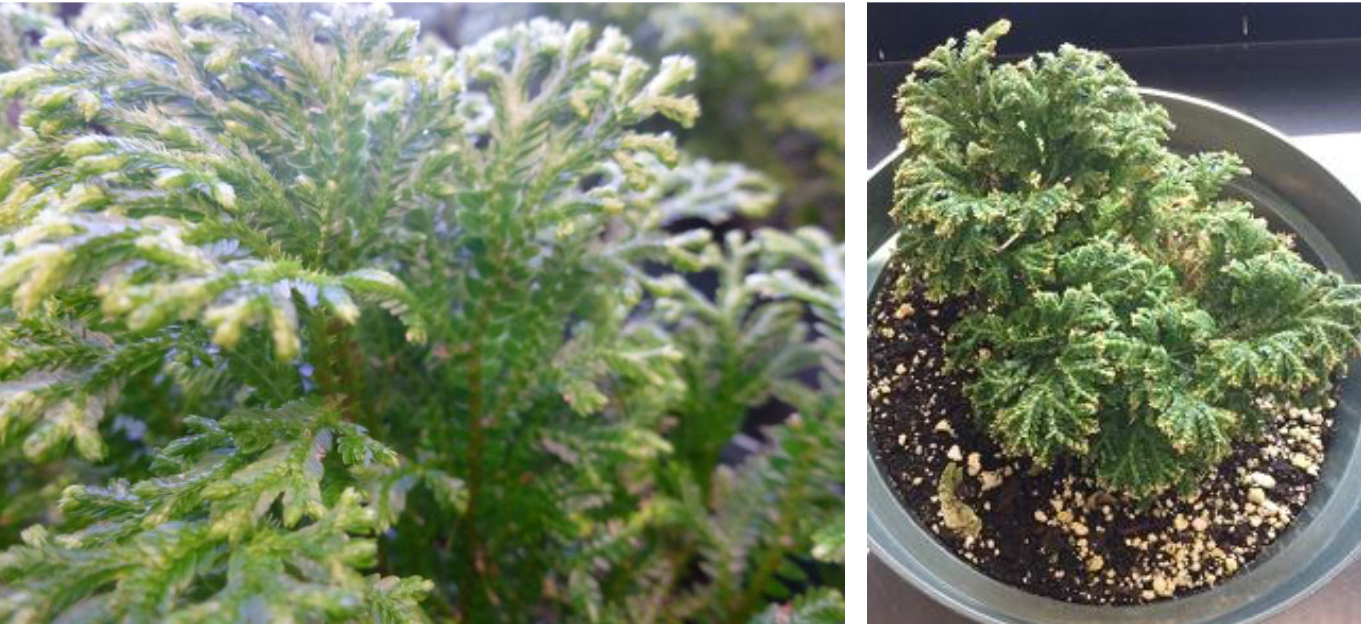

Identify
Selaginella
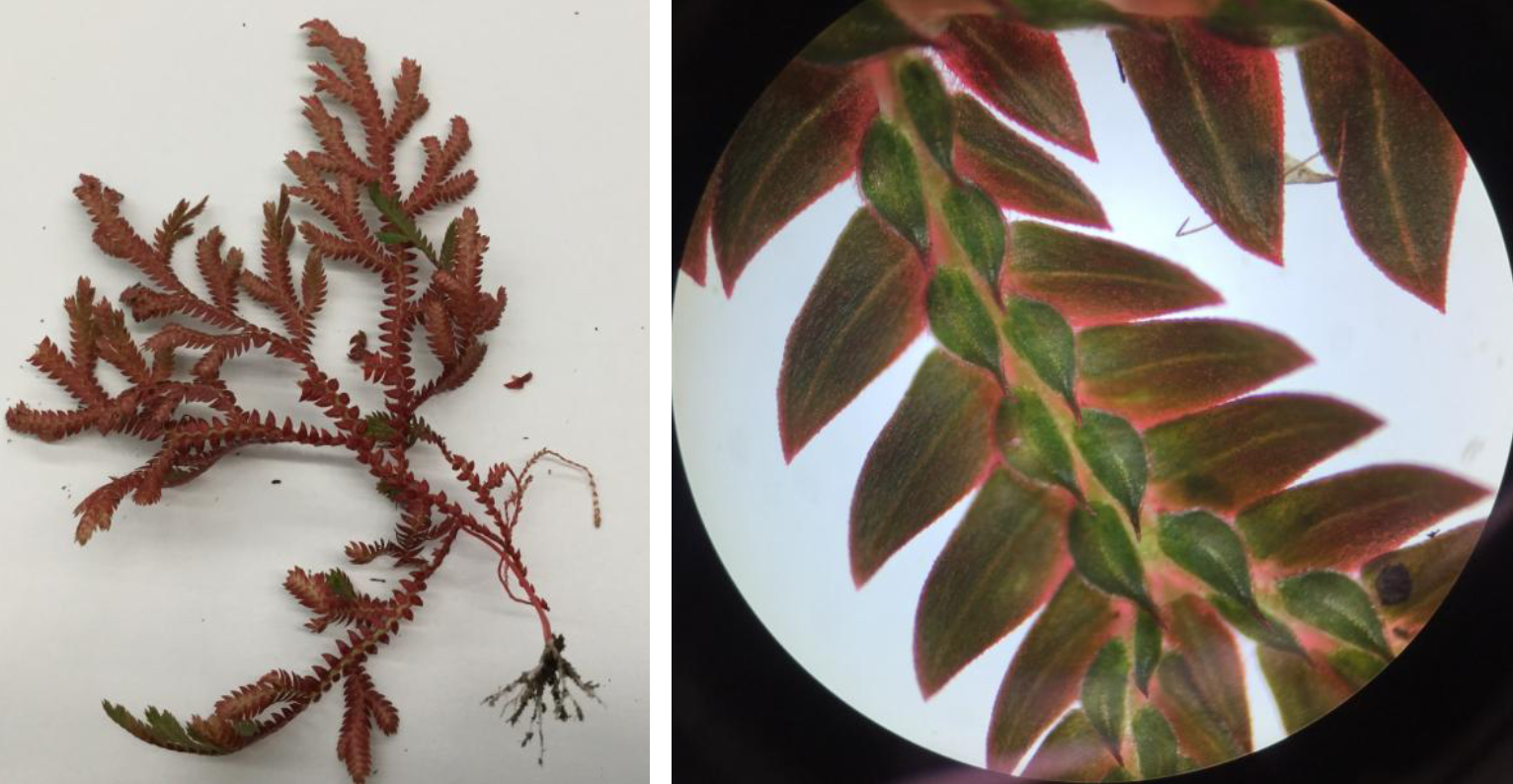

