AQA GCSE Combined Science Physics - Paper 2
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Vector quantities
have magnitude and direction
Examples of vector quantities
force, velocity, momentum, acceleration
Scalar quantities
Only have magnitude
Examples of scalar quantities
speed, distance, time
Vectors
Represented by an arrow
Length of the arrow shows the magnitude
The direction of the arrow shows the direction of the quantity
A force is
a push or pull on an object that is caused by it interacting with something
contact force
when two objects are touching for the force to act
examples of contact forces
friction, air resistance, tension in ropes. etc
If the objects do not need to be touching for the force to act, the force is a ......
non contact force
examples of non contact forces
magnetic force and gravitational force
Two effects of gravity
- makes all things fall towards the ground
- gives everything a weight
What is mass?
Amount of matter an object is made of
Same value everywhere
Measured using a mass balance
What is weight?
The force acting on an object due to gravity
depends on the strength of the gravitational field at the location of the object
Measured using newtonmeter
What is weight directly proportional to?
mass
What are free body diagrams?
Diagrams that show all the forces acting on an object
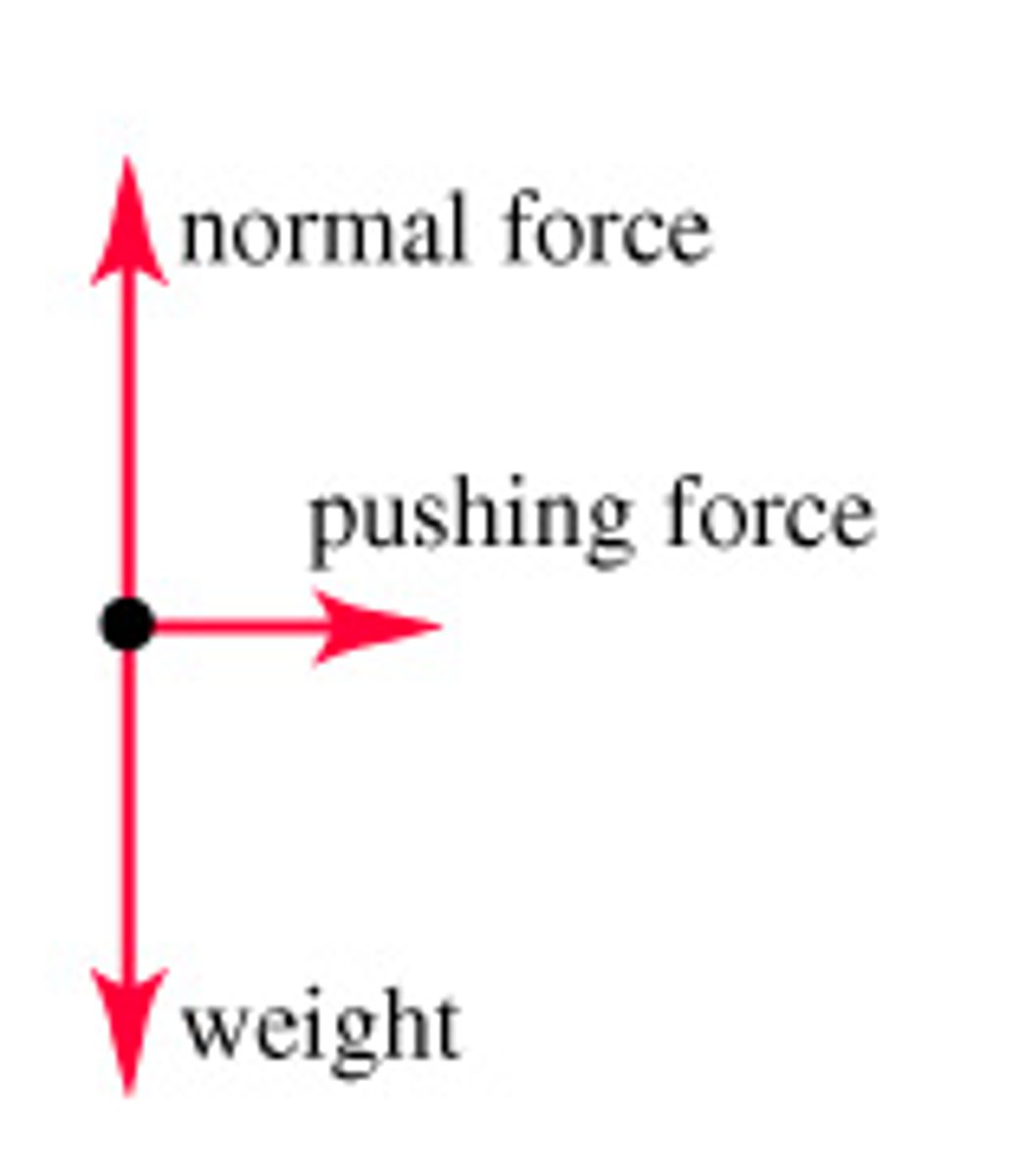
What is the resultant force?
The single force that replaces multiple forces acting at a single point
How is work done?
When a force moves an object through a distance, energy is transferred and work is done on the object
What is 1J equal to?
1Nm
If all the forces acting on an object combine to give a resultant force of zero then the object is in ?
equilibrium
What could happen when you apply a force to an object?
It may stretch, compress or bend
What happens when an object is elastically deformed
The object can go back to its original shape and length after the force has been removed
What happens when an object is inelastically deformed?
The object won't return to its original shape and length after the force has been removed
Extension is directly proportional to? (Hooke's Law)
The force applied
F∝e
What is the limit of proportionality?
