MGMT CH 11
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
planning and organizing
•managers develop organizational strategy and create the structure to use resources most effectively to create value for customers and other stakeholders
2
New cards
controlling
managers monitor and evaluate whether strategy and structure are working as intended, how they could be improved, and how they might be changed if they are not working
3
New cards
steps in control process
1\.Establishing standards for performance
2\.Measuring performance
3\.Comparing actual performance with expected performance
4\.Correcting deviations if necessary
4
New cards
Establishing standards for performance
* criteria against which results are measured
* output standards: productivity, profitability, market share
* behavioural standards: customer responsiveness, absenteeism, punctuality
* output standards: productivity, profitability, market share
* behavioural standards: customer responsiveness, absenteeism, punctuality
5
New cards
Measuring performance
* actual rate of productivity?
* determine ROI
* measure market share
* monitor customer complaints, rates of absenteeism, and punctuality
* determine ROI
* measure market share
* monitor customer complaints, rates of absenteeism, and punctuality
6
New cards
compare actual performance with expected performance
* is performance higher than expected?
* is performance as expected?
* is performance lower than expected?
* evaluate the reasons for variances between the standard and actual performance
* is performance as expected?
* is performance lower than expected?
* evaluate the reasons for variances between the standard and actual performance
7
New cards
correct deviations
* corrective actions can focus on root of the problem when there is significant gap between actual and expected outputs/behaviours
\
* managers must determine the cause
* performance problems may occur because standard too high
* need to change the way in which resources are being used
* lack of training
* org needs restructuring
\
* managers must determine the cause
* performance problems may occur because standard too high
* need to change the way in which resources are being used
* lack of training
* org needs restructuring
8
New cards
types of standards
* output standards
* operating costs
* behavioural standards
* operating costs
* behavioural standards
9
New cards
output standards
refer to quantity of the service or product the employee is to produce
* may include operating costs, inventory levels, market share, ROI
* may include operating costs, inventory levels, market share, ROI
10
New cards
operating costs
measure the efficiency of production by monitoring and evaluating the actual costs associated with producing goods and services
11
New cards
behavioural standards
refer to quality of employees actions
* hours worked, dress code
* hours worked, dress code
12
New cards
operations management
process of managing the use of materials and other resources to produce goods and services
13
New cards
production system
system used to acquire inputs, convert inputs into outputs, and dispose of the outputs
14
New cards
5 Ps of org operations
* people
* plants
* parts
* processes
* planning and control systems
* plants
* parts
* processes
* planning and control systems
15
New cards
control systems
formal target setting, monitoring, evaluation, feedback systems that provide managers with info about org
16
New cards
3 effective control systems characteristics
* flecible so managers can respond to unexpected events
* provide accurate info about org performance
* provide info in timely manner
* provide accurate info about org performance
* provide info in timely manner
17
New cards
improving responsiveness
* managers must correctly identify customers and promote org strat that respond to their needs
* managers try to design production systems that produce the outputs that have the attributes customers desire
* ex: shift to online shopping due to COVID
* managers try to design production systems that produce the outputs that have the attributes customers desire
* ex: shift to online shopping due to COVID
18
New cards
impact of increased quality on org performance
leads to:
* increased reliability
* higher prices
* increased productivity
* lower costs
\
= higher profits
* increased reliability
* higher prices
* increased productivity
* lower costs
\
= higher profits
19
New cards
increasing efficiency
* total factor productivity
* partial productivity
* partial productivity
20
New cards
total factor productivity
* how well an org utilizes all of its resources
* labour, capital, materials, energy
* labour, capital, materials, energy
21
New cards
partial productivity
* specifics measures of efficiency that measures the efficiency of an individual unit
22
New cards
total factor productivity
outputs / all inputs
23
New cards
labour productivitu
outputs / direct labour
24
New cards
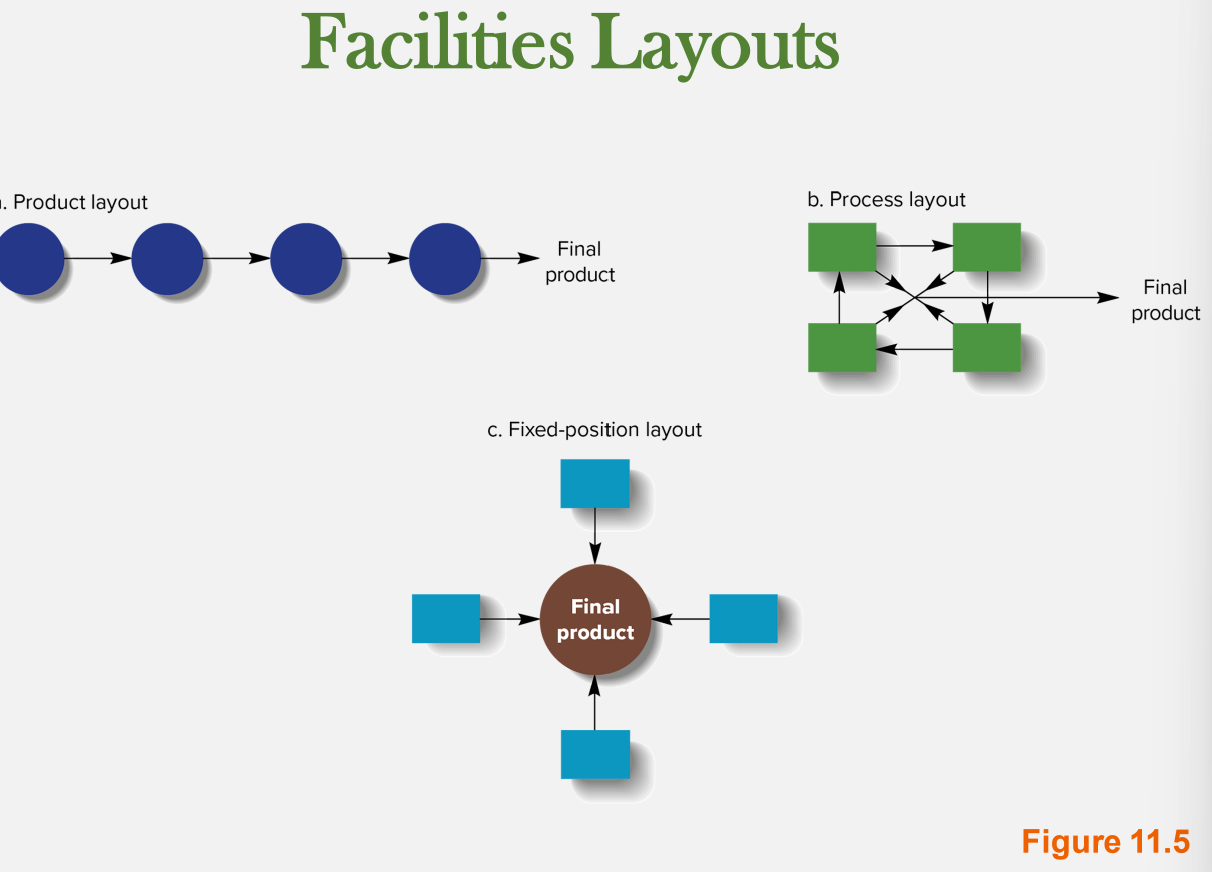
facility layout