Identify
Selaginella; flattened leaves and third row of leaves on underside
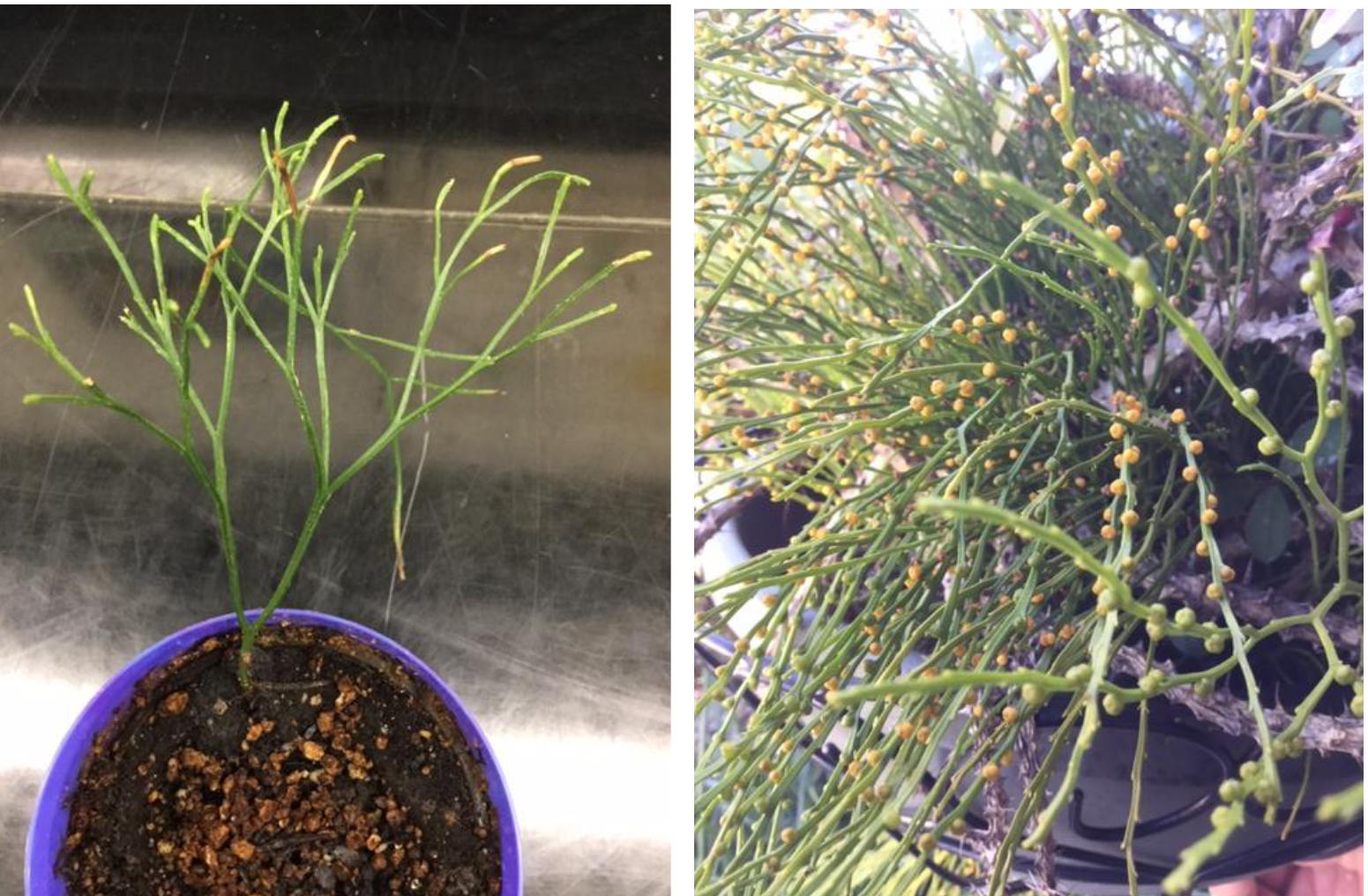

Identify
Psilotopsida
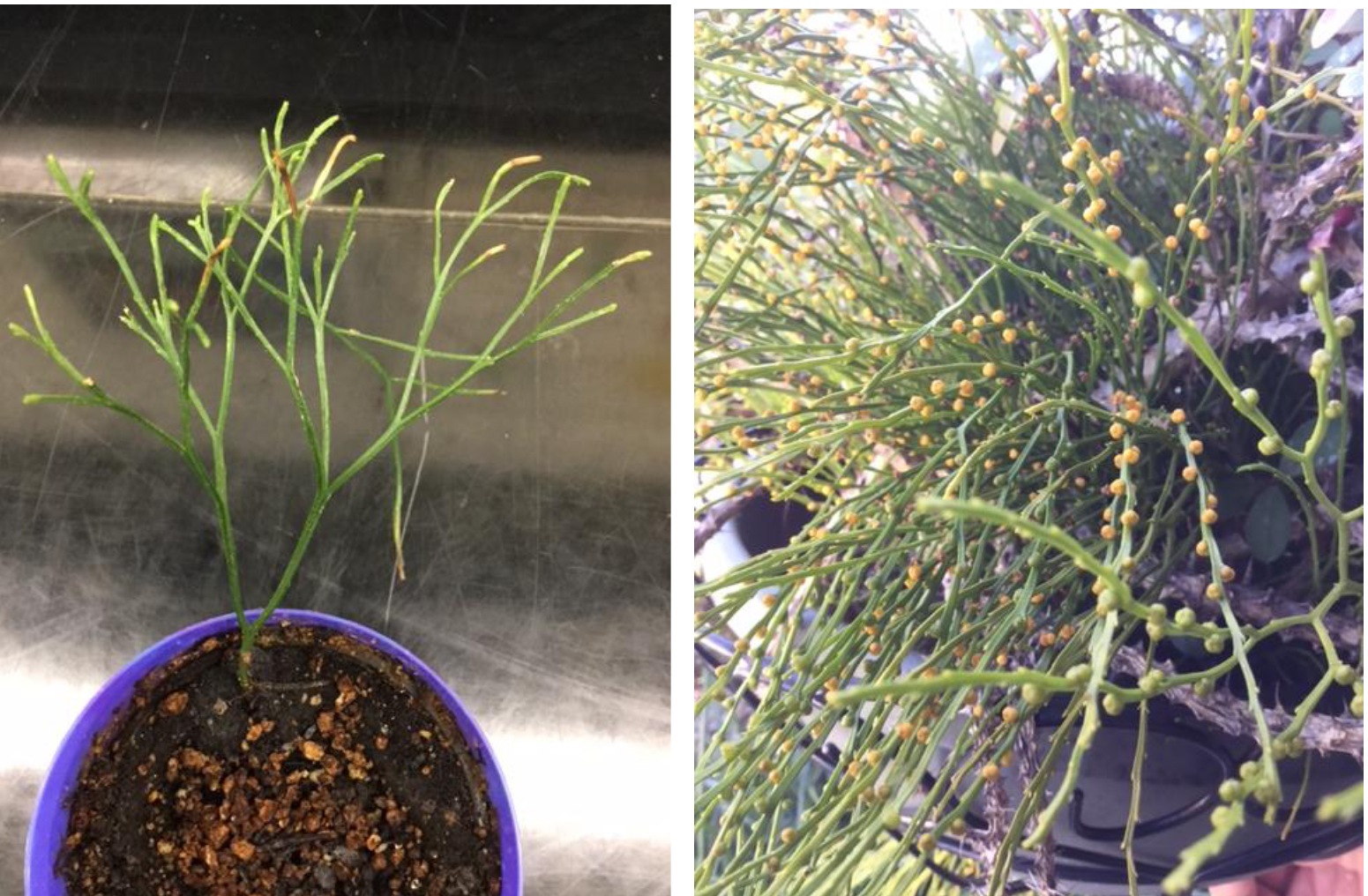