The point at which extension is no longer directly proportional to force
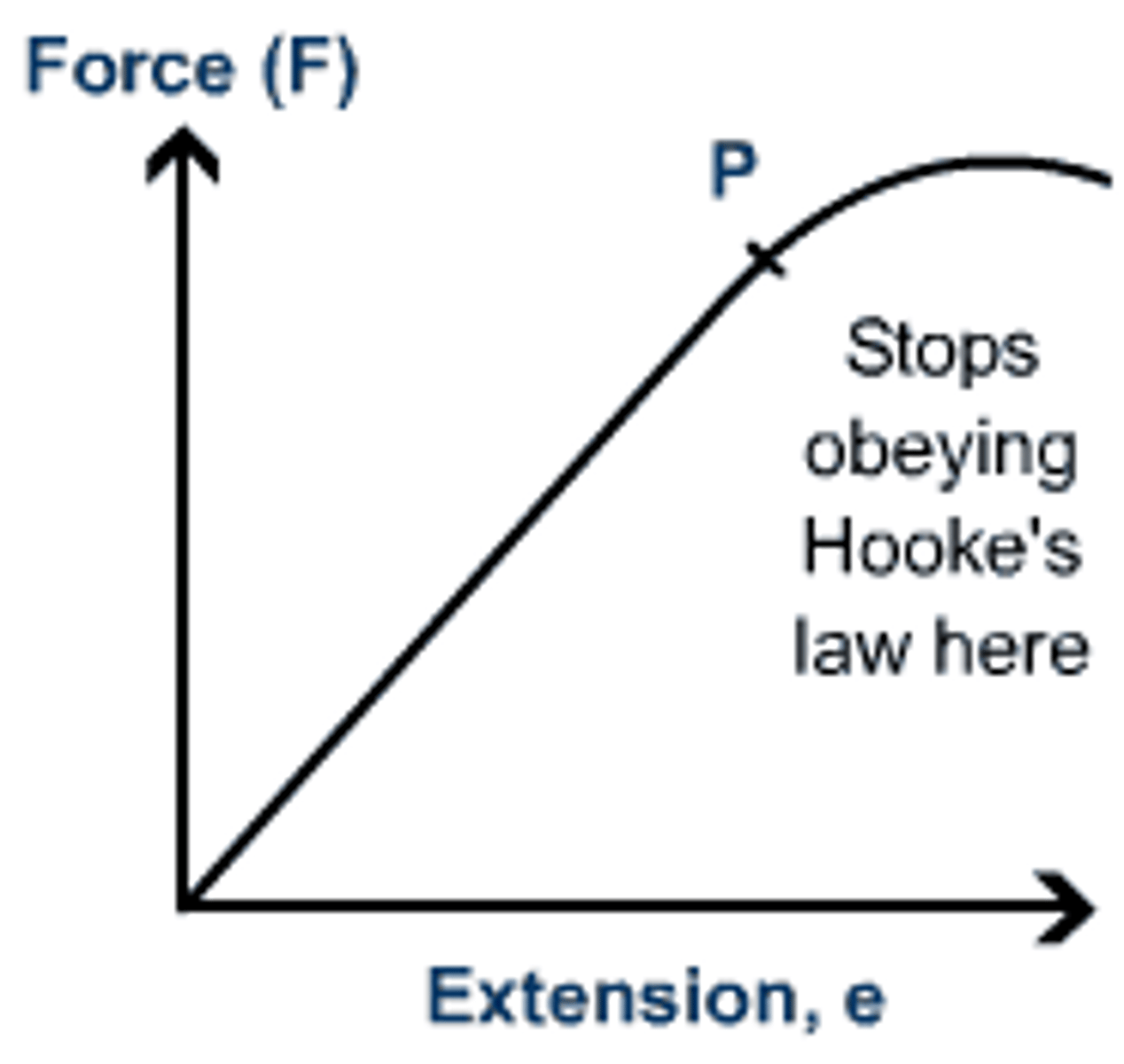
Practical: Investigating the link between force and extension
- First, measure the original length of the spring using a milimetre ruler
- Next, add different masses on the spring and measure the length of the spring in each case.
- The extension = change in length
- Repeat this process until you have enough measurements ( no fewer than 6)
- Plot a graph with extension of the spring on the x axis and force on the y axis.
- The graph will only start to curve if you exceed the limit of proportionality
What is displacement?
Measures the distance and direction in a straight line from an object's starting point to its finishing point
What is velocity?
Speed (how fast you're going) in a given direction
typical speeds
typical speed of a person walking
1.5m/s
typical speed of a person running
3m/s
Typical speed of a person cycling
6m/s
what is the typical speed of a car
25m/s
Typical speed of a train
55m/s
Typical speed of a plane
250m/s
What factors affect speed?
Fitness of the person
Age of the person
Distance travelled
Terrain
Climate
Gender of the person
What factors affect wind speed?
Temperature
Atmospheric pressure
Any large buildings or structures nearby e.g. forests reduce wind speed travelling through them
Acceleration
change in velocity in a certain amount of time
What is deceleration?
Negative acceleration - when something slows down, the change in velocity is negative
What is constant acceleration?