* influences efficiency by way managers decide to lay out or design an org physical work facilities
* important because
* way in which machines and workers grouped together affects the efficiency of the production system
* major determinant of efficiency is the cost associated with setting up the equipment needed to make a particular product
* important because
* way in which machines and workers grouped together affects the efficiency of the production system
* major determinant of efficiency is the cost associated with setting up the equipment needed to make a particular product
25
New cards
product layout
* machiens organized so each operation eeded to manufacture a product is performed at workstations arranged in fixed sequence
* ex: car assembly lines
* ex: car assembly lines
26
New cards
process layout
* each workstation relatively self contained, and a product goes to whichever workstation is needed to perform the next operation to complete the product
* ex: custom made products
* ex: custom made products
27
New cards
fixed position layout
* the product stays in fixed position
* component parts are produced in remote workstations and brought to the production area for final assembly
* ex: airplanes
* component parts are produced in remote workstations and brought to the production area for final assembly
* ex: airplanes
28
New cards
inventory
* stock of raw materials, inputs, and component parts that an org has on hand at particular time
29
New cards
just in time inventory system
* parts or supplies arrive at the org when they are needed, not before
* leaves org without buffer stock of inventory needed if shortage
* inventory can be expensive to store
* sufficient inventory helps respond to increased customer demand
* leaves org without buffer stock of inventory needed if shortage
* inventory can be expensive to store
* sufficient inventory helps respond to increased customer demand
30
New cards
3 systems of control
* feedforward control
* concurrent control
* feedback control
* concurrent control
* feedback control
31
New cards
feedforward control
* anticipate and deal with potential problems before they occur
32
New cards
concurrent control
* immediate feedback on how efficiently inputs are being transformed into outputs
33
New cards
feedback control
* info about customers reactions so corrective action can be taken if necessary
34
New cards
output control
* main mechanisms managers use to assess output or performance
* financial measures
* organizational goals
* operating budgets
* financial measures
* organizational goals
* operating budgets
35
New cards
financial measures of performance
* financial measures of performance are objective and allow comparison to other firms
* profit ratios
* liquidity ratios
* leverage ratios
* activity ratios
* profit ratios
* liquidity ratios
* leverage ratios
* activity ratios
36
New cards
organizational goals
* once an org sets overall goals, they establish performance standards
* specify divisional and functional managers the level at which their unit must perform for orgs to reach overall goals
* managers evaluate how well performance matches up to goals set and determine if adjustments are needed
* provide framework for what is evaluated and assessed
* specify divisional and functional managers the level at which their unit must perform for orgs to reach overall goals
* managers evaluate how well performance matches up to goals set and determine if adjustments are needed
* provide framework for what is evaluated and assessed
37
New cards
operating budgets
* blueprint of how managers intend to use org resources to achieve org goals efficiently
* objective financial measures
* performance standards derived from goals
* appropriate operating budgets
* objective financial measures
* performance standards derived from goals
* appropriate operating budgets
38
New cards
pitfalls of output control
* extremely difficult goals may not motivate
* unachievable goals can lead to unethical behaviour
* inappropriate goals can lead to short term emphasis
* may not be responsive enough if conditions change
* unachievable goals can lead to unethical behaviour
* inappropriate goals can lead to short term emphasis
* may not be responsive enough if conditions change
39
New cards
behavioural controls
* mechanisms that managers can use to keep employee behaviour on track and make org structures work as they are designed to work
* ex:
* corporate governance
* direct supervision
* management by objectives
* bureaucratic rules and standard operating procedures
* clan control
* ex:
* corporate governance
* direct supervision
* management by objectives
* bureaucratic rules and standard operating procedures
* clan control
40
New cards
corporate governance and control
* processes companies use to be accountable to stakeholders, investors, employees, the environment, and communities
* include levels of executive pay, how they conduct audits, internal control systems, and shareholder rights
* transparent corp gov and sustainability strat