What type of branching is seen in Psilotopsida ?
Dichotomous
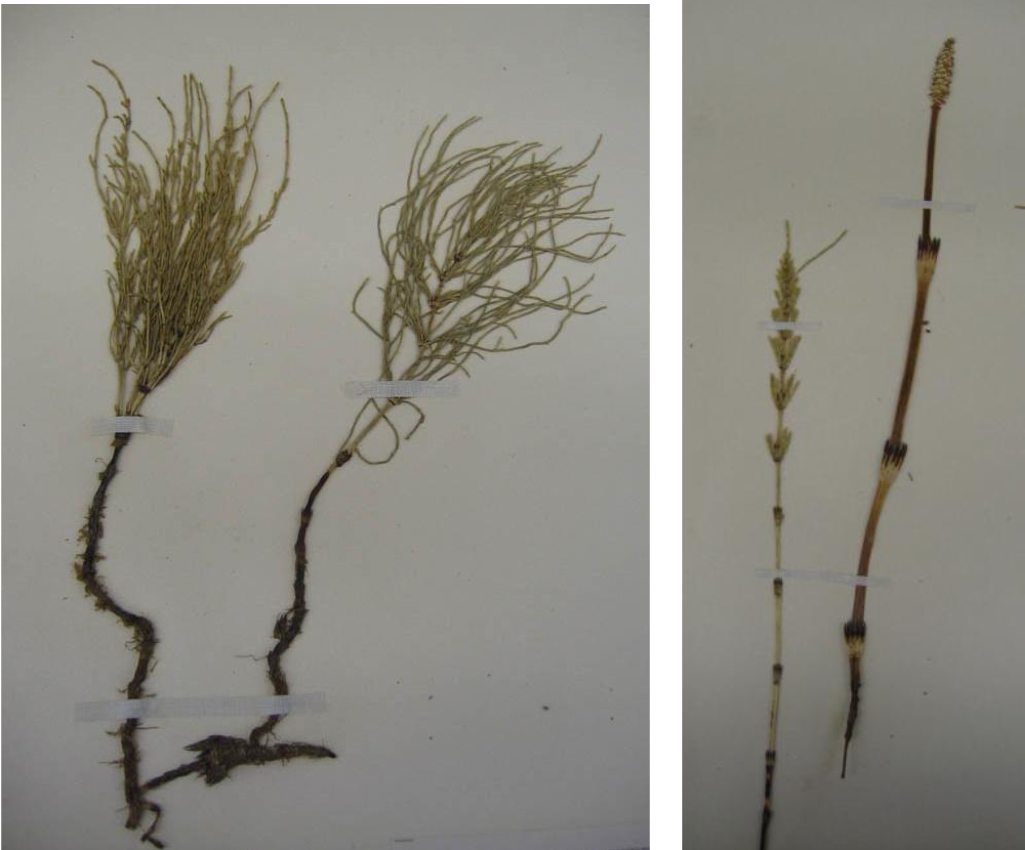

Identify?
Equisetopsida; shows two sporophyte forms (vegetative; left, and reproductive; right)
Microphylls can be found in both ___
Lycopodiophyta and Equisetopsida
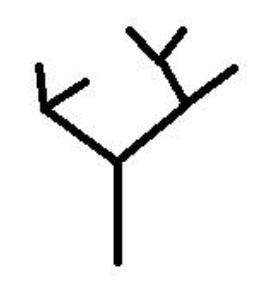
What type of branching
Dichotomous
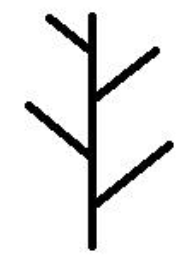
What type of branching
Alternate
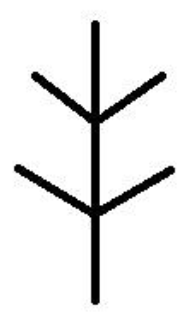
What type of branching?
Opposite
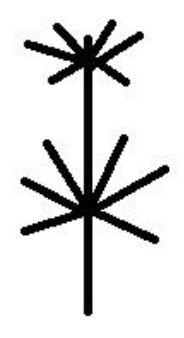
What type of branching?
Whirled
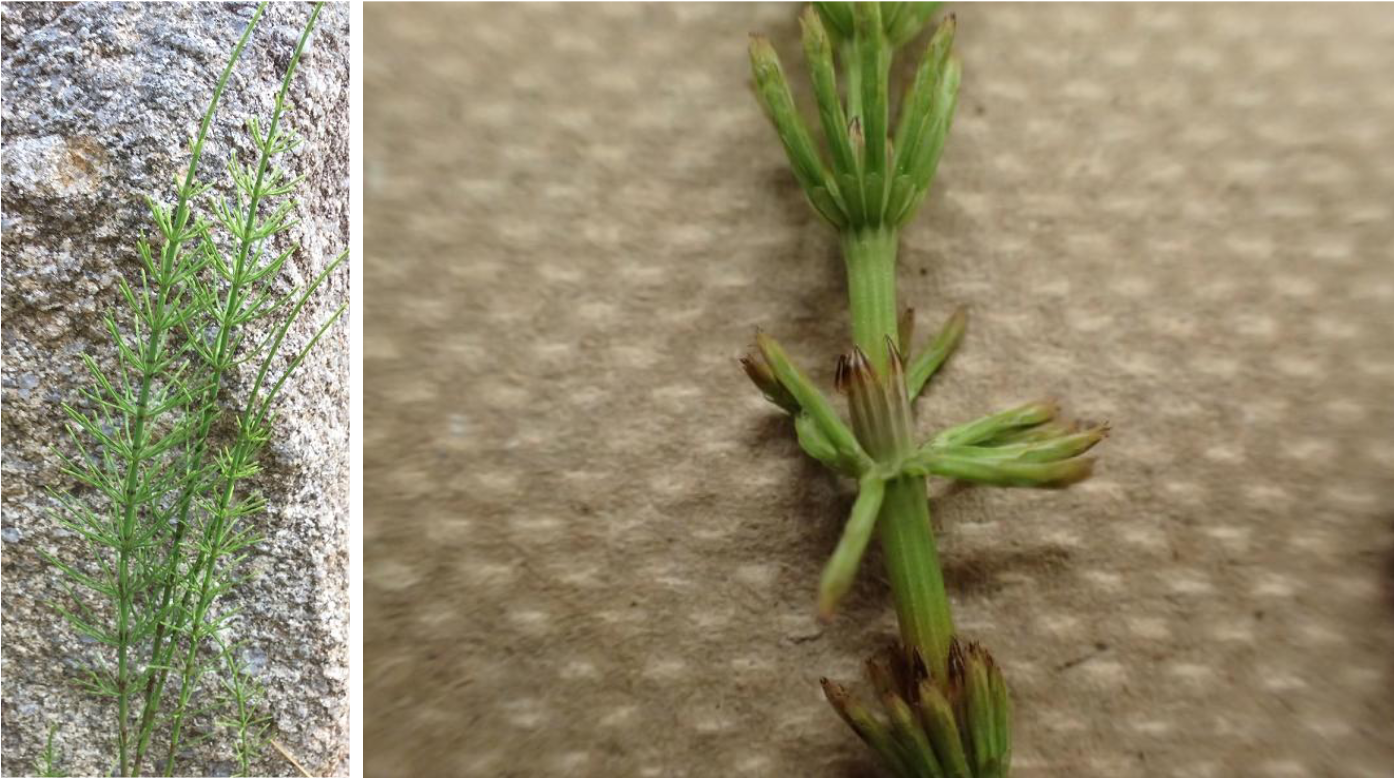

What type of branching?