Uniform acceleration - acceleration due to gravity is uniform for objects in free fall
Distance-Time Graphs - Features
1) Gradient = speed
2) Flat sections = object is stationary
3) Straight uphill sections = object is travelling at a steady speed
4) Curves = object is accelerating or decelerating
5) Steepening curve = object is speeding up
6) Levelling off curve = object is slowing down
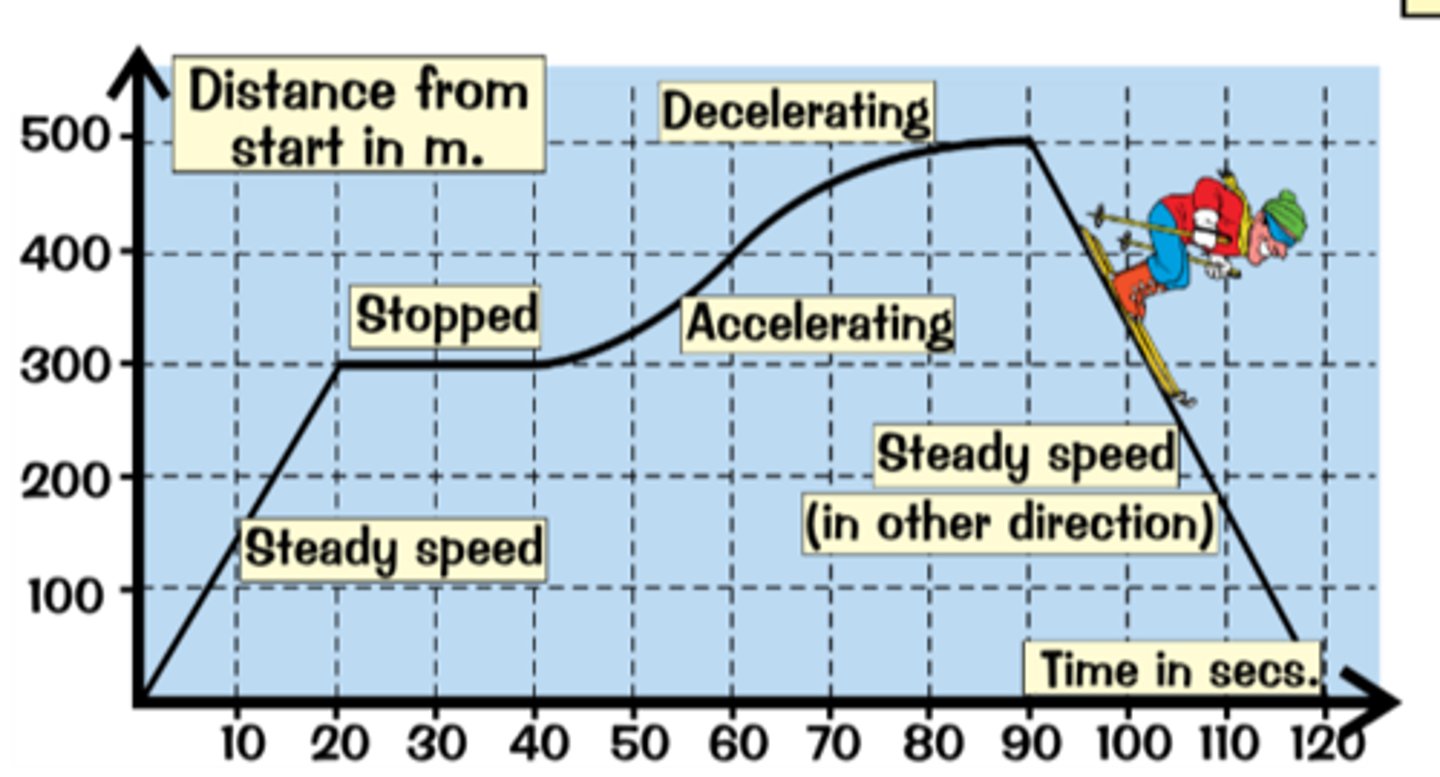
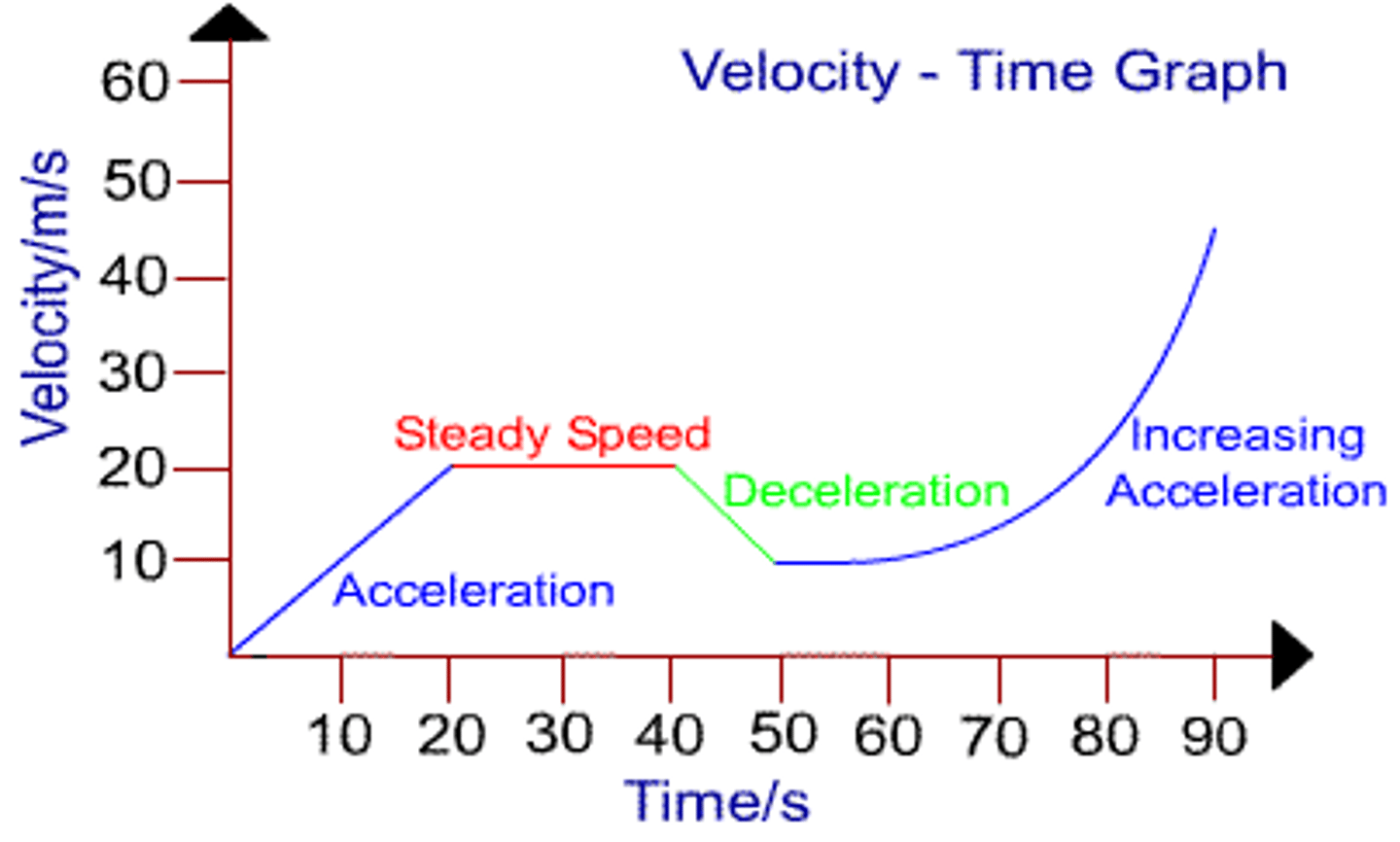
Velocity-Time Graphs - Features
1) Gradient = acceleration
2) Flat sections = object is travelling at a steady speed
3) Uphill sections = object is accelerating
4) Downhill sections = object is decelerating
5) Curves = object is changing acceleration
The steeper the graph, the greater the acceleration or deceleration
What does friction do?
It causes objects to slow down when they rub against another surface
What is drag?
The resistance you get in a fluid
Air resistance is a type of drag
How do you reduce drag?
Keep the shape of an object streamlined
process of a falling object
1) When a falling object first sets off, the force of gravity is much more than the frictional force slowing it down, therefore the object accelerates
2) As the speed increases, the friction builds up
3) The acceleration is gradually reduced until eventually, the friction force is equal to the accelerating force - the resultant force is 0
4) At this point, it will have reached maximum speed or terminal velocity and will fall at a steady speed
What determines the terminal velocity?
Drag in comparison to its weight
In the last few metres of his descent during the parachute stage, the person travels at a terminal velocity. Explain why (2)
- Because the drag had the same force on the parachuter as the weight
- weight pushes him down
- Drag/air resisance keeps him. Hes reached terminal velocity (2)
What is the tendency for objects to continue at the same speed in the same direction called?
Inertia
Newton's First Law - Law of Inertia
Resultant force on a stationary object = zero, the object will remain stationary
If the resultant force on a moving object is zero, it will just carry on moving at the same velocity
Newton's Second Law
Force ∝ Acceleration
Acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass of an object
Newtons third Law
When two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal and opposite
An action always has an equal and opposite reaction
Explain why you don't move when you lean on a wall, even though you are exerting a force (3)
