Ch 13: Chromosomal Inheritance
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
chromosomal theory of inheritance
during meiosis, chromosome pairs migrate as discrete structures
chromosomes sorting from each homologous pair into pre-gametes appears to be random
gametes contain only ½ the chromosomal complement of parent
sperm and egg differ in size and morphology but have the same number of chromsomes
suggests equal genetic contributions per parent
gametic chromosomes combine during fertilization to produce diploid offspring
T.H. Morgan and his work with fruit flies (1900s)
genetic linkage (in this case linked to the sex chromosomes) was the first demonstration that genes were located on chromosomes
white-eyed mutant allele was inherited along with the X chromosome → “X-linked” or “sex-linked”
considered how linkage affects inheritance of 2 different characteristics
linked genes tend to be inherited together and are physically near each other on the same chromosome
violates the Law of Independent Assortment
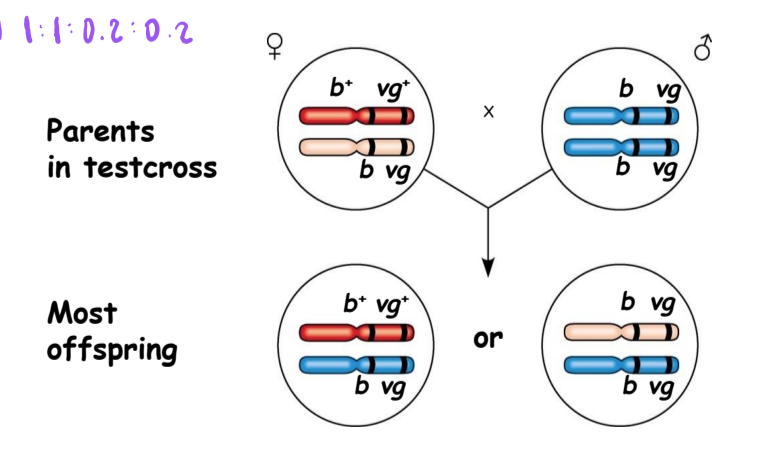
What did Morgan determine regarding genetic linkage?
genes that are close together on same chromosome are linked and do not assort independently
unllinked genes are either on separate chromosomes or are far apart on same chromosome and assort independently
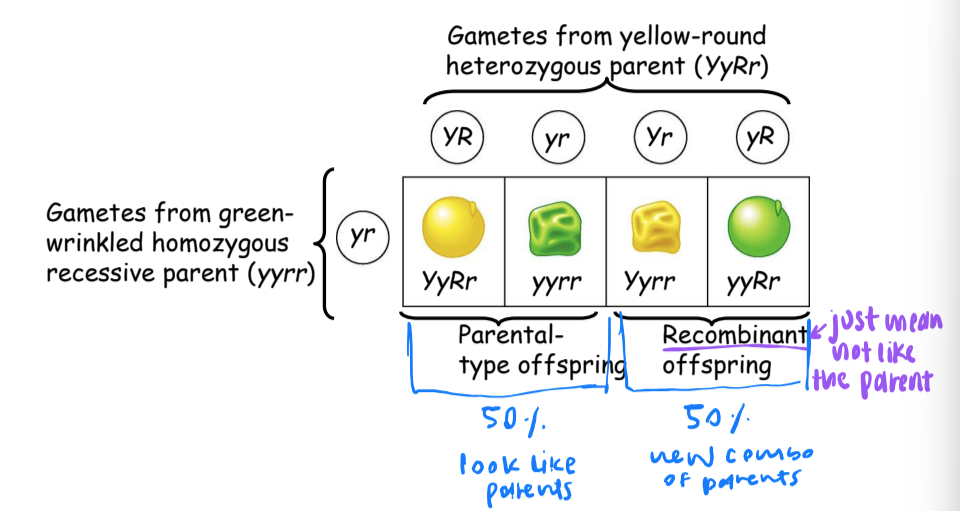
recombination of unliked genes: independent assortment of chromosomes
when Mendel followed inheritance of 2 characters
observed some offspring have combinations of traits that do NOT match either parent in P generation (YYRR x yyrr)
recombination of linked genes: crossing over
recombinant offspring
show new combos of parental traits
when 50% of offspring are recombinants there is a 50% recombination frequency (RF)
linked genes have a RF of less than 50%
related to physical distance on the chromosome (more likely to be inherited together)
Morgan discovered that genes could be linked
but appearance of recombinant phenotypes made linkage appear incomplete
proposed some processes must occasionally break the physical connection between genes on same chromosomes
crossing over of homologous chromosomes
lower RF = less distance between traits
linkage mapping: using recombination data
genetic map
an ordered list of the genetic loci along a particular chromosome
can be developed using recombination frequencies
the farther apart genes are on a chromosome, the more likely it is for a crossover event to occur between them
genes with the least amount of distance between them are most linked
recombination frequency cannot be more than what percentage?
