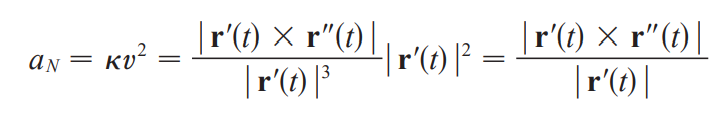Chapter 13 Flashcards MVC
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MVC Chap 13 Flashcards for Stewart goat
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
vector function
domain is a set of numbers & range is a set of functions
component functions
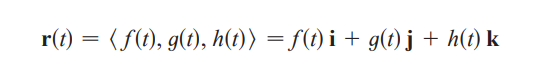
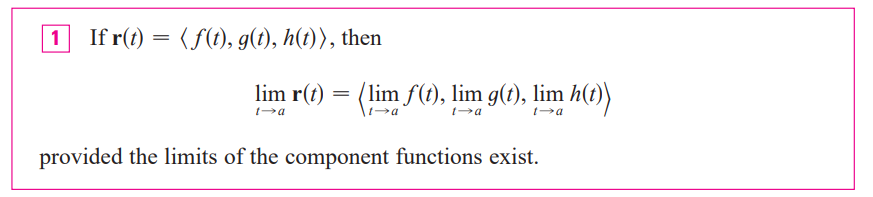
limit of vector function
spaces curve
set C of all points (x,y,z) on x = f(t), y = g(t), z = h(t)
parametric equations of C
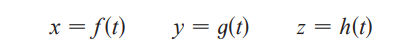
parameter
t
helix
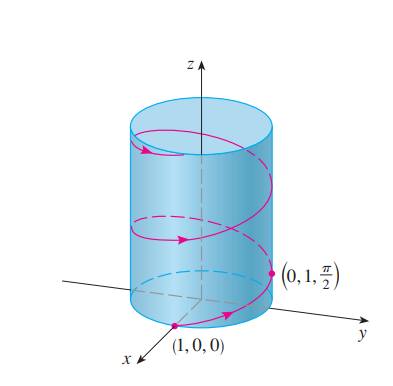
derivative r’(t)

tangent vector
r’(t)
unit tangent vector (T)
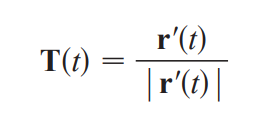
d/dt [u(t) (dot) v(t)]
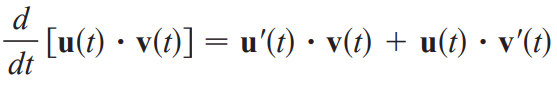
d/dt [u(t) (cross) v(t)]
d/dt [ u( f(t) ) ]
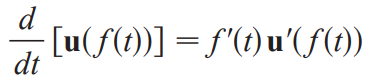
integral of r(t)
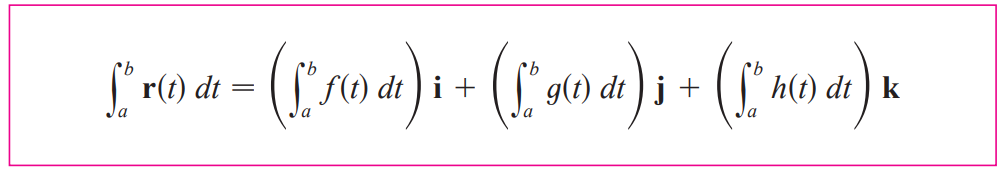
arc length
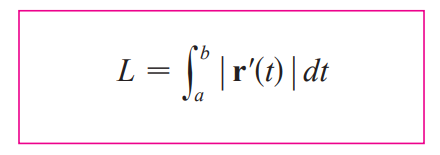
arc length function s
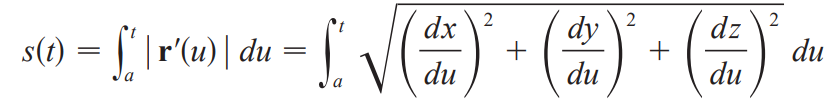
(ds/dt)
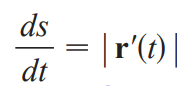
smooth on interval I
r’(t) is continuous in I and r’(t) =/= 0 on I
curvature definition
how fast the curve changes direction at a given point
principal unit normal vector N(t)
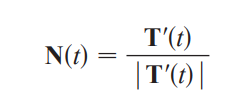
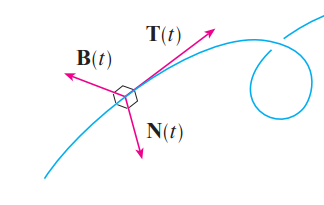
binormal vector B(t)
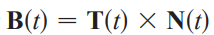
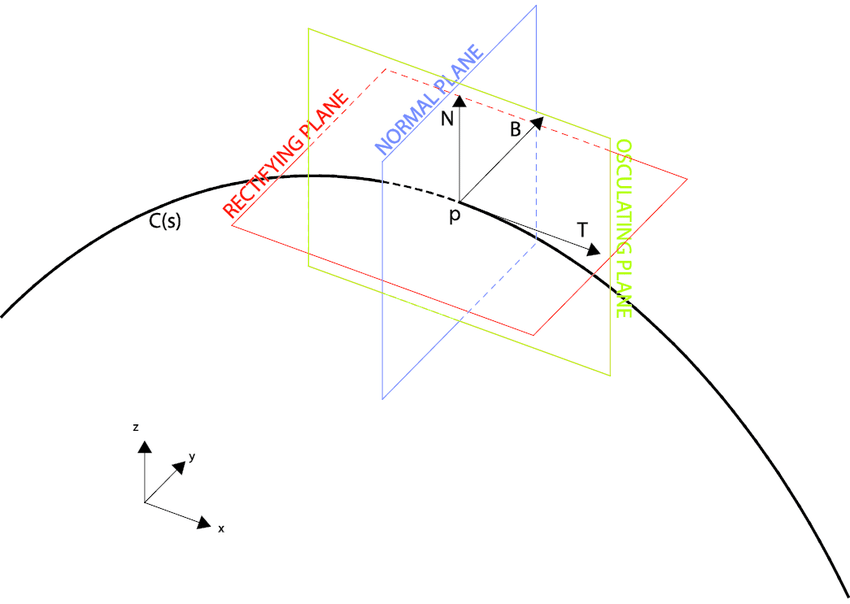
normal plane of C at P
consists of all lines orthogonal to unit tangent T(t), determined by vectors B(t) and N(t)
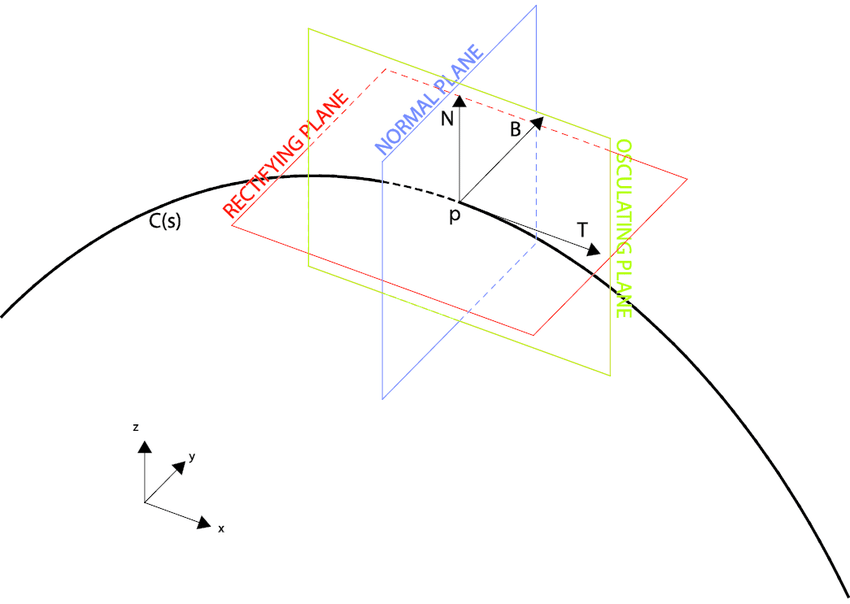
osculating plane of C at P
plane that comes closest to containing the part of the curve near P
curvature (K)
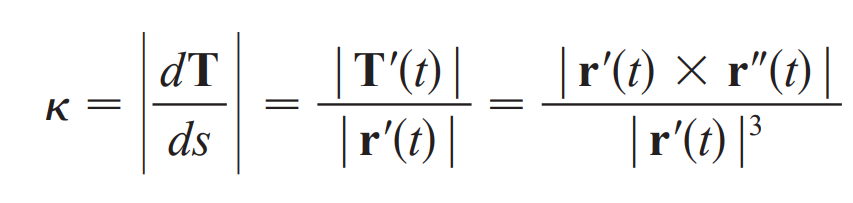
curvature (K) in terms of f(x)
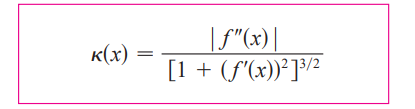
osculating circle (circle of curvature)
The circle that lies in the osculating plane of at P, has the same tangent as C at P, lies on the concave side of C (toward which N points), and has radius p = 1/K (the reciprocal of the curvature)
velocity vector
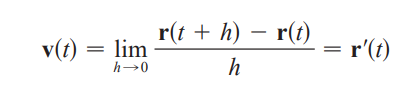
parametric equations of trajectory
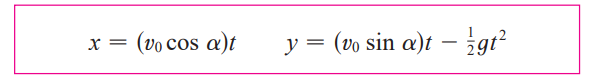
tangent unit curve in terms of velocity
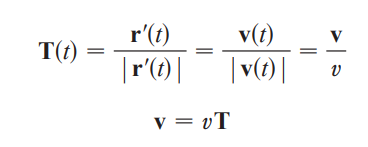
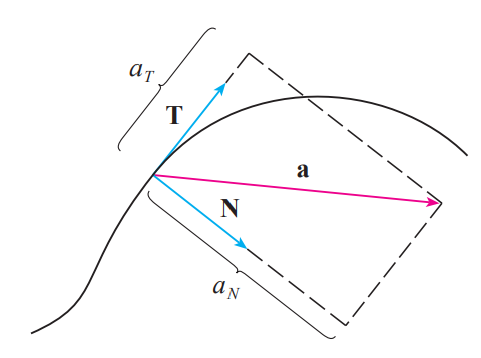
acceleration in terms of T and N
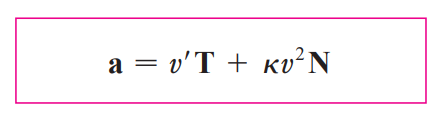
tangential and normal components of acceleration
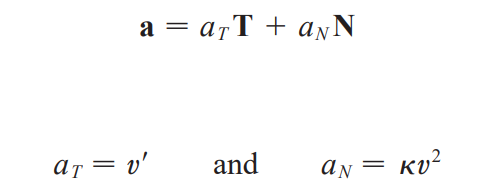
tangential component of acceleration
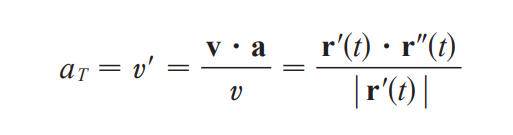
normal component of acceleration