When you lean on a wall, you exert a force on the wall. Due to Newtons third Law, the wall also exerts an equal but opposite force back onto you.(1) You also exert a force on the ground and the ground exerts a force on you(1)The resultant force is zero, so you remain stationary (1)
Investigating effect of mass
Add masses to the trolley one at a time to increase the mass of the system
2)Record average acceleration for each mass
To reduce the effect of friction use an air track.
Investigating acceleration
1) Set up a trolley so it holds a piece of card that will interrupt the signal on the light gate twice.
2) This will measure acceleration.
3) Using a light measure the first and second point it passes.
Work out an average acceleration.
To reduce the effect of friction use an air track.
investigating effect of force
1) Keep total mass of the system the same but the change the mass on hook
2) Start with all the masses onto trolley
3) Transfer the hooks one at a time to the hook, to increase the accelerating force
4) The mass of the system stays the same as you're transferring the masses from one part of the system to another (the hook)
5) Record the average acceleration for each force
To reduce the effect of friction use an air track.
What is the thinking distance?
How far the car travels during the driver's reaction time
What is the braking distance?
The distance taken to stop under the braking force
What is stopping distance?
The distance it takes for a car to stop in an emergency
What is thinking distance affected by?
1) Speed - the faster you're going, the further you'll travel during your reaction time
2) Your reaction time - the longer it is, the longer your thinking distance
3) Alcohol
4) Drugs
5) Sleep deprivation
6) Distractions
What is braking distance affected by?
1) Speed - the faster a vehicle travels, the longer it takes to stop
2) Weather/Road surface - if it's wet or icy, there is less grip (and less friction) between a vehicle's tyres and the road, which can cause tyres to skid
3) Condition of tyres - if the tyres are bald, then they cannot get rid of water in wet conditions, thus leading to skidding on top of the water
4) Quality of brakes - if brakes are worn or faulty, they won't be able to apply as much force as well-maintained brakes, which could be dangerous when wanting to brake hard
What happens when a vehicle is going really fast?
More ekinetic energy
More work needs to be done to stop it
Greater braking force will be needed to make the vehicle stop within a certain distance
Deceleration will be larger
At one time in the investigation, the cyclist was distracted.
The distraction increased the stopping distance of the bike but did not affect the braking distance
Explain why the stopping distance increased
The cyclist's reaction time increased (1)
The thinking distance increased (1)
Stopping distance is thinking distance plus braking distance (1)
Describe how Newtons third law applies to the forces between the bike and the trailer
The forces of the bike on the trailer and the trailer on the bike are equal in size and opposite in direction
Typical reaction time
in between 0.2 - 0.9
Measure reaction time :
- Ruler drop test
- Computer based experiments
What is momentum?
How much 'oomph' an object has
All moving objects have it
The momentum of one thing is always equal to the momentum of another thing e.g. a skateboarder has the same momentum as the skateboard
What is the conservation of momentum?
In a closed system, the total momentum before an event is the same as after the event
Wave
something that transfers energy from one place to another
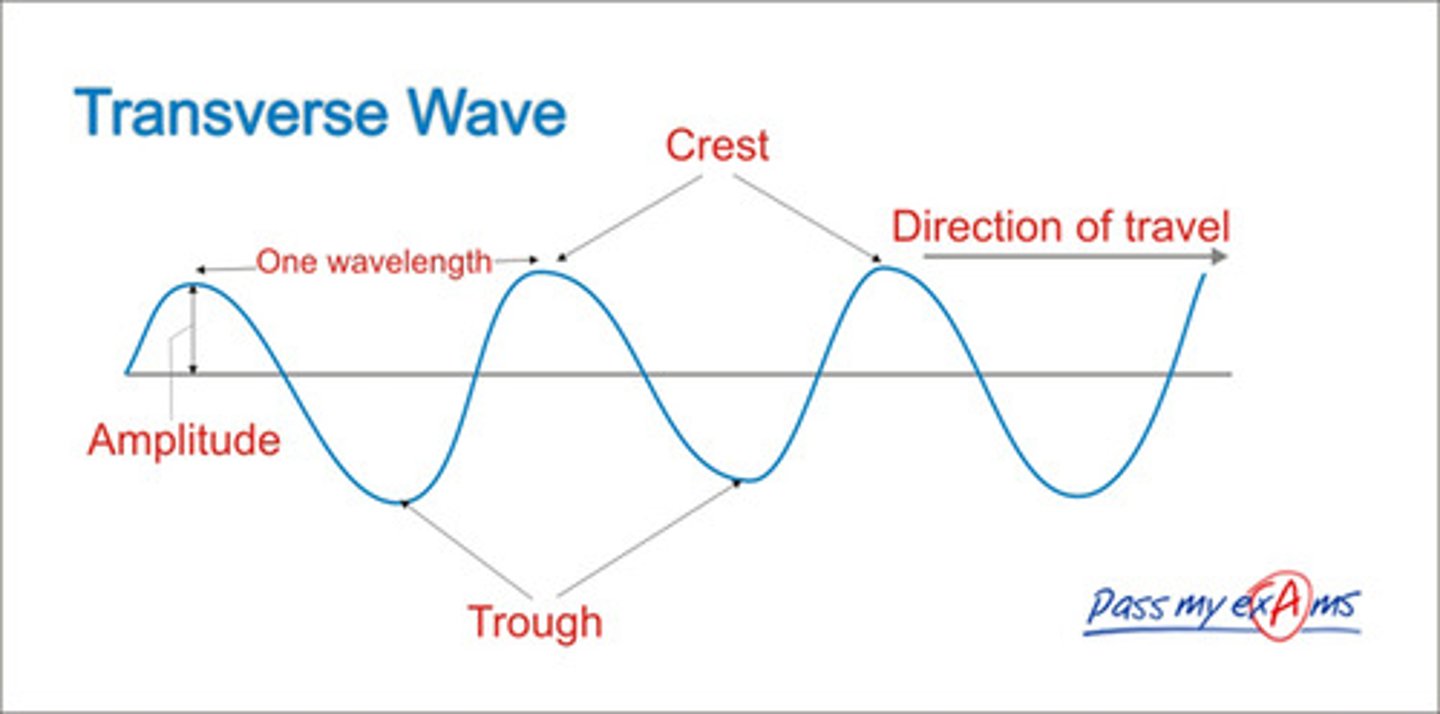
transverse waves
The vibrations are perpendicular (at right angles) to the direction of energy transfer
- direction of energy transfer is sideways - but oscillations are up and down
examples of transverse waves
- electromagnetic waves e.g light
- Ripples and waves in water
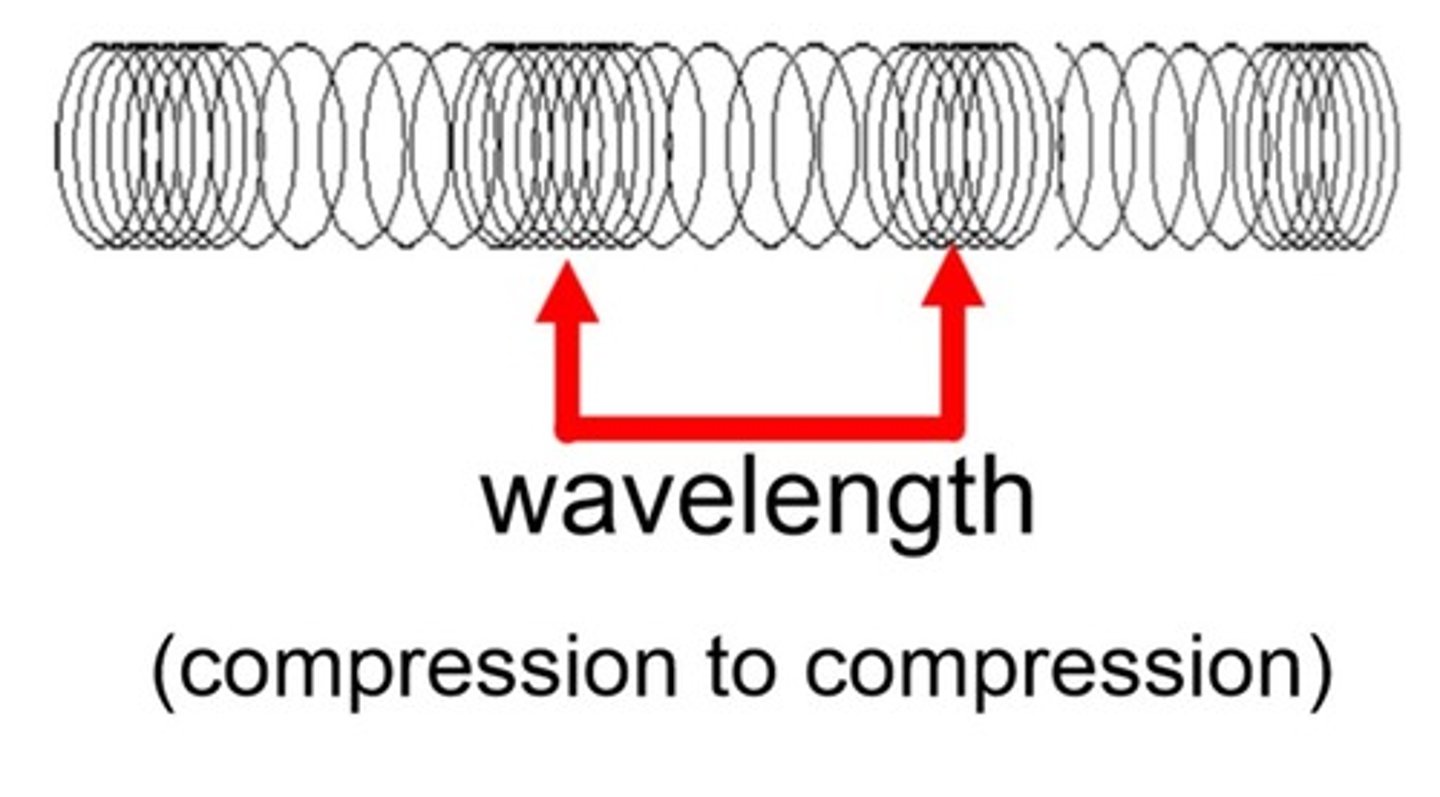
longitudinal waves
The oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer
examples of longitudinal waves
sound waves e.g ultrasound
Explain the differences between the properties of the sound waves produced by the motor and the water waves in the ripple tank
Sound waves are longitudinal, in longitudinal waves the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer
Water waves are transverse. In transverse waves, the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
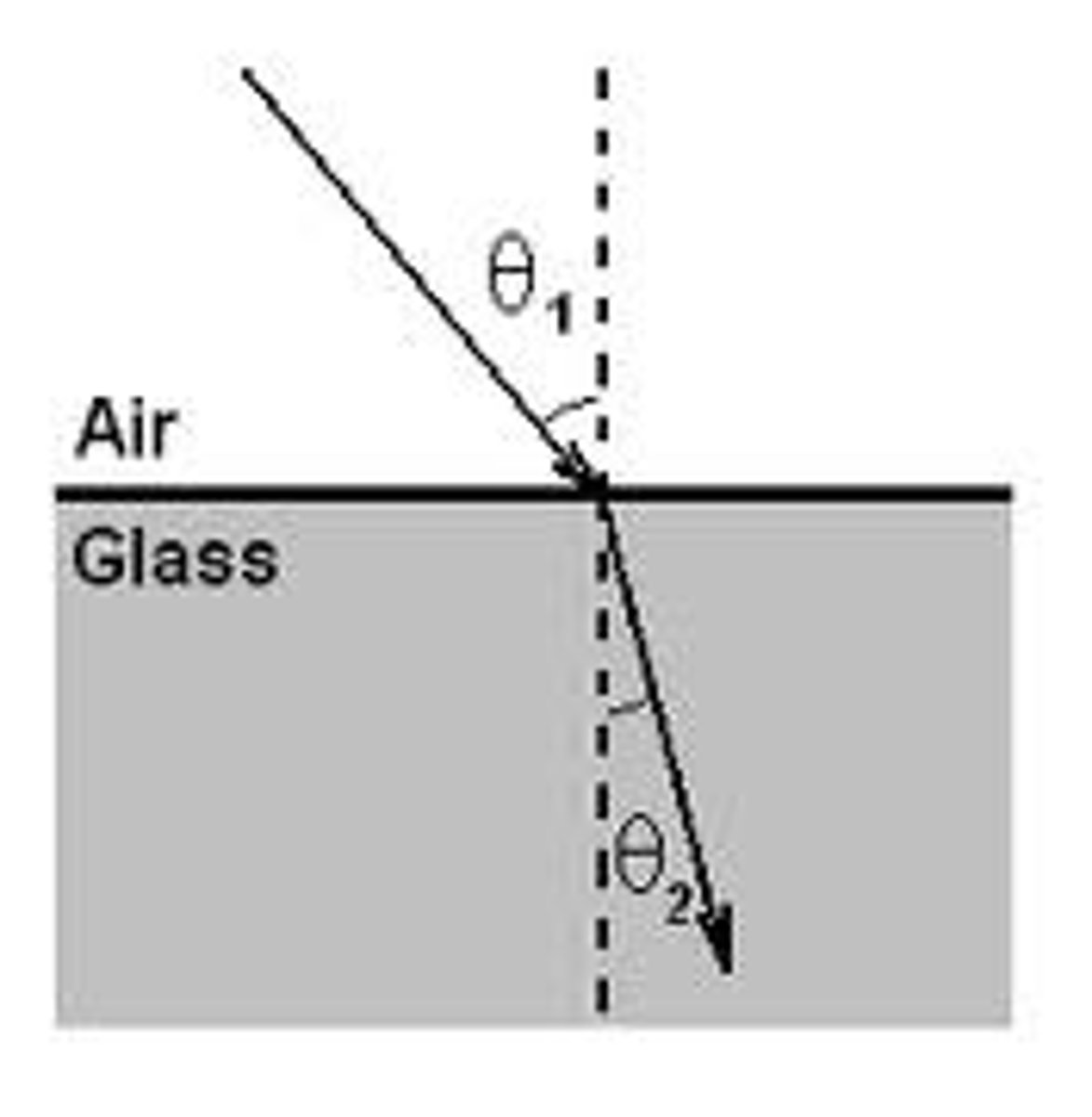
Explain why the light is refracted
Because light travels more slowly in denser so it changes direction
Compression
regions where the air particles are very close together
Rarefaction
regions where the air particles are spaced out
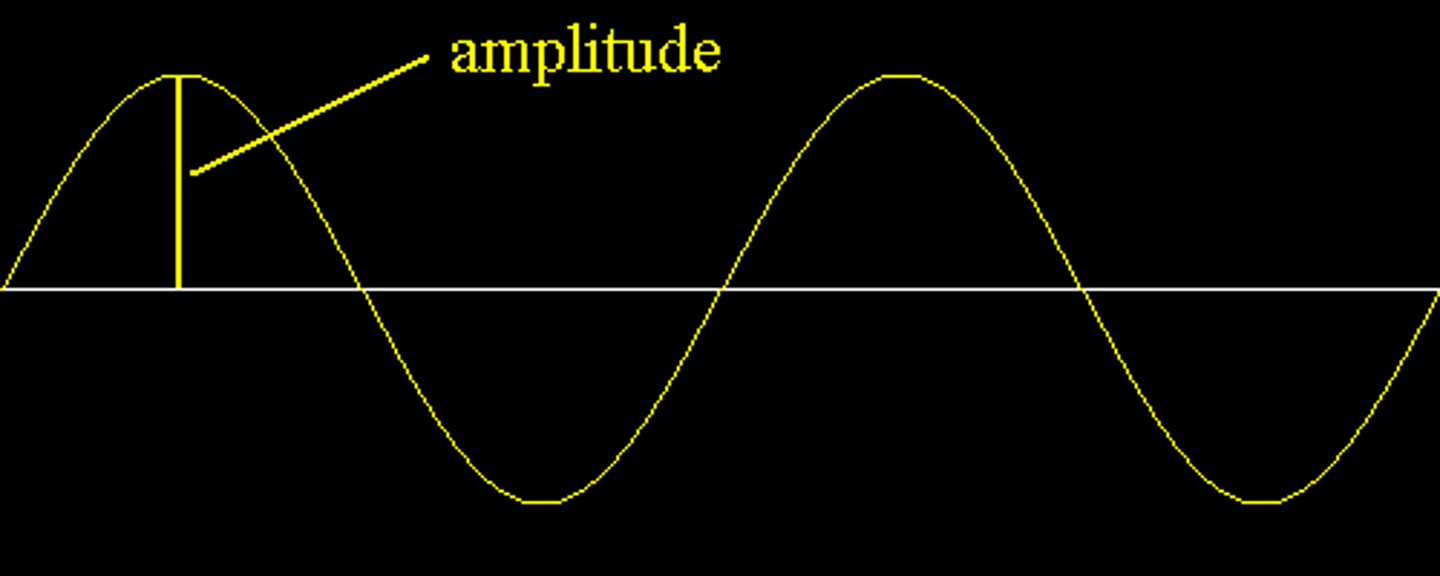
amplitude
The amplitude of a wave is the greatest distance a point on the wave moves from its undisturbed postion
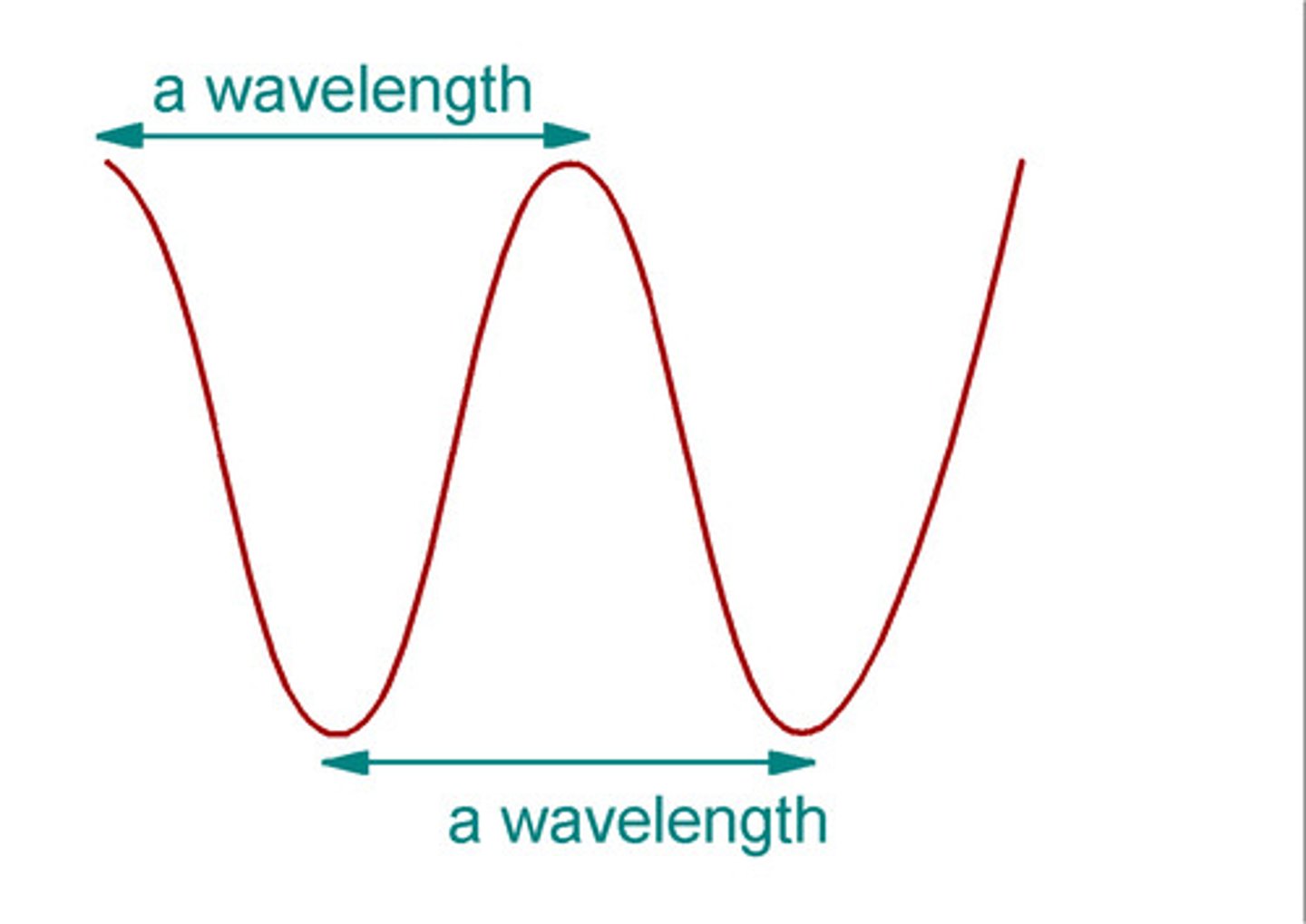
wavelength
The wavelength of a wave is the distance from a point on one way to the equivalent point on the adjacent wave
measure wavelength on longitudinal waves
measure from one compression to the next compression or from one rarefaction to the next rarefaction
frequency
the number of waves passing a point each second
1 Hz = 1 wave per second
period
time (in seconds) for one wave to pass a point
What is the speed of sound in air?
330m/s
measuring the speed of water ripples practical
use signal generator attached to dipper of ripple tank - can create water waves at set frequency
use strobe light to see wave crests on a screen below the tank