Whirled
On what generation do you find rhizomes
Sporophyte
How is a root different from a rhizome
A rhizome is a modified stem that grows horizontally
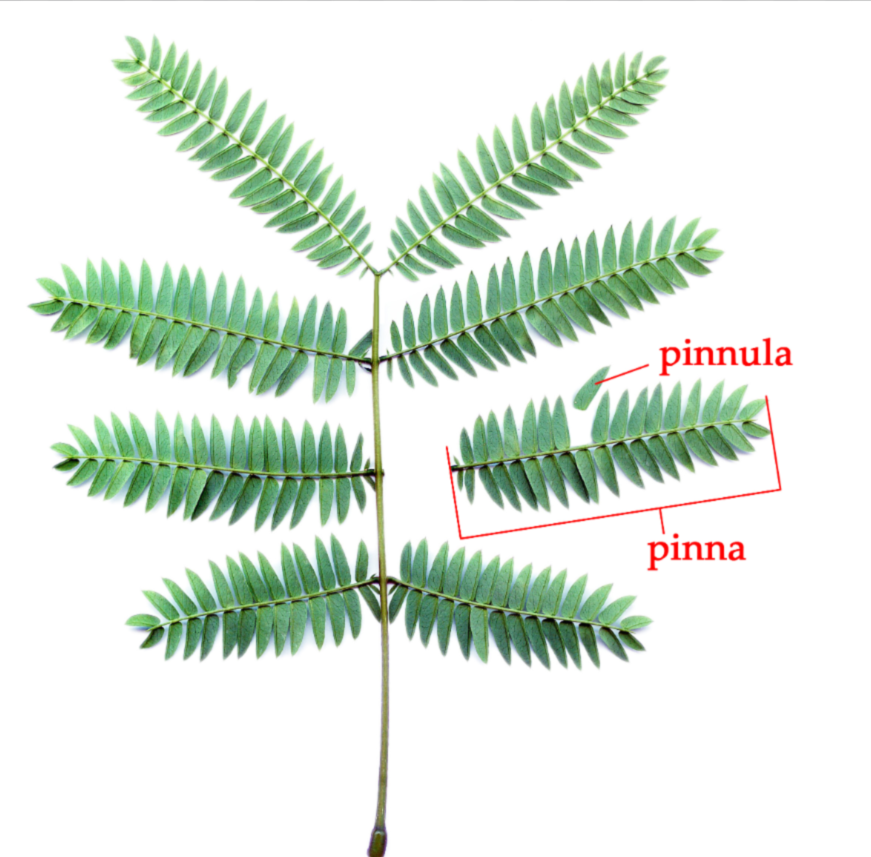
What is the pinna?
One small subleaf of a fern

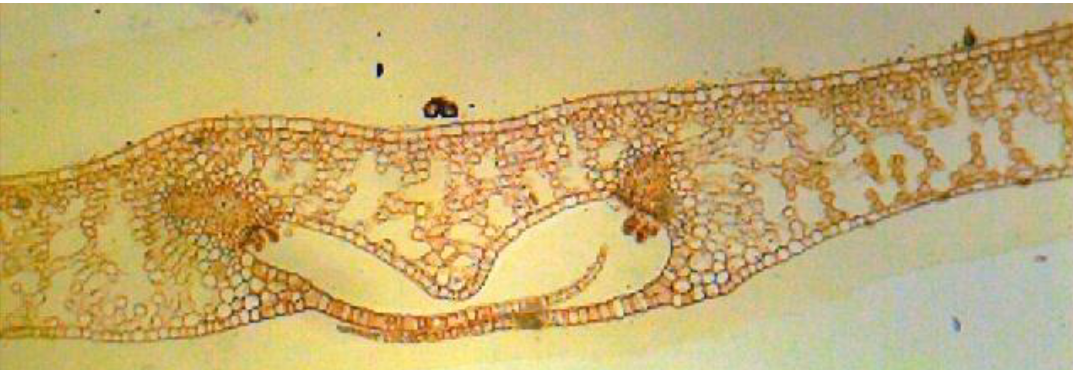
What is this?
A fern sorus
How is the gametophyte connected to the ground? How does nutrients move aroun?
Rhizoids; diffusion