* help create comp advantage
* shareholders demand triple bottom line returns (economic, environmental, social impact)
* include levels of executive pay, how they conduct audits, internal control systems, and shareholder rights
* transparent corp gov and sustainability strat
* help create comp advantage
* shareholders demand triple bottom line returns (economic, environmental, social impact)
41
New cards
direct supervision
* managers actively monitor and observe behaviours of their subordinates
* problems with direct supervision
* very expensive
* can be demotivating to subordinates
* sometimes not feasible
* problems with direct supervision
* very expensive
* can be demotivating to subordinates
* sometimes not feasible
42
New cards
management by objectives
* provide framework within which to evaluate subordinates for their ability to achieve specific goals
* allow managers to monitor progress toward achieving goals
* reviews are held periodically looking at progress toward goals
* allow managers to monitor progress toward achieving goals
* reviews are held periodically looking at progress toward goals
43
New cards
bureaucratic roles and SOPs
* system of rules and standard operating prosedures (SOPs) that standardize the behaviour of divisions, functions and individuals
* SOPs
* written instructions describing the exact series of actions that should be followed in a specific situation
* rules and policies that standardize behaviours
* discipline: administering punishment when undesired behaviours are exhibited
* SOPs
* written instructions describing the exact series of actions that should be followed in a specific situation
* rules and policies that standardize behaviours
* discipline: administering punishment when undesired behaviours are exhibited
44
New cards
progressive discipline
* verbal reprimand
* ex: occasional tardiness/absenteeism
* written reprimand
* ex: booking off sick every friday
* discharge
* theft
* embezzlement
* ex: occasional tardiness/absenteeism
* written reprimand
* ex: booking off sick every friday
* discharge
* theft
* embezzlement
45
New cards
problems with bureaucratic control
* establishing rules easier than discarding them
* increases red tape
* firm can become too standardized and not flexible - people stop thinking for themselves
* incompatible with innovation
* best used for routine activities and programmed decisions
* increases red tape
* firm can become too standardized and not flexible - people stop thinking for themselves
* incompatible with innovation
* best used for routine activities and programmed decisions
46
New cards
clan control
* shared norms and values of org members
* relies on strong org culture
* employees internalize org values and norms and let these guide their decisions and actions
* important for 2 reasons
* provide control where output and behavioural controls do not work
* strong culture and clan control helps employees focus on what is best for org in the long run
* relies on strong org culture
* employees internalize org values and norms and let these guide their decisions and actions
* important for 2 reasons
* provide control where output and behavioural controls do not work
* strong culture and clan control helps employees focus on what is best for org in the long run
47
New cards
clan control and diversity
* values and norms embedded in the org culture may hinder diversity, equity, and inclusion goals
* inclusive cultures create opportunities for team building that are welcoming and respectful of differences
* managers must question assumptions that underpin clan control to dismantle systemic or unintended racism
* cultural norms upon which clan control relies must be inclusive of diversity
* inclusive cultures create opportunities for team building that are welcoming and respectful of differences
* managers must question assumptions that underpin clan control to dismantle systemic or unintended racism
* cultural norms upon which clan control relies must be inclusive of diversity
48
New cards
importance of control
* adapt to change and uncertainty
* discover irregularities and errors
* reduce costs, increase productivity, or add value
* detect opportunities
* deal with complexity
* decentralize decision making and facilitate teamwork
* discover irregularities and errors
* reduce costs, increase productivity, or add value
* detect opportunities
* deal with complexity
* decentralize decision making and facilitate teamwork
49
New cards
control and comp advantage
* control system: includes the measures to asses how efficiently the org is producing goods and services
* if any changes in production, measures tell managers how successful they have been
* without a control system managers have no idea how well their org is performing and how its performance can be improved
* if any changes in production, measures tell managers how successful they have been
* without a control system managers have no idea how well their org is performing and how its performance can be improved