increase frequency of strobe light until wave pattern on the screen appears to freeze and stop moving.
Distance between each shadow line is equal to one wavelength
Measure the distance between shadow lines that are 10 wavelength apart, then divide this distance by 10 to find the average wavelength
use V = f λ
strobe is effective because
it allows you to measure a still pattern instead of a constantly moving one
required practical: waves in a solid
- Turn on the signal generator and vibration transducer. String will start to vibrate
- Adjust the frequency of the signal generator until there's a clear wave on the string
- Measure the wavelength of these waves by measuring the lengths of 5 half wavelengths in one go, then divide to get the mean half wavelength, then double this to get a full wavelength
- Frequency of the wave is whatever the signal generator is set to
- use V = f λ to find the speed of the wave
3 things that could happen when a wave meets a boundary between two materials :
- The wave is transmitted through the material - carries on travelling
- The wave is absorbed by the material
- The wave is reflected - 'sent back' - this is how echoes are produced
Rule for all reflected waves
Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
What is the angle of incidence?
The angle between the incoming wave and the normal
What is the angle of reflection?
the angle between the refracted wave and the normal
What is the normal?
An imaginary line that's perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence
Length of a radio wave
1m-10⁴m
Length of a microwave
10⁻²m
Length of a infrared wave
10⁻⁵m
Length of a visible light wave
10⁻⁷m
Length of an ultraviolet wave
10⁻⁸m
Length of an x-ray
10⁻¹⁰m
Length of a gamma ray
10⁻¹⁵m
EM continuous spectrum
1) Radio waves
2) Microwaves
3) Infrared waves
4) Visible light rays
5) Ultraviolet waves
6) X-rays
7) Gamma rays
mnemonic for EM spectrum
Randy Men Inject Viagra Until eXplosive Growth
on the red end of spectrum, waves have a
lower frequency, longer wavelength
on the violet end of the spectrum waves have a
higher frequency, shorter wavelength
What is refraction?
When a wave hits a boundary at angle it will change direction
What happens during refraction?
The wavelength of a wave changes but the frequency stays the same
What affects the rate of refraction?
How much the wave speeds up/slows down - this depends on the density of the two materials
If the wave slows down, it will bend towards the normal
If the wave speeds up, it will bend away from the normal
What is optical density?
A measure of how quickly light can travel through a material - the higher the optical density, the slower light waves travel through it
ray diagrams
draw boundary between two materials
draw incident ray that meets the normal at boundary
angle between incident ray and normal = angle of incidence
now draw the refracted ray on other side of boundary