50
aneuploidy
results from the fertilization of gametes in which nondisjunction occurred
is a condition in which offspring have an abnormal number of a particular chromosome
usually for one chromosome (if more, organism most likely wont survive
euploidy
having the normal number of chromosomes
monosomy
missing a partner for a chromosome
trisomic
3 copies of a particular chromosome
monosomic
1 copy of a particular chromosome
when does nondisjunction occur?
when chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis I or meiosis II, resulting in an abnormal chromosome number
trisomy 21
nondisjunction on the 21st chromosome, the incidence of having offspring with trisomy 21 increase dramatically with maternal age
polyploidy for specific plants and animals
this is their normal number
condition in which there are more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes in an organism
sex chromosome nondisjunction example
in cats, the gene for coat color is located on the X chromosome (sex-linked, mainly in females)
in the embryonic development of female cats, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly inactivate in each cell, resulting in a tortoiseshell pattern if the cat has two different alleles for coat color
male cats, having only one X chromosome, never exhibit a tortoise shell color
alterations of chromosome structure
breakage of a chromosome can lead to 4 types of changes in chromosome structure
deletion
duplication
inversion
translocation
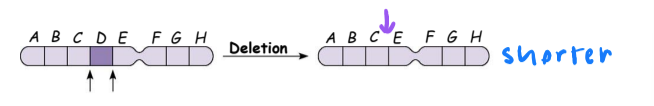
deletion
removes a chromosomal segment
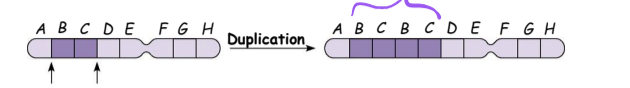
duplication
repeats a segment
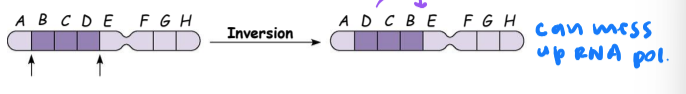
inversion
reverses a segment within a chromosome
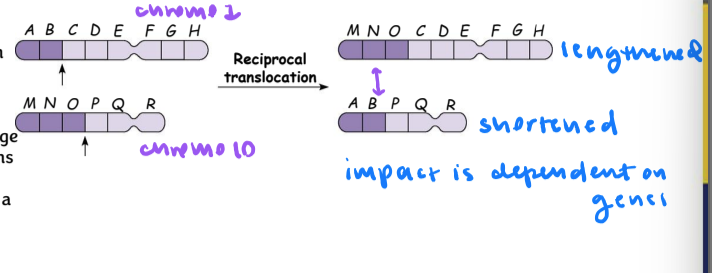
translocation
moves a segment from one chromosome to another nonhomologous one
reciprocal translocation
most common type: nonhomologous chromosomes exchange fragments
nonreciprocal translocation
chromosome transfers a fragment without receiving a fragment in return
Klinefelter syndrome
result of extra X chromosome in a male, producing XXY individuals (likely came from mom)
have male sex organs, but sterile, some breast development
Turner syndrome
result of monosomy X, producing an X O karyotype
sterile, but phenotypically normal if given hormone therapy
Cri du chat
not nondisjunction
caused by deletion in chromosome 5
causes sever mental retardation
chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
cancer results
the inheritance of traits controlled by genes present in the chloroplasts or mitochondria
depends solely on the maternal parent because the zygote’s cytoplasm comes from the egg
some disease affecting the muscular and nervous systems
caused by defects in mitochondrial genes that prevent cells from making enough ATP → no energy → chronic fatigue
mitochondrial myopathy
Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy